As a result of a fall, a directed blow, or excessively intense adduction or abduction of the lower leg, the knee ligaments rupture. In addition to pain in the joint, the clinic presents inflammatory edema, extensive hematoma, and limited mobility. Treatment for grade 1-2 knee ligament rupture is predominantly conservative. But in case of severe injuries, the victim requires surgical treatment.
general information
“An effective and affordable remedy for joint pain exists...” ...
Knee ligament rupture is a common injury that occurs at home or during sports. These connective tissue strands are dense, strong, but not elastic enough. Therefore, when exposed to loads exceeding their tensile strength, partial rupture or complete separation from the bone base occurs, often with a bone fragment.
Causes and degrees of knee ligament rupture
Such injuries are more often diagnosed in young people actively involved in sports. But they are also predisposed to degenerative-dystrophic, inflammatory pathologies, the course of which is accompanied by a weakening of the ligamentous-tendon apparatus. These are gonarthrosis, arthritis of various origins.
| Severity of knee ligament rupture | Characteristics |
| First (easy) | A small number of fibers are damaged. Such an injury is often called a sprain, although these connective tissue cords cannot stretch, but immediately tear |
| Second (middle) | About 50% of the fibers are torn, causing severe pain |
| Third (high) | The ligament is completely torn or torn from the bony base. Often the injury is combined with damage to the meniscus, cartilage lining of the knee, and articular capsule |
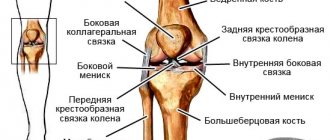
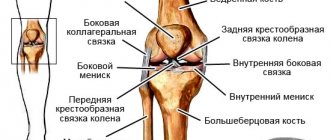
Collateral ligaments
More often, injuries of the internal collateral ligament of 1-2 severity are detected. These connective tissue cords are damaged when there is intense outward deviation of the tibia. Their rupture may be accompanied by a rupture of the internal meniscus and a violation of the integrity of the joint capsule.
Less commonly, the lateral collateral ligament is damaged as a result of excessive inward deviation of the tibia. This traumatic situation occurs when a leg twists. Typically, the ligament is completely torn from its attachment to the bone at the same time as a small portion of the fibula is fractured.
Cruciate ligaments
The main causes of rupture are a direct blow or strong pressure on the back or front surface of the lower leg in a bent state, or its hyperextension. The anterior cruciate ligament is most often injured. Turner's triad may be identified. This is the name for combined damage to the lateral, cruciate ligaments and internal meniscus.
Patella
The patellar tendon ligament ruptures as a result of severe injury, for example, a fall from a height or a traffic accident. It is damaged when the leg is extended at the knee joint, but only under certain conditions. Normally, it is almost impossible to tear a ligament in an adult. Chronic pathologies lead to its damage - tendinitis, tenosynovitis, arthritis, bursitis.
Possible consequences
Most complications develop as a result of the victim’s failure to seek medical help. The ligaments do not fuse correctly, which causes inadequate stabilization of the knee structures. They wear out faster - cartilage is destroyed, the bone surfaces of the tibia and femur change pathologically. Deforming osteoarthritis (gonarthrosis) develops, often leading to disability.
Signs and symptoms of pathology
With a 1st degree rupture, acute pain occurs only at the moment of injury to the ligaments. At rest, it gradually weakens, but can intensify when walking, flexing or straightening the joint. The skin on the knee swells slightly, and pinpoint hemorrhages or a small hematoma may appear.
During a 2nd and 3rd degree rupture of ligaments, a crunching sound is clearly heard, similar to the sound that occurs when a dry stick is broken. The pain is sharp, clearly localized in the knee, but radiating to the lower leg when trying to take a step. With a complete rupture, supporting the leg is impossible due to instability of the joint. After 3-5 hours, inflammatory edema forms, and after it resolves, an extensive hematoma appears.
Diagnostic principles
The basis for making an initial diagnosis is the patient’s complaints, his description of the conditions of injury, and the results of an external examination. A series of tests are performed to assess the functionality of the joint, including range of motion and knee stability. An X-ray examination is required to rule out intra-articular fractures and avulsions of bone fragments. According to indications, MRI, CT, and ultrasound are used to detect damage to the menisci, soft tissues, blood vessels, and nerve trunks.
First aid
“Doctors are hiding the truth!”
Even “advanced” joint problems can be cured at home! Just remember to apply this once a day...
>
Timely first aid can prevent the formation of edema and hematomas and relieve pain. The victim needs to be laid down (preferably on a hard surface), the leg raised to chest level, placing a thick cushion or rolled blanket under the ankle. If the first aid provider has the proper skills, then apply an elastic bandage or fix the joint with a splint.
Then you need to use cold compresses. Fill a plastic bag with crushed ice, wrap it in thick cloth and apply it to your knee for 10 minutes. Repeat the procedure every hour, including when the patient is hospitalized in the emergency room.
To eliminate pain, Nise, Ketorol, Diclofenac, Nurofen are suitable. If there are no such remedies, then you can use regular Paracetamol.
How to make the correct diagnosis
If the injury was minor, then you may not feel much pain. Patients turn to doctors late. To make a diagnosis of a knee ligament tear, the following is carried out:
Treatment for injury is selected based on the results obtained during research. It is important to make a correct diagnosis and begin treatment; sometimes a tear in the knee ligaments can lead to disruption of its functions.
If after an injury a person feels pain, regardless of its nature and intensity, he needs to go to the clinic.
Treatment options
For patients with damage to a small number of ligament fibers, it is recommended to reduce physical activity. To reduce stress on the joint, wearing an elastic knee brace is recommended. In case of serious injuries, it is necessary to provide complete rest to the leg - keep bed or semi-bed rest, move with the help of a cane or crutches. It is necessary to use semi-rigid knee pads, and in case of complete separation of the ligaments from the bone - rigid orthoses. If necessary, a puncture is performed to remove accumulated blood from the joint cavity.
Treatment of grade 1 and 2 injuries is conservative, with the use of medications, massage and physiotherapeutic procedures. In case of rupture of 3rd degree ligaments (except for the internal lateral one), surgical intervention is required 1-2 weeks after their injury.
Medication
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are the first choice drugs for pain relief. To eliminate mild discomfort, it is enough to apply ointments and gels - Fastum, Voltaren, Dolgit, Indomethacin, Ketoprofen. For moderate pain, NSAIDs in tablets are included in treatment regimens. These are Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Nimesulide, Ketorolac. Intramuscular administration of Ortofen, Movalis, Xefocam helps eliminate acute pain.
On days 3-5 of treatment, patients are prescribed external agents with a warming effect - Capsicam, Finalgon, Apizartron, Viprosal. Heparin ointment and Troxevasin are also used to restore damaged blood vessels and resolve hematomas.
Surgical
Complete rupture of the lateral ligament is repaired by applying a Mylar suture or tendon autoplasty. If its dissection occurs, then grafts are installed. In case of combined injuries with avulsion of a bone fragment, it is fixed with a screw to the fibula. Sometimes the lateral collateral ligament is restored with conservative treatment, but it lengthens due to the formation of fibrous tissue. In such cases, reconstructive surgery is performed to stabilize the knee joint.
Surgery is also required for complete ruptures of the cruciate ligaments. To restore their integrity, conservative, endoscopic, and arthroscopic surgical methods are used. For fresh injuries, lavsanoplasty or autoplasty with the kneecap's own ligament is performed.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic measures are used in conservative treatment and at the rehabilitation stage after surgical interventions. The impact of physical factors on the knee joint promotes rapid regeneration of torn fibers by improving blood circulation, accelerating metabolism, and increasing the body's sensitivity to drugs. Patients can be prescribed about 10 sessions of the following physiotherapy procedures:
To eliminate severe and moderate pain, electrophoresis with anesthetics and analgesics is used. Subsequently, when carrying out this physiotherapy, B vitamins and chondroprotectors are used. Also, to accelerate the restoration of all knee functions, patients are recommended mud therapy and sanatorium-resort treatment.
ethnoscience
When carrying out basic treatment, traditional medicine is not used due to their low therapeutic effectiveness. Subsequently, traumatologists do not object to the use of ointments and compresses to eliminate mild pain that appears with increased stress on the joint or after a sudden change in weather. What folk remedies have an analgesic effect:
- compress. Grind 2-3 large fresh plantain leaves to a thick paste, mix with a tablespoon of honey and 3 drops of thyme essential oil. Distribute the mass in a thick layer on the knee, secure with plastic wrap, gauze or elastic bandage, hold for about an hour;
- ointment. In a mortar, mix a tablespoon of gum turpentine with the same amount of linseed oil. Without ceasing to grind, add 100 g of fatty baby cream in small portions. Store in the refrigerator and rub into your knee for pain.
As a drink, you can use chamomile tea, an infusion of rose hips. Such folk remedies strengthen local and general immunity and prevent the development of inflammatory processes.
How long does it take for a torn knee ligament to heal?
If the knee joint is not completely treated, the patient may experience complications that will take much longer to resolve. Recovery after therapy lasts about 8 weeks. The process involves more than just physical exercise.
The patient is prescribed swimming procedures in the pool to restore the functionality of the knee joint without unnecessary stress. Training will help avoid muscle atrophy that occurs as a result of prolonged immobilization of the limb.
Recovery can be carried out in sanatorium conditions. The cost of such rehabilitation is rather high, but it gives a good effect. Reviews about it are positive, since such results are difficult to achieve at home. It is important to know that after surgery, the joint will have to be protected throughout life. From time to time, the victim will need an orthopedic knee brace to secure the joint. During the recovery period, treatment with folk remedies can be carried out. This will help the joint recover faster.
After surgery, it is prohibited to independently rely on the limb without additional supporting elements for the first 7-14 days.
Lifestyle and rehabilitation after injury
At the rehabilitation stage, patients are advised to undergo physiotherapeutic and massage procedures, take chondroprotectors, and balanced complexes of vitamins and microelements. Traumatologists recommend avoiding increased physical activity and replacing active sports with swimming, Nordic walking, and yoga. You should definitely do physical therapy and gymnastics. Daily exercise helps improve knee function by strengthening muscles and accelerating blood supply to tissues with nutrients. Among the exercises, lunges, squats, and imitation of cycling are especially useful.
therapy
therapy
- Open access surgery - dissection of the skin, subcutaneous tissue and capsule is performed to access the damaged structures with their subsequent plastic surgery.
- Arthroscopy is a modern, low-traumatic technique in which an arthroscope with microinstruments is inserted through small incisions into the joint cavity, allowing plastic surgery of damaged ligaments.
Arthroscopy today is the method of choice, since due to less tissue trauma during its implementation, the duration of the rehabilitation period is reduced.