CAUSES
The causes of the pathology can be very different and depend on gender, age, physical activity and location of the joint.
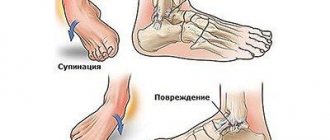
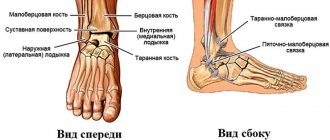
In everyday life, most often damage occurs when a leg is twisted while walking, stumbling, or accidentally falling. Often sprains and pathologies of the ankle joint ligaments can occur in girls wearing uncomfortable shoes, active teenagers, older people when walking on a slippery surface, and from many other reasons. For professional athletes, such injuries are common.
If you fall or injure your arm, there may be a sprain of the ligaments of the shoulder or wrist joint. In athletes, injuries occur due to a sharp throw of the ball or swing; bodybuilders get injured when working with large loads.
Factors contributing to ligament injuries are:
- Excess weight;
- Uncomfortable shoes or clothing;
- Elderly age;
- Features of the structure of the foot - flat feet or high instep;
- Past arthritis, arthrosis, diabetes mellitus;
- Sedentary or very active lifestyle.
SYMPTOMS OF STRAIN
Acute pain after a sprain injury will be the first sign. After some time, puffiness and hyperemia appear at the site of damage. Sometimes a person continues to move after spraining or damaging the ankle ligaments without paying attention to the symptoms that appear, further loading and injuring the damaged area. Then the pain becomes much stronger, and it becomes impossible to use the joint, for example, to raise an arm or stand on a leg. Increased mobility of the damaged joint occurs in the case of ligamentous tissue rupture.
Sprains can be divided into 3 degrees of injury:
1. Mild - the injury to the ligament is minor, several fibers are damaged, the pain is tolerable, it can go away after some time without medical intervention, the joint functions normally. How long does it take for a minor sprain to heal – within 10 – 14 days.
2. Medium – up to half of the total number of fibers is damaged, the pain is quite severe, the performance of the joint is reduced, medical help is required. The average sprain of the foot or knee ligaments takes approximately three weeks to heal, and for successful treatment the limb must be completely immobilized during this time.
3. Severe – ruptures along the entire length of the ligament, unbearable pain, the joint cannot be used, urgent medical attention is required. It may take three to six months to treat a severe ankle sprain.
They can appear very quickly - hematomas at the site of injury or hemorrhage can cover a large area, swelling, tingling or numbness, increased temperature (almost always local).
The symptoms and pain of a severe sprain are similar to those of a fracture. Therefore, you should not self-medicate, but without wasting time, go to the clinic, where you can get a referral for an x-ray, which will help to accurately establish the diagnosis and receive treatment.
Sprains: treatment with NANOPLAST forte medicinal patch
Further treatment for sprains is primarily heat. Compresses and warming ointments are used. that is very effective and convenient at this stage of treatment for sprains . Thanks to its unique properties, the NANOPLAST forte medical plaster not only relieves inflammation, but also has an analgesic effect, improves blood circulation in the injured area, and accelerates the resorption of hematomas. The course of treatment usually ranges from 3 to 9 days.
In the case of a mild sprain, all signs of sprain subside after 5-10 days. For more severe sprains, the treatment process is longer - from several weeks to 6 months. In this case, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), usually in tablet form, are used for anti-inflammatory treatment of soft tissue injuries. And here NANOPLAST forte can provide significant help - its use allows you to reduce the dosage and duration of use of NSAIDs for sprains . Long-term course use of NANOPLAST forte is possible. Consult a specialist. Read more >>>
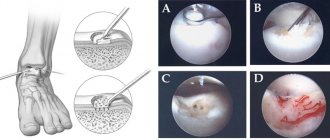
Severe sprains may require surgery to repair the torn ligaments. Such operations are usually performed by an orthopedic surgeon.
When pain disappears and swelling subsides, restorative physical therapy is recommended.
Read more about NANOPLAST forte
CLASSIFICATION
The disease can be distinguished by location and type:
- Sprained ligaments of the foot (ankle) - occurs from any sudden movement. In mild cases, it does not require contacting a surgeon.
- Sprain of the knee joint - occurs after a direct blow or fall. The pain occurs immediately, then passes and appears when trying to make a movement. Accompanied by swelling and poor joint mobility.
- Sprain of the sacral ligament - appears due to sharp twisting of the hip, more often occurs in athletes (football).
- Sprain of the acromioclavicular and sternoclavicular ligaments - occurs after a fall on a straight arm or injury to the upper shoulder. Accompanied by severe pain and the inability to raise your arm.
- Shoulder sprain - occurs when a fall or blow to the shoulder area occurs.
- Sprains of the arm (hand) – the wrist is most often damaged. In children, injuries occur due to a sharp blow or jerk with the hand. In adults - as a result of injury.
- Neck sprains are rare and are mostly due to rapid movement of the neck or awkward positioning during sleep.
Sprains of ligaments, tendons and muscles
P
Damage to the tendon-ligamentous apparatus is one of the most relevant and common reasons that limit the physical activity of people leading an active lifestyle.
The main etiological factor is acute traumatic injury, called sprain, or excessive cyclic load for a long time - overexertion. Sprains of ligaments, tendons and muscles are acute and traumatic due to damage. There are three degrees of severity of a sprain:
Grade I – mild pain due to the tearing of several fibers of the ligament.
Grade II – moderate pain, swelling and disability.
III degree – severe pain due to ligament rupture and subsequent instability of the joint.
Muscle strain
in turn, is a traumatic injury to the muscle fibers themselves or the junction of the muscle and tendon and is also classified into three degrees of severity:
I – moderate.
II – moderate degree of damage, associated with weakness of the affected muscle and its painful contraction.
III - complete rupture of the connection between muscle and tendon, manifested by severe pain and the inability to contract the damaged muscle.
Overexertion is a non-acute, repeated damage to soft tissue structures due to constantly occurring microtraumas, which leads to changes in local microcirculation and, as a consequence, to degenerative processes in soft tissues, where microscopy shows a violation of the structure of local tissues with their lysis, leukocyte infiltration and extravasation of blood .
Repetitive movements during long-term work lead to “overuse” damage in some occupations. Approximately 10–20% of musicians, typists, cashiers and assembly line workers complain of relapses of sprain syndrome; among athletes, this percentage ranges from 30 to 50.
Damage due to overvoltage
(overtraining) are divided into four degrees:
I degree – pain only after physical activity.
II degree – pain during and after physical activity, which does not affect the result of work.
III degree – pain during and after physical activity, affecting the result of work.
IV degree – constant pain that interferes with daily physical activity.
It should also be noted that damage to the tendon apparatus can occur in the form of “tendonitis,” “tendinosis,” and “tenosynovitis.”
Tendinitis
occurs due to tendon injury and associated vascular destruction and acute, subacute or chronic inflammation.
Tendinosis
is a non-inflammatory atrophy and degeneration of fibers within the tendon, often associated with chronic tendonitis, which can lead to partial or complete rupture of the tendon.
Tenosynovitis
is an inflammation of the paratendon, which is the outer sheath of some tendons and is lined with a synovial membrane (for example, damage to the extensor tendon of the thumb in de Courvain's tenosynovitis).
In this review, it makes sense to focus specifically on stress injuries caused by frequently repeated monotonous movements, that is, overexertion, and also take into account mild degrees of sprain of ligaments, tendons and muscles, since injury accompanied by rupture of these structures in most cases requires surgical treatment (damage anterior cruciate ligament and collateral ligaments of the knee joint, rupture of the Achilles tendon).
The most common types of damage due to overexertion (overtraining):
ligaments
–
“baseball player’s elbow”, “swimmer’s knee”, iliotibial tract friction syndrome, “jumper’s knee”, plantar fasciitis;
tendons
–
Achilles tendonitis, suprapatellar tendinitis, biceps brachii tendinitis, tibialis posterior tendinitis, lateral epicondylitis (“tennis elbow”), supraspinatus (rotator cuff) tendonitis.
"Tennis Elbow"
This is lateral epicondylitis. This syndrome occurs as a result of overtraining and is manifested by pain along the lateral surface of the elbow joint. Patients usually associate its occurrence with playing tennis. Today, lateral epicondylitis is considered an inflammatory disease and/or microtear at the insertion site of the extensor carpi brevis. The provoking movement - forced extension of the middle finger of the hand against resistance - causes pain, as the muscle is attached to the base of the metacarpus of the middle finger.
"Golfer's Elbow"
– medial epicondylitis, occurs when the tendons of the pronator and flexor muscles of the forearm are damaged from overtraining at the site of their attachment to the medial epicondyle. This area is subjected to valgus pressure at the apex of the backswing, pain is noted over the medial epicondyle and increases with flexion and pronation of the forearm against resistance.
"Baseball Elbow"
(inflammation of the medial apophysis) - this disease occurs due to a valgus-directed force during frequent movement of the hand along the curve of throwing the ball. The victim experiences microtears in the tendons of the pronator and flexor muscles, and in severe cases, separation and fragmentation of the medial apophysis.
Iliotibial Tract Friction Syndrome
STITUS is pain along the lateral aspect of the knee due to irritation and inflammation of the distal portion of the iliotibial tract as it passes over the lateral femoral condyle. The pain intensifies with palpation of the distal part of the tract at the moment of extension of the leg at the knee joint. STI occurs when running too intensely or running over rough terrain.
"Swimmer's Knee"
– a condition that occurs in the knee joint when a valgus force is applied to the knee due to sudden movements of the leg during breaststroke. This is usually observed when the medial collateral ligament of the knee joint is stretched, which causes pain.
"Jumper's Knee"
– so-called patellar tendinitis. Often found in high jumpers, basketball and volleyball players. It is characterized by pain in the lower pole of the patella, at the site of attachment of the patellar ligament. It develops due to constant damage to this area when the injury does not recover and heal.
Biceps tendinitis
is manifested by pain in the anterior part of the shoulder joint, which intensifies with active movements in the shoulder joint and is less pronounced or absent with passive movements, and is also accompanied by local pain when palpating the area above the long head of the biceps tendon. In the case of concomitant myositis, biceps tendinitis is accompanied by severe muscle soreness.
Patellar bursitis
accompanied by pain, swelling and a local increase in temperature in the patellar bursa, which is located superficial to the patella. Bursitis is caused by repeated trauma or stress, such as kneeling.
Inflammation of the Achilles tendon
manifests itself as pain in the heel, sometimes pain along the back of the leg. Dorsal and plantar flexion of the foot increases pain, the area of greatest pain is 2-3 cm proximal to the junction of the tendon with the calcaneus. The tendon may be swollen and thickened, most often caused by spondyloarthropathy affecting peripheral joints (Reiter's disease, ankylosing spondylitis), as well as trauma.
Plantar fasciitis or heel spur
anatomically arises from the insertion of the flexor digitorum brevis, which is localized along the anteromedial edge of the calcaneal tuberosity, somewhat deeper than the insertion of the plantar fascia. Overexertion of one of these structures is thought to result in reactive inflammatory bone production or spur formation secondary to traction on these structures. However, it remains unclear which mechanism is responsible for this. In any case, the spur is secondary to overexertion.
It is also worth mentioning such a pathology as “shin splints”
is an overtraining injury caused by chronic traction on the periosteum of the tibia. In this case, either the tibial muscles or m. soleus, which is characterized by gradually onset pain along the anteromedial or posteromedial surface of the leg. Pain occurs in athletes at the start of the race, subsides during the run and intensifies again after the end of the race. On palpation, tenderness is detected along the posteromedial edge of the tibia, usually at the border of the middle and lower third. The pain intensifies with dorsal flexion of the foot against resistance.
Treatment
Therapeutic treatment of ligament, tendon and muscle damage includes primary and secondary therapy.
Primary therapy:
- Load protection
- Rest
- Ice
- Pressure bandage
- Elevated position
- Bandage support
Secondary therapy
- Physiotherapy
- Rehabilitation
- Injections
- Physiotherapy
- Examination and re-examination
- Salicylates.
Thus, the basis of treatment is early pain relief and anti-inflammatory therapy for soft tissue injury
, especially in cases of concomitant myositis. Long-term inflammation impairs the healing process of soft tissues, which leads to their detraining and functional failure. With an active inflammatory process, relative rest for the affected area is important. Ice is effective as an anti-inflammatory agent only in the first hours after injury, then heat is preferable. Immobilization with a splint or bandage can be used to enhance protection of the injured limb or part of it from stress.
Corticosteroid injections for chronic processes do not provide a complete cure; moreover, they increase the rate of collagen degradation, reduce the synthesis of new collagen, and reduce the tensile strength of the tendon, which leads to its rupture if injections are performed incorrectly or very often. In this regard, their use is justified only in the acute period and no more than once every 2–3 weeks.
It is also necessary to use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) per os, and in these situations drugs of different groups are approximately equally effective. Their long-term use is recommended for chronic conditions of overstrain; for acute injury, they are effective for 72 hours.
A very effective method of treating traumatic soft tissue injuries is local therapy using ointments and gels containing NSAIDs.
.
The use of local remedies is especially effective in elderly and senile people with a history of ulcers. These drugs can, if necessary, replace systemically used NSAIDs. For sprained ligaments and muscles, accompanying myositis, accompanied by irritation of the nerve roots and peripheral nerves, complex preparations containing NSAIDs and herbal components are used. In Russia, one of the most famous and well-proven drugs in this series is Efkamon
, which has a distracting, analgesic, warming, absorbable and anti-inflammatory effect. Methyl salicylate, which is part of the drug, has an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect by suppressing the synthesis of prostaglandins at the site of inflammation. Capsicum tincture contains capsaicin, which has a strong irritant effect on skin receptors. The unique combination of natural components of the drug, the combined effect of the essential oils included in its composition, which provide a pronounced analgesic effect due to interaction with sensitive skin receptors, makes the drug especially effective for traumatic damage to soft tissues (bruises), myositis, ganglionitis, as well as arthritis and cervical sacral radiculitis, which is especially important in elderly and senile people. It should be noted that the drug does not have the immunosuppressive effect characteristic of almost all synthetic drugs.
The ointment is rubbed into the skin of the affected area in an amount of 3–4 g, 2–3 times a day and covered with a dry warming bandage. The duration of treatment depends on the nature and severity of the disease.
Thus, the use of modern drugs, especially local ones (Efkamon), is an effective method of relieving pain and accompanying inflammation in case of traumatic injury to the tendon-ligamentous apparatus, which contributes to the rapid restoration of physical activity and a return to the previous quality of life of patients.
Literature:
1. Mikheev S.M. The use of local agents in rheumatology. Russian medical journal 2000: v.8 no.7. - With. 300–302.
2. Nasonova V.A., Folomeeva O.M., Amirdzhanova V.N. Rheumatic diseases in the light of the international statistical classification of diseases and related health problems (tenth revision). Ter. arch. 1998: No. 5. – p.5–8.
3. Guide to rheumatology. By ed. V.A. Nasonova, N.V. Bunchuk. – M. – 1997.
4. Silin L.L., Brovkin S.V. The use of gels in the complex treatment of closed soft tissue injuries. Medical assistance 2001: No. 2.
5. Chichasova N.V. Local therapy of chronic diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Russian Medical Journal 2001: v. 9 No. 7–8. - With. 286–288.
6. Data from the American Association of Retired Persons, the Administration on Aging, and the US Bureau of the Sensus. A profile of older Americans, 1994.
HOME TREATMENT
Many people ask what to do for sprains and injuries of the foot ligaments or how to treat sprains on their own. Folk remedies can be used only in case of minor damage or after consultation with a doctor, since they only help medicine, but do not replace it. It is often recommended to use alcohol compresses, which help with sprains, as they relieve swelling and relieve pain.
If you are wondering what to do when you sprain your ankle, you can recommend applications of grated potatoes, onions, ground aloe into a paste, which are applied to the painful area. To treat sprains and ligament injuries in small places on the finger, you can use clay, which is diluted to the consistency of sour cream, placed on a napkin and bandaged to the area of the hand.
If severe pain does not subside within a day or mobility does not return to normal, it is not recommended to do anything with a sprained leg or arm; the victim should immediately consult a doctor.
What happens if tendon injuries are not treated?
The consequences of tendon rupture can be extremely unpleasant:
- constant pain that occurs against the background of “nodules”. These structures form when healing is improper. Nodules increase friction and cause chronic inflammation;
- damaged nerves cause numbness and tingling in the limbs;
- An improperly fused tendon can become damaged at the slightest load on it. Injuries to the Achilles tendon are especially dangerous. There is no guarantee that the patient will return to previous physical activity.
Therefore, limb tendon injuries should be treated immediately after the injury is discovered.
TREATMENT
Medical care includes pain relief and anti-inflammatory medications. Local therapy with ointments and gels has a good effect. The prescribed drug is rubbed into the damaged area 3-4 times a day and a bandage is applied.
To establish the correct diagnosis and timely treatment, you can contact the Center for Restorative Medicine in Naberezhnye Chelny. Qualified specialists will find the cause of the disease and select individual therapy and rehabilitation program.
Restorative physiotherapy procedures and rehabilitation for sprains and other pathologies of the ankle ligaments promote rapid and high-quality healing; in addition, they significantly reduce the risk of severe complications after injuries.
At the Center for Rehabilitation Medicine in Naberezhnye Chelny you can make an appointment with a traumatologist. Prices can be found on the website or by phone.
Symptoms
The best treatment is to prevent injury. However, if trouble does happen - you fall, turn sharply, or lift a lot of weight with a jerk, then it is important to distinguish the signs of a sprain from a dislocation, which can be one of the complications.
The main sign of dislocation is displacement of the head of the joint relative to the notch of the joint capsule. It can be either complete or partial. The injury is accompanied by dysfunction in the joint, swelling, hematoma and local hyperemia.
Signs of muscle strain exclude displacement or other deformation in the area of injury. You will observe:
- swelling in the damaged area;
- pain syndrome of varying severity, depending on the severity of the injury;
- possible hematoma;
- the function of the limb is partially lost in cases of mild to moderate damage and completely in the case of severe tearing of the muscle fibers due to stretching.
How to determine the degree of muscle damage?
- Partly due to the severity of pain - in mild cases, the pain is tolerable and quickly passes when the limb is kept at rest.
- In moderate cases, swelling and severe pain develop, but the person can continue to use the injured limb provided it is fixed with a splint.
- In case of severe sprain, painkillers are required, swelling is pronounced and a hematoma develops.
Severe muscle strain with tears may require surgery and long-term rehabilitation.