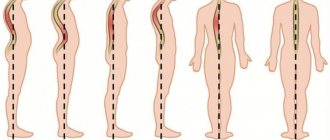
The spinal column of a healthy person has bends forward (in the cervical and lumbar regions) and backwards (in the thoracic and sacral regions). This is the so-called physiological lordosis and kyphosis. But sometimes the spine curves more or less than necessary. This condition is already considered pathological. Pathological lordosis can be a sign of various diseases, including rare (orphan) ones, for example, late-onset Pompe disease. This hereditary disease can manifest at any age. Late onset has a relatively mild course, but as it progresses, new signs of pathology appear1.
With Pompe disease, muscle weakness develops, difficulties appear while climbing stairs, getting up from squatting, and pain occurs in the muscles of the back and limbs. Shortness of breath appears even with small loads, the gait changes - it begins to resemble a “duck’s”. Late-onset Pompe disease is also characterized by spinal deformities, including lordosis1.
What is lordosis?
Physiological curves give the spine an S-shape and perform important tasks by redistributing the load of body weight from the vertebrae to the paravertebral ligaments, stabilizing and supporting the entire structure and allowing movement with ease and flexibility. Cervical lordosis appears in early childhood, when the child begins to hold his head straight, and lumbar lordosis develops around the first year of life. In a 5-6 year old child, the curves of the spine are already clearly visible. They continue to form until the age of 18-202.
If a conditional vertical is drawn through the general center of gravity of the body, the lumbar lordosis will be located in front of this vertical by approximately 5 cm, and the cervical lordosis by 1.5 cm2.
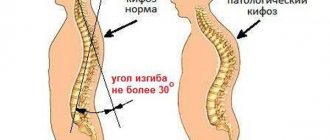
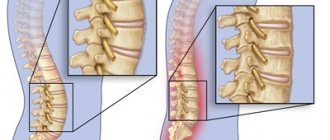
Pathological lordosis is characterized by deviations from physiological parameters:
- Forward deviations, excessive bending - hyperlordosis;
- Smoothing of the bend, flattening of the lines - hypolordosis, or straight back syndrome.
Price for treatment of spinal hyperlordosis
| Services list | Price |
| Initial consultation with a kinesiotherapist | 1500 |
| Interim consultation with a kinesiotherapist (test session) | for free |
| Session with a kinesiotherapist (1 patient) | 3700 |
| Session with a kinesiotherapist (2 patients) | 3700 |
| Group lesson with kinesiotherapist | 2000 |
| Individual lessons with a personal trainer | 2500 |
| Subscription for 1 month of training in the gym on simulators | 10000 |
| Subscription for 6 months of gym training | 40000 |
| Manual therapy 1 department (15 min.) | 2 500 |
| Soft manual techniques (30-60 min.) | 4 000 |
| Magnetic Vacuum Acupuncture | 1 500 |
| Initial OSTEOPATH consultation | 1 500 |
| Repeated OSTEOPATH consultation | 1 000 |
| Consultation with an OSTEOPATH in a cycle | for free |
| Back massage (30-40 min.) | 2 000 |
| Massage of the lumbosacral spine (up to 30 min.) | 1 500 |
| Back massage + cupping massage (40 min.) | 2 500 |
| General therapeutic massage (55 min.) | 2 900 |
Contact us
Call now
8 (495) 803-27-45
Make an appointment through our service
Make an appointment
Causes of spinal curvature
There are three main causes of pathological lordosis2:
- Incorrect posture;
- Unhealthy Lifestyle;
- Individual characteristics and heredity.
Poor posture is a common cause of the disease. When sitting in an incorrect position, the muscles experience excessive tension. If a child or adult frequently adopts an incorrect posture, the spine gradually becomes elongated and excessive convexity occurs3.
The curvature can develop due to excess body weight, which puts too much stress on the lower back. Another risk factor is a sedentary lifestyle, which reduces the tone of the large muscles that support the spinal column3.
Sometimes the disease can be associated with other postural disorders, such as kyphosis, increased scoliosis, as well as a number of diseases, including2,4:
- Rickets;
- Polio;
- Developmental defects;
- Limb-girdle myopathies, including Pompe disease;
- Degenerative-inflammatory diseases of the joints;
- Injuries, etc.
Who will treat you
Karavaev Nikolay Nikolaevich
Chiropractor, Osteopath, Neurologist, Neurosurgeon
Read more
Dremin Evgeniy Vitalievich
Neurologist, reflexologist, chiropractor.
More details
Classification of lordosis
Based on localization, cervical and lumbar lordosis are distinguished, and depending on the cause of development, primary and secondary.
Primary lordosis occurs due to pathological processes in the spine that occur against the background of diseases, for example, rickets, bone tuberculosis, polio. The secondary form of poor posture develops as a consequence of deformation of the lower extremities, forced to stabilize the spinal column in pathological conditions. For example, secondary lordosis can occur with hip dislocation, hip dysplasia, spastic paralysis, and congenital malformations2.
Causes of hyperlordosis:
- the disease is caused by excessively rapid growth of the fetal skeleton during intrauterine development,
- violation of the structure of bone tissue after suffering from rickets,
- hip dysplasia,
- endemic deforming arthrosis - Kashin-Beck disease,
- Achondroplasia is a hereditary human disease manifested in disruption of the processes of enchondral ossification.
A rather rare pathology - congenital hyperlordosis with unfused arches of the lumbar vertebrae, negatively affects the mobility of the spinal column and its ability to withstand even a small load. Patients with hyperlordosis experience difficulty walking. Acquired forms of lumbar spine disease are more common.
Causes of acquired disease:
- The rachitic form of hyperlordosis is caused by an insufficient amount of vitamin D. It occurs in children after birth in the first year of life.
- The paralytic form of hyperlordosis can be caused by cerebral palsy and polio, with a characteristic weakening of muscles. In this case, the lower back, as the part of the spine that is most exposed to stress, is not provided with muscular support and this causes it to sag.
- Traumatic hyperlordosis most often results from back injuries or hip dislocations. In the traumatic form of hyperlordosis, a person’s gait changes, with a characteristic tilt of the body forward and with open knees.
- The functional form - most often occurring in adolescence - is characterized by the rapid development of bone tissue, in contrast to muscle tissue. In this case, there is no sufficient support in the lumbar spine, which leads to a deformation process.
- The compression form, which most often affects the elderly and middle-aged people, is caused by diseases that lead to pathological changes in the vertebrae and their deformation.
The disease can be caused by other causes:
- overweight,
- pregnancy,
- back injury,
- ankylosis,
- discitis,
- kyphosis,
- weak abdominals,
- poor posture,
- spondylolisthesis,
- spinal tuberculosis,
- neoplasms in the spine,
- intervertebral hernias,
- undergone surgical operations on the spinal column.
According to the age category of primary detection of deformity, the disease is divided into the following types:
- infantile lordosis;
- children's lordosis;
- lordosis of adolescence and youth;
- lordosis of adults;
- senile lordosis.
Sign up for a free consultation +7
Symptoms of lordosis
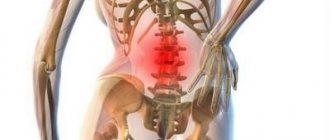
A visible sign of the disease is an abnormally large curve in the lower back. With pronounced lumbar hyperlordosis, a saddle-shaped back is formed, the waist is shortened, flattened, and the buttocks and abdomen protrude. The abdominal muscles stretch, the internal organs of the abdomen lower slightly5.
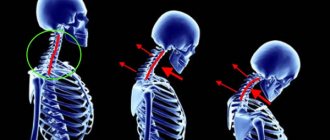
Changes in posture cause muscle tension and stiffness in the lower back, which is accompanied by pain, a common symptom. With lumbar lordosis, pain is localized in the lower back. Their severity can vary - from mild to strong. The pain may get worse with movement. With cervical lordosis, pain extends to the neck, shoulders and upper back. Pain or discomfort in the neck or lower back may limit movement2,6.
Findings from a 2021 study suggest that hyperlordosis may be associated with degenerative joint diseases such as osteoarthritis. People with this condition experience irreversible destruction of joint cartilage and underlying bone, causing pain and decreased joint mobility7.
Lumbar hyperlordosis can lead to a redistribution of load from muscles to nearby tissues, which increases the risk of ligament injury and increases the likelihood of developing a herniated lumbar intervertebral disc8.
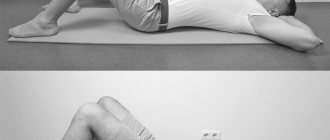
What exercises are contraindicated for lordosis?
With lordosis, any exercises associated with sudden movements or increased pressure on the lower back and neck . It is prohibited to perform complexes that involve lifting weights. Also, you should not perform the permitted exercises a large number of times, since moderation is important in any load.
You should not prescribe exercise therapy or any other procedures yourself, as it is necessary to exclude all contraindications and the presence of concomitant pathologies. In cases of lordosis complicated by other diseases of the musculoskeletal system, even the simplest physical activity and exercises may be contraindicated.
Video: “Exercises for lumbar hyperlordosis”
Treatment of lordosis
Therapy is complex and includes9:
- Relief of pain and inflammation with the help of medications; For this purpose, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and other drugs are prescribed
- Wearing a bandage that helps redistribute the load on the spine;
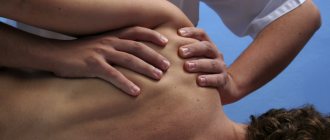
- Massage;
- Weight loss for obesity;
- Physiotherapy.
Therapeutic exercise occupies a special place in the complex treatment of the disease. It helps prevent the development of changes in the functioning of internal organs and create a reliable muscle corset. To get a good effect, you need to train regularly9.
The effectiveness of physical therapy for curvature of the spine has been proven. A 2021 clinical study examining the effects of exercise on spinal curvature showed good results on the severity of symptoms of the disease. An hour-long workout 3 days a week for 12 weeks helped reduce lower back pain and increase muscle strength and flexibility10.
When there is lordosis of the thoracic spine, butterfly swimming is useful, and when lumbar hyperlordosis is combined with kyphosis of the thoracic spine, it is recommended to swim on the chest and do exercises in the pool for the leg muscles9.
References
- Klyushnikov S.A. et al. Clinical case of late-onset Pompe disease // Nervous diseases – 2015. – No. 2. – P.38-43.
- Human anatomy. Textbook for higher educational institutions of physical culture / M. Ivanitsky. – Litres, 2021.
- Levin A.V., Vikulov A.D. Etiology and classification of posture disorders // Yaroslavl Pedagogical Bulletin - 2013. - T. 3. - No. 4.
- Sparrey CJ et al. Etiology of lumbar lordosis and its pathophysiology: a review of the evolution of lumbar lordosis, and the mechanics and biology of lumbar degeneration //Neurosurgical focus.2014;36(5):E1.
- Propaedeutics of internal diseases: a textbook for medical universities / N.A. Mukhin. – GEOTAR-Media, 2012.
- Pediatric orthopedics: Textbook / M.V. Volkov, V.D. Dedova. – Medicine, 1980.
- Murray KJ et al. Characterization of the correlation between standing lordosis and degenerative joint disease in the lower lumbar spine in women and men: a radiographic study //BMC musculoskeletal disorders.2017;18(1):330.
- McGill SM, Hughson RL, Parks K. Changes in lumbar lordosis modify the role of the extensor muscles //Clinical Biomechanics.2000;15(10):777-780.
- Exercise therapy and therapeutic swimming in orthopedics: educational method. Manual / T.I.Velichko, V.A. Loskutov, I.V. Loskutova. - M.: Publishing House of the Academy of Natural Sciences, 2014. - 120 p.
- Ko KJ et al. Effects of 12-week lumbar stabilization exercise and sling exercise on lumbosacral region angle, lumbar muscle strength, and pain scale of patients with chronic low back pain //Journal of physical therapy.y science.2018;30(1):18-22 .
GZEA.PD.18.09.0435a
Diagnostics
Before prescribing treatment, the specialist must obtain detailed information about the pathology. To do this, a preliminary examination, collection of anamnesis and diagnostics using instrumental analysis methods are carried out. The latter include methods such as:
- radiography or computed tomography - techniques use x-rays to obtain detailed images of the spinal column;
- Magnetic resonance imaging - the method is based on the use of electromagnetic waves that pass through the tissues of the body and are recorded using a special device;
- spondylometry – measurement of angular parameters and deformation of the spinal column, which will help characterize the condition of the spine;
- Electromyography is a technique that allows you to evaluate the bioelectrical activity of muscles and determine the normal state of muscle tissue.
All these techniques are effectively used in practice. The difference lies in the data that will be received by the medical professional for further interpretation by the doctor.
[node:field_similarlink]
Pathogenesis
As a result of the negative influence of factors on the spine, posture begins to deteriorate. This happens in this way: the vertebral bodies, under weight or due to concomitant diseases, gradually shift forward, fixing in a fan-shaped position. In the anterior convex part, the vertebrae move away relative to each other and the space of the intervertebral discs expands. In this case, the processes of the spinal segments are pressed more tightly and pinched. A large deviation from the normal curvature of the spinal column is lordosis.
The development of pathological lordosis at a young age leads to deformation of the chest, which in the future will cause complications on the organs of the chest cavity.
Prevention
Poor posture causes a lot of discomfort and prevents you from fully enjoying life. Unpleasant symptoms and visual defects can be eliminated, or better yet, prevented by preventive measures. Prevention of lordosis means that you must:
- Change the mattress. Approximately 20 years of life are spent sleeping, and this is a lot. Sleeping on a soft bed is bad for your back. It is better to choose a bed with a hard, straight surface. Sometimes for “even sleep” they put a board and cover it with a thin blanket.
- Exercise. For beautiful posture and a healthy spine, it is recommended to strengthen the back and abdominal muscles. Swimming, gymnastics, yoga, cycling, exercise on an exercise bike, walking, and fitness are great. Dangerous sports for the spine would be running (due to the sharp load on the spine when landing), football, boxing, Latin American dancing (due to asymmetrical movements and sharp turns of the body, which can lead to displacement of the vertebrae), alpine skiing and tennis.
- Lose excess weight. Excess body weight puts stress on the spine, it becomes vulnerable and weakens. Moreover, this is not the only part of the skeleton that suffers from excess weight. To clearly understand how the spine feels, you need to put a backpack on your back with pre-loaded books or heavy objects corresponding in weight to excess weight and walk like this for several hours. After a while, your shoulders and lower back will begin to ache, and the same thing happens to your spine every day.
- Do the exercises. Doing planks and bridges is good for your back.
- Train beautiful posture. You should avoid a sitting position where your legs are pushed under the chair. Be sure to try to keep your shoulders down and back, and your chest forward. The pose should be relaxed, and for this you need to train the muscle corset.
- Avoid constant stress on your back. Back pain mainly affects loaders, athletes, professional drivers, office workers, miners, doctors, cashiers, janitors and couriers. Therefore, at work you need to do a little warm-up to relieve tension from your back. As for lifting loads, the permissible load limit for adult men is 50 kg, for boys – 16 kg, and for women – 10.
- Consult a doctor if the first symptoms, back pain and numbness in the lower back or neck occur.
- Wear the correct shoes. It is worth giving up constantly wearing high-heeled shoes; it is better to alternate them with comfortable sneakers that support the arch of the foot.
Shoes suitable for preventing lordosis