What is a synovectomy?
Synovectomy is one of the symptomatic treatments for certain inflammatory joint diseases and the consequences of joint damage caused by intra-articular bleeding associated with hemophilia. It involves the use of a surgical method (traditional - open or endoscopic) or radiological (using ionizing radiation) to destroy the pathological synovium.
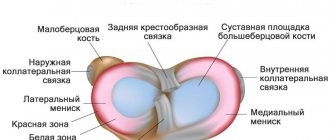
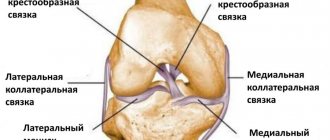
The synovium (synovium) is a special type of connective tissue. It cushions the inside of each joint and produces synovial fluid, a sticky, clear substance that helps the articular surfaces of the bones that make up the joint slide together.
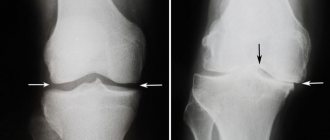
In some inflammatory joint diseases (especially rheumatic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis), the synovium is destroyed and repaired incorrectly, impairing the mechanical properties of the joint and causing pain. The procedure of synovectomy by removing the abnormal synovium is aimed at reducing the pain of the affected joints and slowing down the process of their destruction. Any joint can be treated, most often the metacarpophalangeal joints, wrist and knee joints. The choice of procedure technique depends on which joint or joints are affected, as well as the technical capabilities and experience of the operating physician.
Recovery period
After the operation, the patient is placed in a ward, where he is under medical supervision until he recovers from anesthesia. The rehabilitation period after arthroscopic synovectomy usually passes quickly - within a few days. In case of severe pain, the patient is advised to take painkillers from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Starting from the second day after surgery, the patient must undergo physiotherapeutic procedures that help accelerate wound healing and restore normal functioning of the knee joint.
Simultaneously with physiotherapeutic procedures, patients are prescribed physical therapy. The patient must move with the help of crutches so as not to load the operated joint. When you can give up crutches, only the traumatologist decides, based on the rate of restoration of joint function.
The synovium after complete synovectomy in most cases is completely restored 6 months after surgery.
Synovectomy – what does the procedure look like, how to prepare?
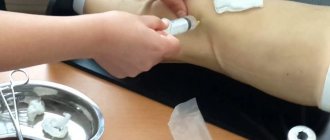
The course of the procedure and the method of preparation for it vary depending on the technique in which it will be performed. Synovectomy is performed under general anesthesia (usually in open operations) or local (or so-called woven) anesthesia covering the entire limb, more often in arthroscopic procedures. Details of anesthesia and preparation for it are discussed with the doctor before the procedure.
To be on the safe side, give your doctor information about all current medical conditions (including chronic conditions such as hypertension or diabetes, even those well controlled with medications), medications (including over-the-counter medications), and allergies (especially to medications and drugs used). during anesthesia).
It is also important to report possible transmission of blood borne pathogens (such as HIV, HBV or HCV). After applying anesthesia, the joint space is cut and opened (using the traditional method) or small incisions are made through which arthroscopic equipment is inserted. The doctor finally assesses the condition of the synovial membrane and performs a partial or complete removal procedure. The resulting wound is then sutured and the joint is immobilized for a period of time depending on the type of joint and the extent of the procedure. In the postoperative period, rehabilitation is necessary to maintain joint mobility and prevent joint stiffness.
About
Progress of the operation
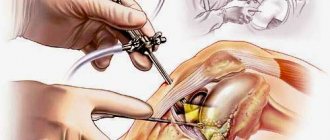
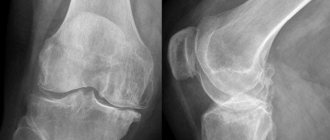
Synovectomy of the knee joint can be open (by opening the joint capsule) or arthroscopic. During the operation, partial (partial) or complete excision of the synovial membrane is performed.
The arthroscopic procedure is considered gentle and causes minimal trauma to the knee. As a result, fewer complications occur after arthroscopic surgery than after open surgery. The procedure is quite complex to perform and requires special qualifications of a doctor.
The operation is performed under general or epidural anesthesia. Arthroscopic synovectomy is performed using a special optical device - an arthroscope, which is additionally equipped with microsurgical instruments. A tourniquet is placed on the patient's thigh to reduce blood flow to the operated limb.
The area of the knee joint is treated with antiseptics, after which 3-4 cuts are made on the skin, each 7 mm long. Arthroscope and microsurgical instrument tubes are inserted through these incisions.
After puncturing the joint capsule, the arthroscope is inserted into the cavity. Using an optical device, the cavity is examined and the area for excision of the membrane is determined. The excised tissue is removed from the joint cavity.
After surgery, drainage tubes must be installed in the joint to drain the exudate that forms during tissue healing.
Arthroscopic synovectomy can be performed as an independent procedure or as one of the stages of intra-articular surgery, for example, removal of tumors, menisci or joint mice (for Koenig's disease). The operation lasts no more than an hour.
Contraindications to synovectomy
Synovectomy is a safe procedure with a low risk of complications, such as joint infection or bleeding into the joint cavity.
Contraindications to its implementation are advanced arthritis, which results in its significant destruction, and incorrect conservative treatment (the procedure is performed only after at least 6 months of ineffectiveness of the selected non-invasive treatment, depending on the disease).
Radioisotope synovectomy during pregnancy is absolutely contraindicated.
Vorobyova Marina
Neurologist of the highest qualification category (work experience 14 years), doctor of neurofunctional diagnostics (work experience 12 years); author of scientific publications on vertebroneurology; participant of scientific conferences on neurology and functional diagnostics of all-Russian and international significance.
Indications and contraindications
Synovectomy is prescribed in cases where pathological changes cannot be corrected conservatively. The purpose of this surgical intervention is to eliminate the synovium as a substrate for the development of inflammation and the production of exudate.
Indications for its implementation are damage to the knee joint due to rheumatoid arthritis, tuberculosis, benign formations in the joint, recurrent infectious synovitis resistant to therapeutic treatment, diffuse collagenosis leading to impaired mobility in the joint.
The intervention is contraindicated in patients with purulent lesions of the skin and subcutaneous fat at the site of surgery, articular ankylosis (immobility), and severe somatic diseases.
Joint arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive, low-traumatic method of performing joint surgery, which allows you to restore functionality and cure serious diseases with virtually no bloodshed and with the shortest rehabilitation. In addition, arthroscopy provides the most accurate diagnoses of joint diseases.
The most popular types of joint arthroscopy in Moscow
- Knee arthroscopy (meniscus arthroscopy). Most often, problems with the knees occur due to rupture of ligaments, as well as due to parts of the joints separated due to injury. Even a small fragment like this can cause severe pain. During the operation, the damage is eliminated.
- Arthroscopy of the shoulder joint. An injury such as a dislocated shoulder can have serious consequences and limit a person's movement. In addition, it may be congenital. During the operation "arthroscopy of the shoulder joint", the surgeon can, for example, sew together the cartilage.
- Arthroscopy of the hip joint is a surgical procedure that is as gentle as possible, minimally invasive, low-traumatic, allowing for serious operations. This operation is increasingly used in the treatment of various pathologies of the hip joint.
- Your doctor may recommend elbow arthroscopy for pain that does not respond to non-surgical treatment. Arthroscopic surgery is performed in cases where ligaments, tendons, cartilage and other soft tissue and bone structures inside the joints are damaged.
Preparation for arthroscopy
After a preliminary examination, the doctor will ask you to undergo an MRI, ultrasound, ECG, fluorography and radiography of the joint in two projections, as well as:
- take a blood test - general, biochemical, hepatitis and HIV;
- take a blood clotting test;
- take a urine test.
This is followed by a consultation with an anesthesiologist. Depending on the condition of the diseased joint, the doctor will choose local, spinal or general anesthesia.
How is arthroscopy performed - joint surgery or diagnostics?
Here is an example of knee arthroscopy:
- two small punctures are made on the knee;
- an arthroscope (microscopic camera) and a surgical instrument are inserted into the incisions;
- the image from the camera is transmitted to the screen, the surgeon clearly sees all the damage in magnification mode and carries out treatment.
Postoperative period and rehabilitation
Arthroscopy is good because the risk is minimal and recovery is very fast. The duration of rehabilitation may vary depending on the area being operated on and other individual characteristics.
Approximate recovery time after arthroscopy of the knee joint (meniscus):
- 1 day – in the hospital;
- until 6 days – dressings every other day and the ability to walk with a cane;
- after 7 days – removal of sutures, minimal load;
- after 21 days – restoration of working capacity;
- after 45 days – the opportunity to play sports.
12 reasons to undergo joint arthroscopy in Moscow at the Miracle Doctor clinic:
- highly qualified specialists with more than 20 years of experience;
- minimal invasiveness of the operation;
- ideal accuracy of diagnosis;
- high rates of successful recovery after arthroscopy;
- minimum rehabilitation period - after 2-3 weeks you will return to your normal rhythm of life;
- quick preparation for surgery;
- operating rooms equipped with innovative equipment necessary for joint arthroscopy;
- prices for arthroscopy in Moscow are significantly lower than similar offers (from 13,200 rubles for diagnostic arthroscopy and from 22,000 rubles for surgical);
- comfortable day and 24-hour hospitals;
- a full range of possibilities for a speedy recovery - massage, acupuncture, UVT, exercise therapy, etc.;
- unconditional improvement in joint condition;
- almost no scars after healing.
Make an appointment with our surgeons, traumatologists and orthopedists! Their magical hands will put your joints in perfect order!
Synovectomy of the knee joint: what is it? The essence of the procedure
Today's:
- Recovery time from coronavirus. Stages of coronavirus disease
- What do dairy products belong to? Dairy products
- Beauty and health of a modern woman: magical recipes. Recipes for beauty and health.
- Eating right and wrong. Consequences of poor nutrition
- Sports nutrition zma, what is it. Sports nutrition ZMA: properties, method of application, effectiveness, reviews
- Pulse oximeter instructions for use. Instructions for use
- How does the weather affect a person’s well-being today? Changes in well-being with increasing atmospheric pressure
- Synovectomy of the knee joint: what is it? The essence of the procedure
- Synovectomy of the knee joint rehabilitation. Features of synovectomy of the knee joint
- What is the method
- Recovery and aftermath
- Open synovectomy of the knee joint. Synovectomy
- How is a synovectomy performed?
- Video arthroscopy of the knee joint
Indications for use
Other operations are also performed on the knee joint, such as arthrotomy, resection, and necrectomy. Synovectomy is most often complemented by arthrotomy.
The tissues of the joint membrane grow as a result of constant injuries, and therefore athletes whose knees bear the load often undergo this surgical intervention. Arthroscopic synovectomy is also performed for chronic low-grade inflammation, which cannot be treated with conservative methods and causes proliferation of the synovial environment. Diseases that can cause this process include:
- tuberculosis;
- gonorrhea;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- pigmented villonodular synovitis.