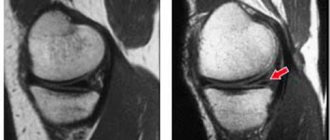
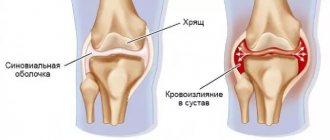
The labrum is a rim of fibrocartilaginous tissue around the glenoid fossa that enlarges the socket cavity and provides stability to the head of the humerus. The labrum also connects the capsular-ligamentous structures of the shoulder joint. Labral tears can occur due to repetitive motion of the shoulder or acute trauma. In athletes with repeated anterior subluxations of the shoulder, tears of the anterosuperior labrum may occur, leading to progressive instability.
Causes
Injuries to the tissues of the rim (labrum) surrounding the shoulder rosette can occur either as a result of acute trauma or as a consequence of repetitive movements of the shoulder. For example, damage to the labrum can occur in the following cases:
- Falling on an outstretched arm
- Direct hit to the shoulder
- A sudden pull with the hand, for example, when trying to lift a heavy object
- Excessive overhead movement of the arm
Labral tears can also occur in throwers or weightlifters and result from excessive repetitive stress on the shoulder. In weightlifters, labral tears can also occur as a result of overuse during exercises such as barbell, bench, or standing presses. Posterior rotator cuff weakness can contribute to labral tears. Labral tears can occur as a result of acute injuries such as a fall on an outstretched arm, but also occur in athletes where there is intense shoulder movement (eg, golfers).
Surgery to treat joint damage
The most popular and expedient method to cure damage to the ligaments of the shoulder joint, the treatment of which should be considered as indicative of all types of damage, is surgery. During it, a special probe is inserted into the joint, which allows you to examine the damage, as well as a surgical instrument that removes protruding bone fragments and regulates the shape and position of the cartilage tissue.
In case of damage to the capsule of the shoulder joint, special titanium clamps are used, which prevent the bones from moving beyond the amplitude of their movement provided by nature. As a result, the cause of the injury and its primary impact are eliminated, and the patient can safely begin the rehabilitation complex.
In some cases, when the shoulder joint is damaged, it becomes necessary to pump out blood or lymph fluid that enters the joint as a result of injury. It occurs through a special puncture made by the surgeon, and, if necessary, is repeated several times, after preliminary diagnosis on a magnetic resonance imaging scanner.
Rehabilitation procedures that are performed after surgery are an important set of measures, without which recovery after damage to the joint capsule is impossible. It is necessary to radically change your diet, to include in it all the necessary minerals and trace elements, vitamins that are necessary to start regenerative processes in the body’s tissues. In addition, the most important factor is physical therapy exercises, which are aimed at strengthening the joint and muscles.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a labral tear resemble those of other shoulder injuries. Symptoms include:
- Shoulder pain is usually associated with raising the arm
- Clicking, crunching, or shoulder locking
- Sometimes pain at night or pain when doing daily activities
- Feeling of instability in the shoulder
- Decreased range of motion in the shoulder
- Decreased muscle strength
Patients with a labrum injury may describe their pain as intermittently interfering with normal shoulder function during certain activities. On examination, they may have discomfort with forced external rotation of 90 degrees, and the pain does not increase with further abduction. Often, a labral tear is manifested by a crunching or clicking sound during forced external rotation. The patient may also experience discomfort with forced horizontal shoulder adduction.
Diagnostics
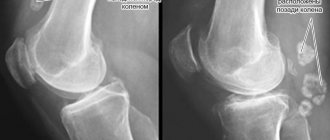
If you have shoulder pain, your doctor will first take a medical history. Often the patient remembers a specific traumatic episode followed by the onset of symptoms. The doctor will perform functional tests to determine range of motion, shoulder stability, and pain symptoms. If there is suspicion of damage to bone tissue, radiography may be prescribed. Due to the fact that radiography does not visualize the soft tissue of the articular cavity, MRI or CT is prescribed to diagnose its rupture. Both methods of examination use contrast, which makes it possible to diagnose even minor damage to the integrity of the articular labrum. In some cases, diagnostic arthroscopy is required. The tears may be located above or below the center of the glenoid cavity.
SLAP injury (tear of the labrum, front to back, with damage to the biceps tendon).
A tear below the middle of the glenoid cavity, with simultaneous damage to the inferior ligament of the shoulder, is called a Bankart injury.
Labral tears are often accompanied by other shoulder injuries such as shoulder dislocation (subluxation or dislocation).
Treatment
Conservative treatment for labral tears includes physical therapy, exercise therapy, anti-inflammatory treatment, and steroid injections into the shoulder. Labral tears are often accompanied by rotator cuff tendinitis. Anti-inflammatory therapy helps reduce swelling and inflammation associated with tendinitis, which helps reduce pain. As a rule, drug treatment consists of the use of NSAIDs (Voltaren, Novalis, ibuprofen, etc.). In addition, injections of steroids combined with local anesthetics into the injured shoulder at the top of the rotator cuff are possible. If necessary, the injection can be repeated. There is no point in carrying out multiple injections, since they can only mask a problem that requires more specific treatment.
Exercise therapy for labral tears begins with emphasis on the muscles of the shoulder blade and torso, abdominal muscles and lower back, and then exercises are performed to strengthen the muscles of the rotator cuff. After selecting exercises with a physical therapy doctor, you can perform the exercises yourself.
Surgery
If there is no effect from conservative treatment and symptoms persist (pain, weakness), arthroscopic restoration of the integrity of the articular labrum is recommended. During the operation, the torn cartilage is sutured and fixed using special anchors of the cartilage to the bony part of the glenoid cavity. The advantage of arthroscopic surgery is its low invasiveness and the possibility of a short stay in a surgical hospital. In addition, arthroscopic operations have a minimal rate of complications. After the operation, the arm is fixed with a splint or orthosis. Sutures are usually removed one week after surgery. Immediately after the operation, passive movements are performed and therapeutic exercises begin 2-3 weeks after the operation. Full restoration of the function of the shoulder joint usually takes 3-4 months.
Labral rupture
This human organ is located near the shoulder joint and looks like a small rim of cartilage tissue fibers enveloping the joint fossa. It allows you to enlarge this cavity, due to which the articular head is held in the shoulder better and more stable. The labrum provides a secure connection to the entire capsular structure of this joint. A tear of this lip occurs due to a sudden movement or injury. An athlete who repeatedly dislocates his shoulder may also suffer a labral tear, which in turn can lead to unpredictable consequences.
Main reasons
Injury to the labrum can occur as a result of repeated trauma to the shoulder joint, or sudden repetition of movement in the shoulder joint. Such injuries occur in different circumstances: When a person falls on an outstretched arm; hit him hard on the shoulder; sharply pulled your hand or lifted a heavy load; made sharp movements of his hand above his head.
Very often there are impulses of this organ in athletes who receive a large load on the shoulder joint, engage in weightlifting, hammer throwing, and so on. Weightlifters can tear this labrum when performing lifting exercises while standing or lying down. Posterior rotator cuff weakness also contributes to this tear. Such ruptures occur with acute injury, falls with an outstretched arm, or with a sudden movement in the shoulder. Mostly, such injuries occur to athletes playing hockey, golf and other outdoor games.
What are the first symptoms?
With such ruptures, the sensation of pain can be the same as with bruises of the shoulder joint, namely: when you raise your arm, you feel a sharp pain in the shoulder. In the shoulder area, there is a clicking and crunching sound, and movement is almost impossible. There is a lot of pain and discomfort in the shoulder. Severe pain at night and difficulty performing daily activities. Movement in the shoulder is limited to a minimum. The muscles are very weakened.
Those people who have been injured and damaged the upper labrum say that they experience pain intermittently, and the normal functioning of the shoulder joint is disrupted when performing any work. Such patients, when examined by a doctor, feel pain and discomfort when turning the arm ninety degrees outward; further rotation stops the pain. When this labrum is torn, clicking and crunching sounds can be heard as the person tries to move and abduct the arm externally. Very often, patients feel pain when they raise their arm upward forcibly.
Carrying out diagnostics
If you have pain in the shoulder area, you need to see a doctor so that he can examine and study your medical history. As a rule, the patient can remember when the pain first appeared and under what circumstances it happened. He will examine and be able to determine the functionality of the shoulder and the occurrence of pain during functional testing. If there is any suspicion of damage to any organs or tissues, he may order an x-ray. An x-ray will not be able to clearly see or analyze the soft tissues near the joint. Therefore, in order to make a more accurate diagnosis in the event of a labral tear, Computed Tomography or Magnetic Resonance Imaging is used.
Both examination methods are used to diagnose and document the smallest damage to this labrum. Sometimes arthroscopy is even used and diagnosed. As a rule, such impulses are located above or below the center of the joint space. Injuries include tears of the labrum from the center to the back and tears of the tendons on the biceps, such injuries are called SLAP. There is another injury called Bankarta, this tear occurs from the middle part of the joint space, and the shoulder ligaments can be damaged. Often with such ruptures, these ruptures can occur with other shoulder injuries. For dislocations and subluxations of the shoulder.
What treatment can be used?
Conservative treatment requires the use of physiotherapeutic procedures, physical therapy, and also to prevent inflammatory processes, steroid injections are given in the area of the shoulder joint. This labral tear is reflected in tendonitis in the tendons and muscles of the rotator cuff. Such anti-inflammatory measures reduce inflammation and swelling from tendonitis, and also significantly reduce pain. During drug treatment, the use of voltaren, ibuprofen, and other drugs is allowed. It is also possible to use injections of mixing anesthetics with steroids, up the injured shoulder. Such injections are done at first, repeated use can dull the pain and mask the injury, and the treatment of such requires a more detailed approach.
Physiotherapy exercises for such impulses begin to be carried out with the emphasis on the muscles of the shoulder blade and torso, as well as on the lower back and abdominal press. Then the rotator cuff is strengthened with special exercises. To perform the exercises on your own, you first need to consult with doctors and physical therapy specialists.
Application of surgical treatment
If you have used and tried all the methods for conservative treatment, but these methods did not bring positive results, then you will have to undergo surgical intervention.
In this operation, special anchors are used to fix torn cartilage tissue to the joint. Arthroscopic intervention has its advantages; the patient's postoperative stay in the surgical department is minimally invasive. After such an operation, complications occur extremely rarely. When the operation is completed, the arm is fixed with an orthosis. The sutures are removed literally on the seventh day. After the operation, you can move your arm a little, and perform therapeutic exercises in the second or third week. The shoulder joint will fully recover in three to four months. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr