Jaw distortions
Our clinic’s specialists have extensive experience in identifying the causes of jaw misalignments and correcting them. If you are concerned about this problem, contact us!
A frequent reason for contacting our clinic is patients’ complaints about “distortions” of the jaws. Some people's jaw moves to the side when opening and closing their mouth. Some people have a jaw on the side even when their mouth is closed.
Such jaw distortions themselves are not a problem, but a sign, a symptom. And always, in order to eliminate the imbalance itself, it is necessary in each specific case to understand the cause and mechanism of its occurrence. And based on the reason, plan response therapy.
And the reasons for such distortions can be completely different.
Diagnostics is the first and key step in the treatment of jaw displacement. Do you want to know why it’s impossible to do without diagnostics?
Sideways displacement of the lower jaw when opening or closing the mouth can be a symptom of temporomandibular joint dysfunction (TMJ). Such distortions may be accompanied by “sound effects” (clicking or crunching in the TMJ area).
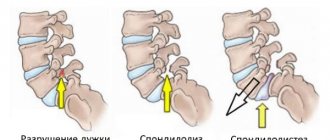
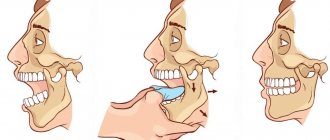
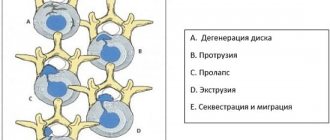
Deflexion and deviation. Trajectory of the lower jaw when opening the mouth with TMJ dysfunction.
A distinction is made between deflexion, when the lower jaw moves to the side when opening and closing the mouth (persistently moves away from the center line) and deviation, when the lower jaw moves away from the center line and then returns to its place.
Also, skew (to one side), displacement of the lower jaw can be caused by cranial problems (see “Deformations of the cranial bones”). Cranial (cranial) problems are the cause of misalignment of the upper jaw. Which leads to an inclined occlusal plane (smile line).
A crooked jaw is a common “related product” of malocclusions (see Malocclusion). In particular, crossbite, distal occlusion, or mesial bite. Accordingly, the misalignments of the jaws themselves must be eliminated as part of the general treatment (correction) of malocclusion in a particular patient.
Sometimes, when jaw misalignments are caused by structural problems, such as different lengths of the articular condyles of the lower jaw, surgical correction may be required.
During a direct examination by a specialist, you will be able to find out your exact diagnosis, as well as receive a referral for diagnosis or a treatment plan.
Sergei Vladimirovich Yashin
author of the article
Dentist-orthodontist, maxillofacial orthopedist
More than 7 years of experience
Dislocation of the lower jaw
Treatment of lower jaw dislocation
The basis of treatment for dislocations of the lower jaw is reduction. During reduction, conduction or infiltration anesthesia is used.
Reduction of anterior dislocation
In the case of anterior dislocation of the lower jaw, reduction is correct according to the methods of Hippocrates, Gershuni, Blekhman, Hodorovich and Popescu (for long-standing dislocations).
Reduction of bilateral mandibular dislocation
When reducing a bilateral mandibular dislocation, it is correct to use the Hippocratic method; for this, the patient is seated on a low chair in such a position that the back of his head is supported, and the lower jaw is placed at the level of the elbows of a specialist (traumatologist, dentist, surgeon). The doctor stands in front of the patient's face and places his thumbs wrapped in gauze on the patient's lower molars, and with the remaining fingers he grasps the lower jaw from the outside. By applying gentle pressure from top to bottom with his thumbs, the doctor moves the jaw back with a small push, after which he quickly removes his fingers from the patient’s mouth (so that the patient does not bite his fingers). The process of moving the articular heads of the lower jaw is accompanied by a clicking sound and a strong closure of the jaws.
Reduction of posterior dislocation
If it is necessary to correct a posterior dislocation, after moving the jaw downward, the doctor moves it forward. To limit unnecessary movements of the lower jaw, consolidate the result, and also to avoid relapses, after TMJ reduction, the lower jaw is immobilized.
The lower jaw is immobilized using a sling-like bandage for seven to ten days for anterior dislocation and two to three weeks for posterior dislocation. During the rehabilitation period, the patient is recommended to follow a gentle diet, which excludes the intake of solid foods.
If conservative methods of jaw realignment do not bring the desired results, the issue of surgical intervention is decided. Chronic dislocations of the lower jaw are often an indication for resection of the heads of the joints of the lower jaw, as well as subsequent mechanotherapy.
Sometimes, with primary dislocations, patients perform reduction on their own, but such experiments are not advisable, since they can lead to many complications.
In some cases, restoring the functionality of the lower jaw may require prosthetics of missing teeth, selective grinding of teeth, massage, novocaine blockade of the masticatory muscles, physiotherapy or therapeutic exercises.
The purpose of surgical treatment may be to enlarge the articular tubercle, strengthen the ligaments, reposition and fixate the intra-articular disc, deepen the articular cavity, etc.
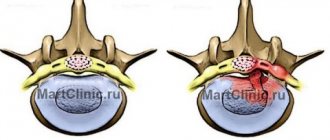
Normal disc position
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI scan) clearly shows the position of the articular disc with the mouth open and closed. The acrylic models of the temporomandibular joint below show the position of the articular disc even more clearly. These models show the bone structures in white and the disc in red.
Acrylic models of healthy TMJ. If the mouth is closed, the articular disc is in its normal position; if the mouth is open, the disc follows the movement of the articular head on the condylar process
Why does the jaw move forward - how to fix it?
In the structure of dental diseases, anomalies in the development of the dentofacial system today make up a significant proportion. They can affect not only the position of the teeth, but also the structure of the jaws. This causes maximum discomfort to patients, as it deforms the proportions of the oval of the face and seriously affects the appearance. Men and women are equally susceptible to anomalies. Most often, when talking about a protruding jaw, they mean a mesial bite. This anomaly is characterized by the fact that the lower jaw is pushed forward, the lower incisors overlap the upper ones. In some cases, patients are bothered by a protruding upper jaw. In this case we talk about distal occlusion. The lower jaw is inexpressive, the lower lip sinks, and the mouth may look slightly open. The diagnosis is made by the doctor based on the results of an examination of the oral cavity and analysis of x-rays. Sometimes the situation is complicated by crowded teeth. This aggravates the aesthetic problem and can also provoke periodontal disease. The key to proper occlusion is the simultaneous treatment of crowding and distal/mesial occlusion.
2. Reasons
The range of reasons that can lead to dislocation of the lower jaw is very wide. Of the mechanical factors, these are primarily injuries. In this case, the release of the articular head is facilitated by degenerative-dystrophic changes in the muscular-ligamentous apparatus (which, in turn, can be caused by inflammation, metabolic disorders, etc.), various sprains (for example, due to frequent traumatic dental procedures, some bad habits ), malocclusion or complete absence of teeth, the presence of certain diseases (arthrosis, oncological processes in the jaws, rheumatoid polyarthritis, and many others), all kinds of acquired deformities and congenital abnormalities of the joint structure. Dislocation can occur during intubation, heart-rending screaming, dental surgical extraction of a tooth, bronchoscopy, biting or gnawing hard food, falling, a blow to the chin and under many other circumstances, especially in combination with predisposing anatomical, morphological and histological factors. There are also congenital and “habitual” dislocations (frequent, occurring even with little impact).
Visit our Traumatology and Orthopedics page
What can be considered pathology?
Normal occlusion is such a relationship of the dentition in which between
All teeth are in contact, the upper incisors overlap the lower ones by 1/3. When turning to an orthodontist, many patients ask the question: when the jaw moves forward, what kind of pathology is this? Unfortunately, this is one of the most complex dental anomalies, which was already mentioned above - mesial bite. Due to the skeletal nature of the anomaly and significant morpho-functional disorders, it is difficult to correct. But this does not mean at all that you need to resign yourself to the situation. It just takes more time and effort than, for example, eliminating interdental spaces. The prevalence of this pathology is about 4% of the total population. According to scientists, the key factor in its development is disturbances during the embryonic development of the fetus. As a result, the child experiences growth retardation in the middle third of the face. During adolescence, the growth of the lower jaw, on the contrary, accelerates excessively. As a result, the occlusion is broken. Evidence also suggests that patients experience poor posture. The psycho-emotional background also suffers. Reverse overlap cannot in any way be called a correct bite. This defect definitely requires treatment.
The lower jaw is pushed forward
Why does the lower jaw move forward? Most often, the matter is in its excessive development and structural features. It is enlarged, pushed forward, the corners are turned. In this case, it is necessary to distinguish between true and false mesial occlusion, or, as it is also called, progeny.
With false progeny, reverse bite is present only in the frontal part of the jaw. In the lateral sections, the closure remains within the normal range, or is slightly disturbed. This condition can develop due to underdevelopment of the upper jaw.
With true progeny, reverse overlap is present in both the anterior and lateral sections. When the teeth close together, a space is formed in the area of the incisors, and there is no contact. Biting and chewing food is seriously difficult due to such a serious violation of the relationship of the dentition. Orthodontic treatment in this case can radically improve the patient’s quality of life. An integrated approach will normalize occlusion and eliminate deficiencies of both an aesthetic and functional nature.
Some disorders in patients are noticed only by the dentist. With progeny the situation is different. Often parents, even in childhood, notice that their child’s bite is not forming correctly. Adult patients are also aware of their problem, but for various reasons they do not consult a doctor. Thanks to the development of technology and orthodontic devices, today it is possible to correct a bite at almost any age. Mesial occlusion sometimes requires surgical intervention. In some cases, for example with false progeny, it is not necessary. Don’t be afraid to consult a doctor - it may not take much time to solve your problem.
The upper jaw is pushed forward
Jaw disproportion can also be observed in the opposite relationship. With distal occlusion, the size of the upper jaw may not correspond to the size of the lower jaw, which turns out to be underdeveloped. The situation can be aggravated by the vestibular inclination of the teeth (they are tilted forward). The anomaly becomes noticeable during puberty, when active growth of the upper jaw occurs. In the lower jaw, the size of which is insufficient, crowding of teeth may occur. Is it possible to correct a distal bite with braces? In adults, this is the only possible method of correction. During the treatment, the relationship of the dentition is normalized. Often the teeth in the frontal region do not close together, which causes a gap to form and diction suffers. After orthodontic treatment, you can take a course of classes with a speech therapist, and normal sound pronunciation will be restored. Thus, when a patient asks the doctor a question: the upper jaw is pushed forward, how to correct it? – the doctor first conducts an examination and examination, and then draws up a treatment plan. Orthodontist Irina Butorina knows how to correct a distal bite.
Why is the jaw pushed forward and why is it dangerous?
When the lower jaw is pushed forward, why is this dangerous? First of all, the act of chewing suffers. It is almost impossible to fully bite and chew food with this type of anomaly. But for patients, sometimes the aesthetic factor is more important. This defect is one of the most pronounced, and the problem of disproportion of the oval of the face comes to the fore. The lower third looks elongated, the chin protrudes forward, and the upper lip sinks. Also, mesial occlusion has a negative impact on the condition of teeth and gums, the temporomandibular joint. The chewing load is distributed unevenly. Sometimes there are significant accumulations of plaque. The risk of developing periodontal disease is very high.
So, the lower jaw is pushed forward, how to correct the situation? Unfortunately, sometimes orthodontic treatment is not enough. Then the surgeon comes to the aid of the orthodontist. During the intervention, the body of the lower jaw is shortened, which allows it to return to its physiological size. Thus, the very root cause of the development of malocclusion is eliminated. What is the name of the operation when the lower jaw is pushed forward? This is an osteotomy. It is performed under anesthesia, the surgeon cuts the bone at a certain angle, removes excess bone tissue, then aligns and fixes the lower jaw in the desired position. The technology for performing this operation is very well developed. It is well tolerated by patients. As a rule, discharge occurs on the 3rd day. But it must be said that osteotomy is performed only after treatment with braces.
Complications
If the patient promptly sought medical help and strictly followed the recommendations while wearing the splint, then the outcome is favorable. In this case there should be no relapses. But early load on the jaw and the presence of deforming joint diseases can provoke a relapse, and, as a rule, more than one.
Make an appointment with our specialists and find out first-hand the main symptoms of a dislocated lower jaw. Remember that only qualified medical care will help you get rid of the problem for a long time and enjoy all the joys of life.
Related services: Dental implantation Treatment of temporomandibular joint disorders
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms depend on the type of dislocation. Common manifestations include:
- difficulty closing and opening the mouth;
- protrusion or distortion of the jaw forward;
- sharp pain radiating to the temple;
- profuse drooling;
- inability to pronounce words normally.
Treatment of habitual jaw dislocation should be carried out exclusively by a specialist. The only thing the patient can do is fix the position by bandaging his chin with a scarf. Painkillers and ice will help reduce pain.
On our website Dobrobut.com you can sign up for a consultation with the right specialist and undergo diagnostics if necessary.
Methods for correcting jaw curvatures in adults
Modern dentistry offers a wide range of methods for treating dental anomalies. Depending on the degree of jaw curvature, the patient may be offered surgical or orthodontic treatment.
Radical techniques are relevant in advanced cases when there is pronounced facial asymmetry, deformation of the cranial vault, chin dysplasia, and speech impairment. After surgery, in a number of clinical situations, orthodontic treatment is additionally carried out, which can improve the results of the operation.
Non-surgical correction of malocclusion is based on the use of braces, which help restore normal occlusion.
Why do my dentures keep falling out?
Answer: Yes, this can happen.
A removable denture, if not worn constantly, may fall out if you put it on and start using it over time. Over time, the jaw changes, but a false plastic jaw does not. Of course, it is possible that the prosthesis was not made entirely accurately right away. At the same time, if initially the impressions were accurately made, and nothing happened to the patient’s general condition throughout, for example, he did not lose weight, then after a while you can put on the teeth and they will stick in the same way.
What should a suction complete removable denture look like? Gentlemen, ATTENTION, please pay attention to this photo: this is what a complete removable denture for the upper jaw looks like from the side of the palate, you need to pay attention to its volumetric border, the edge of the denture has an individual and different thickness everywhere, which is dictated primarily by the impression taken from the oral cavity .
Now compare with your dentures! You can say that everyone’s oral cavity is different and the volume of the border may not be on an already made prosthesis... yes, it can, but this is extremely rare and, most importantly, not along the entire length of the border! Now that you have looked at your individual margin, you can see if it is too thin, lacking volume, what is the reason for the constant loss of removable teeth.
How can this be eliminated?
In this case, only a dentist can help you. As for us, we always take impressions very carefully; they have an individual volumetric border, which in the future positively and necessarily prevents loss! A dentist, if a patient comes to him with a similar complaint, must take a functional impression of an existing denture. In this case, the entire internal surface of the previous prosthesis must be removed to create space for the impression material. By introducing the prosthesis with the impression mass into the oral cavity, we create a volumetric surface with massaging movements. Then the work is transferred to a dental technician, he carries out the polymerization process and here is a removable denture with a new inner part that is perfectly fixed!
The task is to create a suction removable denture! The valve zone serves as the link that allows the denture to be suctioned. If a functional, individual edge is not created, then if the patient uses fixing creams, then the glue consumption will be too high. Denture adhesive will wear out quickly.
Dentist Ivan and Alexey, when making each removable denture in the absence of all teeth on the jaw, are required to create a valve zone to prevent the loss of the false jaw.