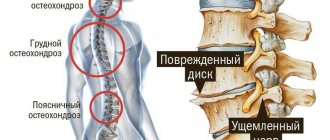
What is osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is a dystrophic pathology of the cartilaginous surfaces of the bones of the musculoskeletal system - vertebrae and discs.
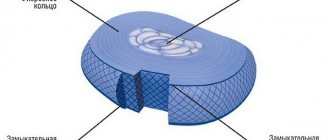
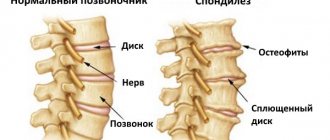
Intervertebral discs are a kind of shock absorbers that are designed to alleviate pressure on the spine.
The reason for the widespread nature of the disease can be attributed to the predominantly vertical lifestyle of modern man. He spends most of his time sitting or standing, and at the same time the load on the spine increases significantly. So, after some time, the outer shell of the intervertebral disc cracks. The result of this process is the formation of hernias that compress the blood vessels or roots of the spinal cord. These changes lead to impaired blood circulation, the development of pain and reflex tension in the back muscles.
Severe chest and back pain
Very severe pain in thoracic osteochondrosis can occur during exacerbations or prolapse of a disc herniation. These conditions require immediate medical attention. When some radicular nerves are damaged, a condition that threatens the patient's life may occur.
Acute chest pain due to thoracic osteochondrosis can be relieved with the help of traction traction of the spinal column. This procedure is performed in combination with massage and osteopathy. For severe back pain due to osteochondrosis of the thoracic region, pharmacopuncture is also used.
Depending on the nature of the pain syndrome and its duration, treatment is carried out using kinesiotherapy and therapeutic exercises.
Chest pain can be caused by excessive tension in the muscular frame of the back. This compensatory function of the muscular system is triggered when the intervertebral disc is seriously damaged. If it fails to cope with its shock-absorbing function, then the muscles responsible for maintaining a certain position of the vertebral bodies become tense. In this way, compensatory protection of the radicular nerves occurs from compression by the bodies of neighboring vertebrae.
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region
With osteochondrosis, a person may feel pain in the neck, shoulders and arms, back or chest. Often, patients are in no hurry to turn to specialists, but try to independently determine the root cause of the discomfort. However, this is very dangerous. One has only to imagine: a person suspects a heart problem, although in reality it is a pinched nerve that is aching. What if it's the other way around?
Important!. Never self-medicate! Pain of any nature is a reason to visit a doctor to determine an accurate diagnosis and treatment method.
Types of thoracic osteochondrosis and complications
Based on the nature of pain, two types of thoracic osteochondrosis are distinguished:
- dorsago, which is characterized by acute sharp pain in the form of a lumbago, localized in the thoracic spine. The condition is accompanied by muscle tension, problems with movement in the neck and thoracic region;
- dorsalgia, in which pain increases slowly. Inhalations and turns of the body, as well as prolonged stay in one position, increase the discomfort. At night, the discomfort deepens and disappears while walking.
In the absence of adequate therapy, the nerve endings are increasingly compressed. As a result, osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine can cause complications:
- kidney pathologies;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- immobility;
- persistent pain;
- disruptions in cardiac activity;
- intervertebral hernia;
- decreased ability to conceive;
- disturbance in the functioning of the lungs caused by the proliferation of connective tissue.
What symptoms are characteristic of thoracic osteochondrosis?
- pain in the chest area and between the shoulder blades, which is especially noticeable when raising arms, bending over and other physical activity;
- pain intensifies at night, with deep inhalation and exhalation, as well as in case of hypothermia;
- the appearance of “goosebumps” on the skin and numbness of its individual areas;
- itching, burning, cold feet syndrome;
- feeling like a hoop is squeezing my chest.
If a person has noticed at least some of these symptoms, he should definitely contact a neurologist or traumatologist. After listening to the complaints, the doctor will conduct an initial examination of the spinal column and determine whether there are problems with cerebral circulation. One of the important steps in diagnosing the disease is referral for hardware examination. Modern medicine uses a number of methods, the most accurate of which are MRI and CT.
Stages of disease development
Experts distinguish three main stages of development of thoracic osteochondrosis:
Stage 1 – the beginning of the development of the disease. Characterized by the absence of clinical manifestations.
Signs of stage 1 thoracic osteochondrosis:
- barely perceptible, slight painful lumbago, accompanied by a nagging pain in the chest. Unpleasant sensations intensify after strenuous work or heavy lifting;
- muscle spasms, constant tone of the muscle frame for no apparent reason;
- discomfort in the heart area.
Seeing a doctor at the initial stage of the disease guarantees a complete cure of the disease.
Stage 2 – the progression of the disease leads to the formation of microcracks in the intervertebral discs, which causes limited mobility and the appearance of severe pain.
Clinical manifestations include:
- visually noticeable deformation of the spinal column;
- decrease in pressure;
- accompaniment of an attempt to place the hand behind the head with palpable pain in the sternum;
- chronic feeling of fatigue;
- discomfort in the area of the heart and spinal column of the thoracic region.
If the disease is detected at this stage, the process of restoring health may require a fairly long period of time.
Stage 3 is an advanced process that has a negative impact on the entire body as a whole.
Dangerous manifestations such as:
- limited mobility of the spine;
- sharp pain;
- the appearance of intervertebral hernias;
- pinching of blood vessels and nerve roots;
- diseases of the biliary tract.
Refusal to treat thoracic osteochondrosis at this stage can lead to disability.
Treatment methods
So, the diagnosis has been established. This means the next stage is the appointment of effective treatment. As a rule, doctors are guided by the characteristics of a particular case and approach the issue of choosing methods individually. There are two types of treatment – conservative and surgical. Which of them will be applied to the patient directly depends on the severity of the disease, the availability of internal resources of the body, as well as indications and contraindications.
What conservative methods are most common:
- taking medications and dietary supplements prescribed by a doctor;
- manual therapy;
- traction;
- acupuncture;
- massage;
- Exercise therapy, etc.
Reference. The human body is a delicate, unique system. If gymnastics helped one patient, this is not an indication for prescribing it to another. The attending physician always selects an individual course based on the physical characteristics of the person.
The main type of treatment for osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is considered to be gentle manual therapy, and massage, medications, etc. play a supporting role.
This is due to the fact that the nutrition of the discs depends on the condition of the muscles surrounding the spinal column. Moreover, the spinal muscles themselves are a component cause of pain in osteochondrosis of the thoracic region. The chiropractor, smoothly influencing the tissue, helps normalize reflexes and muscle tone, eliminates spasms and clamps, relieves and distributes the load from the affected discs, as a result of which the nutrition of the intervertebral discs and spinal circulation improves, and the motor functions of the body are restored.
Description of the disease, what is its danger
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is a chronic disease in which dystrophic changes begin in the cartilage located in the intervertebral space. The pathology is expressed by a decrease in the height of the discs and compression of the intercostal nerve endings.
Thoracic osteochondrosis goes through several stages of progression.
The first is characterized by desiccation of the intervertebral disc, decreased firmness and elasticity, and the appearance of cracks. The pain is mild and goes away after the person rests a little.
At the second stage, the disc decreases in height, the niche in the vertebra is filled with the nucleus pulposus, but it does not go beyond its boundaries. Muscles experience constant tension. The person complains of severe pain, which subsides after being at rest.
The third stage is characterized by the exit of the nucleus pulposus beyond the edges, the crack reaches the vertebral edge. As a result, an intervertebral hernia is formed. The pain becomes constant.
At the fourth stage, a proliferation of connective tissue is detected, which puts pressure on nearby vertebrae. To compensate for the reduced layer, bone tissue begins to grow. More and more growths (osteophytes) appear.
Rehabilitation and lifestyle restoration
Rehabilitation of patients with osteochondrosis requires an integrated approach. To maintain the results of treatment over a long period of time, it is necessary to combine many techniques from various fields of medicine. For example, in addition to following a therapeutic diet, performing special gymnastic exercises and visiting a chiropractor, the patient should include in the list of mandatory procedures:
- Isometric kinesiotherapy;
- Manual therapy;
- Reflexology;
- Underwater hydromassage;
- Traction treatment;
- Magnetic, electrical and vibration stimulation;
- Ultrasound and laser therapy;
- Mobilization-vacuum therapy;
- Psychotherapy.
Important!. At home, it is quite difficult to take into account all the nuances of the rehabilitation period - from training on exercise machines to strict adherence to sleep and wakefulness. Departments of public hospitals do not always have the necessary equipment or personnel. The solution to the problem is often specialized clinics, such as the Kuntsevo Treatment and Rehabilitation Center. Technical equipment, instruments and equipment of world quality standards allow you to undergo effective therapy in a comfortable and safe environment under the supervision of specialized specialists.
With thoracic osteochondrosis, the stomach may hurt
Does the stomach hurt with thoracic osteochondrosis or is it a referred pain due to damage to the lower intervertebral discs? In different situations the answer can be positive or negative. In most cases, abdominal pain with thoracic osteochondrosis is a consequence of dysfunction of the abdominal organs. This is a consequence of a violation of innervation when the structure of the radicular nerves is damaged. The stomach consists of a muscle layer that contracts, mixing the food bolus with gastric juice, and relaxes. If the intervertebral discs T6 and T7 are damaged, then there is a high probability that the muscular wall of the stomach does not contract and atony of this organ appears. Next, undigested food enters the small and large intestines. A complex pathological process is launched, ultimately leading to complete dysfunction of the digestive system. Dysbiosis, colitis, pancreatitis and atonic gastritis are formed. This condition in the future is fraught with the development of ulcerative processes and the growth of oncological tumors.
Therefore, with thoracic osteochondrosis, the stomach may hurt, or referred pain may be felt. Only an experienced vertebrologist can tell you the exact cause of unpleasant symptoms.
Lifestyle with osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
To prevent the disease, as well as to maintain the general condition of the patient’s body with osteochondrosis, doctors advise:
- Correct spinal curvature and postural disorders in a timely manner.
- Actively engage in sports, which will strengthen your muscles and develop your muscle corset.
- Follow a diet to maintain normal levels of vitamins, micro- and macroelements.
- Fight excess weight.
- Ensure even distribution of the load on the spine if you need to lift something heavy.
- Sit so that your back is straight and your shoulders are relaxed.
- Choose chairs and armchairs that support your back.
- Try to “dilute” static time at work with walking, warming up, and office gymnastics.
- Sleep on an orthopedic mattress.
Prevention
We recommend to prevent the disease:
- during the day, lie down for 40-50 minutes - this will relieve the load on the spine;
- if you work a lot at the computer, change your position, get up from your chair every 2 hours, bend a couple of times in different directions, stretch, straighten your shoulders;
- engage in water sports: swimming, diving, water aerobics;
- do not get too cold, keep your back warm;
- Do the following exercise regularly: lying on your stomach, place your hands on the floor and bend back. Stay in this position for 5-10 seconds. Repeat the exercise 8-10 times.
It is also strongly recommended to maintain body weight at the proper level and give up bad habits (including smoking).