A joint injury is damage to any part of it. Injuries can be different: bruises, tears (and ruptures) of ligaments, dislocations, fractures of the bones that make up the joint. When injured, blood may leak into the joint cavity, the edge of the cartilage may come off, and the surfaces may shift relative to each other. With any injury, pain, tissue swelling and limited joint mobility occur. Accurate diagnosis includes instrumental studies: X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI, and sometimes arthroscopy. Treatment depends on what tissues are damaged and how. In some cases, conservative treatment is sufficient, in others surgical intervention is required. The treatment method is determined by a traumatologist after the diagnosis has been clarified.
At CELT you can get a consultation with a traumatologist-orthopedic specialist.
- Initial consultation – 3,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
How is the joint structured?
A joint is a movable joint between two bones. It is needed in order to redistribute the load on the limbs. The ends of the bones or epiphyses are congruent to each other: where there is a bulge on one bone, there is a depression on the other. The epiphyses are covered with hyaline cartilage. The joint is surrounded by a dense fibrous membrane. The cavity is filled with synovial viscous fluid having high viscosity. The joint receives nutrition from this fluid. There are ligaments around the joint that strengthen it on all sides. The movements performed in the joint are strictly defined - flexion-extension, adduction-abduction, rotation and rotation.
For joint health, their correct geometry is incredibly important. At the slightest violation - a ligament tear, a displacement of the articular surfaces invisible to the eye - the remaining parts of the joint receive chronic overload, and their wear accelerates many times over. The reasons for this are manifold: microtraumas, monotonous daily loads, athletic jerks or excessive physical activity. If the joint is left untreated, the biomechanics and structure of the intra-articular cartilage are irreversibly altered. To stabilize the joint, the body grows osteophytes, or bony spurs, that change the joint so much that movement may become impossible.
Injuries and classification
Trauma is the action of a mechanical force that has a different direction. The tissues of the joint, ligaments, and surrounding muscles counteract this force. Depending on the mechanism and force of impact, the following types of injuries are distinguished:
- Open. The skin is damaged.
- Closed. The skin survived, but other structures were damaged.
By type of damage:
- Injury. Soft tissues are damaged.
- Incomplete and complete ligament ruptures, more often called sprains in everyday life.
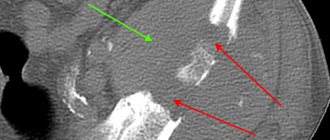
- Intra-articular fracture. Depending on the fracture line, it may pass through contacting surfaces, be located outside the bone contact areas, or be comminuted.
- Periarticular fracture.
- Dislocation. Often accompanied by damage or stretching of the capsule.
- Fracture-dislocation.
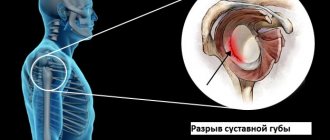
- Meniscus tear. Such an injury occurs only in the knee joint, where there is a special cartilage layer.
Common Causes of Human Skeletal Injuries
Traumatic
Since the topic of our conversation is fractures, bruises, dislocations and sprains, of all the existing causes of injury, we will only be interested in the impact of mechanical external factors.
Among them:
- Jerk;
- Falling from height;
- Hit;
- Push;
- Contusion;
- Compression.
- Compression.
The greatest danger is the consequences of mechanical trauma, which can result in extensive blood loss, as well as disruption of the innervation of an organ or tissue. This leads to the development of a number of general disorders in the functioning of the body.
More details about human anatomy - Skeletal structure
Symptoms
Mandatory symptoms are pain and swelling, sometimes crunching. Pain in the first minutes may not be felt and may be perceived as numbness. However, as swelling increases, the pain intensifies, increasing when attempting to move. Blood from crushed vessels may leak into the tissue surrounding the joint or into its cavity.
When an injury occurs, the range of possible movements always changes: it either decreases or increases. The decrease in range of motion caused by pain and swelling is more physiological - the body is trying to provide rest for healing. The injury is more severe if pathological mobility has appeared in the joint: the limb bends in a place where it should not. This indicates a complete rupture of the ligaments or a bone fracture.
When ligaments or fractures rupture, deformation of the joint appears: the contours change, the visible part of the bone deviates to the side.
With dislocations, the normal line of the limb changes, and the end of the bone that has come out of the joint is identified under the skin. Blood poured into the joint makes it look like a ball, and free fluid is felt to the touch. Trying to rely on the injured limb leads to increased pain.
Causes and types of displacement of bone fragments
When a bone is fractured, the displacement of fragments is caused by:
1) the primary effect of the force of the mechanical factor - the greater the force, the greater the displacement of the fragments;
2) antalgic muscle contraction - the body’s protective reaction to pain, causing muscle contraction;
3) the mass of the peripheral segment (earth gravity). The displacement depends on the place of attachment of individual muscles or their groups in the central and peripheral fragments, and their functional purpose.
So, the following types of displacement of fragments are distinguished:
1) in width;
2) in length;
3) along the axis;
4) rotation of the peripheral segment.
Treatment
Treatment is determined by the severity of the injury. The following methods are used:
- rigid orthosis;
- reposition (comparison of bones) followed by plaster immobilization;
- skeletal traction;
- therapeutic arthroscopy;
- an operation during which metal osteosynthesis is performed, when bone fragments are assembled onto a metal plate and fixed with bolts and screws.
Surgical treatment radically solves the problem of ruptures and fractures, completely restores the geometry of the limb, shortens the recovery time and allows you not to limit your movements after completion of rehabilitation.
From the first hours, analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs are used. For open injuries or large amounts of damaged tissue, antibiotics and other medications are used as indicated.
During the recovery period, the following techniques are used:
- therapeutic massage to activate muscles;
- physical therapy to increase range of motion in the affected and adjacent joints;
- physiotherapy (ultrasound, alternating currents, transcranial electrical stimulation to relieve pain and accelerate tissue repair, etc.).
Common Elbow Injuries
Elbow joint injury is one of the most difficult. A neurovascular bundle runs near the joint, which is almost always damaged. Associated neuritis significantly complicates the course of the injury - this is additional pain, impaired trophism, developing contractures or immobility. In addition, the elbow joint does not respond well to physical therapy and this method is not used, which prolongs the recovery time.
The olecranon often breaks off and cannot be put back into place without surgery. Such a fracture can be successfully treated only with the help of metal osteosynthesis, when the fragment is attached to the ulna with a metal structure. The prognosis in this case is favorable, movements return in full after recovery.
The prognosis for complete recovery is less guaranteed for comminuted fractures, especially intra-articular ones. An open access operation is performed when those fragments that are unlikely to grow are removed. The prognosis depends on how much bone tissue had to be removed. The use of alloplants is sometimes possible, sometimes not - it all depends on the clinical picture and the general level of health of the patient.
Traumatologists consider elbow injuries to be the most “fastidious”; complications can arise at any stage.
Knee
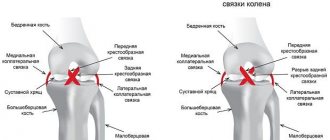
Knee joint injury is the most common and varied in its manifestations. Everything can happen: from a simple bruise to intra-articular fractures, dislocations and meniscus tears. The joint is a large one, bears the weight of the entire body, and experiences constant stress. Three bones connect here: the femur, tibia and patella. There are five synovial bursae and three types of ligaments: lateral, posterior and intra-articular, the largest of which are cruciate.
The most severe cases are ruptures of the cruciate ligaments, fractures of the condyles or spherical ends, and damage to the meniscus.
The knee has a unique structure, and traumatologists always try to preserve tissue as much as possible. Thus, torn ligaments are replaced with synthetic tape, only small fragments are removed, and large fragments are fixed with metal, the meniscus is only partially removed.
Ankle joint
Ankle joint injury is the most common, especially in winter when there is ice, as well as among athletes, skiers and lovers of high-heeled shoes.
Most often, ligaments are torn, followed by fractures. The vulnerable spot is the ankles or lateral processes of the tibia, forming the “fork” of the joint. This joint transfers the full weight of the human body to the foot. Based on the number of broken processes, one-, two- and three-malleolar fractures are distinguished, when the edge of the tibia is also broken.
A fracture may be accompanied by dislocation, subluxation and displacement of fragments. Such fractures are often treated conservatively, but there is a pattern: it takes at least four weeks for one ankle to heal.
You should consult a doctor immediately after a fall, jerk, or joint pain. It is impossible to determine “by eye” what exactly happened in the joint. If a fracture occurs, the strong leg muscles literally “pull” the fragments in different directions, and over time it is very difficult, and sometimes impossible, to reconcile them. What could have been corrected yesterday by applying a splint, today has to be treated surgically.
Traumatologists at the CELT clinic are always ready to quickly come to the rescue. The clinic has unique medical equipment for monitoring the geometry of joints and the position of limbs. You need to understand that a tiny shift in one place inevitably entails changes throughout the entire body. The bones, muscles and ligaments adjacent to the damaged joint adapt to what is there and change too. If you put off visiting a doctor for too long, you can develop arthrosis and many other troubles.
Acute trauma
An orthopedic traumatologist treats injuries and diseases of the musculoskeletal system. These are the bones - the human skeleton - there are more than two hundred of them in the body, the ligaments that connect these bones, and the muscles with tendons that set the entire skeleton in motion.
Treatment methods for various injuries of the musculoskeletal system in orthopedics and traumatology are divided into conservative and surgical treatment methods. As for conservative methods, they are also divided into two types - fixation and extension methods. The fixation method of treatment involves the use of plaster to fix a specific area of the limb. The extension method of treatment is a method of permanent skeletal traction. And finally, the surgical method of treatment involves fixing the damaged limb with special metal structures of various types.
In Greek, "orthopedics" means "right or straight" and "education or training." Orthopedics refers to a branch of clinical medicine that studies the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of various types of deformities and disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Moreover, these disorders can be either congenital or acquired.
If we talk about traumatology, then this is a branch of medicine that studies the very effects of trauma on the human body. Traumatology also studies the consequences of these injuries and methods of their treatment. Both of these sciences are very closely interrelated. There is one more discipline, without which neither orthopedics nor traumatology can exist. This discipline is considered to be prosthetics. Bandages, corsets, orthopedic shoes, prostheses - all these are the results of prosthetics that help return a person to normal functioning of the musculoskeletal system.
It is also worth noting the importance of sports medicine. This science is an integral component of both orthopedics and traumatology. Every orthopedic doctor must know all the nuances of sports medicine in order to tell the patient exactly what set of exercises he should perform to restore the body after a particular injury.
The constituent components of orthopedics and traumatology include such narrow specializations as: physiotherapy, massage, biomechanics of the musculoskeletal system, arthroscopic surgery, bone pathology, spine surgery, and so on and so forth.
Bone fracture is a complete or partial disruption of the integrity of the bone as a result of mechanical impact.
Dislocation is a violation of the congruence of the articular surfaces of bones, both with and without violation of the integrity of the articular capsule, under the influence of mechanical force (trauma) or dysplastic changes in the joint.
Sprains and tears of ligaments, muscles, tendons, cartilage formations.
Long-term compression syndrome is a peculiar pathological condition of soft tissues after prolonged, 2-4 hours or more, compression. A characteristic feature is that after removing the pressing object, toxic products of tissue breakdown enter the blood massively, which determines the severity of the condition and clinical manifestations.
Bruises and abrasions. A bruise is a closed injury to tissues and organs without significant disruption of their structure. Superficially located tissues (skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscles and periosteum) are more often damaged. Soft tissues, which are pressed against the bones at the time of injury, are especially affected by a strong impact.
Wounds are a violation of the anatomical integrity of the integumentary or internal tissues throughout their entire thickness, and sometimes also of internal organs, caused by mechanical stress.
Surgical and conservative treatment of diseases and pathological conditions of the joints (arthritis, arthrosis).
Orthopedics and traumatology services at CELT
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| X-ray of bones and joints of the limbs | 2 200 |
| MSCT of the ankle joint | 7 500 |
| MRI of knee joints (2 joints) | 10 000 |
| Diagnostic arthroscopy | 55 000 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
I. Topic: Open bone injuries and
joints.
In the second half of the 20th century, there was a clear trend towards an increase in the level of injuries, including an increase in the number of open injuries of bones and joints (OPKS). This is explained by the increasing level of technical support for our lives. The frequency of open fractures is 12-15% in relation to all fractures of long bones. The problem of treating open injuries of bones and joints remains relevant today, since untimely and incorrectly provided assistance can lead to serious complications with subsequent disability for the patient. Knowledge on this issue is basic for orthopedic traumatologists and general surgeons, and the need to include it in the training program for students at medical institutes at all levels is beyond doubt.
The course of traumatology and orthopedics includes a lecture on the problem of diagnosis and treatment of open fractures. The methodological recommendations additionally include sections on the etiology and pathogenesis of open injuries, features of the diagnosis and treatment of intra-articular fractures, fracture-dislocations and dislocations, and also discusses issues of patient rehabilitation. Methodological recommendations can be used in the educational process not only by students, but also by trainee doctors and clinical residents.