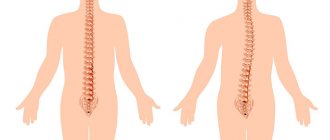
Posture is a body position in which the load on the spine is normally distributed evenly.
Poor posture manifests itself not only in external signs, but also causes a lot of inconvenience, pain, contributes to the occurrence of certain diseases, reduces the body’s resistance to physical stress, and reduces immunity.
It is important not to miss the moment when disorders in posture are reversible. Timely contact with a specialist will prevent the progression of the disease, avoid possible consequences and protect your health.
What is scoliosis?
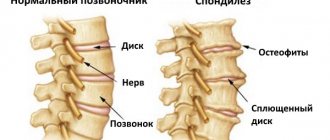
Scoliosis is a curvature of the spinal column to the left or right relative to its own axis . Essentially, this is an asymmetry of the entire body: a curved spine, protruding ribs or a shoulder blade. In most cases, scoliosis of the lumbar and thoracic spine is diagnosed.
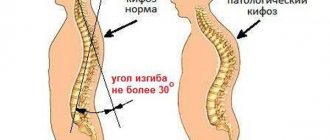
Sometimes scoliosis is confused with ordinary stoop (kyphosis) , although these postural disorders are completely different. In fairness, it is worth noting that sometimes kyphosis is aggravated by scoliosis and kyphoscoliosis occurs. But, in general, scoliosis and kyphosis are different diseases, and they need to be considered separately from each other.
Scoliosis is often confused with kyphosis, which is extremely wrong.
Measurement methods
In modern medicine, several methods for measuring the scoliotic angle are used. Despite the fact that some methods are quite accessible, you should not engage in self-diagnosis. Scoliotic angle measurements should only be carried out by an experienced specialist.
Ishala method
The most informative method available today for determining the degree of scoliosis, which allows us to identify not only the angle of curvature itself, but also the level of inclination of each deformed spine.
First of all, the size of the scoliotic curve is determined. It is necessary to determine the uppermost and lowermost non-deformed vertebra. A line is then drawn through the bases of these two points. Then, parallel to the straight line, another line is formed, indicating the height of the deformed vertebra. The level of inclination of each vertebra is calculated separately.
Ferguson method
On an x-ray, the doctor determines the most protruding vertebra, located at the very peak of the scoliotic curve. A mark is placed in its middle. Next, it is necessary to recognize the vertebrae that are the basis of the scoliotic arch - that is, they protrude the least to the side. A mark is also placed in the middle of these vertebrae. In total, there are three main points in the image. Then, using a ruler, you must first connect the first point to the second, then the second to the third. The angle formed between straight lines will be an indicator of the degree of scoliotic curve according to Ferguson. This method is very informative, but it can be used for deformations of less than 50 degrees.
Chaklin method
This method is widely used in the CIS countries. With this measurement method, not only the angle of deviation of the spinal column, but also the scoliotic arch is taken into account. In order for the doctor to make accurate calculations, it is necessary to take an x-ray in the anteroposterior projection.
Vertebrae that have not undergone deformation are identified from above and below, and two lines are drawn through them. Perpendiculars are drawn from the middle of the neutral vertebra of the upper part and the middle of the lower vertebra. The place where they intersect is called the Chaklin angle.
Cobb method
The most common method for determining the degree of scoliosis. The measurement is carried out as follows - the uppermost vertebra of the arch is marked on the image, and on top the vertebrae least deviated from their normal position. Then two lines are drawn: the first - from the upper vertebra along its uppermost edge; the second - from the lower vertebra along its lowest edge. Next, a perpendicular or angle is measured between these two lines.
Lekum method
This method of calculating the degree of scoliosis is used quite rarely, but is irreplaceable in cases where it is difficult to accurately determine the neutral vertebrae. On the x-ray, the doctor marks the central part of the two vertebrae located on either side of the most convex angle. Two straight lines are drawn through the designated centers, and the angle between is an indicator of spinal deformation.
Diagnosis of scoliosis by an orthopedist
First of all, diagnosing scoliosis involves taking a medical history. The orthopedist’s task is to find out when the deformity was first noticed, whether the patient contacted specialists, and whether treatment was carried out. The doctor must also study the patient’s medical record (especially if there are indications for surgery) and determine the dynamics of the progression of the curvature.
Primary diagnosis of the disease includes:
- Clarifying patient complaints. As a rule, a person with scoliosis complains of back pain and defects in appearance caused by deformation of the spine and chest. At this stage, the type of pain is determined, and concomitant pathologies that could provoke the development of scoliosis are identified.
- Examination of the patient. This stage of the examination is especially important, which means it must be carried out especially carefully. After a visual examination, the patient is referred to a neurologist to make the correct diagnosis.
The most popular methods for diagnosing scoliosis are:
. It is a visual study of curvature in all planes. A man undresses to the waist, leans his body forward and tries to reach the floor with his fingers. At this moment, all pathological changes become obvious. The doctor also checks reflexes, range of motion in joints, symmetry of body parts and muscle strength.
An orthopedist may order an x-ray to make a diagnosis. Physical examination- Scoliometer study . Designed to determine the rotation of the vertebrae, the severity of the costal hump, and indirectly determine the angle of curvature. A scoliometer makes it possible to make a diagnosis without the use of X-rays.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), CT (computed tomography). Prescribed in preparation for surgery, as well as in cases of suspected malfunction of the nervous system.
- X-ray of the spine . Allows for high-quality diagnosis of the disease. It is necessary to take photographs at different stages of scoliosis development for comparison and monitoring of the patient’s condition.
The stage of development of the disease and the type of therapy depend on the degree of curvature of the spinal column and the angle of rotation of the spine. These factors are measured in degrees and, as a rule, are related to each other .
Diagnosis of posture status
The best way to assess the posture of an older child is by parents, who are always in front of him. A child who is rarely ill visits the doctor less often, and there are fewer and fewer nurses in schools. Therefore, once every 3-4 months, undress your child down to his underpants and carefully examine his back. Assess the position of the head, the symmetry of the shoulders, the line of the spine, the symmetry of the knees and feet. Standing from the side, evaluate the curvature of the spine, and from the front, the symmetry of the chest.
When examining your back, pay attention to its symmetry. The spinal column and the intergluteal fold should form one straight line. A head tilted to one side, shoulders of uneven height, the edges of the shoulder blades lagging behind the chest wall, a reduced triangle of the waist on one side, one leg shorter than the other, an emerging hump and a clear curvature of the spine - all these symptoms require immediate contact with an orthopedic doctor or pediatrician, who will refer the child to orthopedic treatment.
Diagnosis of scoliosis at home
Early diagnosis of scoliosis is very important. The main symptom of the disease is a violation of body symmetry.
The following symptoms indicate its presence:
- unnaturally protruding shoulder blades;
- curved waistline;
- back asymmetry;
- deviation of the head to the left or right from the center of the body;
- asymmetrical hips or shoulders;
- tilt towards the left or right side of the body.
If you notice at least one of these signs in yourself or your child, immediately contact an orthopedist.
Video: “Signs of scoliosis”
1st degree
Scoliotic curvature of the spine of the 1st degree is hardly noticeable.
The presence of first-degree scoliosis can be recognized by the following signs::
- curvature of the spinal column along the lateral line (the angle of deviation is no more than 5-10 degrees);
- straightening the spine in a horizontal position, slight twisting of the spine around its axis in a vertical position;
- asymmetry of the shoulder blades or waist due to curvature in the thoracic and lumbar regions, respectively.
Stage 1 scoliosis can be diagnosed by asymmetrical placement of the shoulder blades
To diagnose stage 1 scoliosis, you can ask a person to take an upright body position, lean forward and freely lower his arms, or lie down on a flat, hard surface.
Scoliosis may be accompanied by a curvature of the spine in another plane , and if it exists, the orthopedist will detect it during the diagnostic process.
2nd degree
Scoliosis of the 2nd degree is easier to detect at home, because the curvature becomes noticeable in a standing position.
The presence of scoliosis of the 2nd degree is indicated by the following signs:
- there is a violation of posture;
- on one side the muscles are more pronounced than on the other (this can be detected by visual inspection and palpation);
- body asymmetry becomes obvious;
- when bending forward, a “rib hump” is clearly visible in the area of the upper vertebrae;
- The height of the shoulder blades often differs.
To recognize the 2nd degree of scoliotic curvature, the patient just needs to bend forward
If you consult a doctor at this stage of scoliosis development, an x-ray will show a deviation of the spinal column of up to 25 degrees. It is important to start treatment as soon as possible, because... During this period, the chest begins to actively deform.
Find out more about the treatment of scoliosis in childhood and adulthood:
- Therapy for scoliosis in adults
- You can find out which doctor to see if you have scoliosis on the page
- You can read all about children's massage for scoliosis here
- If you want to get acquainted with exercise therapy for scoliosis of 1 and 2 degrees in children, go here
- Gymnastics for scoliosis grades 1 and 2: a set of exercises
3rd degree
Did you know that...
Next fact
Stage 3 scoliosis can be recognized by:
- severe pain that occurs when moving the body;
- limited mobility and stiffness;
- taking an unnatural pose;
- visible changes in the spine;
- asymmetry of the shoulder blades and shoulders.
Grade 3 lateral curvature has a clearly visible displacement of the spine to the side. Often, with grade 3 scoliosis, the nerve roots of the spinal cord are pinched, which contributes to the appearance of the following symptoms:
- headache;
- problems in the functioning of internal organs;
- increasing pain when moving the body;
- loss of sensation in some areas of the body;
- tingling or numbness in the upper or lower extremities;
- depression and other nervous system disorders.
These signs of scoliosis can be detected at home. Diagnosis of scoliosis in a doctor’s office involves :
- radiography;
- Ultrasound;
- magnetic resonance or computed tomography of the spine.
X-ray allows you to determine the angle of the arc of curvature, MRI or CT allows you to determine as accurately as possible the area of the lesion and the accompanying complications of the disease, and ultrasound allows you to study the condition of internal organs, the functioning of which could be impaired due to curvature of the spine or compression of the nerve roots..
4th degree
Scoliosis 4 degrees is characterized by the presence of a pronounced curvature of the spine , with the angle of curvature being 50 degrees or more. This is the most advanced stage of scoliosis.
The spine with this pathology resembles the letter “S” (if there are two bending arcs) or the letter “Z” (if there are three bending arcs). Since the curvature changes the inclination of the torso, the patient's body becomes asymmetrical. As a rule, the bend begins at the top and ends at the bottom of the thoracic region.
Because of this, the chest is deformed and looks distorted. On the one hand, the area of the shoulder blades increases, on the other, the liver area protrudes. Violation of body symmetry leads to the formation of a hump.
At the last stage of scoliosis, the spine takes on an S-shape. In grade 4 scoliosis, internal organs are displaced. If they are compressed, the patient faces :
- shortness of breath;
- intestinal problems;
- surges in blood pressure;
- numbness of the limbs;
- back pain;
- inability to stay in an upright position for a long time.
It is not difficult to detect the listed symptoms, so diagnosing grade 4 scoliosis is not difficult even at home . In most cases, grade 4 scoliosis is found in adult patients with a mature skeleton.
However, in some cases, rapidly progressing forms of the disease also occur in children. The doctor may recommend X-rays and other studies to examine the condition of the spine and detect other disorders caused by scoliosis.
Video: “Preventive exercises for scoliosis”
Types of spinal curvatures - what are they?
There are three main types of curvatures. But it should be taken into account that in addition to these types, there are combined forms in which the deformation simultaneously affects several departments.
- Most often, increased physiological bending is diagnosed in the lumbar or cervical region in the anterior direction - this is the so-called lordosis . The deformity can be round or angular - then the vertebrae protrude into angles, and the position of the surrounding structures also changes: vessels, nerves, organs - depending on the degree of deformation.
- If there is excessive physiological bending in the thoracic region, we will talk about kyphosis . Deformation in this part of the spine can affect the function of the respiratory system, since the effective flow of air into the lungs is difficult.
- Scoliosis - a curvature of the spine to the side - is diagnosed most often; it can appear in different parts of the spinal column, while the deformation can take on different shapes: C or S-shaped, and even in the form of the letter “Z”.
Why does spinal curvature occur? Only about 25% of all disorders are congenital in origin. In other cases, the causes of the pathology can be very different, among which injuries and deformations as a result of numerous diseases predominate, for example, after paralysis of the spinal muscles due to cerebral palsy, tuberculosis or polio. Curvature can also be caused by tumors, scars, myositis, and even incorrect body position when sitting or walking.
Recommendations for prevention at home
Prevention of scoliosis should be carried out from birth, because The most dangerous age for the development of this disease is considered to be childhood and adolescence.
Scoliosis can be prevented by following these recommendations::
- During pregnancy, it is necessary to eat properly (include foods rich in vitamins and microelements), lead an active lifestyle, and avoid overwork.
- Small and newborn babies need to be constantly moving. It is advisable that parents teach them to systematically perform physical exercises.
- It is necessary to eat a balanced diet. The diet should contain useful components that take part in the development of internal organs, the formation of correct posture and the spinal column.
Prevention of curvature in children comes down to the following recommendations::
- Do not sit the baby until he learns to do it on his own.
- Walk with your child every day, regardless of the weather. Sunlight promotes the production of vitamin D, which is necessary for the normal condition and functioning of bones.
- Make sure that the newborn sleeps on a special orthopedic mattress.
- Properly equip the student’s workplace in accordance with his height and age. The distance between the eyes and the table should be 30 centimeters or more.
- Buy a schoolchild a backpack or briefcase with two straps so that the load is distributed evenly.
- Engage your child in sports. Physical activity has a positive effect on the development of internal organs, the muscular system and the musculoskeletal system.
- Make sure that the child does not slouch and keeps his back straight.
Pathological curvature of the spine can also be observed in adult patients.
To avoid developing the disease, older people need:
- Lead a healthy lifestyle, do not neglect physical activity. People who sit or stand for work should change their body position from time to time and do light exercises during breaks. The workplace should be well lit and properly equipped so that there is no need to assume awkward postures.
- Include foods rich in nutrients in your diet.
- Find time for sports. Swimming, exercises on the horizontal bar and any other physical activity helps improve muscle tone and achieve beautiful posture.
Prevention of scoliosis is especially effective during the period of active growth of the child . Therefore, parents should instill in their children a love of sports, wean them from the habit of slouching and staying in the same position for a long time.
How to determine the stability of scoliosis
Self-test for scoliosis
To do this, you will need two x-rays taken at the same time. One image of the spine should be with the patient standing, the second - with the patient lying down. Measure the angle of curvature in two photographs using the method described above. At the same angles of curvature, scoliosis is considered fixed or stable. If in a lying position, that is, in an unloaded state, the angle of curvature decreases, then they speak of unstable or unfixed scoliosis.
Classification of the disease
There are several types of classifications, depending on the angle of deviation, direction and cause of occurrence.
According to the angle of curvature of the axis, scoliosis in degrees:
- Up to 10 degrees – 1st degree scoliosis.
- Within 11 – 25 degrees – 2nd degree scoliosis.
- From 26 to 50 degrees – 3 degrees scoliosis.
- Over 50 degrees – 4 degrees scoliosis, the most advanced degree.
Causes of degrees of spinal scoliosis include:
- Idiopathic form of pathology - a diagnosis is made if it is problematic to identify the nature of the onset of the disease in a particular person.
- Acquired scoliosis is the most common cause of deformity. Occurs during puberty, when children go to school. Due to improper sitting with excessive deviation to the right or left, incorrect posture is formed. This creates an imbalance in the development of the spine and muscles, which negatively affects the health of the back.
- Age deformation. Develops against the background of other skeletal pathologies - osteoarthrosis, osteoporosis or osteochondrosis. The reasons are a violation of metabolic processes in bone tissue associated with the lack of calcium and magnesium entering the body in normal quantities.
- The congenital form is the result of intrauterine deformations of the human skeleton.
In direction, scoliosis can be right-sided or left-sided.