Arthrosis of the toes Stages of development of arthrosis Nutrition correction Medicines for the treatment of arthrosis of the toes Causes of development of arthrosis of the toes Insoles and orthopedic correctors The opinion that arthrosis of the toes is a disease of older people is erroneous. The first symptoms of arthrosis of the toes begin to appear at a young age. It is important to monitor your health and regularly visit doctors for preventive examinations. Advanced cases of pathology provoke limited mobility of the foot and severe pain.
Causes of the disease
The disease can be triggered by traumatic tissue damage, metabolic problems, excess stress, and age-related changes in the body. If it is not possible to establish the exact cause of the disease, it is called primary. The risk of primary arthrosis increases in the following categories of people:
- Elderly;
- Women during menopause;
- People who have relatives suffering from the disease;
- Athletes, people involved in heavy physical labor.
Reasons for the development of arthrosis of the toes
Secondary arthrosis is a pathology caused by infection, inflammatory processes occurring in the body, due to which toxins begin to destroy the joint. Due to endocrine and hormonal disorders, destructive processes prevail over restorative ones. Metabolic failure causes a lack of produced substances, without which bone and cartilage tissue cannot regenerate normally.
Note!
People who are overweight and obese most often suffer from arthrosis. The reason is that they have problems with metabolism, and their joints are constantly exposed to excessive stress.
Mechanical damage to the joint due to bruise or dislocation can also cause pathology. The disease in some cases is the result of injury to the knee, ankle and other parts of the leg, as a result of which small joints are subjected to greater stress.
Other causes of arthrosis of the foot and toes:
- Inconvenient, narrow, tight shoes, too high a heel;
- Flat feet, club feet;
- Vascular diseases;
- Hypothermia;
- Endocrine diseases.
Causes and risk factors
Arthrosis is a pathology characterized by a destructive process in the cartilage tissue on the surface of the joint. The disease is diagnosed more often in older people, but sometimes it also occurs in young people. The disease affects different joints of the legs. Patients often experience arthrosis of the toes.
The disease is formed due to disruption of metabolic processes in cartilage. Metabolic failure can be caused by many factors. Reasons include:
- Wearing shoes that don't fit and are too tight for your feet.
- Standing for a long time.
- Fascination with high heels.
- Injuries of the lower extremities.
- Development of flat feet.
- Hypothermia.
- Excess body weight.
- Excessive physical activity.
- Vascular pathologies.
- Diseases of the endocrine system.
- Penetration of infection into the body.
- Joint diseases present in other parts of the legs.
- Stress.
Doctors also note that a person may have a hereditary predisposition to the occurrence of the disease in question.
How the disease develops
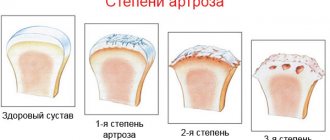
Osteoarthritis of the phalanges of the toes does not occur overnight. The disease develops gradually and goes through 4 main stages:
- At the first stage, the disease has no obvious signs, the patient does not feel it. Mild pain appears and there may be slight stiffness in the foot. The symptoms do not interfere with movement or cause discomfort, so patients often do not pay attention to such signs.
- The second stage is accompanied by more obvious signs of pathology. Stiffness appears and the pain intensifies. Muscle atrophy begins.
- With third degree arthrosis of the toes, a person feels pain not only while walking, but also while at rest. The bone tissue begins to grow, the foot becomes deformed, and seals appear on the toes. Lameness may occur.
- The fourth stage of the pathology is complete destruction of the joint, it is no longer possible to restore it. It is possible to preserve motor function only through prosthetics.
It must be remembered that the lack of treatment when diagnosing arthrosis in the legs can lead to disability. Symptoms that resemble pathology should not be ignored.
Stages of development of arthrosis
Diagnostics
- How to treat arthrosis of the foot at home: folk remedies and medications, video
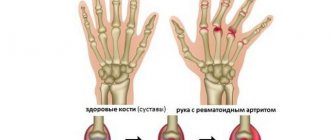
Diagnosing arthrosis in the toes is not always easy, especially in the initial stages of its development. The doctor can confirm the assumption by ordering additional studies. Differential diagnosis with rheumatoid arthritis, reactive arthritis and gout is urgently needed. The following signs indicate the presence of arthrosis of the toes:
- Leukocytosis and an increase in ESR in a blood test - excessively elevated values are a sign of an inflammatory process occurring in the body;
- Normal urine test. If urate, uric acid, is present, the patient may have gout;
- Rheumatoid factor is not detected.
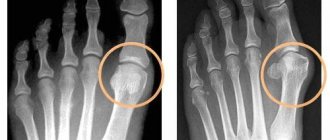
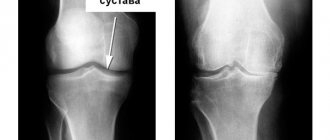
The results of the x-ray depend on the stage of development of the disease. In the initial stages, there is a decrease in bone density and a narrowing of the joint space - photo images can be seen below. Later, as the pathology develops, the image will show osteophytes, the formation of ankylosis, and a complete absence of joint space.
The mechanism of development of arthrosis of small joints of the foot
With arthrosis, dystrophic-destructive disorders of the osteochondral tissue and ligamentous apparatus occur with a predominance of hyperplastic processes. In pathogenesis, 4 stages of disease development can be distinguished.
Stage 1.
At stage 1, metabolic disorders occur. Cartilage tissue consists of chondrocytes and matrix. The matrix contains collagen fibers and proteoglycans. At the onset of the disease, the synthesis of proteoglycans by chondrocytes decreases, as a result, the binding of intercellular fluid is disrupted, and the elasticity of the ligaments is lost.
Stage 2.
Intercellular fluid penetrates into the collagen fibers, they are destroyed, metalloproteinase, which destroys cartilage, falls out of them, and the synthesis of prostaglandin E2 increases.
Stage 3.
Metalloproteinase continues to destroy cartilage, its breakdown products lead to fibrosis of the joint capsule. The joint space narrows.
Stage 4.
At the final stage, the tendons and muscles surrounding the joint are involved in the process. Calcifications form in the tissues and in the joint itself. All these changes disrupt the blood supply to the periarticular tissues. As a result, the nutrition of the joint is disrupted. Bone tissue is involved in the process, its growth and deformation begins. The bone growths of the phalanges begin to touch each other. The deformation of the fingers increases.
Signs of arthrosis of small joints of the foot
Signs of arthrosis of the toes appear unnoticed and gradually. But as the disease progresses and the hyaline cartilage is destroyed, the symptoms become obvious and begin to seriously bother the patient.
1st degree of arthrosis.
First, a person notices increased fatigue after walking, aching pain in the toes, and when standing for a long time. But in the initial period, the pain quickly passes after rest and does not cause inconvenience, so the asymptomatic period lulls a person’s vigilance. Doctors classify arthrosis as one of the insidious diseases, since the patient begins to worry only when obvious signs appear, indicating already 2-3 stages of the disease, when it is impossible to cure arthrosis.
2nd degree arthrosis.
In the second degree, the pain becomes more pronounced, it bothers the patient even after light exertion. At rest, the pain does not go away immediately. But after taking analgesic drugs, the pain goes away. During this period, patients already consult a doctor.
An increase in the bone of the first toe (halus valgus) in the second degree of arthrosis is visible to the naked eye, the toe deviates to the outer edge of the foot, a plantar callus is formed, and there may be redness in the area of the “bone” of the big toe. Finding comfortable shoes becomes a problem. The gait changes.
3rd degree arthrosis.
Stage 3 arthrosis is characterized by severe pain that cannot be relieved by analgesic drugs. Compensatory osteophytes grow, which compress nerve endings and soft tissues. Deformation develops not only of the first toe, but also of the other toes. The gait changes, the patient limps and spars the inner surface of the foot, and clubfoot appears. Walking is difficult. In an advanced situation, the fingers are tightly fixed in the wrong position, which aggravates all the symptoms of arthrosis.
Diagnosis of arthrosis of small joints of the foot
Confirmation of the diagnosis is carried out on the basis of examination, listening to the patient’s complaints, interviews, laboratory and instrumental examinations.
Grades 2 and 3 arthrosis are easily determined. It can be difficult to detect the early stage. There are no visual changes yet, laboratory tests (blood for biochemistry) are not indicative.
An X-ray image helps make the diagnosis. It shows changes occurring in the bones and joints of the foot:
- the size of the joint space decreases;
- bone growths (osteophytes) appear;
- cystic formations form due to bone damage
In some cases, to clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe CT and MRI.
Treatment
Treatment of arthrosis of the toes should be comprehensive, systematic and continuous. It consists of medication, physiological and manual therapy, exercise therapy, and massage. The patient is recommended to periodically visit sanatorium-resort institutions, adhere to a diet, and also limit the load on the legs. Good results are achieved by wearing special shoes, orthopedic insoles, finger braces and orthoses.
Drug treatment
Treatment of arthrosis of the little toe, like other fingers, can be carried out with medications. Medicines can restore cartilage tissue, relieve inflammation and relieve pain in the affected area. Recommended use:
- Chondroprotectors – promote cartilage regeneration. Teraflex, Chondro. Tablets, ointments, compresses and injections are used.
- Analgesics - do not cure, but eliminate pain in the affected fingers and feet. Spazmalgon, Analgin.
- NSAIDs – relieve inflammation and pain. Diclofenac, Ibuprofen.
- Hormonal pharmaceutical compounds are administered intra-articularly to relieve severe pain. It is forbidden to use frequently, because such drugs destroy cartilage tissue.
- Vasodilators - help normalize blood circulation in the extremities, which improves the nutrition of periarticular tissues and the metatarsophalangeal joint. Teonicol.
Medicines for the treatment of finger arthrosis
Physiotherapy, massage and exercise therapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures qualitatively improve the patient’s well-being and make it possible to reduce the amount of NSAIDs used.
Note!
It is not recommended to attend physiotherapy during periods of exacerbation of arthrosis of the phalangeal joints.
Sessions need to be held regularly. On average, 10-12 procedures will be required. The most effective treatments for arthrosis of the toe are:
- Magnetotherapy;
- Ultrasound;
- Electrophoresis using analgesic and anti-inflammatory compounds;
- Shock wave therapy.
It is recommended to use such methods after the onset of remission. The procedures are aimed at consolidating the results obtained from treating arthrosis of the toe joints in other ways. You can also massage your feet to strengthen muscles, increase blood flow, and activate metabolism. Experts advise not to forget about exercise therapy. Therapeutic physical exercises for the lower extremities will restore joint mobility and also strengthen weakened leg muscles.
Orthopedic correctors and insoles
Thanks to orthopedics, if the toes are affected, joint deformity can be eliminated or significantly corrected. Pain sensations are also reduced. Experts advise using special orthopedic devices for these purposes:
- What is arthrosis of the foot and how to treat it?
- Plaster boot;
- Shoes with arch supports;
- Special orthopedic pads.
Insoles and orthopedic correctors
A plaster boot for arthrosis of 1 toe helps to fix the joint and return the deformed area to its normal position. Special pads help the toes to lock in the correct position and return to the desired position. Special shoes protect the feet well from the formation of growths, relieve pain and discomfort.
You need to pay special attention to the choice of shoes. It should first of all be comfortable, and only then beautiful. It is necessary to select models from natural materials or high-quality artificial ones. It is important to buy shoes in your size. Women should not wear high heels for long periods of time.
Nutrition correction
Symptoms and treatment of arthrosis of the toes largely depend on the patient’s diet. Therapy with folk remedies, like classical therapy, requires adding foods rich in protein, calcium, collagen, phosphorus and vitamins to the menu. The patient's diet should be complete; the menu should include fruits, vegetables, and lean meats.
Note!
There is a direct connection between the risk of developing arthrosis and a person being overweight. Correcting your diet will help you avoid the accumulation of extra pounds, and therefore reduce the risk of developing pathology.
Experts advise drinking enough water, practicing split meals, eliminating smoked foods, fried and fatty foods, and processed foods. It is recommended to bake foods in the oven and steam them; you can also boil them. It is advisable to enrich your daily diet with dishes containing gelatin - jellied meat, fruit jelly, aspic. You should choose fermented milk products with a reduced percentage of fat content.
Nutrition correction
When is surgery indicated?
Surgery is used only in extreme cases when the toes are affected. If treatment with conservative methods does not help in combating pain, pronounced deformation of the phalanges of the toes is a reason for surgery. Several types of operations are performed:
- Osteotomy – cutting, removal of growths, deformed areas of bones;
- Endoprosthetics is the replacement of a natural but already destroyed joint with an artificial one;
- Arthroscopy – removal of particles of destroyed cartilage, filing of osteophytes through micro-incisions. The operation relieves pain, but the effect is short-term;
- Chondroplasty is the placement of a soft implant that replaces natural cartilage;
- Arthrodesis is the fixation of a joint in an anatomically correct position until immobility.
In the case of arthrosis of the toes, the patient is usually not assigned a disability. And yet, such a pathology at a later stage can impair gait and requires constant use of painkillers. Curing arthrosis is much more difficult than preventing it. Prevention measures include weight control, proper healthy eating and timely treatment of endocrine and inflammatory diseases.
29.11.2020Arthrosis
- What is arthrosis of the foot - symptoms and treatment, causes, how to treat foot disease
Arthrosis of the toes is associated with disruption of metabolic processes in the cartilage tissue of the joints, which leads to its destruction. Then all parts of the joint are affected - bone, ligaments and periarticular muscles. Symptoms and treatment of arthrosis of the toes depend on the age of the person; for example, medications in adults can only slow down the progression of the disease.
Treatment of arthrosis of small joints of the foot
Arthrosis does not go away on its own. The most unpleasant thing is that cartilage tissue cannot be regenerated, which is why it is so important to start treatment before its degeneration, when the progression of arthrosis can still be prevented. The goal of treatment is recovery in the early stages, and stopping the progression of arthrosis in later stages.
The treatment is complex. It consists of the following steps.
1. Relieve the load on the joint with arthrosis of the toes.
Removing excessive stress on the toes will already be a salvation for the joints of the leg. Therefore, you need to analyze your habits and learn to reduce your load during the day. You should avoid long walks or alternate walking with rest. You should not often go up and down the stairs; it is better to use the elevator. Remember that standing in one place for a long time is worse for your joints than moving.
2. Use of special devices for arthrosis of the toes.
For this you need to use special devices. Nowadays many varieties of finger clamps and splints, all kinds of orthopedic pads, and interdigital separators are sold. An orthopedic surgeon will always help you make your choice. Relieves the load by choosing the right shoes with corrective individual insoles. We will focus on some orthopedic devices and leg correctors.
Orthopedic correctors
Special orthopedic correctors provide the legs with a stable position and evenly distribute the load over the entire foot. In special salons they will help you choose the best option, taking into account the individual anatomical features of the foot. Correctors can be gel, plastic, silicone. Correctors are very convenient - they are easy to clean, lightweight, hypoallergenic and reliably hold your fingers in the desired position. Correctors are divided into soft ones for everyday use and hard adjustable ones for use at night.
Cane
The cane creates an additional support point, which provides greater stability when walking and reduces the load on the foot. Nowadays many types of canes are sold (solid, telescopic, folding, with different types of handles, made of different materials, etc.)
- if the patient has combined arthrosis of the hand and foot, doctors recommend a cane with a semicircular handle;
- if the patient is left-handed, a cane designed specifically for the left hand is sold;
- if the patient has difficulty getting up and sitting down, you can purchase a cane with two support handles;
- if the patient likes to walk, a cane-chair will suit him; when unfolded, it turns into a comfortable chair on 3 legs; if a person is tired, he can rest at any time.
The cane should be held in the hand opposite the painful or weak foot. During icy conditions, special anti-slip tips are available for canes.
Walkers
Walkers can be walking (they move with the patient’s step), non-walking when the patient moves inside them, and combined (universal). Walkers are not very convenient to use (they cannot be used to climb stairs or lean on them when getting up from a chair). But in some situations, they are used for the movement of people suffering from arthrosis.
All of the above devices allow you to slow down the progression of arthrosis, relieve the load on the foot, increase mobility in the joints, relieve pain and alleviate the patient’s condition.
3. Proper balanced nutrition for arthrosis of the toes.
It is necessary to adhere to a strict diet with the exception of smoked meats, spicy and fatty foods at the third stage of the disease. But even at stages 1 and 2, you need to ensure a balanced diet, eat more vegetables and fruits, and dishes containing gelatin. Doctors advise minimizing salt. The diet should include dairy products, fish and lean meat. For arthrosis, nutritionists recommend including avocados, bananas and soy in your diet. You need to watch your weight and avoid extra pounds. Excess body weight seriously increases the stress on joints.
4. Plasma therapy Arthrex ACP System for arthrosis of the toes
Treatment with your own platelet-rich plasma is gaining increasing popularity, as its effectiveness is noticeable after the first course of treatment.
5. Physiotherapy for arthrosis of the toes.
Physiotherapy plays a large role in the treatment of arthrosis. Laser therapy, paraffin baths, electrophoresis, pulsed magnetic therapy, electrical stimulation, shock wave therapy, and phonophoresis are very helpful (especially in the first stages).
6. Massage and manual therapy.
The massage should be performed by an experienced specialist. Self-massage is possible, but only after consultation with a qualified massage therapist. Movements should be smooth, stroking. In the subacute period, tapping and kneading can be done.
7. Therapeutic exercise for arthrosis of the toes.
Physical therapy begins with dosed minimal loads. It is performed first in a lying position. The patient is on a hard surface, bends and straightens his toes, and then makes rotational movements with his feet in different directions.
The next position is sitting. Without lifting the soles from the floor, the patient makes movements simulating walking or semicircular movements. You can pick up pebbles scattered on the floor with your toes, grab pencils and pens with your toes. As your condition improves, you can resort to exercises using special devices. All exercises should be performed at a slow pace.
8. Drug therapy for arthrosis of the toes.
Drug therapy plays a significant role in the treatment of arthrosis, since it is impossible to restore the cartilage layer. Therefore, pharmacological drugs are aimed primarily at reducing pain.
- To relieve pain, drugs from the NSAID group (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) are used. NSAIDs are prescribed for a short course, as they have serious side effects. After pain relief, they are canceled.
- a good analgesic effect in the first stages is provided by external therapy - ointments, rubbing, gels, warming creams;
- Usually, in addition to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, chondroprotectors are used, which structurally modify cartilage; the course of treatment with these drugs should be long-term;
- for severe pain, glucocorticoids are prescribed; corticosteroids are injected into the joint;
- local intra-articular injection of hyaluronic acid improves joint nutrition and mobility;
9. Surgical treatment for arthrosis of the toes.
As a last resort, they resort to orthopedic surgery. Typically, surgical intervention is recommended for cosmetic purposes, because a protruding thumb bone and curved phalanges do not look entirely aesthetically pleasing. In today's surgical orthopedics, operations are performed using endoscopic minimally invasive technology, which reduces rehabilitation time and eliminates the risk of postoperative infection.
Causes and types
The causes of the disease are:
- hereditary or acquired disorder of the shape of the foot;
- inflammatory processes due to incipient arthritis;
- flat feet, as a result of which the foot becomes wide;
- joint injuries;
- wearing shoes with high heels or too narrow;
- endocrine diseases and metabolic disorders;
- heavy physical labor with stress on the legs;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- hypothermia of the legs;
- alcohol abuse;
- long-term stress.
Depending on the location of the disease, the following types of arthrosis of the toes are known:
- osteoarthritis of the big toe;
- little finger;
- deforming;
- first metatarsophalangeal joint of the foot;
- second metatarsophalangeal joint of the foot;
- phalanges of the toe.
The video from the “HEALTHY JOINTS” channel explains what deforming arthrosis of the foot is.
Factors for the occurrence of arthrosis of the feet
To date, several factors have been identified that can lead to arthrosis of the feet. With prolonged and constant exposure to one of the factors listed below, there is a high probability that a degenerative disease will begin to actively progress:
1. For congenital pathologies and foot diseases. For example, with chronic flat feet, club feet and deviations from the anatomical norm. In this regard, it is recommended to regularly diagnose arthrosis by a specialist.
2. The presence of any injuries, especially with dangerous fractures leading to deformation of the bone skeleton of the feet. This can lead to changes in gait, as well as the general psychological state of a person. In medical practice, there have been cases where even a small bruise led to the development of degenerative-dystrophic foot disease. Refusal of timely treatment allowed the disease to progress.
3. Arthrosis is quite often an occupational disease in such professional fields as service, trade, production, and the like. This is due to the fact that workers have to be on their feet most of the time they work.
4. Severe obesity and even a few extra pounds can put serious stress on the feet. In a woman, arthrosis of the feet may begin to progress during a multiple pregnancy.
5. Incorrectly chosen shoes. Arthrosis occurs when wearing shoes that are inappropriate for the season, and this also leads to frostbite.
6. Presence of diabetes mellitus, as well as diseases related to endocrinology. They can lead to poor blood supply and clogged blood vessels.
7. Dependence on nicotine, alcohol, lack of physical activity, abuse of fatty foods - sooner or later this will lead to a deterioration in the general condition of a person and the possible appearance of disorders in the joints.
8. Uncomfortable shoes. As a rule, female representatives' excessive love for high heels inevitably leads to disorders in the musculoskeletal system and arthrosis.
The presence of simultaneous exposure to several factors increases the risk of developing such a disease. Degenerative-dystrophic disorders in the foot occur locally, at the site of exposure to the source of discomfort. For example, long walks on a high platform or uncomfortable last will cause pain on the toes. Regular discomfort will cause foot deformation. Moreover, pain will appear on both feet. While pain resulting from a fracture or bruise will appear only on one foot.
Stages and symptoms of the disease
Arthrosis of the toes has 4 stages of development:
- Pain and swelling occur after moderate physical activity and disappear after rest.
- Symptoms of the first stage are constantly present and intensify, the cartilage tissue along the edge of the joint begins to collapse.
- Large areas of disappearance of cartilage appear and damage to the bone, which has been deprived of its protective surface, begins.
- The functioning of ligaments and muscles changes, the joint becomes deformed, accompanied by severe constant pain. The cartilage is completely destroyed. Bone deformation increases. The musculoskeletal system becomes unable to perform its functions. Disability sets in.
Arthrosis of the thumb
Regardless of the causes of the disease, arthrosis of the big toes is distinguished by a number of symptoms that make it possible to understand the nature and severity of the disease.
The most characteristic:
- pain when walking due to damage to cartilage tissue;
- cessation of pain in a calm state after an hour to an hour and a half;
- swelling around the joint during exacerbation;
- signs of inflammation - swelling.
The manifestation of the disease depends on the stage of the disease process:
- First, the patient feels mild pain and slight stiffness in the metatarsophalangeal joint and hears a specific crunch.
- Joint pain and crunching intensify. An inflammatory process appears.
- In the final stage of the disease, there is continuous pain day and night. Bone growths form on the joints of the thumb, which leads to its complete immobility.
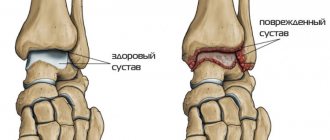
The photo shows the difference between normal cartilage and arthrosis affected. Schematic representation of arthrosis of the thumb. The beginning of arthrosis changes.
What is arthrosis of the foot?
Osteoarthritis of the foot that occurs at an early stage is almost impossible to detect. At first it is asymptomatic. Therefore, if you experience any symptom of pain in the feet, you must immediately contact a specialist who will carry out the necessary diagnostics. The presence of the following symptoms may indicate progressive arthrosis:
1. A dull pain, usually occurring in the area of the damaged joint. It clearly manifests itself during any physical activity, including walking, running or standing for long periods of time.
2. Regularly occurring crunching in the joints. Quite often it occurs when moving the feet, toes, running or performing strength exercises.
3. Frequent swelling in the feet, which appears after physical activity. Quite rare, but there are cases of foot arthrosis, when swelling occurs for no reason. As a rule, some kind of physical activity is necessary for the manifestation of edema in this disease.
4. Numbness in the muscles. Quite often it appears in the morning upon waking up.
5. When the feet are deformed due to a degenerative disease, resting on the leg becomes extremely uncomfortable. This subsequently manifests itself in the form of clubfoot and lameness. There is a change in gait that is obvious to others.
6. A person with arthrosis of the foot experiences disturbances in their general psychological state over time. This is due to regular pain in the feet, which causes insomnia, loss of appetite (up to its complete loss), fatigue and nervousness.
It is worth noting that it is women whose age has reached thirty years who are most often susceptible to arthrosis of the foot. According to statistical medical studies, about eighty percent of females have already experienced arthrosis or are predisposed to its occurrence.
The trouble with degenerative-dystrophic foot disease is the permanent pain and complete deformation of the feet, which in some cases does not even make it possible to purchase comfortable shoes. In rare cases, the patient is unable to move without assistance.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is carried out by the attending rheumatologist in several stages:
- The medical history of the patient and his family members is studied to determine whether relatives have arthrosis of the toes.
- The patient is interviewed to find out the speed and characteristics of the disease. The pathologies accompanying arthrosis are clarified.
- Palpation is performed to determine the extent of damage to the toes.
- An x-ray examination of the foot is done.
- If the second and third stages are suspected, computed resonance tomography is additionally prescribed.
- A urine test is taken to determine the level of uric acid. This is necessary to exclude a disease similar to arthrosis - gouty arthritis.
- Thumb densitometry is performed to determine bone mineral density.
Symptoms and diagnosis
At the initial stage, arthrosis of the toes manifests itself very weakly and therefore goes unnoticed. With each subsequent degree of development, the clinical picture becomes more pronounced. The following symptoms are observed:
- The pain is aching in nature, disturbing first when moving, and then at rest.
- Swelling of the legs.
- Limbs get tired quickly.
- Redness of the skin of the fingers.
- Increase in local temperature.
- Amyotrophy.
- Stiffness in the legs.
- Characteristic crunching sound when walking.
- Thickening of the affected joint.
- Deviation of the diseased joint to the side.
During the examination, the doctor first conducts an external examination of the foot, asks the patient to move his fingers, and studies the symptoms. Then the doctor prescribes a laboratory blood test, which checks for the presence of inflammation in the joints.
An informative method for making a diagnosis is radiography. In the photographs you can notice thickening of the bone tissue, changes in the shape of the joint, and the proliferation of osteophytes.
Densitometry is also performed. The technique helps determine bone density. This allows us to identify pathologies associated with arthrosis - osteosclerosis and osteoporosis.
Treatment methods
Treatment methods for arthrosis include:
- taking analgesics, chondroprotectors, vasodilators, hormonal medications;
- physiotherapy;
- manual therapy;
- folk remedies;
- surgical intervention.
Using traditional medicinal methods, arthrosis can be cured in children and adolescents before the end of skeletal formation.
Analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs
Arthrosis of the toes begins to be treated with the following medications:
- Ibuprofen. It does not treat arthrosis of the legs, but relieves pain and swelling. Can be used in the form of tablets, ointments or injections. Admission is allowed from the age of 6 years.
- Ketoprofen. Eliminates acute pain due to arthrosis. It should be used with caution by people suffering from diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Admission is permitted from the age of 15 years.
- Butadion. May be prescribed in the form of tablets or ointment. Taking the drug is aimed at relieving pain and reducing body temperature, which accompanies the inflammatory process. Admission is permitted from 14 years of age.
Ibuprofen - from 65 rubles Ketoprofen - from 104 rubles Butadione - from 52 rubles
Chondroprotectors
Prescribed for the purpose of restoring cartilage and the composition of synovial fluid. Based on substances contained in the tissues of a healthy joint. Application period is up to two months.
The most commonly used drugs are:
- Teraflex. The most popular and effective drug. It must be taken for a long time in order to stop the process of cartilage destruction as much as possible. Allowed to take from 15 years of age.
- Artra. Glucosamine, which is part of the medication, stops the process of destruction of cartilage tissue and promotes its restoration. Admission is permitted from the age of 15. Contraindications for use: bronchial asthma and diabetes.
Teraflex - from 1200 rubles Arthra - from 858 rubles
Drugs that dilate blood vessels
They increase the flow of blood and nutrients to the joint due to an increase in the size of the vessel. Most often, Teonicol (price from 345 rubles) and its derivatives are used for arthrosis of the toes. Reception is prohibited for pregnant women.
Hormone-containing medications
Injected directly into the joint as an injection. They are used only as prescribed by a doctor for severe pain that cannot be eliminated by anything. The use of such medications reduces pain, the intensity of inflammation decreases and the person feels better. Prescribed in accordance with analyzes and preliminary studies.
Side effects of use:
- immunity is suppressed;
- the process of removing dead cells is disrupted;
- a drop in the level of production of your own hormones;
- violation of metabolic processes.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy methods are used only after the end of the acute period in order to consolidate the achieved results and prevent a new exacerbation:
- UHF therapy reduces inflammation and pain;
- Magnetic therapy works similarly;
- electrophoresis helps administer medications through the skin to accelerate the analgesic effect;
- Ultrasound therapy (phonophoresis) helps the body create restorative and protective systems;
- Cold and heat treatment is sometimes used.
Manual therapy
An effective method of treating diseases of the musculoskeletal system, which is characterized by a high percentage of complete healing.
Results of the impact on the patient’s body:
- pain reduction;
- eliminating the cause of the disease;
- stopping the progression of the disease.
Treatment methods are as follows:
- stretching, bending, squeezing, rubbing, twisting;
- manual drainage that improves blood flow;
- acupuncture and pressure on points (methods of ancient Chinese medicine).
Exercises for arthrosis are simple, but very effective, as a result of which the blood supply to the joints and phalanges of the fingers increases. For example, repeatedly (up to 100 times) clench and unclench your toes.
Contraindications for the use of manual therapy:
- old age;
- tumor diseases;
- low blood clotting;
- some cardiovascular diseases.
Folk remedies
The most effective folk remedies at home for the treatment of arthrosis of the toes are:
- Tincture of dandelion flowers with iodine (infused for 4 days). On the fifth day, a mesh of tincture is applied to the steamed legs. The procedure is carried out every day for two weeks.
- Compresses, rubbing, baths of infusions and decoctions prepared from herbs, plants and natural products.
- Pain-relieving compress made from fresh burdock leaves.
- The use of bee products in decoctions, ointments and creams.
- Compresses from herbal tinctures with alcohol.
Surgery
If there are no results from using the described methods of healing, you have to turn to surgery. An effective method of getting rid of arthrosis of the feet is surgery to remove growths (“bones”) on the joints of the big toes. The goal is to remove the deformability of the finger axis.
Two methods are known:
- Minimally invasive. surgery using mini-incisions (no more than 3 mm). Using a microscalpel, the surgeon saws through the bones in certain places. As a result, joint deformity is eliminated. It is carried out under the control of an X-ray machine.
- Reconstructive. This method of eliminating joint deformity is characterized by low trauma and a short rehabilitation period. But this technique is possible only at the first stage of the disease.
The sequence of its implementation:
- The surgeon, through an incision on the inner surface of the big toe, dissects the capsule of the first metatarsophalangeal joint, which is removed.
- Removal of callus.
- Sawing of the metatarsal bone.
- Moving its fragments with fixation with titanium screws.
The operation is performed under anesthesia. Patients are back on their feet the very next day, but wearing special orthopedic shoes.
The results of this type of treatment, with rare exceptions, are as follows:
- cessation of pain;
- restoration of finger joint movement;
- disappearance of a bump on the finger and its deformation.
You can verify this by reading reviews of those who have undergone surgery.
Indications for surgery
The main indications for which the doctor decides to perform surgery:
- severe constant pain, almost unresponsive to drug therapy;
- joint inflammation;
- damage to bone tissue.
Complications in the absence of treatment for arthrosis of the feet
If treatment for arthrosis of the foot is ignored, as well as without timely intervention in the progressive process of damage to the joints of the foot, the disease develops quite quickly. Ultimately, this provokes the complete destruction of cartilage tissue and the occurrence of inflammatory processes in the muscle corset. These internal processes are expressed not only by severe pain in the feet, but also by complete deformation, as well as the proliferation of bone tissue in the joint. Thus, the foot loses the ability to move and a person with foot arthrosis cannot move independently. There is a worsening of the psychological state caused by the patient’s discomfort from his inferiority.
Video
Symptoms and treatment of arthrosis of the toes. Published by the “Treatment of Joints” channel.
Arthrosis interferes with a person’s life, regardless of which area is affected and how much it is affected. Destruction that occurs in the lower extremities is especially difficult to bear. Osteoarthritis of the toes occurs in a minority, so very few people know what to do. The likelihood of developing disability over time is very high, therefore, it is extremely important to seek help immediately after the first minor symptoms appear. To do this, you need to familiarize yourself with the clinical picture of the disease. You don't have to be an expert to do this.
Inside view
Elimination of damaging factors
Before you begin to treat arthrosis of the toes, it is necessary to exclude all factors that can provoke the progression of the pathology.
- If you are overweight, you should try to reduce it. Then the load on your legs will be significantly less.
- You should also pay attention to shoes. If it is too narrow or uncomfortable, you need to replace it. Women who love high heels will have to stop using them.
- When playing sports, it is necessary to control the degree of load so that it is not high, so as not to overload the feet. It is better to avoid heavy physical labor altogether.
- If the provoking factor for joint destruction is any pathology, it is necessary to urgently treat it.
Factors and causes of arthrosis of the toe joints
Arthrosis of the toes, the symptoms and treatment of which pose some difficulties for the doctor, often begins due to an incorrect lifestyle (ICD code - M19). The patient may experience various manifestations, for example, arthrosis of the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint. Osteoarthritis of the metatarsophalangeal joints of the feet requires long-term treatment, because the metatarsophalangeal joints are easily damaged and difficult to restore. This group also includes pathology of the interphalangeal joint of the right or left foot.
Despite the stereotype about the “age of arthrosis,” people under 30 can get this pathology, and here’s why:
- Phalanx injury, sprain, fracture, bone crack, minor bruises. This often affects athletes or people whose work involves heavy loads;
- Hereditary predisposition to a particular disease. If among your relatives there are people who have ever suffered from arthrosis, it is important to monitor your well-being, especially as you approach old age;
- Inflammatory processes occurring nearby;
- Metabolism. Its disorders are caused by a lack of minerals and auxiliary components in the human body;
- Obesity;
- Diabetes;
- Incorrectly selected shoes;
- Heavy load.
Prevention measures
You can prevent arthrosis of the big toe, little toe or other parts of the foot using the following rules:
- Wearing comfortable shoes.
- Avoid frequent use of high heels.
- Body weight control.
- Gymnastics for legs.
- Reducing the load on the feet.
- Taking massage courses.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Arthrosis of the joints is a serious disease that leads to complete destruction of joints and disruption of a person’s motor activity. It is important to treat the pathology at the first stage in order to prevent its progression and avoid adverse consequences.
Symptoms
The changes that occur in the joint are very often irreversible. This is especially true for the thumb. Arthrosis of the joint of the big toes is a consequence of severe deformation:
- Initially, pain appears only after a long walk;
- Touching your fingers can cause pain;
- The foot increases in size and swells;
- During movement, the joints in the affected area crunch.
In addition, each stage is characterized by an individual set of symptoms, identifying which we can talk about the degree of deformation. There are three of them, and the more behavior that influences the progression of the disease is observed, the more quickly they replace each other and cause the patient more and more discomfort, the processes become irreversible.
Degree of severity in the development of the disease
The first stage is distinguished only by pain, redness and swelling of the foot, and crunching. The second stage involves:
- Thickening of the articular membrane of all toes. Fluid accumulates in them, pathological growths appear;
- Pain appears not only when walking, but also in a state of calm, minimal physical activity;
- The thumb is deformed, this is due to the growth of osteophytes. The natural position of the fingers changes, they shift;
- Small nodules that are soft to the touch become harder and cause severe discomfort.
With the onset of the third stage, the bones inside begin to grow together, connecting. The person’s condition resembles a disability: he practically cannot walk, he is bothered by constant pain, and movement is unlikely. The feet cannot move. Muscle tone first decreases, and then they completely atrophy completely. In this situation, a surgical treatment method will be required; others will be ineffective and will simply contribute to the further development of the disease.
Degree of damage
How is arthrosis of the toes treated?
Treatment of the patient depends on the stage of the disease.
| First | Second | Third |
| The treatment proceeds without much difficulty. You can only get by with some physiotherapy procedures and medications. | After the diagnosis, the doctor must stop the destruction, preferably before severe deformation begins. Complete restoration of cartilage, unfortunately, is not possible. | The patient is hospitalized for the duration of complex therapy. The prognosis is disappointing, treatment is often surgical, followed by a recovery process. |
Otherwise, treatment methods are very different.
Deformation at the last stage
The role of physiotherapy, massage and exercise therapy in recovery
You should not resort to such methods of treatment during an exacerbation. This will not only cause severe pain to the patient, but will also have no effect. The procedures included in this list are aimed at restoring motor function and improving the general condition of the patient. It is very important to prevent the next exacerbation. There is a list of manipulations that help with this:
| UHF | Magnetotherapy | Electrophoresis | Massage | Physiotherapy |
| Helps improve blood flow and reduce pain. | Suppresses the inflammatory process not only in the lesion, but also in other nearby organs. | Enhances the effectiveness of medications, especially painkillers. | Increases muscle tone, accelerates metabolism, removes toxins. | Has a beneficial effect on joint mobility. The leg muscles become stronger. With the help of a specialist, you can achieve good results. |
Effect after surgery
You can learn more about the treatment from the video: