Author of the article: Victoria Stoyanova, category 2 doctor, head of the laboratory at the diagnostic and treatment center (2015–2016).
Article publication date: 01/20/2013
Article updated date: 01/27/2020
Today, the medical terms “knee meniscus tear” or “Achilles tendon rupture” are repeated in the sports news section of football as often as penalties and goals. Of course, football is a contact game, and injuries to the lower extremities cannot be avoided, and during matches the risk of injury is much higher than during training.
And the cause of the injuries is obvious: high speeds, rapid changes in direction of movement and sharp impacts. To reduce the risk of injury, to play without pain, fatigue, and just to play comfortably, properly selected shoes, knee bandaging and accurate calculation of your strength help.
The human knee joint is the most complex in its structure, and for us the most important. Knees experience enormous stress throughout life. But a person, and an athlete in particular, sometimes demands the impossible from his knee joint. Here is the desire to be first, and big money, and exorbitant workloads.
So, let's take a closer look at the problem.
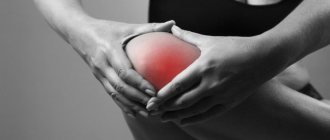
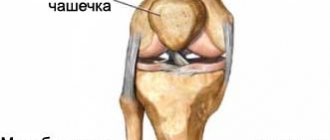
The photo on the left shows a healthy knee joint. On the right - meniscus damage
What is meniscus
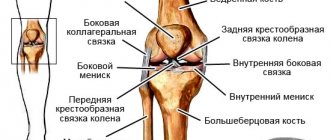
The meniscus is a dense semicircular spacer between the condyles of the tibia and femur. The menisci in the knee provide adherence to the articular surfaces and fill the lateral cavities of the joint. They act as a kind of seal, soften the pressure on the cartilage and stabilize the movement of the joint under heavy loads.
The menisci are made up of collagen and complex proteins and have a tendon-like consistency. They are highly elastic and wear-resistant, and take part in the nutrition and lubrication of the joint.
Mechanism
The pathogenesis of damage involves the implementation of several mechanisms, which include:
- Sudden excessive flexion, which causes stretching of the ligaments, as well as the cartilages themselves.
- Rotation (rotation) of the femur with the tibia fixed and vice versa.
- Bruise with a blunt object or a fall (quite often changes develop when falling on objects with sharp edges - the edge of a step, curb).
These damage mechanisms are more often implemented in relation to the internal meniscus. This is due to the fact that it is fixed more rigidly by ligaments, therefore, under any mechanical influence it practically does not move, which is accompanied by a violation of its integrity.
The outer cartilage is less susceptible to injury, since it has high mobility. A frequent variant of integrity violation is pathological changes in the properties of cartilage tissue, leading to a decrease in its strength.
What are the dangers of meniscus injuries?
During training or at home, a person falls on his kneecap or the knee is subjected to a strong blow, for example in football. The meniscus ruptures or tears. If the body already has disorders, for example, the endocrine system suffers, or there is a history of gout or rheumatoid arthritis, recovery will not occur. A damaged meniscus ceases to perform its functions and does not alleviate pressure on the joint. This creates the preconditions for knee arthrosis.
With an injured meniscus, the cartilage layer is not able to smooth out dynamic loads on the knee joint. The joints begin to deform, friction of the cartilage causes pain. The situation is aggravated if a person is overweight.
Meniscus injury is the first step to knee arthrosis
CT scan
CT scan
- X-ray is a study that allows you to identify significant changes, in particular a complete rupture. To more accurately establish the localization of changes, a study is carried out in frontal and lateral projections.
- MRI is a diagnostically informative technique that involves performing layer-by-layer scanning with tissue visualization due to the physical phenomenon of resonance of the nuclei of hydrogen atoms. They are part of the molecules of organic compounds in a strong magnetic field. This study makes it possible to assess the severity of damage according to Stoller. This is necessary to determine further therapeutic tactics.
- Computed tomography is a technique for layer-by-layer visualization of tissue. X-ray radiation is used for this. The method is very accurate and informative. It allows you to detect even minor traumatic or pathological injuries.
- Ultrasound examination is a diagnostic method characterized by the absence of radiation exposure to the patient’s body. It makes it possible to detect inflammatory changes and assess the volume of intra-articular fluid.
- Arthroscopy is an innovative invasive technique characterized by direct visual examination of internal structures using an optical arthroscope equipped with a video camera and lighting.
Today, arthroscopy is not only a method of diagnostic research. It has also become widespread for performing minimally invasive surgeries with minimal damage to healthy knee tissue.
How to recognize a meniscal injury
The blow to the knee is very painful, but after a few hours the pain subsides. Alarming symptoms indicating a meniscus tear appear later, when a person has long forgotten about the injury. Pay attention to these signs:
- acute pain in the knee that spreads to the outside of the kneecap;
- local increase in body temperature - redness of the skin in the knee area;
- swelling and swelling of the knee joint;
- difficulty going down stairs;
- pain during dynamic movements - when jumping or running;
- a specific click when bending the knee.
The above symptoms are characteristic of various diseases of the musculoskeletal system, including bruises and subluxations of the ankle or knee. Therefore, you should not diagnose yourself: go to an orthopedist and get diagnosed.
What is a meniscus tear and what does it mean? Answers to all questions are in the video:
Physiotherapy
Sports activities help improve blood circulation in the problem area. The greater the access of blood to the joint capsule, the faster the regeneration of the meniscus will occur. By loading muscles, a person redistributes blood flow. To supply blood to the muscles of the lower extremities, the corresponding vessels dilate. Blood access to the joint increases.
If the meniscus is torn, in order to restore it, you can only train under the guidance of an experienced specialist. Because many loads can be harmful. The axial load on the knee should not be allowed to increase. After all, this will entail a mechanical effect on the meniscus and slow down the regenerative processes.
How is a meniscus injury treated?
Injuries to the meniscus can be different: the tendon can be partially torn or completely torn, separated from the joint capsule longitudinally or transversely. The problem can be eliminated conservatively or surgically, but only after the inflammation has subsided.
After a severe knee injury, it is important to rest the leg, cool the affected area and secure the joint with an elastic bandage. If the patient is transported to the hospital in a horizontal position, the leg is placed above the chest to prevent swelling of the knee.
To make a diagnosis, MRI or CT is prescribed, sometimes together with arthroscopy. If the meniscus is displaced, a cast is applied for 20 days, and a course of restorative therapy is also prescribed.
For meniscus injuries, the following is prescribed:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- chondroprotectors to stimulate cartilage tissue and improve the structure of synovial fluid;
- rubbing agents with anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effects;
- collagen, for example in food (strengthens tissue trophism and nourishes the meniscus).
Most often, meniscal injuries are treated with medication.
PRP
In recent years, the treatment of meniscal tears using platelet-rich plasma has become increasingly popular. This drug is prepared directly from the patient's blood. It is either prepared each time before administration, or a large volume of blood is taken once and then frozen. In this case, at each subsequent patient visit, the blood is thawed to prepare the drug.
The essence of the method is as follows:
- Blood is taken from the patient.
- It is centrifuged.
- Excess cells are removed, primarily leukocytes, as they aggravate inflammatory reactions.
- The platelet concentration increases 5 times or more.
- The resulting plasma is injected into the knee.
The procedure is repeated several times. PRP is administered once a week. The injection process is painless because the injection area is preliminarily anesthetized with local anesthetics.
More and more clinics are choosing to treat meniscal tears in this way. The secret to the effectiveness of the technique is that platelets contain growth factors. They enhance reparative tissue processes. Therefore, meniscus regeneration occurs much faster. The use of PRP shortens the duration of conservative therapy and increases the chance of a favorable outcome. By injecting plasma platelets, doctors are often able to treat a meniscus tear conservatively.
Does physiotherapy help with meniscus injuries?
If the clinical picture allows the injury to be treated conservatively, drug therapy is supplemented with physiotherapeutic procedures. Laser, shock wave, ultrasound and magnetic therapy help speed up recovery.
If the patient is not allergic to bee products, he may be offered bee stinging under the supervision of a specialist. The principle is this: on the first day, one bee is planted on the sore spot, on the second - three, on the third - 5. The maximum number of bees is 9. Many patients say that after just one or two stings the healing effect is impressive.
For meniscus injuries, compresses of honey and alcohol are often made
Principles of therapy
The choice of therapeutic tactics is made by the doctor individually for each patient. It is based on the results of a clinical examination and imaging techniques of the components and tissues of the knee. In modern medical institutions, therapeutic tactics include several main areas, which include:
- Therapy without surgery.
- Surgical intervention.
- Rehabilitation.
All stages of treatment are prescribed sequentially. Regardless of the main stage of therapeutic measures (surgery or conservative therapy), the final restoration of knee function necessarily includes rehabilitation.
In what cases is surgery necessary?
Unfortunately, conservative treatment does not always help. If, after several weeks after a knee injury, the pain does not go away, the joint bends with difficulty, the doctor suggests surgery. Surgical intervention is also indicated in the following conditions:
- if the result of a meniscus injury is hemorrhage inside the articular cavity;
- if the meniscus is severely deformed - torn or radically displaced;
- if the meniscus has separated from the joint capsule.
Most often, damaged menisci are sutured; in severe cases, they are replaced with artificial analogues. The operation is as complex as joint replacement for gonarthrosis, and requires a long recovery - at least four months. After meniscus replacement, the pain goes away almost immediately. Training on an exercise bike, swimming in the pool, proper nutrition and therapeutic exercises help speed up recovery.
A meniscus injury can cause no less discomfort than arthrosis of the knee joint. Moreover, it often leads to degenerative-dystrophic changes in the knee joint. Therefore, be especially careful if you are injured. Don’t let the situation take its course: see a specialist.
Classification
Classification
by severity can be:
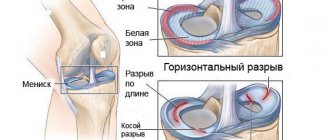
- Incomplete rupture - injury or changes are characterized by the formation of a pathological focus that does not extend through the entire thickness of the cartilaginous component, therefore its shape and general anatomical structure are not disturbed.
- A complete rupture is a severe violation of integrity, accompanied by the spread of changes through the entire thickness of the cartilaginous component, disruption of the shape, as well as the frequent formation of a fragment that can displace and wedge into the joint space.
MRI is used to determine the extent of damage in modern medical institutions. Using this technique, the severity of damage is assessed according to Stoller, which implies 4 degrees of severity.
Based on the location of the damage, a rupture in the anterior or posterior (horn) area, body, or a combination thereof is identified. Also, after identifying the main etiological factor that led to the corresponding injuries, a pathological or traumatic rupture is determined.
Indications for surgery
For what diagnoses is surgery indicated - suturing the meniscus of the knee joint, cutting off the disintegrated edges or its complete removal, inserting a synthetic implant? Common problems requiring corrective surgery include the following types of injuries, confirmed by MRI and radiography:
- separation of a flap (fragment) of the meniscus;
- central longitudinal gap;
- large-scale fragmentation;
- rupture along the periphery with or without displacement.
Types of meniscal tears.
Regarding the separation of the cartilage flap: here it is urgent to perform surgery on the meniscus of the knee joint
, the postoperative period will need to be taken as seriously as possible. If the necessary measures are not taken in time, the free existence of the severed body will impede movement, cause terrible pain and block the knee. The separated fragment, however, like the dangling piece, will begin to create a mechanical obstacle, since during the motor act it will fall into the main working center of the joint.
Schematic representation of the result of suturing the meniscal horn.
Important! It should be clearly understood that the speed and fullness of the return of functional potential subsequently depends on compliance with a special postoperative regimen, and it does not matter what type of manipulation was carried out - correction or removal.
meniscus surgery
knee joint is no less significant than the plasticity of the functional element itself. Therefore, in no case should you neglect the basic recommendations that will be given by a specialist. Only flawless adherence to a recovery program based on improvement of the ligamentous apparatus and regeneration of the operated area will allow for a quick and successful rehabilitation, as well as avoiding quite dangerous complications.