Author
: Grachev Ilya Illarionovich
Editor
: Efremov Mikhail Mikhailovich
Date of publication: 05/13/2014 Date of update: 05/05/2021 All doctors of the clinic
- Shoulder pain due to coronavirus and ARVI
- Arthritis
- Diagnostics
A significant proportion of patients complain about pain and limited movement in the shoulder during outpatient visits with an orthopedist-traumatologist, rheumatologist and therapist. What and why it hurts, how to get rid of pain can be found in this article. Do not be afraid, the doctor will eliminate shoulder pain at any stage of the disease.
Qualified specialists can be found in medical, Moscow.
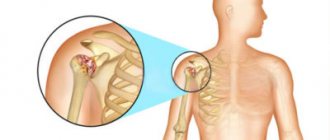
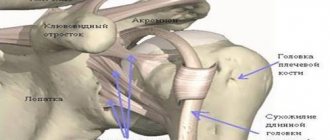
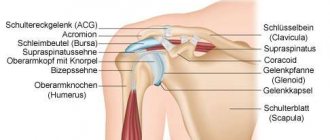
Anatomy and functions of the shoulder joint
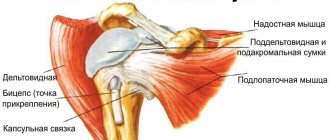
The shoulder joint is formed by the round head of the humerus and the glenoid cavity of the scapula. This joint connects the upper limb to the shoulder girdle. The head of the humerus is much larger than the glenoid cavity, which creates an increased range of motion in the joint. At the same time, the spherical head is sufficiently strengthened by increasing the depth of the articular cavity with a cartilaginous roller (which is also responsible for shock absorption) and muscle tendons, some of which pass inside the articular cavity.
From above, the articular joint is protected by an arch formed by the coracoid process of the scapula and the coracoacromial ligament. The synovial membrane forms branches (bursae, bursae) that improve the gliding process of articular surfaces.
This structure allows for a wide range of movements:
- flexion - movement of the arm forward and upward;
- extension – back and up;
- abduction – to the side and up;
- adduction – down to the body;
- pronation - rotation around the vertical axis of the lowered hand with the palm facing inward;
- supination - rotation around the vertical axis of the lowered arm with the palm outward;
- Roundabout Circulation.
Flexion and abduction of the arm above the horizontal position are carried out with participation in the movement of the shoulder girdle.
The structure of the shoulder joint
Diagnostics
Traumatic injuries are managed by traumatologists; for pain of non-traumatic origin, patients turn to rheumatologists or orthopedists. Specialists collect complaints, conduct an external examination, establish the time and circumstances of occurrence, the dynamics of the development of symptoms, and their dependence on external circumstances. The examination may include the following techniques:
- Radiography.
Performed in one or two projections. The presence of disorders is indicated by changes in the contours of the humeral head and glenoid cavity, a decrease in the size of the joint space, areas of rarefaction in the thickness of the bone tissue, marginal defects, and osteophytes. - Ultrasonography.
When assessing the condition of periarticular soft tissues, it detects hemorrhages, signs of inflammation, degeneration, and foci of calcification. Sonography visualizes loose intra-articular bodies, fluid in the joint, and often allows one to determine the cause of pain. - and MRI.
Prescribed at the final stage of the diagnostic search when the data from other methods are unclear, to clarify treatment tactics. They allow you to accurately determine the localization, prevalence and nature of pathological changes of traumatic, inflammatory, tumor origin. - Joint puncture.
It is performed if there are signs of synovitis. The resulting liquid is sent for microbiological or cytological examination and studied using immunological methods. - Biopsy of the synovium.
It is carried out for rheumatological diseases, specific arthritis, tumor processes for subsequent histological examination. - Arthroscopy.
It is carried out for a visual inspection of the elements of the joint and collection of a biopsy sample. When determining pathology, diagnostic measures are complemented by therapeutic measures (for example, removal of loose bodies). - Lab tests.
In rheumatic pathology, specific markers of various diseases are identified. In inflammatory processes, an increase in ESR and leukocytosis with a shift to the left are confirmed. In case of oncological lesions, the severity of anemia, the degree of dysfunction of organs and metabolic disorders are assessed.
What to do at home if your shoulder hurts
If you suddenly experience severe pain, you must first of all calm down and make the right decision: seek medical help.
You should know: any acute diseases, including those accompanied by severe pain, are easier to treat and are often completely cured. Therefore, the sooner you see a doctor, the more favorable the outcome of the disease will be.
But there are situations in life when it is not possible to immediately visit a doctor. What to do if shoulder pain does not improve? The advice is still the same: consult a doctor, he will help even in advanced conditions: he will relieve pain and stop the progression of the disease.
How to help yourself
The pain can be very severe and then the question arises, how to help yourself, how to survive this condition and get to a specialist? You can call an ambulance or help yourself:
- Take painkillers:
- Ibuprofen
- quickly and effectively relieves pain, swelling and fever; if there are no contraindications for use, you can take 1 – 2 tablets of 200 mg, washed down with half a glass of water (this will make the drug work faster); contraindications: erosive and ulcerative diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), increased bleeding; - Paracetamol (Panadon, Efferalgan)
is also an effective drug in sufficient dosage; To eliminate pain, take 1 tablet of 500 mg; There are practically no contraindications; - Ibuklin
is a combination drug; 1 tablet for adults contains 400 mg of ibuprofen and 325 mg of paracetamol; It acts quickly and effectively, but has the same contraindications as Ibuprofen. - Use external agents - gels, ointments. They can relieve pain well, especially in combination with painkillers or injections:
- Diclofenac gel (Voltaren, Diclovit, Ortofen)
– applied in a thin layer to the painful area; very effective ointment; - Ketoprofen gel (Artrum, Bystrumgel)
- after application to the skin, the ointment for shoulder pain is quickly absorbed and has an analgesic effect; - Menovazin
is an alcohol combination solution that contains painkillers and sedatives.
Carrying out pain relief on your own is a necessary measure and it does not in any way cancel a visit to the doctor!
Exercise can help too. Training is carried out after the acute pain has been eliminated. Regular exercise helps improve blood circulation and metabolism in affected tissues, and prevents the development of irreversible changes that block the motor activity of the hand.
Basic training requirements:
- regularity – classes should be held daily;
- lack of heavy physical activity and sudden movements;
- all exercises must be performed smoothly;
- if there is a sharp increase in pain, stop training; exercises are continued after the intensity of the pain syndrome has decreased with lower loads, increasing them very gradually.
Several exercises designed specifically for patients with glenohumeral pain syndrome:
- Starting position (IP) – lying on your back, arms along the body, palms up, legs slightly apart. Inhale: raise your hands and place them behind your head; exhale: smooth return to IP.
- IP - lying on your back, arms outstretched to the sides. Inhale: without lifting your hands from the surface, make a sliding upward movement. Exhale - return to IP. Repeat the exercise moving down and back.
- IP - lying on your stomach, arms extended forward, legs spread. Inhale: raise your right arm and left leg, exhale - move to IP. Repeat the exercise with your left arm and right leg.
Exercises for shoulder pain
What not to do
In case of chronic pain syndrome in the glenohumeral region, the following is contraindicated:
- some hand movements - which ones are determined by the doctor after clinical tests and additional examinations; it all depends on which structures are affected;
- any sudden hand movements and heavy lifting;
- frequent smoking and alcohol abuse - has a negative effect on blood circulation and metabolism, which aggravates the problems;
- self-medication - the result will be impaired hand function and increased pain; treatment must be carried out at a professional level.
When you need to see a doctor urgently
A doctor’s consultation is required if there is pain in the glenohumeral region:
- appeared immediately or some time after the injury; they intensify when the hand moves in a certain direction;
- the shoulder hurt against the background of existing chronic arthritis affecting other joints;
- accompanied by fever, redness, swelling and pain in the shoulder area;
- appeared against the background of cervical osteochondrosis with painful lumbago in the neck, extending to the glenohumeral region;
- discomfort, crunching when moving and occasional minor pain have been bothering me for more than 3 months.
Self-medication for such diseases almost always ends in the development of persistent pain and impaired movement in the hand. You will be provided with qualified assistance at the Moscow Medical Center.
What to do for various types of pain
The shoulder joint has a complex structure; surrounding muscles, tendons, and ligaments take part in its work. When various structures are affected, shoulder pain appears, having different localization and character. To save the patient from suffering, you need to find out the cause of shoulder pain. This can only be done by an orthopedic traumatologist or rheumatologist. The patient must correctly describe his condition, tell where it hurts, when the pain appeared and what he associates with its occurrence. So, the pain can vary.
Shoulder pain due to coronavirus and other viral diseases
Coronavirus infection is absolutely unique, as it manifests itself differently in each patient. In this case, heredity obviously plays a big role. For example, if a person has close relatives suffering from rheumatoid arthritis, then the risk of developing this disease after suffering from Covid-19 increases many times over.
Moreover, the disease in many patients begins with damage not to small, but to large joints, including the shoulder. During the course of the disease, some patients may also experience symptoms of acute arthritis with severe pain in the shoulder joint. After recovery they completely disappear.
Many viral infections can be accompanied by acute arthritis (influenza, rubella, infectious hepatitis, etc.). As a rule, they have a benign course and end with complete recovery. But it is better to treat them under the supervision of a doctor.
Shoulder pain when moving your arm
When the periarticular tendons and ligaments are damaged, acute short-term pain in the shoulder appears during movement. After this, even at rest, some people are still bothered by aching waves of pain. The reasons for their appearance can be different from acute injuries and microtrauma to unnoticed chronic arthritis and arthrosis. To eliminate such pains, you need to find out their nature. Only a doctor can do this.
Pain in left or right shoulder
The causes of shoulder pain on the right or left can be different. One shoulder can hurt during inflammatory processes, after injuries, in old age against the background of degenerative-dystrophic disorders in the tissues. In acute arthritis, pain in the shoulder joint is intense and constant, accompanied by swelling and redness of the tissues, and an increase in body temperature. After an injury, severe bursting pain in the shoulder often appears, associated with intra-articular hemorrhage (hemarthrosis). When ligaments or tendons rupture, pain is combined with impaired movement.
Sometimes acute pain in the left shoulder is a symptom of myocardial infarction or cervicothoracic osteochondrosis. It can be difficult to distinguish one from the other, since osteochondrosis pain is practically indistinguishable from infarction pain. Such patients are hospitalized and in the hospital they figure out what exactly happened.
The cause of pain in the right shoulder may be acute cholecystitis. It radiates to the right shoulder girdle along the phrenic nerve.
The doctor’s task is to identify the causes of the painful symptom and provide pain relief therapy. This can only be done in a clinic!
Shoulder pain when inhaling
When a tendon ruptures, dislocates, or fractures, taking a deep breath increases the pain. The victims require emergency surgical care.
But pain in the shoulder when inhaling can also be a sign of a serious illness of the internal organs. Thus, with myocardial infarction or pleurisy, pain waves often radiate to the shoulder and intensify with inhalation. These patients also require emergency care and hospitalization.
If there is pain when inhaling, you need to call an ambulance: this patient may need to be hospitalized.
Shoulder pain after injury - fracture or dislocation
Injuries are always painful. But sometimes the victim cannot assess the severity of his condition and does not immediately seek medical help. This significantly complicates the condition and often leads to the appearance of chronic glenohumeral pain syndrome. Main symptoms of traumatic injuries:
- An intra-articular fracture of the humeral head is usually combined with a fracture of its neck.
The most common cause is a fall on an outstretched arm. Symptoms: severe pain in the shoulder girdle, crunching, deformation of the injured area and limitation of movements. Emergency hospitalization required. - Dislocation
- often combined with rupture of the joint capsule and tendon-ligamentous apparatus, so there is a risk of dislocation becoming habitual, recurring with minor injuries. Since the shoulder joint is very mobile, dislocations often occur due to falls or impacts. Sometimes a person gets dislocated while lifting a heavy object. Symptoms: swelling of the periarticular tissues, inability to move the arm, pain in the arm from the shoulder. It is necessary to reduce the dislocation followed by rehabilitation to prevent habitual dislocation. - Bruise
- even a minor bruise causes damage to soft tissue cells - synovium, ligaments, tendons and muscles. An aseptic inflammatory process develops. During a bruise, acute pain appears in the shoulder, which after a while becomes aching. Then the aching pain in the shoulder goes away, but there is a risk of acute inflammation becoming chronic with a gradual loss of joint function. Therefore, after bruises it is necessary to carry out rehabilitation measures. - Ligament rupture
is the most common injury, which initially occurs acutely, with severe pain, tissue swelling and impaired movement. Then the symptoms decrease or disappear, and after a while slowly increasing pain and limitation of movements appear. Therefore, it is very important to carry out proper adequate treatment of such injuries with subsequent rehabilitation.
Crunching in joints - when to worry
Joint pain at rest
Shoulder and arm pain
Shoulder pain radiating to the arm may be due to:
- acute arthritis or exacerbation of chronic arthritis with swelling of tissues compressing nerve trunks; pain in the shoulder is acute and can radiate throughout the arm to the forearm, hand and fingers; Depending on the type of arthritis, it is treated by a surgeon or rheumatologist;
- humeroscapular periarthritis - inflammation of periarticular (surrounding the joint) tissues - muscles, tendons, ligaments - this is the most common cause of the development of chronic pain syndrome; pain in the arm from the shoulder is aching, debilitating, often appears at night or after any physical activity; tissue swelling can lead to compression of nerves and irradiation of painful waves in the forearm and hand; The cause of such pain in the shoulder can be both purely inflammatory processes and the consequences of injuries, ruptures of tendons and ligaments; long-term speech and rehabilitation are required;
- cervical osteochondrosis - it can cause pinching of the spinal nerve roots; pinching at the C5 – C6 level leads to severe pain in the shoulder with irradiation to the right or left forearm and hand; requires treatment from a neurologist;
- coronary heart disease with attacks of angina or myocardial infarction; a sharp spasm of the coronary arteries (vessels supplying the heart with blood) causes severe pain in the heart, often radiating to the left shoulder girdle, as well as pain in the arm from the shoulder; in order to remove the spasm, you need to take a nitroglycerin tablet under the tongue; if there is no effect, call an ambulance.
Neck and shoulder pain
Often strong pain waves occur simultaneously in the shoulder and neck, so it is difficult for the patient to figure out where they begin. Sometimes the pain starts in one shoulder and radiates to the neck. The cause of such shoulder pain is shoulder arthritis or glenohumeral hyperarthritis with tissue swelling and compression of the spinal nerves. In other cases, the pain begins in the neck and shoulders on both sides. This is a sign of cervical osteochondrosis with pinching of the spinal nerve roots and radicular pain. To remove pain and help the patient, you need to establish the correct diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.
Shoulder pain radiating to the scapula, elbow, collarbone, back, head
Many patients complain of such symptoms. They are characteristic of cervicothoracic osteochondrosis with entrapment of the spinal nerve roots at the level of 5 - 7 cervical vertebrae (C5 - C7) and 1 -2 thoracic vertebrae (Th 1 - Th2). First, pain appears in the back and side of the neck, then severe pain in the shoulder. The pain can spread from the shoulder to the elbow, move to the collarbone, radiate to the frontal region of the head and down to the scapula area.
If the motor fibers of the roots are damaged, paresis or paralysis of the upper limb may occur. Treatment by a neurologist will help.
Shoulder pain when flexing and extending
Pain that increases with flexion and extension of the shoulder joint is a symptom of damage to nearby muscle tendons. These are 4 tendons that are part of the rotator cuff and the biceps tendon. When they become inflamed (tendonitis), movements in the shoulder joint become impaired and become painful. Damage to the biceps muscle (biceps) also manifests itself in severe pain when bending the elbow. Tendinitis can be the result of injury or inflammation in the joints. The treatment is carried out by an orthopedist-traumatologist; the pain can be removed after high-quality rehabilitation.
Shoulder pain at night
Night pain in the shoulder is characteristic of inflammatory processes in the shoulder joint and periarticular tissues. During sleep, the body warms up, blood vessels dilate, the liquid part of the blood leaks into the surrounding tissues, forming swelling and squeezing nerve endings. To get rid of night pain in the shoulder joint, you need to treat the underlying disease.
Shoulder pain after exercise
Training accompanied by severe pain is unacceptable. They contribute to the exacerbation of the pathological process and its chronicity. Severe pain in the shoulder during exercise should be a reason to stop training. You can resume classes only after it has stopped. The load should be reduced in this case.
Shoulder pain with swelling
These signs are characteristic of acute arthritis and exacerbations of chronic arthritis. In addition, shoulder pain and tissue swelling appear after injury. In both cases, urgent assistance from a specialist is required.
This cannot be left to chance: a slow and imperceptible decrease in joint function with the formation of pain is possible.
Pain in the shoulder joint due to inflammatory processes can be eliminated
Shoulder pain and numbness
The causes of shoulder pain in combination with numbness are pinching of the spinal nerve roots of the cervical spine due to osteochondrosis and herniated intervertebral discs. Sometimes this is combined with movement disorders - paresis and paralysis. A similar symptom can appear with plexitis - inflammation of the nerves of the brachial plexus. The pain can be very severe, so you should not delay your visit to a neurologist.
Pain when raising your arm
This symptom is characteristic of pinched tendons of the rotator cuff and biceps muscles between the acromion and the head of the humerus. Severe pain appears in the shoulder when raising the arm up to a level below the shoulder joint. An orthopedic traumatologist treats injuries.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of shoulder arthrosis include:
- pain: occurs due to decreased smoothness of articular surfaces, proliferation of osteophytes and bone deformation; the intensity, duration and nature of the sensations depend on the degree of damage;
- crunch: one of the characteristic symptoms of the disease that appears in the early stages; differs from the physiological one in a coarser tone, and is also often accompanied by pain;
- limitation of mobility: associated with the appearance of pathological growths and particles of destroyed cartilage inside the joint; in the first stages it is represented by slight morning stiffness, which later increases until complete immobility (ankylosis);
- deformation: a change in the contours of first only the joint, and then the arm, occurs in the later stages of the disease and indicates complete destruction of the cartilage and involvement of bones, muscles and ligaments in the pathological process.
The progression of symptoms can occur over years or even decades, but eventually arthrosis of the shoulder joint leads to the inability to move the arm and severe pain.
Diseases that cause shoulder pain
Pain syndrome can appear against the background of various diseases and injuries over time leading to increased pain. If left untreated, they will all impair joint function.
Arthritis
Joint inflammatory processes can occur acutely and chronically. Acute arthritis causes severe pain, swelling, redness of tissues, limited mobility of the limb and disruption of the general condition of the patient. But they are easier to treat, so doctors try to prevent the acute course of inflammation from becoming chronic. With chronic inflammation, pain in the shoulder is often aching in nature, swelling is not expressed, but in the absence of medical care, slow destruction and pain in the shoulder joint occurs with the formation of ankylosis (immobility). Arthritis is dangerous because it causes numerous complications that are dangerous not only to the health, but also to the life of the patient. Depending on the type of arthritis, it is treated by a surgeon or rheumatologist.
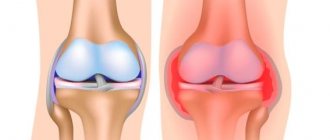
Arthrosis
With arthrosis, degenerative-dystrophic processes occur in the shoulder joint with gradual thinning and destruction of cartilage tissue, which acts as a shock absorber during movement in the joint. The causes of shoulder pain are friction of the bone surfaces of the joint with their destruction, deformation and irritation of the nerve endings of the periosteum. Arthrosis can be the result of injuries, arthritis, or metabolic age-related changes. Arthrosis can and should be treated. It is quite possible to relieve patients from constant pain.
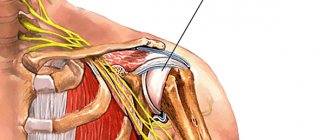
Humeroscapular periarthritis
This is a collective concept that includes all periarticular (periarticular) lesions of the shoulder joint area. The term "humeral periarthritis" was first used in the mid-19th century by the French surgeon Duplay and has been used for more than a hundred years to refer to all pain syndromes in this area.
It has now been established that the main cause of chronic pain in the shoulder region is a degenerative-inflammatory pathology of the deep muscles and tendons involved in the movement of the shoulder - tendinitis. The onset of the process is associated with repeated microtraumas, degenerative processes, and the deposition of calcium salts.
A degenerative-dystrophic process develops in the muscular-ligamentous system, which is periodically accompanied by inflammation of the tendons, accompanied by pain. The next stage is the growth of fibrous (connective) tissue and the development of ankylosis - joint stiffness. The tendons lose their elasticity, and the slightest injury causes them to rupture, which further aggravates the patient’s condition. There are a number of diseases that are included in the concept of “humeral periarthritis” and have their own characteristics:
- Tendinitis
is an inflammation of the 4 muscles that rotate the shoulder joint and maintain the stability of the joint. The muscles are located around the shoulder joint. Disorders in them often develop after lifting weights with arms outstretched - an action that is unusual for a given person. Tendonitis manifests itself as painful sensations in the outer part of the shoulder girdle, sometimes radiating to the elbow. Soreness sometimes arises again, which is associated with an exacerbation of the aseptic inflammatory process in the muscles. With any movement it increases. If timely therapy is not started, limb dysfunction will appear. - Biceps (biceps) tendinitis
. Develops after a one-time sharp lifting of weights or systematic microtrauma in athletes, tennis players, and miners. It manifests itself as a painful wave in the upper part of the shoulder region, spreading along its front surface to the elbow. The painful waves become more intense when bending the elbow and lifting heavy objects. When pressed, the most sensitive point located in the intertubercular groove is revealed. Rotation and abduction of the arm are not impaired. If left untreated, the tendon may rupture and cause loss of significant function of the arm. - Calcific tendonitis
. The disease is also associated with microtraumas, against the background of which calcium crystals are deposited in the muscles and tendons. Why this happens is not precisely established. Some experts associate the formation of crystals with hereditary characteristics. During the accumulation of crystals, pain in the shoulder along the affected tendon is periodically bothered. It intensifies during the destruction of crystals, accompanied by inflammation. - Rupture of ligaments and tendons.
Rupture of healthy periarticular tissue is rare and is a consequence of acute trauma. Much more often, rupture occurs against the background of degenerative-inflammatory processes in the muscle tendons. Moreover, even a minor injury, for example, a sharp swing of the arm, can lead to complete or partial rupture of the tendon. At the time of injury, the patient feels severe pain and cracking (crunching). When the biceps tendon ruptures, the muscle moves toward the elbow joint. A rupture can be detected by performing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). In case of a complete rupture, surgical treatment is provided. - Retractile or adhesive capsulitis
. Also called frozen shoulder. The causes of the disease cannot always be identified. Various metabolic disorders contribute to its development - diabetes, atherosclerosis, thyroid diseases. The essence of the pathological process is that in the capsule and synovium there is a slow gradual proliferation of connective tissue, leading to a decrease in the functioning of the limb. There are no inflammatory and degenerative-dystrophic processes in the articular cavity. Symptoms: first, over the course of 3 to 4 months, there is an increase in pain, which intensifies when turning the arm inward. Then the pain in the shoulder decreases, but stiffness of movement appears. In the absence of adequate therapy, patients are bothered by constant painful attacks and impaired joint function. - Impingement syndrome
. This syndrome is associated with pinching of the soft tissues of the shoulder joint under the coracoacromial ligament (arch). Develops against the background of injury and with constant prolonged raising of the arms above the head. Severe aching pain appears in the shoulder when raising the arm above the head. Over time, it is accompanied by dysfunction of the joint: rotation in any direction is limited. To eliminate symptoms, it is necessary to undergo a course of treatment and rehabilitation.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
With cervical osteochondrosis, pain may radiate to the shoulder
Painful sensations in the shoulder girdle, radiating to the arm, can develop when the roots of the spinal nerves of the lower cervical vertebrae are pinched by altered intervertebral discs due to osteochondrosis. They can be both acute and aching in nature. Pain waves appear on the back and side of the neck and spread from behind down the shoulder blade, from the front along the collarbone, forearm to the hand. A neurologist will provide assistance for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
Degrees
Doctors distinguish 3 degrees of deforming arthrosis of the shoulder joint, determining its symptoms and the choice of treatment tactics:
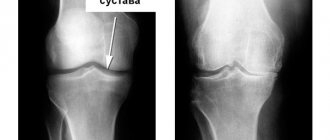
- Grade 1 is characterized by minimal manifestations: pain occurs only during intense or prolonged exercise and quickly goes away after rest, and x-rays reveal subchondral sclerosis of the articular surfaces;
- with arthrosis of the 2nd degree, the pain becomes much stronger, the person has to use painkillers to feel better; The x-ray shows a pronounced narrowing of the joint space, extensive areas of cartilage destruction, as well as bone growths (osteophytes);
- Stage 3 of the disease is accompanied by constant intense pain, joint mobility is significantly limited, and the image shows complete destruction of cartilage tissue, deformation of bone structures and a large number of osteophytes.
Shoulder Pain Treatment
Treatment of shoulder pain should be carried out strictly individually, taking into account examination data and the established diagnosis. It is performed by an orthopedist-traumatologist or rheumatologist. In case of very severe pain, pain therapy is carried out by an anesthesiologist-resuscitator. A specialist will always find something to treat even very severe shoulder pain.
Diagnostics
A correct diagnosis is the path to prescribing adequate treatment and relieving the patient of pain. In diagnosis, examination and clinical examination of the patient by the attending physician using special assessment tests is of particular importance. They allow you to preliminarily determine which structures were damaged. The location of the damage is determined in more detail using functional tests.
Clinical data are confirmed by laboratory and instrumental studies that reveal inflammatory reactions, the presence or absence of infectious, autoallergic processes, the degree of destruction of articular and periarticular tissues. In identifying tendonitis and capsulitis, the main instrumental diagnostic methods are ultrasound and MRI.
How to treat shoulder pain
Treatment for shoulder pain begins with limiting the load on the affected limb. The patient is allowed movements that he can perform painlessly. Immobilization of the limb (scarf bandage) is carried out in short courses if the severity of the pain syndrome is very great. Prolonged immobilization contributes to the consolidation of hand dysfunction. Today, for partial gentle immobilization, taping is often used - fixing muscles with adhesive tapes in a certain position to prevent injury. This significantly improves the quality of conservative therapy.
After acute pain in the shoulder has been eliminated, treatment is continued by prescribing courses of physical therapy (physical therapy) and massage. At any stage of the disease, conservative therapy includes physiotherapy and reflexology courses. In case of severe pain, this is electrophoresis with novocaine, then warming procedures, mud and baths.
At the same time, drug therapy is prescribed. We remove pain by prescribing drugs from the NSAID group in tablets, injections, ointments (the drug with the best analgesic properties is Ketorol). For very severe shoulder pain, treatment includes narcotic painkillers (Tramadol) and glucocorticosteroids (GCS - Betamethosone). Sometimes folk remedies are also used.
To restore cartilage, chondroprotectors (Dona, Artra, Structum) are prescribed. Drugs in this group also help restore damaged periarticular tissues - tendons and ligaments, since they have the same origin as cartilage cells.
Surgical assistance will be required for some types of fractures, dislocations, ruptures of tendons and ligaments. If joint function is completely lost, if conservative treatment does not help, the destroyed joint must be removed and replaced with an artificial one (endoprosthesis surgery).
To prevent pain from reoccurring, a complex of rehabilitation measures is carried out using exercise therapy, massage, reflexology courses, and sanatorium-resort treatment.
What injections to give for shoulder pain
Injections are prescribed for severe pain that is not relieved by pills and external means:
- Analgin (Baralgin)
- one ampoule contains 1 ml of solution or 500 mg of active substance - a single dose for an adult; may have a toxic effect on hematopoiesis, so use it with caution; - Ketorolac (Ketorol)
– in one ampoule 30 mg of active ingredient – a single dose for an adult; contraindications: peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, increased bleeding.
Blockades are widely used - injections of painkiller solutions into the most painful points.
The Moscow Paramita clinic uses the most modern methods of diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation of all diseases that cause shoulder pain syndrome.
If necessary, if the disease threatens the patient’s life, after examination by a doctor, he is urgently sent to the hospital. But we treat most pain syndromes on an outpatient basis. Detailed information about treatment can be found on our website.
Injections for shoulder pain
Advantages of the clinic
The Health Energy Clinic offers its patients:
- comprehensive health screening programs;
- extensive examinations for an accurate diagnosis;
- consultations with narrow specialists of various profiles;
- modern treatment regimens, including not only medications, but also physiotherapy, massage and exercise therapy;
- affordable prices for all services.
Arthrosis of the shoulder joint is a problem that can completely change a person’s life. Don’t let the disease reach an irreversible stage, come for a consultation with an orthopedist at Energy of Health.
How to prevent shoulder pain
To prevent pain from occurring, the following conditions must be observed:
- lead an active lifestyle, move more, engage in feasible sports;
- Avoid prolonged periods with your arms raised above your head, as well as movements associated with unilateral load on the shoulder joint; At risk are weightlifters, tennis players, and miners; If a representative of one of these groups feels persistent pain in the shoulder, perhaps he should change his occupation or at least reduce his exposure to harmful factors as much as possible.
Diet
For shoulder arthrosis of any degree, it is important to monitor your diet:
- avoid overeating and excess weight;
- minimize harmful foods: fatty, spicy, salty, alcohol, canned food, smoked foods;
- consume a sufficient amount of foods high in collagen (jelly, aspic) and omega-3 (fatty fish, olive oils);
- give preference to boiled, steamed or stewed food rather than fried foods;
- reduce the amount of quickly digestible carbohydrates.
The diet should be complete and include the required amount of vitamins, minerals and nutrients.
FAQ
In what cases does pain radiate to the shoulder?
With cervicothoracic osteochondrosis, it begins in the neck and extends to the shoulder girdle and arm.
Why might shoulder pain occur during pregnancy?
As a woman's body prepares for childbirth, the ligaments and tendons relax. This happens not only in the pelvic area, through which the fetus passes during childbirth, but throughout the entire body. This includes the shoulder joint becoming slightly unbalanced. With light loads, it may become sore. This is not dangerous.
With adequate conservative therapy, the patient can be relieved of pain, achieving complete recovery or stable remission. In medicine they know how to do this.
Literature:
- Belyaev A.S. Principles of treatment of myofascial pain syndromes / A.S. Belyaev, O.M. Maslova, I.V. Eliseeva // Manual medicine. 1994. No. 7. pp. 24-25.
- Mironov S.P. et al. Shoulder pain syndrome: monograph. Volgograd: VolgMU Publishing House, 2006. 287 p.
- Campbell CC, Koris MJ Etiologies of shoulder pain in cervical spinal cord injury. Clin-Orthot. 1996. 322(2). 140-145.
Sign up for a free initial appointment
General information
Cartilage tissue is a smooth layer between the adjacent areas of bones. It ensures their easy sliding relative to each other, ensuring free and painless operation of the joint. Excessive stress, inflammation or injury can trigger a degenerative process that gradually spreads over the entire surface.
As a result, the smoothness of the articular surfaces is disrupted, and movements begin to cause pain. At the same time, bone growths begin to appear along the edges of the joint, replacing the affected cartilage. As the degenerative process progresses, it involves not only bones, but also surrounding tissues. The limb becomes deformed, the muscles spasm, and the ligaments become weak and lose elasticity. Without treatment, a person loses the ability to move his arm.
Make an appointment