08 October 2021
According to the International Classification of Diseases, osteochondrosis is included in the group of diseases of the musculoskeletal system, mainly the spine, and connective tissue
According to the International Classification of Diseases, osteochondrosis is included in the group of diseases of the musculoskeletal system, mainly the spine, and connective tissue. Wearing out, collapsing and flattening over time, the intervertebral disc loses its shock-absorbing and protective function. The intervertebral space narrows, where the radicular nerves and blood vessels become compressed. This leads to various unpleasant symptoms, which force a person to see a doctor.
Based on localization, they distinguish between cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and widespread osteochondrosis. The most commonly diagnosed osteochondrosis is lumbar osteochondrosis (over 50% of cases), cervical (over 25%) and widespread (about 12%).
Symptoms of osteochondrosis.
- pain in various parts of the spine;
- dysfunction of organs that are innervated by the nerves of the affected area of the spine;
- headache;
- disturbances and loss of tendon (muscle) reflexes (they can be increased, decreased, uneven or not evoked at all).
At the stage of collecting anamnesis, the doctor assesses the symptoms inherent in each individual segment of the musculoskeletal system.
Thus, with cervical osteochondrosis, headaches are observed, aggravated by turning the neck, dizziness, flickering “spots” in the eyes, fainting, and others. Sometimes a headache is accompanied by nausea or vomiting, sensations of noise in the head, ringing in the ears, visual disturbances in the form of flickering, pain in the eye, and perhaps a sensation of a foreign body in the throat.
With lumbar osteochondrosis - acute pain (“shooting”) in the back and below, numbness of the legs, disturbances in the functioning of the genitourinary organs. Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is characterized by pain in the interscapular region. Often the pain in the chest becomes girdling and is felt in the area of the ribs.
Patient reviews
After being diagnosed with osteochondrosis, many patients do not know where to start. Feedback from people who have encountered a similar situation and found a solution can help in this matter.
Alena M., 39 years old “I have been tormented by pain in the cervical spine since I was young, but I attributed everything to constant overexertion, because I often worked at the computer. But over the past few years, turning my neck has become almost impossible. I first turned to a therapist, who referred me for a consultation with a neurologist. After a comprehensive examination, osteochondrosis was determined. A course of medications was prescribed, anti-inflammatory and to relieve tension. The effect was immediate, but when I went back to the doctor, he said that to consolidate the result and lasting remission, I needed exercise therapy and massage. Now I try to practice every day.”
Tatyana R., 48 years old “Osteochondrosis in the neck is my occupational disease, with which I have been suffering for many years. At first I took courses of medications, but they only blocked the pain and helped for a while. Gradually the attacks returned again, and treatment had to be started all over again. I have now started a course of chondroprotectors, plus I constantly do physical therapy in the gym, and a health worker monitors the entire process to make sure everything is done correctly. I hope for a more lasting result."
Valeria K., 49 years old, “Pharmaceutical patches have helped a lot in coping with pain during an exacerbation of osteochondrosis, but they don’t last long. To make the result more lasting, you need to constantly exercise and adjust your lifestyle. The doctor prescribed dietary supplements to restore cartilage tissue and exercise therapy. When I have time, I try to do the complex, it doesn’t seem difficult and doesn’t take much time, but I often forget to do it. And in this matter, the main thing is regularity to get a lasting result.”
Cervicothoracic osteochondrosis is a chronic degenerative process occurring in the intervertebral disc. It negatively affects the condition of the musculoskeletal system as a whole, and provokes a narrowing of the space between the vertebrae, leading to the proliferation of bone tissue and the appearance of osteophytes. The condition is especially dangerous in cervicothoracic localization, therefore, when the first signs of the disease appear, it is recommended to consult a doctor for comprehensive treatment.
Causes of osteochondrosis.
Osteochondrosis is a consequence of biological aging of the body. As the intervertebral disc wears out, collapses and flattens over time, it loses its shock-absorbing function. The intervertebral space narrows, and the radicular nerves and blood vessels become pinched in it. This leads to the above-mentioned unpleasant symptoms.
Other causes of this disease include:
- sedentary, sedentary lifestyle;
- excessive loads (lifting objects with a large mass, physical overload);
- autoimmune diseases;
- metabolic disorders with critical excess body weight;
- imbalance of calcium in the body;
- pregnancy (provokes osteochondrosis in women due to depletion of the body in calcium and inadequate distribution of increasing body weight relative to the vertical axis);
- spinal injuries;
- flat feet or daily wearing of shoes with too high heels;
- household or professional lifestyle features (long standing, sitting on uncomfortable furniture, sleeping on an uncomfortable mattress, etc.).
A common consequence of osteochondrosis is the formation of a herniated intervertebral disc, which may require surgical intervention. Depending on the degree of complication, symptoms can range from mild to severe.
Lifestyle with osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
To prevent the disease, as well as to maintain the general condition of the patient’s body with osteochondrosis, doctors advise:
- Correct spinal curvature and postural disorders in a timely manner.
- Actively engage in sports, which will strengthen your muscles and develop your muscle corset.
- Follow a diet to maintain normal levels of vitamins, micro- and macroelements.
- Fight excess weight.
- Ensure even distribution of the load on the spine if you need to lift something heavy.
- Sit so that your back is straight and your shoulders are relaxed.
- Choose chairs and armchairs that support your back.
- Try to “dilute” static time at work with walking, warming up, and office gymnastics.
- Sleep on an orthopedic mattress.
Diagnostics.
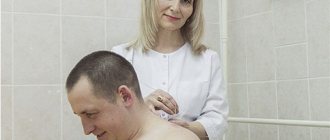
Most often, the diagnosis of “osteochondrosis” is made by a neurologist. At the initial examination, the doctor conducts an examination in connection with the patient's complaints of pain or limited mobility of the spine. The patient's spine is examined in standing, sitting and lying positions, in states of rest and movement.
Feeling the spine allows you to supplement the examination data (presence or absence of deformation), determine the location, degree and nature of pain. When palpated, tension in the muscles located next to the spine is noted. The patient is asked to bend or squat to determine the range of motion in various parts.
The final diagnosis is made by a neurologist based on a physical examination, as well as the results of radiography, CT or MRI. With the help of these examinations, the level of damage is determined, the diagnosis is specified, and hidden pathologies are revealed. After diagnosis, the attending physician determines treatment tactics and selects the most effective treatment method.
Rehabilitation and lifestyle restoration
Rehabilitation of patients with osteochondrosis requires an integrated approach. To maintain the results of treatment over a long period of time, it is necessary to combine many techniques from various fields of medicine. For example, in addition to following a therapeutic diet, performing special gymnastic exercises and visiting a chiropractor, the patient should include in the list of mandatory procedures:
- Isometric kinesiotherapy;
- Manual therapy;
- Reflexology;
- Underwater hydromassage;
- Traction treatment;
- Magnetic, electrical and vibration stimulation;
- Ultrasound and laser therapy;
- Mobilization-vacuum therapy;
- Psychotherapy.
Important!. At home, it is quite difficult to take into account all the nuances of the rehabilitation period - from training on exercise machines to strict adherence to sleep and wakefulness. Departments of public hospitals do not always have the necessary equipment or personnel. The solution to the problem is often specialized clinics, such as the Kuntsevo Treatment and Rehabilitation Center. Technical equipment, instruments and equipment of world quality standards allow you to undergo effective therapy in a comfortable and safe environment under the supervision of specialized specialists.
Treatment of osteochondrosis.
The first stage of treatment is pain elimination. For this, the patient is prescribed nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), for example, Movalis, Voltaren. It should be noted that these medications are not recommended to be taken without a doctor’s prescription, since most of them have a detrimental effect on the gastrointestinal tract.
Further treatment of osteochondrosis can be conservative or surgical, depending on the severity and advanced stage of the disease. As a medical treatment, the patient is also prescribed B vitamins and muscle relaxants, for example Mydocalm, to relieve muscle hypertonicity and relieve pain. In some situations, the doctor may recommend physiotherapy.
After the pain has been relieved, that is, the symptoms of the disease have subsided, the patient is recommended physical therapy and massage. Physical therapy exercises help strengthen the muscular corset of the spinal column, develop the flexibility of the ligamentous apparatus, thereby increasing the amplitude of movements. By strengthening the muscles, decompression of the nerve roots occurs, as a result of which blood circulation and metabolism in the intervertebral discs are normalized. As a result, pain in the spine is significantly reduced. Therapeutic massage, in turn, relieves muscle spasms. Controversial treatments that are not traditional medicine include manual therapy, osteopathy and reflexology.
It is also worth noting that osteochondrosis, like any chronic disease, has periods of exacerbation and remission. Sometimes pain appears depending on the time of year or weather conditions. Knowing the characteristics of your body, you can prevent exacerbations in advance.
Functions of intervertebral discs
The main function of intervertebral discs is to absorb shock when walking and running. Few people think about the load placed on the spine during movement. Every step gives a push to the vertebrae. If there were no discs between them, the bones would very quickly wear out, and the nerve endings of the spinal column would continuously be pinched between the vertebrae.
Its shock-absorbing abilities depend on the quality of the intervertebral disc. The younger the person, the more elastic the discs. In newborns, articular cartilage and intervertebral discs consist of almost 80% water, which gives them the ability to be as elastic as possible, like a sponge. With age, tissues deteriorate, dry out, become less flexible and lose their shock-absorbing properties. The older a person is, the higher the risk of developing complications of osteochondrosis, manifested by:
- hernias;
- radiculitis;
- protruises.
Prevention of osteochondrosis.
The main recommendation for those who want to maintain the health of the osteoarticular system is an orthopedic regimen. It is important to learn how to sit correctly, stand correctly, lift and carry heavy objects, and sleep. For example, the patient is advised to avoid upholstered furniture, including for sleeping. The work chair should have lumbar support. It is not recommended to stand in one position for a long time; it is advisable to periodically warm up. It is not recommended to lift and carry things weighing more than 15 kilograms. Every morning it is recommended to do short exercises for 15-30 minutes to pre-warm up the muscles.
Back to articles
Classification
Thoracic pain syndrome is characterized by severe pain in the chest of an intense nature. The syndrome is associated with damage to peripheral nerves. The damage is due to compression of the nerves by muscles and ligaments.
Degrees of thoracic osteochondrosis:
- The first degree is characterized by the absence of pronounced clinical manifestations. There is a loss of elasticity in the intervertebral discs, and their protrusions form.
- The second degree is marked by a further loss of elasticity of the intervertebral discs and a decrease in their height. The likelihood of a hernia increases. Pain syndrome appears, and concomitant pain symptoms are possible.
- In the third degree, the pain syndrome intensifies. A herniated disc located between the vertebrae may occur. The severity of symptoms depends on the location of the hernia.
- Fourth degree with complete disruption of elasticity and loss of function of the intervertebral discs, destruction of the bone structure of the vertebrae. Neurological disorders are most pronounced.
According to the types of pain symptoms:
- Vertebrogenic thoracalgia is based on spinal pathology.
- Nonvertebrogenic thoracalgia is caused by the formation of pathologies of internal organs: cardiovascular diseases, gastroduodenal reflux, traumatic and inflammatory lesions of the musculoskeletal system.
- Psychogenic thoracalgia is caused by panic attacks and damage to organs of neural origin.
Complications
When establishing a diagnosis of thoracic osteochondrosis, one should take into account a possible cascade of probable organ pathologies that develop over time.
- Damage to the cardiovascular system: persistent pain leads to destabilization of the ion exchange of the myocardial muscle, which is a prerequisite for the development of coronary heart disease.
- Disorders of the functioning of the abdominal organs: stomach, duodenum, pancreas. This is due to the high secretion of adrenaline during persistent pain, which leads to increased secretion of VIP (vasointestinal peptides).
- Dyskinesia of the gallbladder is due to an increase in the lithogenicity of bile against the background of a chronic inflammatory process.
With regular adherence to the principles of therapy, the exercise therapy system, maintaining posture and eliminating risk factors, the course of the disease is reduced to regression. The prognosis is considered favorable if the pathology does not develop further and the disease does not actively manifest itself.