At the SportClinic you can undergo accurate diagnosis and effective treatment, including arthroscopy, for damage and rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament.
Playing sports without preparation is a major risk factor for ACL rupture.
The cruciate ligaments are stabilizing elements located at the “heart” of the knee joint. They connect the femur (thigh) and tibia (shin) bones, forming a decussation between them (hence the name). The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) connects the lateral epicondyle of the femur and the tibial plateau. Its main function is to prevent the tibia from turning inwards relative to the thigh (internal rotation) and moving it anteriorly. This is what typically happens with ACL injuries.
The cause of injury is a sharp landing on the leg with a change in direction, a fall on alpine skiing, a snowboard (where the lower leg is fixed, and the thigh continues to rotate) or a blow. The rupture most often occurs in the thinnest place, where the ligament attaches to the femur. ACL rupture is one of the most common types of traumatic injury. This is due to the fact that more and more people lead an active lifestyle, but do not always approach the load with proper preparation and correct technique, neglecting knee protection, etc. Often combined with damage to the meniscus, as well as the internal collateral ligament (“unlucky triad”).
Structure of the anterior cruciate ligament
The structure of the knee joint and the location of the ACL.
All ligaments in our body are connective tissue structures. The peculiarities of the connective tissue of the ligamentous apparatus are that it contains a large number of elastic fibers located longitudinally in the direction of the forces acting on the ligament. This provides sufficient elasticity and stretchability, but less strength compared to tendons. Age-related changes mean a decrease in their elasticity and an increase in susceptibility to rupture.
The ligament is represented by two separate bundles - anterior-external and posterior-internal. They change (stretch and contract) differently depending on the movement of the knee. There are nerves inside it that give the brain a signal about a bent or straightened position. Based on the direction of the beams - from bottom to top, from front to back and from outside to inside - it becomes clear that damage to the ACL occurs when the lower leg is displaced forward and inward.
Symptoms of damage
The patient can often associate the onset of symptoms with exposure to a traumatic factor. When the ligament ruptures and the joint is dysfunctional, the vessels are damaged and hemorrhage occurs – hemarthrosis. Its increase leads to increased pain to the point that it is impossible to touch the sore spot. This can make diagnosis difficult. To avoid extensive hemarthrosis, it is necessary to apply cold and hold it until arriving at the clinic.
Symptoms appear quite acutely and increase over time. There are complaints about:
- Sensation of displacement, twisting of the lower leg, instability of the knee joint.
- Cracking in case of injury.
- Severe acute pain not only in the area of the bruise, but also in the area of the joint cavity.
- Swelling that appears on the first day.
- The pain intensifies with movement.
Ligament rupture
The shoulder joint is an extremely active joint with a wide range of motion. A large number of ligaments are attached to the area of this joint. Taking into account the location, injuries to the acromial ligament (ACL), damage to the sternoclavicular ligament, damage to the tendons of the short and long heads of the biceps and damage to the rotator cuff formed by the tendons of the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis and teres minor muscles are distinguished.
The cause of rupture of the ligaments of the shoulder joint can be external rotation of the arm, a fall on an outstretched arm, a blow to the collarbone, or a sharp extension of the arm during a throw. The joint is swollen, deformed, its contours are smoothed. Bruising may be visible. Movements are limited. With ruptures of the biceps tendons, shortening of the biceps brachii muscle is observed when trying to bend the arm. Damage to the ligaments of the shoulder joint can be either complete or incomplete; with complete ruptures, the symptoms are more pronounced.
The diagnosis is made on the basis of the clinical picture and X-ray data of the shoulder joint, indicating the absence of bone damage. If damage to the labrum and complete ruptures of other ligaments are suspected, an MRI of the shoulder joint is prescribed. In some cases, arthrography and ultrasonography are used. If, using the above studies, it is not possible to establish the location and extent of the damage, the patient is referred to arthroscopy of the shoulder joint, which can be used as both a diagnostic and therapeutic method (for suturing the defect).
Treatment is often conservative. Young patients are given a cast for 3 weeks, older patients are immobilized using a wide scarf for 2 weeks. All patients are referred to physiotherapy (in the absence of contraindications). After stopping immobilization, it is recommended to perform special exercises to develop the joint. At the same time, for 1.5 months it is necessary to avoid forced movements, especially those repeating those in which the rupture occurred.
Surgical operations are indicated for complete, severe and repeated ruptures. The operation can be performed either classically, using open access, or through a small incision, using arthroscopic equipment. The ligament is sutured, immobilization is carried out in the postoperative period, physiotherapy, massage and exercise therapy are prescribed. The outcome of shoulder ligament rupture is usually favorable.
Main reasons for the breakup
Sharp unnatural rotations of the knee joint relative to the ankle provoke a rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament.
There are two mechanisms for rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament:
- Contact – when there is a blow to the femur or tibia with their displacement relative to each other during a fall, sports or other physical activity. A direct blow to the knee joint provokes its excessive extension, which results in a rupture. This doesn't happen often.
- Non-contact – twisting of a limb during an unsuccessful landing, braking or jump. Football players and basketball players often get injured when turning sharply on one leg. Skiers and snowboarders have their feet fixed in rigid, high shoes, so when they fall or make a wrong turn, the hip often twists if the skis or snowboard rest against something.
Predisposing factors are:
- large angle between the lower leg and thigh in the frontal projection;
- small size of the intercondylar fossa;
- hormonal imbalances;
- weakness of the thigh muscles.
These factors are more common in women, which is why they are injured more often. With age, the risks increase due to a decrease in the elasticity of connective tissue.
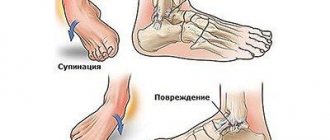
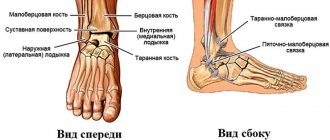
Gymnastics for the ankle after a ligament rupture
Rehabilitation after a ruptured ankle ligament is carried out by specialists from the Yusupov Hospital. Its duration depends on the severity of the injury and the individual characteristics of the patient. The rehabilitation course is carried out in 3 stages:
- the use of physiotherapeutic procedures and massage - begin immediately after the acute period, on the second or third day after the injury, actively use phonophoresis and the method of electrical stimulation in combination with a course of massage of the ankle joint, calf muscle and knee area;
- the use of a set of physical therapy measures - first passive and then active exercises, which make it possible to finally remove joint swelling, reduce the risk of muscle atrophy and develop primary mobility of the ankle joint;
- the final stage, at which the loads are gradually increased to the maximum possible, which allows the muscles to return to their natural tone and the joint to regain its usual mobility.
A course of rehabilitation is also necessary after surgery on the ankle joint. Rehabilitation specialists at the Yusupov Hospital select a set of exercises that will help relieve swelling in the shortest possible time, develop habitual mobility of the ankle joint, and strengthen ligaments to reduce the risk of re-injury.
Immediately after restoring the integrity of the ligamentous apparatus, they resort to general developmental exercises in a sitting position - breathing exercises with smooth rotations of the arms and bending of the body in combination with diaphragmatic breathing. It provides a good mood and raises the overall tone of the body, which is important for recovery processes. 3-4 days after the injury, rehabilitation physical therapy begins. Its main goal is to reduce swelling of the ankle joint, develop the necessary plasticity of the ligaments and strengthen the muscles that ensure the functioning of the ankle joint.
The patient performs the first group of exercises while sitting on a chair:
- in a “sitting” position, rolls a stick or bottle back and forth with his foot;
- gradually increasing the amplitude and frequency, bends and straightens the toes without straightening the knee joints;
- puts his feet together and moves them along the plane of the floor, as if stroking it;
- places the feet parallel to each other and makes movements simultaneously with all fingers inward, like clenching a hand into a fist;
- places a light rug under the feet and gathers it under the feet with the toes;
- puts the foot on the heel and moves it gradually to the toe, and then in the opposite direction.
The second group consists of exercises with the ball:
- put the sore foot on the ball and roll it back and forth;
- make an attempt to grab the ball with bent fingers and rise to a height;
- grab the ball with the middle of the foot;
- The feet are tilted so that the ball can be rolled between the soles.
Then move on to the third group of exercises with a gymnastic stick:
- roll a stick with a certain effort;
- grab the sticks with clenched toes, while making sure that the foot does not lose contact with the floor;
- They try to lift the stick from the floor by grabbing it with their toes.
In order to restore the natural elasticity of the muscles and give them their usual tone, they do special exercises with a chair and a ball. For 5 minutes, the patient walks first on his heels and then on his toes.
When using an orthosis, the rehabilitation course begins without waiting for the end of treatment, even if pain and swelling of the joint remain. Its hinged design allows you to exactly repeat all movements of the ankle joint, developing it without discomfort and significant pain. The procedures are carried out in a “sitting” position, with the legs bent at the knee joint.
The orthosis is often replaced with a bandage. It is simple and easy to use, and its compression and heat-retaining properties have a beneficial effect on the injured area. The use of an orthosis and bandage significantly reduces the patient’s fear of re-injury, which allows the body to quickly cope with the consequences of injury.
Classification
Because the anterior cruciate ligament has two bundles, only one or both of them can be damaged. There is a possibility of complete tearing off along with a section of the bone at the place of its attachment to the lower leg (Segond fracture).
There are three degrees of ACL rupture:
- The first is characterized by stretching, accompanied by moderate pain and swelling. As a rule, the ligament is restored after such cases.
- Second , there are also small tears. Recovery is longer and the regimen plays a decisive role. However, relapses are likely due to a decrease in its strength.
- The third degree is a complete break. The pain is sharp, intense, accompanied by limitation of movement and joint instability. Hemarthrosis (free blood due to vascular damage) is most likely. In this situation, the issue of surgical treatment is resolved.
Also, according to age, fresh ruptures are distinguished - up to 3-5 days, stale - up to 3 weeks and old - more than three weeks. The choice of treatment tactics depends on the determination of these parameters.
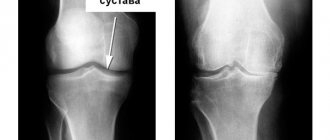
Diagnostics
Visualization of the mechanism of anterior cruciate ligament rupture.
After an injury, there is no need to delay going to the clinic. When visiting a doctor, the patient talks about how this happened. Details matter a lot. Then the doctor conducts a detailed examination, performing functional tests to identify instability, the presence of abnormal fluid, and limited mobility. When diagnosing, the best visualization in great detail is provided by magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography.
Will there be consequences?
Many people who experience injury worry that they will not be able to recover properly. At the same time, doctors say that it is quite possible to rehabilitate. “If the patient followed the specialist’s instructions and followed all the instructions, then gradually the person after the injury will return to his normal lifestyle,” notes the orthopedic traumatologist.
So the key to successful recovery is correctly provided first aid and detailed treatment prescribed by a specialist.
There are contraindications. Be sure to consult your doctor.
Treatment of ACL rupture.
As a rule, advantage is given to conservative treatment. Only in cases of persistent dysfunction and instability is surgical treatment indicated. It is also necessary, when transporting the patient to the clinic, to provide rest to the leg and cold to the injured area to reduce swelling and to avoid an increase in hemarthrosis. For fixation, orthoses are used as the most convenient option for limb immobilization.
Conservative technique
To relieve pain and reduce the inflammatory response, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. If hemarthrosis is present, blood is removed from the joint using a syringe. Sometimes intra-articular glucocorticosteroids are prescribed. After reducing inflammation, a course of intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid or platelet-rich plasma can be prescribed to speed up the regeneration of damaged structures. For a speedy recovery, exercise therapy, mechanotherapy, physiotherapy, etc. are prescribed.
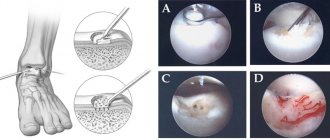
Anterior cruciate ligament arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is the most modern and effective method of repair for ACL rupture.
Arthroscopy is performed in cases where there is instability of the joint or other tissues are damaged. The operation is a minimally invasive method of diagnosis and treatment, since the cavity is not opened, and surgical instruments are inserted into it through two small incisions in the skin. The arthroscope allows you to visualize all structures at multiple magnification, thanks to which the doctor can most accurately make a diagnosis and begin surgical treatment.
ACL plastic surgery
The cruciate ligaments are under constant tension, so applying sutures to restore their integrity is ineffective. Only in case of a Segond fracture is the integrity of the bone restored by fixing the torn fragment. For reconstruction, plastic surgery is performed using an autograft, that is, using the patient’s own tissues. This is usually the semitendinosus tendon. The efficiency of such operations is high. After completing rehabilitation measures, functionality is restored. However, plastic surgery is not required in all cases.
The need for it is based on:
- results of analysis of the intra-articular cavity, the absence of pronounced consequences of inflammation in the joint with extensive fibrosis and adhesions;
- presence of knee instability and other functional disorders;
- sports activity (the desire to return to sports with certain expected intense loads).
Plastic surgery is not performed immediately, but some time after the injury. However, it is not worth postponing the operation for a long time, since instability causes microdamage to the articular cartilage, which can result in the development of arthrosis. The key condition for surgery is the absence of internal inflammation. Preparation for surgery includes conservative treatment methods. Then plastic surgery is performed using the autotransplantation method. The rehabilitation period after such an operation is very important, and compliance with the recommendations of a rehabilitation physician plays a significant impact on the recovery process.
Content
- Symptoms of the disease
- Diagnostic methods
- Treatment methods
- Expert opinion
- Treatment programs
- Who carries out the treatment?
- Why do they contact us?
- Reviews from our patients
- Sign up for treatment
An injury such as a rupture of the ankle ligament is a loss of the integrity of the ligaments that connect and stably hold the bone structures of the foot and lower leg. This is a fairly common type of injury that occurs in people of all ages. Restoring the normal functioning of the lower limb is possible with timely treatment and compliance with medical prescriptions during the rehabilitation period.
Rehabilitation
After arthroscopic plastic surgery, the patient goes home on the day of surgery. It is recommended to apply cold to the knee for 24 hours and immediately fix the leg with an orthosis. Then they begin to perform exercises, which are given with a gradual increase in load. Physical therapy is a set of exercises developed individually for each person. At first, the exercises are performed when visiting a clinic, then independently at home. Mechanotherapy - exercises on simulators are given in a later period of rehabilitation. Physiotherapeutic procedures, including electromyostimulation, magnetic therapy, and electrophoresis, also provide significant assistance. After arthroscopic surgery, recovery is faster and easier than after open knee surgery.
Forecast
The vast majority manage to fully restore the functionality of the limb after treatment and rehabilitation, and athletes are able to return to training. However, this is a rather slow process and takes about six months on average. It is important to adhere to the recommendations of specialists and not to provoke new injuries.
This patient suffered an ACL and collateral ligament injury 2.5 months ago. In this video, he is undergoing conservative treatment for anterior cruciate ligament injury. Subjectively, the knee is stable, but we continue to use various rehabilitation tools, such as flossing.