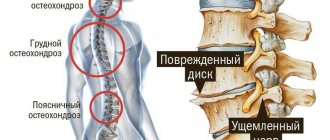
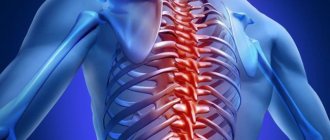
Osteochondrosis of any localization is characterized by aching pain in the affected areas, complicated by spontaneous spasms of the muscles serving the problem segment and a crunching sound during careless movements.
At night, it does not allow patients to sleep, making it difficult for them to find a comfortable position in which their backs do not hurt, and during the day - to live due to forced stiffness of movements and pain even at rest.
Therefore, the question of whether it is possible to go to the gym with osteochondrosis is equally of concern to those who worked out there constantly before the illness, and to those who, after its onset, can hardly imagine lifting grocery bags, much less barbells.
How to deal with the disease
Medicine views it precisely as an age-related phenomenon - the beginning of aging of the spinal column. But during this period, disturbances from the spine and its structures are not yet so great.
They are limited only by the “weakening” of the outer shell of the disc and a slight convergence of the bones that separate the intervertebral disc.
Therefore, exercising in the gym for osteochondrosis is not contraindicated - there are not enough reasons to refuse them at this stage, although they may appear in the foreseeable future if the problem cannot be solved.
Possibility of bodybuilding with osteochondrosis
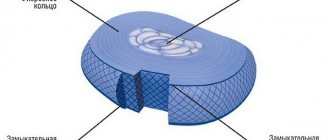
Osteochondrosis is characterized by irreversible degenerative disorders in the intervertebral discs. The disease occurs due to improper metabolic processes in cartilage tissues and their early wear. When doing bodybuilding, aching pain occurs in the shoulder blades. When performing certain core exercises, the athlete experiences shooting pains in different parts of the body. The disease can simultaneously affect:
- back;
- knees;
- hips;
- neck;
- Feet;
- elbows.
With osteochondrosis, the thickness of the intervertebral discs becomes thinner, as a result of which the nerves are pinched, which cause various pains. More often than others, the disease affects the lumbar region, since there is the greatest load on the vertebrae. As the disease develops, cartilage cannot regenerate quickly. Therefore, the main goal of the training process is to relieve pain and improve blood supply to the spinal column.
Is there any benefit
As for exercises in the gym for osteochondrosis, weightlifting, like any other sport, can both further harm the back and help it slow down degeneration.
Our spine needs an even alternation of feasible loads with proper rest, and it is adapted to movement much better than to sitting for a long time in the same position.
Therefore, everything will be fine if:
- work strictly in the correct technique;
- take only feasible weights;
- relieve spasms, fatigue and inflammation in the back muscles after each workout through relaxing procedures.
In addition, the gym for cervical osteochondrosis requires special attention when performing all exercises on the muscles of the arms and shoulders. It is not recommended for this:
- stretch your neck forward, “helping” the muscles contract;
- use momentum by swinging the weights instead of just lifting them;
- do exercises for the upper abdominals, since stretching the neck and overstraining its muscles is inevitable.
The gym for osteochondrosis of the lumbar region is also not at all contraindicated, and even, on the contrary: let’s say, running with it is an incomparably worse idea.
However, with such localization of the process, it is more reasonable to perform deadlifts, chest presses and other exercises that create a high load on the lower back in a machine rather than with free weight. Or, in any case, they should not be attempted without a tanned leather securing belt.
Working with really heavy weights (for example, in order to gain muscle mass) should only be done in an orthopedic rigid corset. If the sports complex where we work out has a swimming pool, you should not deny yourself a half-hour “swim” in it after each workout, as it perfectly relieves the entire musculoskeletal system.
Rules of training and lifestyle
Warm-up exercises will prepare the spine for training.
For comfort (as much as possible) during bodybuilding training, you need to follow these rules:
- Small movements to warm up the spine should be done after every hour of rest.
- It is recommended to swim on your back in the pool twice a week. It is advisable to engage in exercise therapy.
- It is advisable to replace exercises with a skipping rope and running with a “bicycle”.
- You should sleep on a hard surface with a low pillow.
- Objects from the floor must be lifted without bending over them, but by squatting with a straight back.
- Weights should be carried with equal weight on each hand.
- Elements that include a compressive axial load on the spine should be discarded.
- You should stretch your spine after any exercise, including hanging on a horizontal bar.
- You should not lift heavy weights when exercising.
- It is recommended to wear a weightlifting belt and corset when performing physical elements.
- It is necessary to strictly monitor how the exercise technique for the spinal region is performed.
- If you are overweight, you should lose weight.
- It is necessary to consume vitamins, as well as add seafood, red fish, nuts and oils to the diet.
- Consuming fish oil twice a day will be beneficial.
- To improve cartilage structures, you should use products containing hyaluronic acid and chondroitin.
- For local anesthesia, it is recommended to use Dikul Balm.
- Treatment courses of manual therapy and acupuncture are recommended.
During the training process, it is necessary to avoid a number of exercises that place stress on the spine or areas affected by the disease.
The exercise must be abandoned.
In case of osteochondrosis, the following are excluded:
- bent over rows and deadlifts;
- lunge and squat with a barbell;
- the use of French and military presses.
What not to do
With regard to bodybuilding, the worst limitation of all that osteochondrosis imposes is the inability to perform half of the exercises with free weights, especially a barbell. In particular, both cervical and lumbar (the most common) types of osteochondrosis exclude:
- squat and half squat with a barbell on the shoulders from behind;
- squat with a barbell on the shoulders in front (that is, when the bar rests on the collarbones);
- deadlift of a barbell or dumbbells;
- bending over with a barbell on your shoulders;
- pulling dumbbells or barbells to the chest or stomach;
- classic deadlift.
And the good news is that almost all of these exercises can be replaced by working in a simulator. In this case, the rate of mass gain will, of course, decrease, but the detailing will go “like clockwork,” and we will maintain the overall good shape. You can strengthen your back and buttocks without a barbell using:
- pull-ups on the horizontal bar;
- traction of the upper block (both behind the head and to the collarbones);
- traction of the lower block to the stomach;
- active work with a Roman chair - performing direct and reverse hyperextension, but without weights on the shoulders and with the hands not behind the head, but crosswise on the chest.
As we will see for ourselves soon after starting training, they quickly relieve the initial symptoms of osteochondrosis in any department due to their ability to accelerate the regeneration of bones and cartilage. This is the natural result of the body's attempt to provide stressed muscles with everything they need to repair and grow.
However, it is precisely at this moment that it is important for us not to overstrain ourselves - in the sense that the rate of tissue regeneration cannot be infinitely high, and it always increases gradually.
Therefore, for the next six months, or even more, we need to forget about performing the approach to failure or use the 1-2 repetition technique (work with maximum weight).
“Warming up” before training also needs to be done with caution. Jogging and jumping rope, which are classic in all respects (most often used before training the lower leg muscles) are no longer suitable for us. Therefore, it is better to use a bicycle or skis, setting the route to difficulty 2 or higher.
It is better to complete each approach not by simply stretching the muscles being loaded this time, but by hanging on the horizontal bar - of course, without weights, swinging and other “acrobatics”. You should visit the pool 2-3 times a week.
It is advisable to do this after training, but only if there is such an opportunity. And it is doubly advisable to attend regular (not sports/therapeutic/exotic) relaxing massage sessions twice a week.
If you want to get more information like this from Alexandra Bonina, check out the materials on the links below.
Additional useful information:
- My free books, videos and master classes
- My exercise programs and video courses
- My printed books (available in major online stores)
- Free online marathon “How to save your face from old age”
See more useful materials on my social networks:
YouTube | VKontakte | Yandex.Zen | Instagram | Telegram | Facebook
Denial of responsibility
The information in the articles is for general information purposes only and should not be used for self-diagnosis of health problems or for therapeutic purposes. This article is not a substitute for medical advice from a doctor (neurologist, therapist). Please consult your doctor first to know the exact cause of your health problem.
I will be very grateful if you click on one of the buttons and share this material with your friends 
Kinds of sports
What kind of sports can you do with cervical osteochondrosis? Lumbar? Grudny? The final conclusion must be made by your attending physician. It depends on the degree of the disease and your level of physical fitness.
For example, for some patients tennis is completely harmless and even useful, but for others it is contraindicated. Weightlifting, any kind of jumping (pole jumping, long jumping, parachute jumping), sports with an increased risk of back injuries - hockey, alpine skiing - are prohibited.
What is the reason?
It is a misconception to believe that complaining about osteochondrosis is the fate of older people. People of different ages or lifestyles are equally susceptible to the appearance of osteochondrosis. As a rule, the cause of the disease is quite difficult to identify. However, risk factors are: hereditary predisposition, mechanical trauma, metabolic disorders, etc.
It is important to remember that osteochondrosis is a chronic disease. It requires you not only to reconsider your lifestyle, but also your training style.
Stages of physical rehabilitation
Subcompensation stage
At the first stage (subcompensation stage), the task is to start the process of creating compensatory structures for the affected segments of the musculoskeletal system. of the spine , limbs, and joints cannot perform
The subcompensation group includes people who have recently been discharged from the hospital or those who have very severe back pain. Such patients undergo a rehabilitation course using special programs for a month.
The main means of these programs are physical exercises without machines, breathing exercises and relaxation exercises. Together, these exercises help restore nutrition, neuroendocrine regulation and unload the affected spinal . Other means used include hygienic environmental factors and sauna therapy.
Additionally, we offer didactic teaching materials for independent work at home. Experience shows that such an integrated approach to solving a problem contributes to a rapid improvement in the well-being of our clients.
At this stage, the level of pain decreases, patients lose fear, and a feeling of self-confidence appears.
After completing the course of physical rehabilitation, at the first stage, a transition to the unstable compensation group is carried out. Why unstable? Because the compensation mechanisms that are formed at this stage are still unstable, they have not fully formed and therefore relapses of the pain syndrome are possible.
Unsustainable compensation stage
The duration of the stage of unstable compensation varies from person to person—from two months to six months. At this stage, rehabilitation sessions consist of two parts. The first part includes classes in the gym. But the exercises here are different than at the previous stage, more complex. The problems they solve are expanding. As mentioned above, we proceed from the fact that the body is a single system. And solving a local problem is impossible without improving the health of the whole organism. Therefore, in parallel with the dominant task - to form compensatory structures - related tasks are being solved to improve the activity of the central nervous, cardiovascular systems, internal organs, and the reproductive sphere.
As part of solving the dominant problem, the main emphasis is on the formation of optimal muscle mass. Why this is needed is described in detail in the didactic material “The role of kinesiotherapy in the rehabilitation of people with neurological manifestations of spinal and its complications.”
The task of optimizing lean body mass is solved in the second part of the lesson, which takes place in the gym.
At this stage, pain in the back or limbs almost always disappears, the quality of life is normalized, and working capacity is completely restored.
Sustained compensation stage
This is followed by the third stage, the “Sustainable Compensation Stage.” Its duration is 2-3 months. At this stage, structures are finally formed that take on the function of the damaged spinal . The patient feels absolutely healthy. The problem only sometimes reminds itself.
Often people at this stage lose caution and behave as if the spine is absolutely healthy. At the same time, they either stop regular kinesiotherapy classes or overload themselves with physical activity. The result is a relapse of the disease.
Exercises to improve your spine
By working out in the gym, you can not only lose weight or gain the necessary muscle mass, but also improve the condition of the muscles and ligaments of the spine . Developed back muscles relieve excess stress from the spine , slowing down the aging process of this organ, and the active blood circulation that occurs during training helps restore the intervertebral discs.
Rules for conducting training to improve the health of the spine
- You should start doing fitness after the acute back pain goes away.
- If you experience discomfort while performing an exercise, you should temporarily eliminate this exercise or reduce the weight of the weight.
- It is best to do 2 - 3 workouts per week.
- The workout should consist of 2 parts: warm-up and main part.
- The vast majority of gym injuries are caused by neglecting to warm up. Active warm-up is a mandatory element of training.
- The workout should take place at an average pace. Pauses between approaches are 5 - 6 minutes. You can monitor your own breathing - if it has recovered, we begin to do a new approach.
- When restoring your back in the gym, you must definitely use a wide weightlifting belt.
What is forbidden to do when doing fitness with a problem back:
- Work with maximum weights. This applies to all exercises for any muscle group.
- To do exercises:
- Squats with a barbell.
- Deadlift (lifting a barbell from the floor with straight legs).
- Twisting the body along a vertical axis, especially with a load on the shoulders . Sometimes this is done to train the oblique abdominal muscles.
- Excessively bending or arching your back when performing exercises with a barbell or dumbbells.
- Avoid exercises that excessively vertically load the spine (barbell press from the chest, barbell press from behind the head).
Sample training plan for back recovery
Monday
Warm up. Easy jogging for 5 - 10 minutes. Circular swings with straight arms in the shoulder girdle 15 rotations forward and 15 backwards. Rotation of the shoulders, arms freely lowered along the body, 10 movements forward and 10 backwards. Main part. The first approach, when performing exercises with weights, is done with minimal weight and maximum amplitude in order to stretch the joints and feel the movement technique.
Pull-ups on the bar with a wide grip behind the head. Perform 4 sets with 8 - 10 repetitions. This exercise stretches the thoracic spine and trains the muscles of the upper back.
Pull-down on a vertical block behind the head with a wide grip. Perform 4 sets with 8 - 10 repetitions. The effect of this exercise is similar to the previous one, but allows you to work out the muscles being trained in more detail, since you can use a small weight of weight.
Place your hands on a support (table, chair) approximately waist high. Move away to such a distance that when bending forward, your arms and torso are parallel to the floor. Perform springy movements with the shoulder girdle down. Perform 2 sets of 20 - 30 repetitions.
When performing all exercises, focus on cervical spine and the area of the back between the shoulder blades.
Raising the torso to the feet on an inclined board. The legs are higher than the head and slightly bent. Perform 3 sets with 15 - 20 repetitions. The upper part of the abdominal muscles develops and the spine along its entire length.
Wednesday
Warm up. Light jogging or cardio exercise (treadmill, exercise bike) for 5 to 10 minutes. We bend our torso forward, try to reach the floor with our palms, straighten our torso, bend back, and use our hands on the belt to move the pelvis slightly forward. Repeat 10 - 15 times.
Main part. When performing an exercise with weights, we do the first approach with minimal weight and maximum amplitude in order to feel the technique of movement.
Pull to the stomach on a horizontal block, we try to place our elbows as far behind our back as possible. The back muscles are tense, the back is always straight. Perform 4 sets with 8 - 10 repetitions. The exercise works the latissimus dorsi muscles.
Pullover. the knee height . Place a weight (barbell, dumbbells) behind your head on the floor. We take the load in our hands, they are slightly bent at the elbows and lift them in a circular motion to a position above the body. Perform 4 sets with 8 - 10 repetitions. For comfort, it is better to place your feet shoulder-width apart. The exercise works the pectoral and latissimus dorsi muscles, and also increases mobility in the thoracic spine .
Hanging on a wall bars, facing the wall. We move our straight legs back, lifting our pelvis off the wall bars, and fix the position for a few seconds. Perform 3 sets with 10 - 15 repetitions. When performing exercises, focus on the thoracic spine .
Raising the legs towards the body on an inclined board (head above the legs). Perform 3 sets with 15 - 20 repetitions. The lower abdominal muscles develop and the spine .
Friday
Warm up. Easy jogging for 5 - 10 minutes. Rotation of the torso around the hips, hands clasped at the back of the head, 10 movements clockwise and 10 counterclockwise. Then we clench our hands into fists, place them behind our backs and press forward with springy movements on the lumbar region. Perform 10 - 15 movements.
Main part.
We stand straight, hands on the back of the head, feet shoulder-width apart. We slightly bend our knees and tilt our straight torso forward until it becomes parallel to the floor. We return to the starting position. The exercise works the muscles in the lumbar spine . Perform 4 sets of 15 - 20 repetitions.
Bending the torso back with fixed legs and emphasis on the lower abdomen. Hands can be on the back of the head or along the body. The long back muscles are worked, especially in the lumbar region. Perform 4 sets of 10 - 15 repetitions. When performing exercises, we focus on the lumbar spine .
Having set a goal to improve the condition of the spine through fitness, remember that the load must be increased gradually and go from simple to complex exercises.