Cough with osteochondrosis can be provoked both by direct compression of the radicular nerves and by secondary pathological changes in the internal organs. Very often, cough with spinal osteochondrosis is a consequence of impaired innervation of the vocal cords, trachea, bronchitis, and palatine tonsils. With this pathology, there is a disturbance in the secretion of mucus, which moistens the respiratory tract and prevents infections from penetrating into the tissues. Therefore, the first thing that should be ruled out when a cough appears against the background of long-term osteochondrosis of the spinal column is all kinds of viral and bacterial infections.
Cough with cervical and thoracic osteochondrosis can be dry or wet, provoked by certain actions (for example, tilting the head to the side or inhaling too deeply). This symptom may indicate the development of pathology of internal organs. Therefore, you should not engage in self-diagnosis and treatment. This can lead to negative consequences for your health.
Preliminary diagnosis depends on how cough manifests itself in osteochondrosis. If a symptom appears suddenly, after stress or prolonged muscle tension in the neck and collar area, this may indicate that osteochondrosis is not complicated by protrusion and extrusion of the disc. If the cough is constantly present, and the patient experiences a feeling of lack of air when breathing, then complicated osteochondrosis can be diagnosed, in which degeneration and dystrophy of the intervertebral discs is observed.
If you have a cough and there is pain in the neck, chest, or collar area, you should seek medical help from a neurologist or vertebrologist as soon as possible. Upon examination, the doctor will be able to exclude the possibility of pulmonary and bronchial pathology. After a preliminary diagnosis has been made, directions for the necessary additional examinations can be given. This is an X-ray of the spinal column in the cervical and thoracic regions, fluorography and MRI examination.
In Moscow, you can make an absolutely free appointment with a vertebrologist and neurologist in our manual therapy clinic. Experienced doctors work here who can make the correct diagnosis and develop an individual treatment plan. Don't hesitate, seek help as quickly as possible. By doing so, you will increase the chances of quick and successful healing.
Can there be a cough with osteochondrosis?
Many patients wonder whether osteochondrosis can cause coughing and why this symptom occurs when the integrity of the intervertebral discs is damaged. Let's try to talk about whether a cough can be caused by osteochondrosis and what it is connected with.
Osteochondrosis does not always cause a cough - it depends on in which part the foci of pathological changes are located and how damaged the radicular nerves and their branches are.
Cough from osteochondrosis occurs if the following radicular nerves are damaged:
- C4 – adenoids enlarge, making it difficult to breathe through the nose, which provokes frequent colds, accompanied by coughing and sore throat;
- C5 – sore throat occurs, tonsillitis and laryngitis often develop;
- T1 – the esophagus may be affected and a reflex cough may occur, the trachea is also affected, and sometimes bronchial asthma develops;
- T2 – is responsible for the innervation of the heart and coronary arteries; with severe damage, signs of heart failure appear, accompanied by attacks of shortness of breath and coughing (especially when moving to a horizontal position);
- T3 - innervates the tissues of the bronchi and lungs; compression can also affect the pleura; bronchitis, tracheitis, bronchial asthma of unspecified origin, pleurisy and pneumonia often develop);
- T8 - innervates the diaphragm; when it is compressed, respiratory failure and secondary cough can occur.
Can there be a cough with thoracic osteochondrosis if the radicular nerve is not pinched? This condition can occur when there is excessive tension in the intercostal respiratory muscles.
Can there be a cough with cervical osteochondrosis if there are no complications of this disease in the form of protrusion and disc herniation? Yes, this is quite possible if pulled muscle fiber syndrome is present. Spasmed muscles in the collar area disrupt blood flow through the posterior vertebral arteries. They are responsible for the blood supply to the posterior parts of the brain.
The respiratory center is located there. It regulates the frequency and depth of breaths. Cough impulses are also generated here if the body needs to clear something from the lung and bronchial tissue. Any irritation of the mucous membranes of the upper and lower respiratory tract transmits a signal to the structures of the medulla oblongata. The respiratory center located there sends the opposite command to activate the cough reflex. If the medulla oblongata does not receive sufficient nutrition, then serious disruptions begin in its functioning. A cough can occur just like that, for no apparent reason.
Can thoracic osteochondrosis cause a cough if there is no cold? Yes, as mentioned above, damage to certain intervertebral discs in this department leads to disruption of the innervation of the respiratory system. Lung tissue loses its ability to clean itself in a timely manner, so the cough reflex mechanism is triggered to remove accumulated sputum, mucus and exfoliated cells.
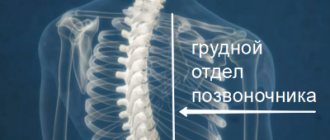
Features of spine disease
The cause of the development of osteochondrosis is associated with the progress of degenerative changes affecting the thoracic and cervical spine. These zones are penetrated by an extensive network of blood vessels and nerve endings, which provide brain control over the internal organs.
Sore throat and cough syndrome, atypical for osteochondrosis, are considered to be well-known symptoms of respiratory pathology, which are treated by a therapist. True, it is not always problems with the respiratory system that cause discomfort in the throat and cough syndrome.
If, against the background of the respiratory reflex, pain sensations spread to the cervicothoracic spine, this may signal the development of a cervical or thoracic type of osteochondrosis.
What is the danger of cervical type of pathology?
The onset of degenerative-dystrophic processes in the neck area is often asymptomatic. When the ability of the vertebrae to resist stress decreases, osteochondrosis is signaled by spasms in the throat, causing coughing, as well as other symptoms:
- Head and neck pain, dizziness, increased irritation;
- Muscle tension and spasms, pinched nerve endings;
- Decreased performance, deterioration of vision and hearing;
- Oxygen starvation of the brain due to impaired blood circulation;
- The development of joint diseases, ischemia with the threat of stroke.
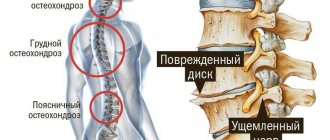
Further progression of the disease leads to the formation of an intervertebral hernia. The fact of compression of the endings of the nerve fibers results in increased pain and coughing, especially when the head is turned sharply. The possibility of numbness in part of the face along with the appearance of false symptoms of other ailments cannot be ruled out.
- Night cough in children and adults - causes of dry and wet cough, diagnosis and treatment methods
Signs of osteochondrosis in the thoracic region
In this case, the focus of localization of the symptoms of osteochondrosis becomes the thoracic zone, but without compression of the vertebral artery, as with cervical pathology. As the disease progresses to the chronic stage, concomitant diseases develop and the structure of bone tissue changes. The formation of hernias leads to pinching of the nerves connected to the spinal cord, which causes increased pain and coughing. In addition to manifestations reminiscent of cervical pathology, among the symptoms of the thoracic type of osteochondrosis, dangerous symptoms are recorded:
- An acute burst of pain when coughing, during inhalation and exhalation;
- Pain in the left hypochondrium due to cardiac arrhythmia;
- Deterioration of skin sensitivity, shoulder discomfort;
- Problems with thyroid function, as well as shortness of breath, heartburn;
- Signs of a dry cough with its transition to a wet form.
Doctors say the causes of problems with the musculoskeletal system are the consequences of a sedentary lifestyle and increased stress on the back area. It is also possible that the influence of heredity and the spinal column remaining in an unnatural position for a long time cannot be ruled out. Due to excess weight, which creates additional stress on the joints, severe coughing attacks are sometimes annoying.
Cough with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
Cough with cervical osteochondrosis can also occur for another reason. Here is the radicular nerve responsible for the innervation of the thyroid gland. It is located between the C7-T1 vertebrae. When it is compressed, dysfunction of the thyroid gland is observed. It stops producing enough hormones, which negatively affects the state of the autonomic nervous system. Also, an increase in thyroid tissue can provoke a reflex cough.
Cough with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is a negative clinical sign; it indicates that:
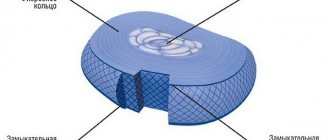
- there is a decrease in the height of the intervertebral disc due to dehydration of the cartilage tissue of the fibrous ring;
- there is a secondary static overstrain of the muscles of the collar zone;
- the intensity of blood supply to the structures of the posterior parts of the brain decreases;
- there is a risk of rupture of the fibrous ring with partial exit of the nucleus pulposus beyond its limits (formation of an intervertebral hernia).
If a cough occurs due to osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, then it is necessary to carry out differential diagnosis. For this purpose, the patient is prescribed fluorography (to exclude pathology of the lung tissue), consultation with a pulmonologist and otolaryngologist. If a visual examination reveals hyperemia of the tissues of the upper respiratory tract, then most likely the cause of the cough is a cold.
Also, during differential diagnosis, the possibility of developing pathologies of the esophagus and thyroid gland should be excluded. This may be gastroesophageal reflux disease and thyrotoxicosis. They may cause a reflex cough, unrelated or indirectly provoked by osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
Causes of osteochondrosis
Since the advent of computers, the number of patients with osteochondrosis has increased significantly. Now people of different age categories are susceptible to this disease. A sedentary lifestyle and lack of physical activity negatively affects the spine and can cause deformation at a young age. The lumbar and cervical spine are most often injured due to the fact that they bear the majority of the load.
Unlike the cervical region, the thoracic region is secured by ribs, which help reduce the load. However, if you remain in an incorrect position for a long time, it is impossible to avoid destruction of the spinal discs. The main causes of the disease include:
- Passive lifestyle.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Obesity.
- Poor nutrition.
- Weakening of the back muscles.
- Metabolic disease.
- Lack or excess of physical activity.
- Injuries.
Due to the impact of negative factors, the cartilage of the spine begins to shrink and become deformed. The nerve roots are pinched, and this is characterized by acute pain. All internal organs are affected and symptoms of heart, lung and stomach diseases may appear.
Dry cough with osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
Cough with osteochondrosis of the thoracic region can be caused by both reflex irritation of the mucous membranes of the upper and lower respiratory tract, and tension of the intercostal and diaphragmatic respiratory muscles. But most often, cough with osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is associated with impaired innervation. It can be provoked by complications of the degenerative dystrophic process in the tissues of the intervertebral disc. Gradual dehydration occurs and the height of the disc decreases, and it begins to protrude beyond the edges of the vertebrae.
Dry cough with thoracic osteochondrosis can only be stopped with pharmacological agents that act directly on the respiratory center located in the medulla oblongata. If a dry cough appears due to osteochondrosis of the thoracic region, then it is strictly forbidden to take mucolytic (sputum thinning) pharmacological agents. They will only strengthen the cough reflex.
The best way to remove a dry cough due to osteochondrosis is to begin treatment for degenerative dystrophic disease of the intervertebral discs.
Preventive measures
Any disease is easier to prevent than to treat, and this is especially true for osteochondrosis of the thoracic and cervical spine. It is enough to follow simple tips to reduce the risks of spinal deformation:
- To live an active lifestyle.
- Eat well.
- During prolonged sedentary work, change position and do gymnastics every 2 hours.
- Do not lift heavy objects alone.
- Include healthy foods in your diet and avoid harmful ones.
- Watch your posture.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- At the first symptoms of discomfort, seek qualified help and refrain from self-medication.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is a disease that is easier to prevent than to treat. A healthy lifestyle, moderate physical activity, giving up bad habits and proper nutrition are the key to a healthy spine and the whole body.
Symptoms of cough with osteochondrosis
There are characteristic symptoms of cough with osteochondrosis, which help to exclude other pathologies of the respiratory system. They should be taken into account during initial diagnosis. If you have them, then you should immediately seek medical help from a vertebrologist.
Pay attention to the following symptoms of cough with thoracic osteochondrosis:
- body temperature is normal;
- there is no chills, aches in the muscles of the arms and legs, headache and other signs of general intoxication;
- sore throat and cough reflex occur due to pain in the shoulder blades or collar area;
- after rest or use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, the cough stops, but then reappears;
- there is no sputum production;
- there is no lag on one side of the chest when taking a deep breath;
- The breathing movements of the chest themselves cause discomfort, and in some cases pain;
- palpation of the spinous processes and intercostal spaces is painful;
- percussion of the chest does not cause pain;
- When making movements, the pain intensifies and a cough reflex occurs.
If you have these symptoms of cough due to osteochondrosis of the thoracic region, then you need to make an appointment with a vertebrologist or neurologist. If timely treatment is not started, pathological changes in the lung and bronchial tissue will inevitably begin to occur. Vital lung capacity may be significantly reduced. This will provoke chronic oxygen starvation of the tissues of the brain, heart and other vital organs.
Diagnostics
For correct and effective treatment of cough accompanied by pain in the chest area, it is necessary to undergo mandatory comprehensive diagnostics. It is this that will help identify osteochondrosis of the thoracic region.
Diagnostic measures will include:
- general blood and urine tests;
- X-ray examination of the lungs.
And since there are no obvious destructive processes in the lungs with thoracic osteochondrosis, the following additional examinations are carried out to identify the exact causes of cough:
- projection x-ray of the spine. Pictures are taken in a straight and lateral position. They allow you to fully assess the condition of the vertebrae and determine the presence of osteophytes;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. This type of examination allows you to obtain the most complete picture of the condition of the spine. The doctor can see the presence and location of pinched blood vessels and nerve roots, and also assess the degree of destruction of the vertebrae and cartilage tissue;
- myelography, which is an x-ray examination, but thanks to the use of a special coloring pigment injected into the spinal canals, it allows you to see pinching;
- contrast discography, which allows you to determine the presence of cracks in the vertebrae, as well as displacement of the fibrous ring.
The most effective methods for diagnosis are computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. However, their use is very limited due to the high cost of the procedures, as well as the presence of a large number of contraindications.
Confirmation of the relationship between symptoms during diagnosis
Confirmation of the relationship between cough and thoracic osteochondrosis occurs with the diagnostic detection of the following factors:
- unnaturally small distance between the vertebrae;
- the presence of osteophytes on the vertebrae and articular processes;
- hernias and protrusions on intervertebral discs;
- pinched blood vessels and nerve endings;
- inflammatory process in the vertebral area.
Also, one of the confirmations of the nature of the cough is the presence of severe scoliosis.
Treatment of cough in thoracic and cervical osteochondrosis
There is only one effective treatment for cough with osteochondrosis - restoration of the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral disc. Until the compression of the radicular nerve is eliminated, the cough will persist.
It is necessary to begin treatment of cough with thoracic osteochondrosis with an accurate diagnosis. To do this, the patient is prescribed an X-ray or MRI examination. Then the doctor develops an individual course of treatment. As in the treatment of cough with cervical osteochondrosis, individual recommendations for changing lifestyle and diet are first given. It is necessary to ensure sufficient intake of clean drinking water and nutrients into the body intended to restore the structure of the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral disc. The patient is recommended to make changes to his daily routine, add physical activity, review his diet, and properly organize his sleeping and working space.
Then, to treat cough due to thoracic or cervical osteochondrosis, the following methods are used:
- traction traction of the spinal column – physiological intervertebral spaces are restored, pressure is removed from the radicular nerves;
- osteopathy – to restore microcirculation of blood and lymphatic fluid, which will create the necessary conditions for the regeneration of damaged cartilage tissue;
- massage – to increase the elasticity and permeability of all tissues;
- reflexology – to start the process of restoration of damaged intervertebral discs;
- kinesiotherapy and therapeutic exercises - to strengthen the muscular frame of the back and neck.
- Laser treatment, physiotherapy, electrical myostimulation and much more can also be used.
The course of treatment is developed individually. You can sign up for a free consultation with a vertebrologist or neurologist at our manual therapy clinic. During the initial examination, the doctor will tell you about all the prospects and possibilities for using manual therapy in your case.