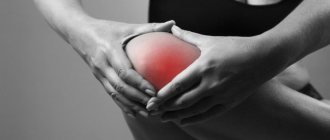
The knee joint is quite often susceptible to various traumatic effects. This is due to its relatively high mobility, as well as the stresses associated with the impact of body weight on the lower limbs. These lesions may involve cartilaginous components. One of the changes is a torn meniscus of the knee joint. Without surgery, modern clinics can treat such conditions only after a comprehensive diagnosis with determination of criteria for the possibility of conservative therapy.
meniscus
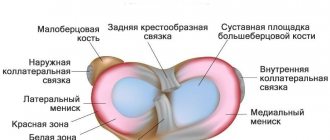
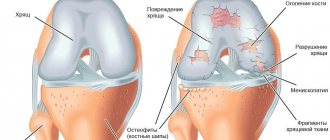
meniscus The knee is a complex component of the musculoskeletal system, which is formed by the surfaces of 3 bones - the patella, the femoral condyles, and the tibia and fibula.
Since it can withstand significant loads caused by body weight, paired crescent-shaped cartilage components are located in the joint space. They are called the lateral (outer) and medial (inner) meniscus. These components have a body (the wider part) and two horns (tapered parts that face forward and backward). Due to such anatomical features of structure and localization, these components provide shock absorption, strengthening and certain stabilization of the joint.
Description of operation
The operation begins with anesthesia and treatment of the surgical field. The skin in the area of the knee joint is carefully shaved, after which it is treated several times with antiseptics. This is necessary in order to prevent infection from entering the synovial cavity where manipulations are performed.
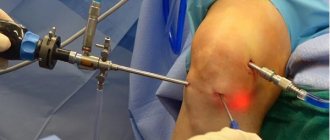
All arthroscopic interventions are performed under visual control. To visualize intra-articular structures, an arthroscope is inserted into the joint cavity, which is a tube and an ocular head rigidly connected to each other. The image from the arthroscope is displayed on a screen in the operating room, allowing the surgeon to control his actions and the patient to monitor the progress of the surgical procedure.
First, the patient's leg is bent and a cannula is inserted through a small incision. Then it is unbent and the arthroscope is inserted through the cannula. Instruments for arthroscopic manipulation are inserted through small incisions 4-5 mm long. After the operation, the arthroscope and all instruments are removed, and the postoperative wounds are sutured and sealed with adhesive tape.
Arthroscope.
Mechanism
The pathogenesis of damage involves the implementation of several mechanisms, which include:
- Sudden excessive flexion, which causes stretching of the ligaments, as well as the cartilages themselves.
- Rotation (rotation) of the femur with the tibia fixed and vice versa.
- Bruise with a blunt object or a fall (quite often changes develop when falling on objects with sharp edges - the edge of a step, curb).
These damage mechanisms are more often implemented in relation to the internal meniscus. This is due to the fact that it is fixed more rigidly by ligaments, therefore, under any mechanical influence it practically does not move, which is accompanied by a violation of its integrity.
The outer cartilage is less susceptible to injury, since it has high mobility. A frequent variant of integrity violation is pathological changes in the properties of cartilage tissue, leading to a decrease in its strength.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic techniques help improve blood circulation in the knee joint. Various forms of electrical energy, ultrasonic waves, magnetic, electromagnetic fields, laser, infrared radiation, etc. are used. The impact of all these physical factors contributes to a local increase in temperature, which leads to vasodilation.
Massage is one of the types of physiotherapy. It involves a mechanical effect on soft tissues located in the immediate vicinity of the injured joint. It leads to local hyperthermia and dilates the blood vessels, thereby increasing the blood supply to the joint capsule. Usually 10-15 massage sessions are prescribed.
Etiology
The causes of meniscal tears can be different; the most common triggers include:
- A person’s young age, as well as a life of high physical activity.
- Playing sports (amateurs or professional athletes) that are characterized by high mobility. These sports include football, volleyball, hockey, and athletics.
- Congenital defects of cartilage tissue caused by changes in certain genes that are inherited. In this case, a rupture can occur already in childhood, even in the absence of excessive physical activity.
- Acquired deterioration in the density of cartilage tissue, which is predominantly formed against the background of a decrease in its trophism and leading to degeneration. This provoking factor leads to pathological damage in elderly people after moderate loads on the legs.
- Long-term inflammation caused by specific (tuberculosis, syphilis) or nonspecific infections, as well as an autoimmune condition in which antibodies are produced to one’s own cells (rheumatoid arthritis).
Identification of provoking factors is carried out during a comprehensive examination of the person, which is required to select adequate therapy, as well as prevent changes in the future.
Preparation and anesthesia
Even at the planning stage of surgical intervention, the patient undergoes a series of tests and undergoes a full examination. If there are no contraindications, the doctor sets a date for the operation and tells you how to properly prepare for it. During preparation, the patient should carefully follow all the specialist’s recommendations. At least 12 hours before arthroscopy, the patient should stop eating, drinking and smoking (as anesthetic drugs must be administered on an empty stomach). 30-40 minutes before the administration of painkillers, the patient is given premedication. Its essence lies in the administration of tranquilizers and hyposensitizing drugs. Premedication reduces the patient's anxiety and enhances the effect of anesthetics.
Arthroscopic meniscus procedures are usually performed under spinal or regional anesthesia. In the first case, painkillers are injected into the spine and thereby block the nerve roots that are responsible for the innervation of the lower limb. In the second case, the femoral and sciatic nerves are blocked, infiltrating nearby soft tissues with anesthetics.
In rare cases, for special indications, the operation is performed under general anesthesia. In this case, anesthetics are administered intravenously, and the patient is breathing independently or breathing through a laryngeal mask. Local anesthesia for arthroscopy is used extremely rarely due to its weak analgesic effect and short duration of action.
Classification
Classification
by severity can be:
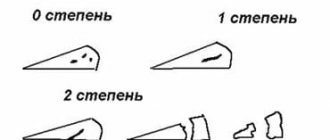
- Incomplete rupture - injury or changes are characterized by the formation of a pathological focus that does not extend through the entire thickness of the cartilaginous component, therefore its shape and general anatomical structure are not disturbed.
- A complete rupture is a severe violation of integrity, accompanied by the spread of changes through the entire thickness of the cartilaginous component, disruption of the shape, as well as the frequent formation of a fragment that can displace and wedge into the joint space.
MRI is used to determine the extent of damage in modern medical institutions. Using this technique, the severity of damage is assessed according to Stoller, which implies 4 degrees of severity.
Based on the location of the damage, a rupture in the anterior or posterior (horn) area, body, or a combination thereof is identified. Also, after identifying the main etiological factor that led to the corresponding injuries, a pathological or traumatic rupture is determined.
First aid
Conservative treatment begins with first aid, which should be received by a person who has injured his knee. Initially, he does not yet know what kind of injury he received. After injury, he feels pain. The knee swells and its function is impaired.
Typically, first aid consists of placing a cold pack on the injured limb. This could be snow or ice in the winter season. In sports medicine, special cooling aerosols are used. If the injury occurred at home, you can apply frozen food from the refrigerator to your leg.
Thanks to the cold, the hematoma decreases. Tissue swelling, pain, and inflammation are reduced. After this, you should immediately go to see a doctor. The doctor must assess the nature of the injury and select the necessary treatment.
Clinical picture
Damage to the cartilage of the knee joint after an injury is characterized by the appearance of quite characteristic symptoms. Among them:
- Pain that appears immediately after exposure to a traumatic factor. It is usually pronounced, localized on the outer or inner surface of the knee, and also intensifies when trying to perform movements in it.
- Decreased range of motion in the knee, the severity of which depends on the degree of damage. In the case of the formation of a cartilage fragment, a block of movements may develop, which is accompanied by intense pain.
- Signs indicating the development of an inflammatory reaction, which always accompanies changes in cartilaginous components. These include hyperemia (redness of the skin), swelling of the soft tissues with an increase in the joint in volume, as well as a local increase in temperature, manifested by the skin becoming hot to the touch.
Pathological changes, prolonged inflammation, as well as damage due to a congenital decrease in the strength of cartilage tissue are accompanied by a longer development of clinical symptoms. At first, pain may be absent or appear only during exercise. Then it intensifies and becomes permanent. Movements in the knee are accompanied by the appearance of “crunching” or “clicking” sounds.
Immobilization
To create optimal conditions for repairing a meniscus tear without surgery, long-term immobilization of the affected limb is necessary. Movement in the knee joint should be limited. For this purpose, a splint is applied. Compared to leg casting, this method of immobilization has a number of advantages:
- the blood supply to the knee is not disrupted, so the regeneration of the meniscus does not slow down;
- no negative effects on the skin of the feet;
- the possibility of performing physical exercises remains.
The splint is applied for 4-5 weeks. At the discretion of the doctor, it is possible to extend the period of immobilization of the knee joint.
CT scan
CT scan
- X-ray is a study that allows you to identify significant changes, in particular a complete rupture. To more accurately establish the localization of changes, a study is carried out in frontal and lateral projections.
- MRI is a diagnostically informative technique that involves performing layer-by-layer scanning with tissue visualization due to the physical phenomenon of resonance of the nuclei of hydrogen atoms. They are part of the molecules of organic compounds in a strong magnetic field. This study makes it possible to assess the severity of damage according to Stoller. This is necessary to determine further therapeutic tactics.
- Computed tomography is a technique for layer-by-layer visualization of tissue. X-ray radiation is used for this. The method is very accurate and informative. It allows you to detect even minor traumatic or pathological injuries.
- Ultrasound examination is a diagnostic method characterized by the absence of radiation exposure to the patient’s body. It makes it possible to detect inflammatory changes and assess the volume of intra-articular fluid.
- Arthroscopy is an innovative invasive technique characterized by direct visual examination of internal structures using an optical arthroscope equipped with a video camera and lighting.
Today, arthroscopy is not only a method of diagnostic research. It has also become widespread for performing minimally invasive surgeries with minimal damage to healthy knee tissue.
Principles of therapy
The choice of therapeutic tactics is made by the doctor individually for each patient. It is based on the results of a clinical examination and imaging techniques of the components and tissues of the knee. In modern medical institutions, therapeutic tactics include several main areas, which include:
- Therapy without surgery.
- Surgical intervention.
- Rehabilitation.
All stages of treatment are prescribed sequentially. Regardless of the main stage of therapeutic measures (surgery or conservative therapy), the final restoration of knee function necessarily includes rehabilitation.
Therapy without surgery
Any intervention involving tissue dissection is invasive, so modern traumatologists and orthopedists try to carry out treatment without surgery whenever possible. Conservative treatment is possible in certain cases:
- Diagnosed incomplete rupture with the absence of cartilaginous fragments.
- Localization of damage - due to certain anatomical features, an incomplete tear of the lateral meniscus of the knee joint is diagnosed; treatment in this case is possible without surgical intervention.
- The patient has absolute contraindications to surgery - usually conservative therapy is prescribed to elderly patients with pathological changes in the cartilaginous components.
Therapy without surgical intervention can be carried out in a hospital or on an outpatient basis, but only if the patient follows medical prescriptions in a disciplined manner.
Traditional medicine
Folk remedies are ineffective in treating meniscus injuries. They can only be used as an addition to the main therapy. Traditional medicine is aimed at relieving pain, reducing swelling, and removing inflammation from the affected area.
Pine baths
To improve blood circulation, take pine baths. The procedures help strengthen and treat the affected joint. To prepare a bath you will need pine needles (dry or fresh). The proportions vary in each case. 500 g of fresh is enough, and 700 g of dry should be used. Pour the pine needles with water (2 liters), boil for 30 minutes, then add the decoction to the water. You can do such baths every other day; they should last 20–30 minutes.
Sea salt baths
These water procedures are intended to relieve tension and calm. Follow the instructions on the packaging.
Compresses
Our grandmothers used compresses to treat knee pain. Their effectiveness has been proven over time. You can use one of the options below to treat meniscus injuries.
Mud compresses
Usually the use of mud is resorted to in mud baths. At home, you can also spread mud on the sore area, insulate it with a wool scarf or film, leave for 2 hours. Then wash off the mud with (warm) water.
Honey compress
To prepare a compress, just mix honey. alcohol, honey (1:1). Apply this mixture to your knee and leave for 2 hours.
Compress with onions
To make such a compress, you should initially prepare a product for it. Take the onion, peel it, then chop it on a grater. Add sugar (10 g) to the onion. Apply the mixture onto gauze and place on the affected area. The duration of the procedures is 30 days.
Onion compress with sugar
Take onions (2 - 3 pieces), grate to get a paste. Mix with sugar (1 tsp). After thoroughly mixing the components, apply to the skin.
Burdock for making a compress
You can use fresh, juicy leaves (in summer), dry leaves (in cold winter). Dry ones will need to be soaked with water. After wrapping it around the knee, apply a retaining bandage. Leave for 3 – 4 hours.
Burdock leaf compress
Making such a compress is not difficult. It is enough to wrap a sheet of paper around the affected joint, securing it with a bandage. Recommended duration of exposure is 3 – 4 hours.
Cabbage leaf compress
Perform a compress using the same method as with burdock. After washing the leaf, pour boiling water over it. Apply to the painful area, wrap with cloth and polyethylene for insulation.
Compress of honey and medical alcohol
For preparation we use honey (2 tsp), alcohol (2 tsp). Having mixed everything, put it on the fire to simmer. When the mass becomes homogeneous, remove from heat, cool, and apply in a thin layer. Cover with polyethylene. Leave for 2 hours.
Vegetable leaf compress
Many people recommend using burdock and cabbage leaves to relieve pain and eliminate swelling. Vegetable leaves are wrapped for 6–8 hours.
Sweet onion compress
To prepare this remedy, you need to mix 1 tbsp. l. sugar, a small onion, grated. Use at night.
Flower compress
Dandelion and lilac flowers are used to prepare it. Flowers are poured with alcohol. It should be left for 2 weeks. In the dark. You can add chestnuts. Moisten a bandage with the tincture and apply it to the affected area and leave it overnight.
Tendinitis of the knee ligament: causes, symptoms and treatment
Healing mud compresses
Almost everyone has heard about the healing effect of mud. Therapeutic mud is also used in the treatment of meniscus injuries.
Clay compress
This compress is used to quickly relieve pain and speed up the healing of a torn meniscus. Clay is mixed with water, spread on the knee joint, and wrapped. You should make this compress before going to bed.
Tinctures for internal use
In the treatment of pain caused by meniscus injury, settings that are taken orally will also be effective. They are prepared from ingredients found in every home.
Horseradish root
To prepare the product, take horseradish root, chop it, then pour boiling water over the mixture. After tuning for 20 minutes. the product will be ready for consumption. The therapeutic course is 20 days, it is enough to drink 1 tbsp per day. l. twice a day.
Bay leaves
To prepare you need laurel leaves (50 g), boiled water, cooled. Bring the water with the leaves to a boil, turn off the gas, and let it brew. Drink the prepared liquid for 4 days, then prepare a new one. Duration of therapy is up to 6 months.
willow bark
In addition to willow bark, you will need parsley root and dried nettle. Fill the mixture with hot water (150 ml), leave for a day. Then we use the tincture daily, 70–100 ml.
Tinctures for external use
Also, for pain relief, relief of swelling and signs of inflammation, the means that we describe below are used.
Garlic tincture
Grate 2 heads, fill the mass with vinegar (it’s better to take apple vinegar) 300 - 400 g. After infusing for a week in the dark. The place should also be warm. Use to rub the affected area for 20 minutes.
Tincture of iodine
The product is prepared from an equal amount of the following components: iodine, alcohol. They are mixed and kept for a day. After the specified period, the rubbing is ready. After rubbing, do not wrap your knees.
Potato flower tincture
Collect fresh flowers, clean them of greenery. The flowers should be filled with alcohol and the tincture should be placed in a cool place. After 10 days. The rub is ready. Use the rub twice a day. The procedures should be stopped after all pain disappears. Longer than 1 month use is not recommended.
Homemade ointments
Remedies for relieving pain after a meniscus injury can be prepared independently at home. When prepared correctly, the effect of their use is noticeable immediately.
Honey ointment with salt, mustard powder, water
Take the above ingredients, mix honey (100 g), water, mustard powder (1 tsp each). The resulting product helps relieve pain and warm the affected area.
Dried St. John's wort, nettle + yarrow
We prepare an ointment from dried herbs yarrow, nettle, St. John's wort and petroleum jelly. The prepared ointment should be used before bedtime.
Egg
Place a chicken egg in a container, having previously crushed its shell. Fill the mixture with vinegar essence until the egg is completely covered. You need to infuse the mixture in a dark place. Five days is enough. Then add vegetable oil (200 ml), mix everything thoroughly and leave for another 2 days. in a warm place. The product is stored in a cool place.
Rubbing
There are a lot of recipes for rubbing that will relieve pain when the meniscus is damaged.
Garlic tincture
Garlic (a couple of heads) is grated and poured with apple cider vinegar (400 ml). Keep for a week in a warm place. The product is ready for rubbing.
Essential oil rub
Essential oils provide tissue nutrition and blood supply. The following oils can alleviate the condition of meniscus damage:
- Eucalyptus;
- birch;
- basil;
- geranium;
- juniper;
- thyme;
- cedar;
- chamomile;
- sage.
Pork fat
To cope with swelling and pain in the knees, use an ointment based on pork fat. The product is prepared from the following ingredients:
- Pork fat (0.5 kg);
- raw eggs (4 pcs.). They should be ground with the shell;
- ginger powder (50 g);
- vinegar essence (500 ml.).
After mixing, place the mixture in a glass container and leave for another 3 days. Mix the mixture thoroughly for another 6 days. Then use it.
Ligamentosis of the cruciate ligaments of the knee joint: treatment and prevention
Other folk methods
In addition to the funds from the people described above. you can use one of the following.
Dry birch leaves, violet and nettle herbs
The ingredients listed above are used to prepare the tincture. You will need to take it internally. Pour boiling water over all herbs and leave for 30 minutes. It's worth drinking 100 g. You should drink tincture 4 rubles per day.
Honey mixture with aloe pulp
This product is used to cleanse joints. A medicine is prepared from aloe juice (500 g), butter (500 g), honey (500 g). After steaming, drink the medicine on an empty stomach. 4 tbsp is enough. l.
Application of horseradish
We use horseradish root. Grind this part of the plant and pour boiling water over it. Let stand for 30 minutes. The course of therapy is 20 days. We drink 1 tbsp of java per day. l.
Herbal decoction
A decoction of willow bark, parsley (root), and dried nettle is prepared. Fill the mixture with hot water and leave for a day. We drink 70–100 ml daily.
Bile
Medical bile is used to reduce pain. You can buy the product at the pharmacy; at home, warm the mixture to room temperature. Apply with rubbing movements to the affected area twice a day. Therapy lasts 2 months.
Apple cider vinegar and garlic
Chop the garlic (2 heads), pour the mixture with vinegar (0.5 l.). Keep inside a glass container for 7 days. To rub, use massaging movements. 2 procedures per day for 10-15 minutes are enough.
Wormwood applique
The drug is also used in the treatment of myositis. To prepare a solution for lotions, take wormwood powder (15 g). Pour boiling water over it (1 tbsp), leave for 1 hour, strain. For a lotion, soak gauze in the solution and apply to the affected area. Leave the lotion on for 30 minutes.
With onions and sugar
To prepare a compress, use onion pulp mixed with sugar. It is applied to the surface of the knee and wrapped with cloth. You need to do it at night.
Rejection of bad habits
Rejection of bad habits
- Functional rest - during the entire stage of the main course of therapy, as well as partially during rehabilitation, the knee should not be subjected to stress. To ensure rest, a special motor regimen is used for the patient, and a tight bandage is applied to the joint using an elastic bandage or plaster splint.
- Diet – Dietary recommendations include eating high-calorie, highly digestible foods with sufficient fat, protein, carbohydrates and vitamins. Also, organic compounds that are directly involved in the synthesis of the intercellular substance of cartilage tissue must enter the body with food.
- Quitting bad habits - during the main course of therapy, it is advisable to give up smoking and drinking alcohol-containing drinks, since nicotine and alcohol are vascular toxins, they significantly slow down the processes of tissue regeneration (healing).
The implementation of such general recommendations (with the exception of functional rest) is desirable at the rehabilitation stage.
Drug therapy
In almost all cases of conservative treatment without surgery, medications of various groups are used. The most widespread are:
- Hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs based on adrenal hormones and glucocorticosteroids. They are used in the development of a pronounced inflammatory reaction in the form of intra-articular, intravenous or intramuscular injections.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - reduce the intensity of the process, the synthesis of mediators of the inflammatory reaction by cells of the immune system, thereby reducing the severity of manifestations. These drugs are mainly used in the form of injections or tablets for oral administration. Additionally, local therapy may be prescribed in the form of a cream or ointment.
- Chondroprotectors are a large group of medications, the active substance of which is the main structural component of cartilage tissue. These drugs have the ability to slow down degeneration processes, as well as restore damaged cartilage tissue.
- Vitamins are an essential component of drug therapy, helping to improve the course of metabolic (metabolic) processes in the body and accelerating healing.
Medicines are used over a long period of time, which is determined individually by the attending physician.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Physiotherapeutic treatment involves the use of physical factors that have a therapeutic effect. Most medical clinics use procedures such as electrophoresis with topical medications, treatment with a magnet, ozokerite, and mud therapy.
They help reduce the intensity of inflammation and also accelerate the healing of damaged tissue. As a rule, physiotherapeutic procedures are combined with the prescription of drug therapy.
introduction of platelet mass into the joint cavity
introduction of platelet mass into the joint cavity
In modern traumatology and orthopedics, the acceleration of regeneration processes is carried out using alternative methods of non-surgical treatment. The most common of them is the introduction of platelet mass into the joint cavity. This is a suspension of platelets in a saline solution with a high content of growth factors. They are produced by formed elements of blood.
These compounds affect the functional activity of cells of cartilage, bone and connective tissue with an increase in the intensity of the process of synthesis of components of the intercellular substance. The duration, frequency of administration of biological drugs, as well as the dosage are determined by a medical specialist individually.
Recovery
After surgical or conservative treatment, rehabilitation is carried out, which is aimed at restoring knee function. This result is achieved through the use of special exercises with a gradual increase in the load on the joint. They enable the cartilage components to fully adapt and also prevent their re-injury in the future.
The duration of such measures may vary, depending on the nature of the damage, as well as the direction of the main course of therapy. It may only last a few months. In some cases, after open surgery, the rehabilitation period may exceed 1 year.
Types of knee pads
To distribute the load, prevent excessive friction of joints, and prevent coxarthrosis, doctors recommend a knee brace after meniscus surgery. They relieve fatigue and stiffness after meniscus injuries, and stabilize blood circulation.
Taping
Tapes are used to immobilize the joint. This product is an elastic tape with an adhesive base. After stretching, the product adheres to the skin and is fixed. Thanks to this fixation of the tape on the code, movement of the affected joint is limited.
Bandages
These products are designed for easy fixation and joint support. They do not have inserts for rigidity (plastic, metal). Used to treat joint pathologies and prevent relapses.
Orthoses
This type of product is represented by a semi-rigid, rigid bandage. The product has stiffening ribs. It limits the mobility of the knee more than a brace.
Splints
The difference between this product is the presence of stiffeners and belts. The splints ensure complete immobility of the joint. The joint is immobilized 100%.
Material
Depending on the material, the following types of knee pads are distinguished:
- Made from wool;
- made of cotton;
- made of neoprene;
- made of elastane, polyester.
Price
Prices for knee pads depend on a number of nuances: material, manufacturer, type of fixation, therapeutic effects that the knee pad has. The cost starts from 500 rubles to 5000 rubles.
Posterior horn of the meniscus: structure, injuries, symptoms, treatment