What is Prevention of Scoliosis?
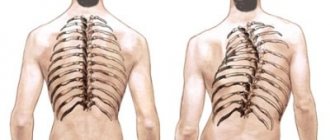
Scoliosis is a persistent lateral curvature of the spine that occurs at an early age. After 16 years in boys and 14 years in girls, the pathology is practically untreatable. Curvature of the spinal column leads to diseases of the functional systems of the body and internal organs. People who did not pay attention to the development of scoliosis at an early age, after 25 years of age, begin to treat what hurts, although the cause lies in the spine.
The condition of the spine should be monitored from birth. Problems can continue from the moment of birth trauma. It is not for nothing that in European countries, an osteopathic doctor is invited to childbirth, who immediately checks for the presence of pathologies or birth injuries in the child.
After birth, it is recommended to show the newborn to specialists (chiropractor, vertebrologist, osteopath) as soon as possible. To develop coordination of movements and strengthen muscles, experienced pediatricians strongly recommend giving children massage. A mother can master the basics of a simple (mostly stroking) massage. Also, after 3 months, you can contact specialists to take measures to prevent scoliosis.
Causes of poor posture
Provoking factors that trigger the mechanism of spinal deformity include:
- hereditary predisposition
- physical inactivity
- “school-office” lifestyle
- static disorders (incorrect postures)
- individual anatomical features
- traumatic injuries
In accordance with the generally accepted classification, the following causes of poor posture are distinguished:
- insufficient development of the muscular-ligamentous apparatus
- metabolic disorders (rickets-like diseases)
- degenerative and neurogenic pathologies of the spine
- injuries and tumors
- congenital anomalies of vertebrae and ribs
- neuroses, psychoemotional disorders
- idiopathic (unknown causes)
Curvature of the spinal column can be caused by asymmetrical sports, in which the muscles of one part of the body develop more than another (tennis, badminton, javelin throwing, etc.), playing bowed musical instruments, carrying heavy weights on one hand, and other characteristic professional and non-professional factors.
start of treatment
Treatment of scoliosis in our center begins with an appointment with a vertebroneurologist. The initial appointment is conducted by the candidate of medical sciences, chief medical doctor Lyudmila Ivanovna Mazheiko.
At your appointment, a vertebroneurologist will make the correct diagnosis: scoliosis or some type of postural disorder. Then the cause of this condition is determined, and if necessary, additional examinations are prescribed. The doctor examines the spine, limbs, nervous system, and the condition of internal organs. After this, a course of treatment is prescribed.
The course of treatment allows you to eliminate all muscular forms of poor posture, as well as mild and moderate degrees of scoliosis. Even with severe forms of scoliosis, there is a significant improvement in the condition.
Appointments with a vertebroneurologist are carried out by appointment. To begin treatment, make an appointment.
Types of posture disorders
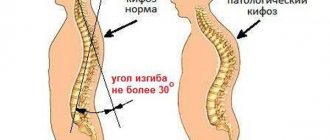
Postural disorders refer to curvatures in various parts of the spine. There are 6 main types of deformities:
- stoop (increased kyphosis, smoothed lumbar curve)
- round back (kyphotic posture, hyperkyphosis)
- flat back (smoothing physiological curves)
- increased deflection in the lower back (lordotic posture, hyperlordosis)
- postural scoliosis (lateral deviation of the spine to the right or left)
- kyphoscoliosis (combination of scoliosis and pathological kyphosis)
In most cases, all known types of postural disorders form and progress during the period of active growth and development of skeletal bones (10-17-20 years). Until this time, a significant part of the deformations is reversible and can be easily corrected.
about the problem
Scoliosis (impaired posture) is a disease in which there is a three-plane deformity of the spine associated with impaired growth and development of the skeleton.
A mandatory sign of scoliosis is twisting of the spine around a vertical axis (vertebral torsion). If the x-ray clearly shows twisting of the vertebrae and deviation of the spinal column from the midline, then the diagnosis of scoliosis is confirmed. When examining the back while bending forward, a rib hump or muscle roll is visible.
Most often, scoliosis is detected at the ages of 6–8 years and 11–14 years. For a long time, the main cause of scoliosis remained unknown. Modern research has shown that the basis is a malfunction in the hormonal system and impaired blood flow in the cerebellum. The combination of these two factors interferes with the proper growth of the spine.
The causes of scoliosis in rare cases are injuries and inflammatory diseases of the spine, shortening of the leg, congenital muscle anomalies, and neuromuscular diseases.
Many types of postural disorders are mistaken for scoliosis.
Poor posture is a symptom manifested by curvature of the spine. The following types of postural disorders are identified: stoop, round back, round-concave back, flat back.
In children, poor posture develops from incorrect postures, weakness of the back muscles, chronic diseases and associated poor physical development. Improper physical education and disturbances in the child’s psycho-emotional state (“psychological pressures”) also lead to poor posture.
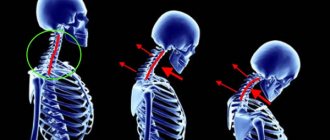
The most common cause of poor posture is birth trauma of the cervical spine. With a birth injury, postural disturbances often develop, in which one shoulder is higher than the other, or mild forms of scoliosis develop. Such children have complaints of pain, discomfort in the spine and legs, rapid fatigue and the need to assume a horizontal position after prolonged sitting, standing, or physical work. Such symptoms require specialized diagnosis and assistance.
Diagnostics
Poor posture is detected during a medical examination by determining the coordinates of anatomical landmarks. If it is necessary to differentiate compensatory postural deformities from persistent deforming diseases of various parts of the spine, instrumental diagnostic methods are prescribed:
CT
(additional information about the condition of the curvature area)
Radiography
(functional spondylography in direct and lateral projections, to determine the degree of displacement in relation to the vertical line)
MRI
(clarification of the diagnosis in the presence of neurological symptoms).
Magnetic resonance imaging is recognized as the safest and most informative method. Advanced imaging technology, without radiation exposure, creates a three-dimensional reconstruction of the spine, assesses the condition of the spinal structures and their true relationship with the vertebrae.
our treatment
As an alternative to conventional methods of treating scoliosis, we offer an integrated approach with correction of hormonal levels and restoration of blood flow to the cerebellum.
The course of treatment consists of successive stages to eliminate the deficiency of blood supply to the areas of the brain that regulate the proper growth of the skeleton and spine, and to restore the proper functioning of hormones.
The treatment course is supplemented with exercise therapy classes, osteopath sessions, kinesiological taping, medical massage, physiotherapy, radon baths and mud.
The harmonious growth of the skeleton depends on the correct selection and implementation of treatment, which is aimed at eliminating the cause.
Posture correction in rehabilitation
One of the leading areas of work of the rehabilitation center, based on the Center for Medical Radiology in St. Petersburg, is the correction of postural disorders in adults and children. Rehabilitation measures aimed at eliminating provoking factors, unloading the spine, stopping the progression and reversibility of the deformity take place in comfortable conditions, under the supervision of experienced professionals. The individual treatment and rehabilitation program includes:
- differentiated, acupressure, vacuum massage
- Exercise therapy (symmetrical and asymmetrical exercises to develop the femoral, tibial, gluteal, lumbar-iliac muscles, stretching and strengthening of the back, corrective gymnastics)
- physiotherapeutic procedures (electromyostimulation, ozokerite, ultrasound, magnetic therapy, SMT therapy, fluctuarization, electrophoresis, etc.)
- acupuncture
- kinesiotherapeutic techniques
- exercises on therapeutic simulators
- correction with orthopedic corsets
- mechanotherapy
- health systems of yoga therapy, Pilates
- psychotherapeutic correction
The integrated use of non-drug treatment methods allows, without pharmacological load, to form and consolidate the skill of correct posture, stabilize the functioning of internal organs, and achieve the possible complete correction within the existing defect.
standard treatment
Children diagnosed with scoliosis are recommended to systematically unload in a horizontal position, be sure to prescribe physical therapy, swimming, systematic massage courses, physiotherapy, and sanatorium-resort treatment.
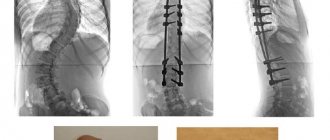
If the effect is mild and scoliosis progresses, an individual corset is selected for constant wear.
Quite often, observation by an osteopath and repeated courses of treatment are recommended.
In case of poor posture, these types of treatment are quite effective, but in case of true scoliosis, treatment does not bring the desired results and scoliosis usually progresses.
Gymnastics and massage for spinal curvature
To prevent the development of scoliosis and begin appropriate treatment of the spinal defect, massage and gymnastics are consistently prescribed. Massage can relax spasmed muscles and tone weak ones. The course of exercises must be carried out under the guidance of a qualified physical therapy doctor. It is important that the instructor shows you how to perform the movements correctly, as formal repetition of the exercises will not produce results. Only a specialist can determine which muscles should be relaxed and which ones should be stressed. He will also select the necessary set of exercises.
After completing the course, massage and gymnastics should be continued at home. This is a mandatory point, without which a lasting result in the prevention and treatment of scoliosis cannot be achieved.
In addition to massage and gymnastics, a specialist can provide significant assistance with spinal curvature. Osteopathy gives patients something that they will not get from any other treatment method: balancing of muscle chains, anatomical alignment of the vertebrae.
Timely prevention of scoliosis will make the spine straight and slender, and your posture correct. This will help prevent the development of pathology and save patients from many health problems in the future.
Prevention of scoliosis in adults
It is no longer possible to completely correct scoliosis after 20 years, but you can visually give the silhouette a straight, slender look and correct your back. If you have to sit constantly at work, don’t hunch over, change your position, do a few light physical exercises, and take breaks. The chair must be adjusted so that it supports your back in the area of the shoulder blades and lower back, while removing excess stress from the muscles in this area.
Train on the horizontal bar and swim more, this will help strengthen your back and spine. Organize your night's sleep in such a way that it also becomes part of the prevention of scoliosis. You can use a bolster pillow that supports the cervical vertebrae so that the hollow between the back of the head and the shoulder blades is filled and the spine remains straight. The fetal position, with legs slightly bent, on the right side, is the most optimal for sleeping. Sleeping on your back or stomach is not recommended.
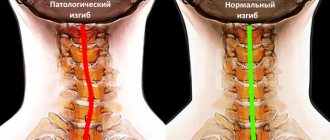
Lordosis and kyphosis
KYPHOSIS AND LORDOSIS - CLOSE RELATIVES
By definition, these are antagonistic disorders (kyphosis - backward deflection of the spine, lordosis - forward deflection of the spine). However, there is a lot in common between them. Most often, kyphosis and lordosis are caused by the same reasons. As a rule, if kyphosis develops in one part of the spine, then compensatory lordosis almost inevitably develops in another part, and vice versa. Normally, a slight kyphosis is required in the upper part of the thoracic spine, as well as in the area of the sacrum and coccyx. Lordosis is considered normal if, to a certain extent, it manifests itself in the lower thoracic and lumbar, as well as the cervical spine.
Pathology is considered to be kyphosis of the thoracic region, exceeding the normal physiological bend, and backward deflection, even very slight, in those parts of the spine where lordosis should normally be present (in the cervical, lower thoracic and lumbar regions). In childhood and adolescence, such a defect, mistaken for stoop, is simply unsightly, but in adulthood it can become a source of severe pain. Lordosis is considered a pathology if the spine bends forward in the upper thoracic region and if in other regions it exceeds the norm. When a child slouches, but tries to keep his head more or less straight, a second hypertrophied forward curve inevitably appears at the spine in the lumbar region. This is hyperlordosis: the pelvis moves back and the stomach protrudes. In childhood, little attention is paid to kyphosis and lordosis. They say about kyphosis: “Well, just think, the child is hunched over! So, he studies a lot, plays the piano, and sits at the computer... But he also goes to a sports school, and sleeps on a hard surface - he must straighten out!..” Parents, of course, from time to time remind their child: “Don’t slouch!” - but that's all there is to it. You can't change the shape of a skeleton with sheer force of will. Lordosis receives even less attention. This is a big mistake. With lordosis of the thoracic region, the chest is deformed, the tidal volume of the lungs decreases, the work of the heart becomes difficult and the shock-absorbing properties of the spine deteriorate. With hyperlordosis of the lumbar spine, resistance to increased loads decreases, the functioning of the hip joints worsens, and the abdomen sag. Kyphosis of the thoracic region is often accompanied by such defects as barrel-shaped, keeled, or “chicken” chest, funnel-shaped deformation of the costal arches and sternum. Sometimes the collarbones are shortened: with this defect, the shoulders are constantly turned forward. Diagnosis is carried out visually (during examination). In order to note the degree of impairment, you can place the patient on a hard couch and measure the distance between the shoulders and the support. Normally, the shoulders should lie tightly on the couch or be no more than 2-3 cm away from it. Poor posture cannot be preserved. Both scoliosis, kyphosis, and lordosis tend to develop. During the period of rapid growth of a child, this tendency manifests itself very strongly, but in adulthood and old age, postural disorders continue to progress in a person. In other words, the development of spinal curvatures cannot be stopped - they can only be cured.
CAUSES OF SPINAL CURVATIONS
In their pure form, scoliosis, lordosis and kyphosis are rare; more often they are combined with some other disorders and appear in all sorts of combinations. 1. Birth defects. Deformations of the vertebrae and ribs are of great importance. This applies, first of all, to wedge-shaped vertebrae, hemivertebrae, fused and extra ribs. Fortunately, such defects are rare (no more than 0.25-0.5% of all cases). As a rule, they appear very early and require intensive treatment. With congenital defects, scoliosis is usually combined with chest deformation, kyphosis and lordosis. 2. Birth injuries. During a difficult birth, the child’s brain suffers, the symmetry of innervation is disrupted (from the Latin in - “inside” + nervus - “nerve”. On the one hand, the regulation of brain functions will be normal and sufficient, but on the other hand, it will not. Defects in the development of the spine after Such injuries begin to appear around the age of 5-6. The form of the disease can be very different - from mild to severe. 3. Induced disorders. As a rule, they are caused by external causes, which include playing sports that require asymmetrical load of different muscle groups ( tennis, archery, fencing, throwing sports equipment, etc.), as well as playing the violin, accordion, the habit of sitting lounging or tucking one's legs, etc. Induced scoliosis can develop due to different leg lengths.In this case, a skewed pelvis causes a bend of the spine in the lumbar region towards the shortened leg. In the thoracic region, as a rule, a counter-bend appears in the opposite direction. Both fashion and congenital shyness can lead to posture disorders. In some youth groups it is common to walk hunched over. And large breasts in a young girl often make her want to hide them - the easiest way to do this is to bend your back. All this can lead to permanent changes in the spine. The critical age for induced disorders is 11-13 years, when hormonal changes begin in children, accompanied by a sharp acceleration in the growth of skeletal bones. 4. Osteochondropathy - underdevelopment of the osteochondral apparatus. Usually a consequence of decreased motor activity in childhood. 5. Excessively rapid growth of the child. During puberty, there are periods of explosive growth: in a few months - up to 15 cm. At the same time, muscle growth in length lags far behind the growth of the skeleton. As a result, the spine may become skewed. 6. Spinal injuries. When jumping off a swing, a child may be hit in the back by the seat. It is no less dangerous to go down snow slides on flat objects like plates or cardboards - when bouncing, strong blows are applied to the buttocks, and the straightened lumbar spine (while sitting with bent legs on a plane) does not allow to dampen (dampen) these blows. Therefore, it is much safer to ride a regular sled. 7. Consequences of surgical interventions and burns. Extensive damage to certain areas of the skin, muscles, and nerves during serious abdominal operations or burns stops the development of the affected areas and often causes certain postural disorders. 8. Intervertebral hernia and pinching of large nerves. They occur more often in adults and cause functional, adaptive scoliosis or kyphosis. If the treatment of a hernia or strangulation is carried out on time, such a defect disappears without a trace.
The sooner, the more effective
Early and correct diagnosis helps to take adequate measures in time and quickly get rid of the disease. But curvature of the spine is not only a defect in posture. This is a disease that does not allow a person to live a full life. Severe forms of the disease are extremely difficult to treat because they are accompanied by deformation of the ribs, sternum, collarbones, pelvis and shoulder girdle. Unfortunately, posture defects are now much more common than 10-20 years ago. They are especially dangerous for girls, because they are facing motherhood. During pregnancy, connective tissues, which include ligaments, tendons, and intervertebral discs, become softer and more elastic. This is a natural process that makes childbirth easier. But this also provokes the further development of scoliosis, because carrying a child (and after childbirth, carrying it in your arms) leads to increased stress on the spine. However, do not despair - you can get rid of scoliosis, kyphosis and lordosis. The 1st degree is treated for about a month, the 2nd - 3 months, the 3rd - six months or more, the 4th - several years. True, not every person has the perseverance to work on his posture not for months, but for years!.. However, the speed of treatment largely depends on motivation. There are patients over 30 who managed to get rid of grade 3 scoliosis in a few weeks, and children 6-10 years old who took months to overcome grade 1-2 scoliosis. Still, treatment should be started as early as possible. With advanced scoliosis, the final results of treatment are worse - usually more or less pronounced residual deformations of the ribs and vertebrae remain.
Make an appointment by calling the center: 8 (495) 911-36-62,.
Preventive measures for spinal curvature in children
To avoid spinal curvature in a child, the expectant mother needs to take folic acid and vitamin B12 6 months before conception. And after the birth of the baby, from the first days of his life, start preventing scoliosis. Initially, this may be a massage, and then - performing simple actions that easily become a habit.
To improve posture and prevent the development of scoliosis, an older child should follow simple recommendations:
- while sitting at the table, change the position of your feet as often as possible;
- keep your back straight;
- move for at least half a minute every 15 minutes;
- do not stand in such a way that your body weight rests on one leg;
- ensure that the load on the supporting and motor systems is distributed evenly.
You also need to purchase a high-quality school backpack, an orthopedic mattress (the bed should not be too soft) and a spacious desk. Throughout the day, let the child lie flat on his stomach or back on a hard surface several times for 10–15 minutes to relieve the load on the spine. To stretch out displaced vertebrae, it is useful to hang on a horizontal bar. In this case, you should descend to the ground smoothly, on your tiptoes, and not jump off.