Scoliosis and osteochondrosis are often concomitant diseases. Both are associated with degeneration of the spinal column. But in the case of scoliosis, there is a violation of posture in the lateral projection, and in the case of osteochondrosis, degeneration of the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral discs occurs.
Curvature of the spine can lead to the development of degenerative disc disease. And, on the contrary, against the background of destruction of the intervertebral disc, a decrease in its height on one side (protrusion) often occurs, and secondary curvature of the spinal column is observed.
Scoliosis and osteochondrosis of the spine that develops in adolescence often leads to deformation of the chest and disruption of the functions of internal organs. In such patients, there is a decrease in the vital volume of the lungs, changes in heart rate, and hemodynamic pathology in the cavity of the pulmonary and systemic circulation.
Scoliosis is a severe pathology that is associated with disruption of the muscular frame of the back. Although the exact causes of poor posture are still unknown to doctors, they have come to the conclusion that in addition to genetically inherited factors of family predisposition to spinal deformity, the development of the back muscles plays a huge role. The frame is responsible for maintaining the balance of the spine. Any disorder or dysfunction entails degeneration of cartilage tissue. There is a partial displacement of the vertebrae and fixation in the wrong position due to the formation of bone anastomoses, fusion of osteophytes, etc. The longer scoliosis develops, the more severe the consequences of this disease.
Osteochondrosis, by its nature, is also associated with dysfunction of the muscular frame of the back. Important negative impact factors:
- disruption of the diffuse nutrition of the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral discs, which can only be achieved through interaction with the surrounding muscle fibers;
- accumulation of breakdown products under conditions of low efficiency of myocyte performance;
- lack of physical activity leads to an imbalance in the position of the vertebral bodies, they are not fixed in a vertical position and begin to have a traumatic effect on the intervertebral cartilaginous discs located between them;
- degeneration of the ligamentous and tendon apparatus due to low muscle performance
Osteochondrosis is degeneration of the intervertebral disc. It consists of a dense membrane (fibrous ring), inside which the nucleus pulposus is located in the form of a gelatinous body. Nutrition of cartilage tissue can only be carried out with active contractile work of the surrounding muscles, since the fibrous ring and nucleus pulposus do not have their own blood supply. A small portion of fluid and nutrients enters the lower part of the disc through diffuse exchange with the endplates. They have their own circulatory network. But it can be subject to sclerosis due to prolonged compression. This is typical for an increase in vertical pressure on certain areas of the intervertebral disc during the development of scoliosis.
Timely treatment of these diseases will completely restore the functionality of the spinal column. The risk of developing serious irreversible consequences can only be avoided if you consult a doctor in a timely manner.
In Moscow, you can make a free appointment with a vertebrologist or neurologist at our manual therapy clinic. To do this, call the administrator and agree on an appointment time. During the consultation, the doctor will conduct an examination, establish an accurate diagnosis and tell you which manual therapy methods will be effective in the case of your disease.
Back pain and atlas adjustment
What causes lower back pain? What causes lead to these and other spinal diseases? Why are these diseases so difficult to cure?
In medicine, it has been known since ancient times that identifying the real cause can cure the disease or, at least, alleviate the symptoms.
In this article we will try to highlight one of the most important reasons affecting the health of the spine and the functioning of the musculoskeletal system in general, and we will also talk about the Swiss method of adjusting the atlas and how this technique can be useful for people suffering from various pains in the atlas. neck, back and lower back areas.
Before treating scoliosis and osteochondrosis
Before treating scoliosis and osteochondrosis, you need to conduct a thorough differential diagnosis. It begins with an examination by a specialist. A vertebrologist will be able to detect, during palpation examination, a decrease in the height of the intervertebral disc, muscle fiber tension syndrome, and curvature in the lateral projection. Then he orders an x-ray in different projections. This examination allows us to clarify the localization of pathological changes and the degree of destructive impact.
If it is difficult to make an accurate diagnosis, an MRI examination is prescribed. It allows you to identify all structural changes in the tissues of the musculoskeletal system. Ultrasound, duplex scanning, etc. are also indicated.
Osteochondrosis: symptoms
Cervical osteochondrosis, thoracic osteochondrosis, osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine - all these are diseases of the same order. Osteochondrosis refers to pathological processes in articular cartilage.
Intervertebral discs are often affected by this disease, although the disease can spread to almost any joint.
The most common symptoms of osteochondrosis are constant aching back pain, which can be aggravated by sudden movements, heavy lifting, and even coughing or sneezing.
With cervical osteochondrosis, pain is noted in the neck and shoulders. In this case, the vertebral artery is often damaged, which, in turn, can cause severe headaches and noises in the head.
With osteochondrosis of the thoracic region, patients often complain of acute pain in the chest, in the heart area.
Osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine is felt as pain in the lower back, radiating to the legs.
Classifications of scoliosis
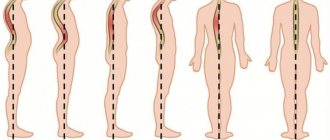
- According to the angle of curvature, 4 degrees of scoliosis are distinguished (according to V.D. Chaklin 1973): scoliosis 1 degree - angle up to 10 degrees,
- scoliosis 2 degrees - angle from 11 to 30 degrees,
- scoliosis 3rd degree - angle from 31 to 60 degrees,
- scoliosis 4 degrees - an angle greater than 60 degrees, usually severe fixed kyphoscoliosis, significant skeletal deformation, dysfunction of the heart and lungs
highlight:
- C-shaped scoliosis (with one arc of curvature), also uncompensated, is considered the most complex pathology in official medicine.
:
- cervicothoracic scoliosis
Congenital scoliosis is very rare and is characterized by a severe course. There is no scientifically confirmed data on the possibility of inheritance of this disease.
Scoliosis: symptoms
Scoliosis is a lateral curvature of the spine. It is believed that weak back muscles and incorrect posture contribute to the occurrence and development of scoliosis. There are several stages of development of this disease.
At the first stage, scoliosis appears only temporarily, with severe fatigue of the back muscles. After rest, the curvature disappears.
At the second stage, the curvature becomes permanent. The spine loses mobility, and the symmetry of the chest and the position of the shoulder blades are disturbed.
The third stage is the most severe, since as a result of severe curvature of the spine, internal organs begin to suffer, and the slightest loads become a real test for the patient.
Symptoms of scoliosis and intervertebral osteochondrosis
The clinical symptoms of scoliosis and osteochondrosis are similar, since both pathologies to one degree or another disrupt the physiological configuration of the spinal column. Scoliosis and intervertebral osteochondrosis can manifest as:
- constant dull pain, which with significant physical exertion turns into acute;
- stiffness of movement, especially in the morning or after a long static position of the body;
- limitation of the amplitude of mobility;
- neurological clinic (paresthesia, numbness, pain spreading along the compressed nerve).
If such signs appear, you should seek medical help as soon as possible. Scoliosis and osteochondrosis are treated by a vertebrologist, neurologist or orthopedist. In our clinic you can also sign up for a free consultation with a chiropractor or osteopath.
What causes spinal diseases?
Despite the seemingly extensive list of spinal diseases, it has long been believed that most of them are acquired and provoked by a lifestyle in which the spine is subjected to various force loads.
Heavy lifting, sudden bending, turning, prolonged sitting or standing, professional sports, and age are all factors that are believed to contribute to the development of spinal diseases.
However, it is quite difficult for a modern person to completely remove physical activity, prolonged sitting or standing (for example, during professional activities) from his daily life, and even more difficult not to grow old.
Thus, it turns out that every person has a predisposition to the occurrence of spinal diseases.
It is worth noting that the age of the patients is completely different. Back pain and neck pain bother not only older people, but also fairly young people.
Causes
The most common causes of a pathology such as scoliosis include:
- congenital pathologies due to trauma during childbirth and developmental anomalies;
- excessively intense or, on the contrary, insufficient loads on the spine;
- disturbances in the formation and growth of the spine that appear in childhood;
- excess body weight;
- flat feet or club feet.
Often there is so-called idiopathic lumbar scoliosis, in which it is impossible to determine the cause.
Traditional Treatments
Traditional treatments are carried out under the supervision of a doctor. Depending on the nature of the disease, the doctor prescribes a treatment regimen.
However, most traditional methods are not aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease, but rather at relieving symptoms during a period of inflammation and recovery.
After some time, the attack of the disease, for example, radiculitis, stops (remission occurs), and after some time it returns with the same or greater force (relapse occurs).
Traditional symptomatic treatment methods include pain-relieving injections and warming physiotherapeutic procedures, as well as taking B vitamins, which help restore damaged cartilage tissue.
The most lasting results, for example, in the case of scoliosis, are provided by physical exercises and therapeutic exercises. This is due to the fact that regular physical exercise strengthens the muscles of the back and neck, and they, in turn, keep the spine from further deformation.
Treatment of back pain with warming ointments and patches is not a cure
Taking advantage of the high prevalence of spinal diseases, various ointments, patches and electrical devices are widely advertised on television and radio.
However, you need to understand that applying a warming and anesthetic composition to a sore back will only hide for some time and certainly will not delay the onset of pathological processes in the spine, such as the destruction of intervertebral discs and the formation of intervertebral hernias and protrusions.
Therefore, treatment of osteochondrosis at home is unlikely to be effective.
Treatment of scoliosis and osteochondrosis of the spine
It is necessary to begin treatment of scoliosis and osteochondrosis of the spine by eliminating the action of pathogenic factors. Currently, drug treatment for osteochondrosis and scoliosis is impossible, since there are no drugs that could eliminate the curvature of the spinal column.
Manual therapy methods allow you to restore the configuration of the spine only at the 1st-2nd stage of scoliosis. With more pronounced deformation of the spinal column, surgery is indicated to restore its integrity.
For the treatment of osteochondrosis combined with scoliosis, the following treatment options are used:
- traction traction of the spinal column - allows you to return the physiological height of the intervertebral discs and restore the normal position of the vertebral bodies;
- osteopathy and massage increase the elasticity of all cartilage, ligament, tendon and muscle tissues;
- therapeutic exercises and kinesiotherapy correct the performance of the muscular frame of the back, create conditions for correcting posture, increase muscle tone, and enhance diffuse nutrition of the intervertebral discs;
- reflexology starts the process of regeneration of all damaged tissues;
- physiotherapy, laser treatment and electrical myostimulation accelerate the healing process.
The course of treatment is always developed individually. If you would like to receive an individual consultation with a vertebrologist on this issue, make an appointment for a free appointment at our manual therapy clinic.
Methods for preventing osteochondrosis and scoliosis
The main methods of preventing osteochondrosis and scoliosis are to eliminate negative impact factors. It is necessary to monitor the physical condition of the muscular frame of the back. It is also recommended to lead an active, mobile lifestyle. When sitting, you need to keep your back straight.
Proper organization of the sleeping and working space allows you to eliminate long-term static overstrain of the neck muscles. A balanced diet and sufficient consumption of clean drinking water allow the tissue of the intervertebral disc to be fully restored.
Whenever possible, it is necessary to exclude injuries, inflammatory processes, and the presence of foci of chronic inflammation in the human body.
Manual therapy and its disadvantages
Manual therapy refers to a complex of forceful effects on the patient’s spine using the hands of a doctor.
Using various manipulations, the doctor warms up the muscles surrounding the vertebra, and then forcefully adjusts it, returning it to the correct anatomical position.
Forceful impact on the spine is associated with certain risks, so there is still controversy surrounding manual therapy, and the methods themselves cause a lot of criticism.
There is a so-called muscle memory that strives to keep the spine in a certain state. This explains the inconsistent results of manual therapy: after a certain period of time, the reduced vertebra may return to its previous painful position.
Spine surgery
Surgical intervention in the spine area, perhaps, has been and will remain in the minds of many doctors and patients as a last resort. And, nevertheless, such operations are carried out when the disease progresses and begins to threaten the life of the body.
The essence of these methods usually comes down to fixing one or more vertebrae in a certain position using various metal devices and implants.
However, the effect of such operations is short-lived, and relapses of the disease are possible, which may lead to the need for new surgical intervention.
The connection between back pain and spinal health
What distinguishes a healthy person from a sick person? Why do some people rarely have back pain, while others suffer from it all the time? Where do low back pain, cervical osteochondrosis, radiculitis, intervertebral hernias and protrusions come from?
Obviously, all people suffering from various diseases in the spine have one thing in common - the health of their spine is undermined.
The first cervical vertebra (atlas) is an important component of spinal health.
Sometimes the cause of a disease is not where the patient expects to find it. If a person suffers from back pain, then he is inclined to think that the cause is located exactly in the place where it hurts.
In the case of the spine, this is not always the case. Each part of the spine is very closely connected to the others. A problem in one part of the spine will inevitably affect neighboring parts.
Recent studies in Switzerland (in the 90s) found that the vast majority of people suffering from various diseases of the spine are diagnosed with displacement of the first cervical vertebra - the atlas.
At the same time, a person may not know that his atlas is displaced, and live with such a displacement (sometimes significant) all his life.
The atlas has a very important function - it connects the spinal column to the skull and forms a balance point at the junction.
Unlike other vertebrae, displacement of the atlas can affect the entire spine as a whole and can bend it, cause scoliosis and premature abrasion of the intervertebral discs, which in turn can lead to radiculitis, intervertebral hernias and, of course, osteochondrosis.
Reviews of doctors providing the service - Scoliosis of the lumbar spine
In 2000, Andrei Arkadyevich performed spinal surgery on me.
Four days in the clinic and I have been living a full life for 20 years without restrictions on movement and I remember with gratitude Dr. A.A. Khodnevich. God bless him. And in 2000 he could walk no more than 10 meters. Read full review Viktor Alexandrovich
20.05.2020
Low bow to Alexander Semenovich Bronstein and Andrei Arkadyevich Khodnevich. I arrived at CELT on July 2, 2021 with extreme pain that I endured for 10 days. Hernia C6-C-7. I was given two blockades in Ivanovo, about 9 complex IVs, I lost 6 kg in a week and was in a panic, I didn’t see a way out and nothing happened to me... Read full review
Elena Nikolaevna L.
20.10.2019
Operations for diseases of the spine
- Cost: 100,000 - 250,000 rubles.
- Duration: 40-60 minutes
- Hospitalization: 2-3 days in hospital
More details
In what cases is the atlas displaced?
Mostly, displacement of the atlas occurs during childbirth. Due to the heavy load on the neck, the baby's atlas (the first cervical vertebra) can become dislodged and then remain in that position for the rest of its life.
Displacement of the atlas will cause the spine to curve, and the intervertebral discs will begin to wear out quickly with age.
With a stronger displacement of the atlas, the atlantoaxial joint (the joint at the junction of the spine with the skull) stops working normally. In this case, the head will be turned by the entire body, which will create additional stress on the connective cartilaginous tissue between the vertebrae and lead to degeneration of the intervertebral discs in the neck or lumbar region (or in both sections at once).
What is the difference between osteochondrosis and scoliosis?
The main differences between osteochondrosis and scoliosis lie in the pathogenesis of the diseases. The difference between scoliosis and osteochondrosis is that in the first case, the vertebral bodies are displaced in the lateral plane and, as a result, a section of the spinal column (or several) is deformed. With osteochondrosis, the configuration of the intervertebral discs changes in their height. They seem to sag, they are compressed by the weight of the body, they undergo protrusion. As the height decreases, the area of the intervertebral disc increases compensatoryly.
The next difference between scoliosis and osteochondrosis is its effect on other organs and systems. Thus, scoliosis leads to the following severe complications:
- deformation of the chest with changes in the position of the lungs, pleura, esophagus, heart, aorta, etc.;
- degeneration and destruction of the costovertebral and costothoracic joints, which entails a change in respiratory activity;
- dystrophy of the intercostal muscles on the side of the curvature;
- diaphragm deformation;
- pressure on the pancreas;
- dislocation of the kidney with a change in its functionality.
Osteochondrosis leads to other unpleasant complications. The most common is an intervertebral hernia, which can cause severe pain and disruption of the innervation processes of certain parts of the body. Intervertebral hernia appears as a result of active destruction of the intervertebral disc with complete loss of its tissue to regeneration and independent recovery with increased diffuse nutrition. This occurs due to the gradual calcification of the surface of the intervertebral disc. Against the background of a violation of diffuse nutrition, dehydration of the fibrous ring occurs, it becomes brittle and loses its typical elasticity. Numerous cracks appear, which, in order to restore integrity, are covered with deposits of calcium salts. These areas cannot participate in the diffuse exchange of fluids in the future. They lead to protrusion and the appearance of an intervertebral hernia.
What makes the spine sick?
The desire to keep the head straight is an innate feature of the human body, acquired over thousands of years of evolution of the human body.
However, with a displaced atlas, this desire leads to curvature of the spine, scoliosis and other serious consequences that only progress with age.
Thus, back pain, neck pain, lower back pain, osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernia and other diseases are becoming an integral part of modern life.
Is there an effective method to combat spinal diseases?
Today, a doctor trained in the Atlas-Standard technique can identify displacement of the atlas, and also carry out a procedure to correct it without surgery and without sudden force on the cervical spine.
An important feature of the technique is its safety, since the effect on the first cervical vertebra is not direct, but indirect, through the muscles of the cervical spine.
The method allows the Atlas to return to its natural place in one procedure and for life.
Correction of the atlas allows you to eliminate the main reason why the spine is in the wrong position. As the experience of using the procedure shows, after the atlas is realigned, the process of self-straightening of the spine begins in the body.