Knee arthroplasty is a modern method of surgical treatment of the knee using high technology. In some cases, when a person suffers from pain in this area and is severely limited in mobility due to knee pathologies, knee replacement surgery becomes the only effective solution for improving the quality of life and getting rid of pain.
Indications
Knee replacement surgery is called arthroplasty. Like any other serious invasion, it is carried out only when indicated.
The latter include:
- severe limitations in knee mobility due to wear and tear or injury;
- severe pain in the knee area, felt even in a stationary position;
- irreversible changes in the joint caused by osteoarthritis;
- knee damage as a result of injury;
- deformations;
- diagnosed death of bone tissue as a complication of impaired blood supply;
- deformations or destruction resulting from a number of diseases (gout, rheumatoid arthritis, hemophilia);
- disorders that provoke abnormal bone growth of the lower limb.
Installation of a knee joint prosthesis is an operation of a fairly high level of complexity.
This is a radical treatment method. Replacement is usually done if the disease progresses despite best efforts with therapy.
Recommendations for the home
The following are some recommendations that will make your return home easier during the rehabilitation process.
- Firmly fixed grab bars in the bathroom or shower.
- Strong handrails along all stairs.
- A stable chair with a durable, high seat, a strong back, two armrests, and a footrest.
- High toilet seat.
- A stable bench in the shower or a chair in the bathroom.
- Removing loose carpets and electrical wires from areas where you walk.
Knee replacement surgeries
Knee replacement can be done entirely (total) or partially. In the first case, the endoprosthesis replaces both parts of the joint, in the second - only one of its sides (less time in the hospital, better results in terms of restoring mobility, surgery is sufficient for approximately 25% of patients with osteoarthritis).
There are alternatives to arthroplasty, but practice shows that in the long term their results are inferior to knee replacement . Alternative treatments include:
- Osteotomy is an operation to straighten the leg bone so that the load shifts from the damaged part of the knee to the healthy one.
- Mosaicplasty is the transfer of healthy hard cartilage tissue along with the underlying bone (partially) from another part of the knee to the affected area in order to restore it.
- Arthroscopy - washing and treating the affected area to remove pathological formations from pieces of bone and cartilage.
Preventive measures after endoprosthetics
In order for the rehabilitation period after endoprosthetics to be successful, you must strictly follow all the doctor’s instructions. First of all, return to physical activity as quickly as possible. Gradually begin to sit down, then stand up, go up and down the stairs. Strong physical activity will help avoid swelling and congestion, as well as the formation of blood clots. Yes, it is not so easy to overcome postoperative weakness, but if you distribute the load wisely, follow the prescribed diet during this period, and take vitamins, then the recovery will be painless.
If medications are prescribed, they must be taken strictly according to the schedule, without skipping the appointment time. The same applies to medical procedures.
UVT will help speed up the rehabilitation process after endoprosthetics. In the Health Plus network of clinics, this procedure is carried out by highly professional doctors using the latest Swiss equipment, which allows the prescribed technique to be performed as accurately as possible. At the same time, prices for UVT therapy in Health Plus clinics are quite affordable, which makes this treatment method accessible to almost all segments of the population. If you care about your health, consider visiting our medical center.
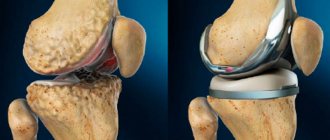
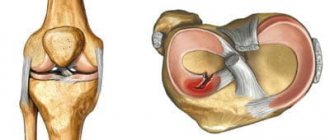
Knee endoprosthesis
What is a knee prosthesis? This is a complex design that follows the anatomy and dimensions of the joint being replaced. In other words, an endoprosthesis is the same knee joint, only artificial.
Today, many companies offer a wide range of knee and hip prostheses of various types and configurations. Their designs are constantly being improved to extend their service life after installation and increase the likelihood of normal healing in the knee.
The specific type of prosthesis is selected for each clinical case individually. Only a qualified specialist, after diagnosis and examination, can decide which knee joint prostheses are suitable for restoring the mobility of the patient’s lower limb.
Moreover, all modern endoprostheses (Diamond, Freedom, Lotus, Optimus, Oprtma, Titan) must meet a number of general requirements, including:
- biocompatibility (lack of rejection by the natural tissues of the knee and allergic reactions to the implanted knee joint endoprosthesis );
- load capacity (not lower than that of a real joint);
- the ability to maintain its original shape (during the entire service life, the prosthesis and its components should not be deformed);
- sufficient functionality (knee joint replacement is carried out, among other things, with the aim of restoring normal mobility; accordingly, the endoprosthesis must provide a good range of motion in the lower limb);
- anatomical shape (the knee joint prosthesis must repeat the structural features of the prototype, correspond to the natural dimensions and bends of the leg bone).
Tibial insert FREEDOM
More details
All knee replacements
Classification of endoprostheses
Materials for the manufacture of a knee joint prosthesis to replace the latter: ceramics, metal alloys, polyethylene. Depending on the design features, endoprostheses are divided into models with a movable and fixed platform.
Prostheses with a movable platform have an insert that can rotate in the metal part. This gives additional amplitude when moving the knee after surgery in the medial, lateral direction. In endoprostheses with a fixed platform, the elements - part of the tibial element and the metal component - are firmly connected to each other.
Another classification divides knee replacements into 3 types.
- Unilateral or unicondylar endoprosthesis. It is used for partial replacement of the knee joint in its upper part (prosthetic replacement of an area on one of the femoral condyles).
- Total or bilateral knee replacement (usually metal). Used to replace both parts of the joint (both femoral condyles are covered). The design of such an endoprosthesis differs from the unicondylar one in that it has more powerful attachments to the bone and increased width.
- Total endoprosthesis with axial stabilization. It is also used in total knee replacement operations, when its parts (upper and lower) are fixed with long pins along the longitudinal axes of the femur and tibia. Pins for secure fixation are driven into the space filled with bone marrow (medullary cavity).
Another sign of the classification of knee prostheses is the method of their fixation. There are 2 options: structures installed with cement and cementless methods. In the first case, when replacing a knee joint, its artificial analogue is stabilized (fixed) with quick-curing medical cement. With the cementless method, fixation is carried out as bone tissue grows into the implant.
Cemented knee joint prostheses are more reliable and versatile (used in any type of replacement surgery). An endoprosthesis for cementless installation has a special surface - porous, textured (it provides the opportunity for bone to grow into the implant).
Physical therapy, massage, physiotherapy, manipulation
Session with a physical therapy and sports medicine doctor/rehabilitation specialist (movement therapy/physical therapy/physiotherapy/massage/manual techniques). 60 min. 3 800 Session with a physical therapy and sports medicine doctor/rehabilitation specialist (movement therapy/physical therapy/physiotherapy/massage/manual techniques). 30 min.2 00016 rehabilitation sessions (motor therapy/physical therapy/physiotherapy/massage/manual techniques) - 5% discount57 760Massage session (massage/manual techniques/manual lymphatic drainage/joint mobilizations and other manual techniques)3 600Shock wave therapy (1 zone)2 700 Physiotherapy session (electrical stimulation/ultrasound therapy)2 000How is the operation performed?
Knee replacement surgery can be performed either under general anesthesia (more often) or under spinal/epidural anesthesia (less often). Takes 1–3 hours. Progress of the procedure:
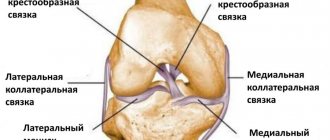
- an incision is made in the front of the knee (the surgeon opens the kneecap and displaces it to gain access to the tissues of the joint located behind it);
- removal of damaged tissue (femoral head, tibia);
- measuring bones and preparing the prosthesis (the dimensions must be kept extremely accurately);
- cleaning the ends of the bone and installing an endoprosthesis;
- replacement of a section of femoral bone tissue with a curved metal element;
- the end of the tibia is replaced with a plate (also metal, but flat);
- installation of a plastic gasket between the elements of the knee prosthesis (it replaces the cartilage necessary to reduce friction during movements);
- replacing the back of the kneecap if necessary;
- applying sutures or clamps and a bandage (sometimes it is replaced with a splint to fix the limb in a stationary position).
Rehabilitation
After knee replacement, the patient remains under observation (in the hospital) for 3–5 days. During this time, he undergoes a special course of exercises (physiotherapy to strengthen the knee).
Features of the rehabilitation period:
- swelling of the feet and legs is likely;
- movement - with the help of special means (metal frame or crutches);
- classes can be carried out on a simulator for passive movement (the patient remains in bed, the leg is fixed in an elevated position, and a special support makes movements of the knee, which improves its blood supply and helps reduce swelling);
- There may be noticeable discomfort when walking and making leg movements (this is normal).
Complete rehabilitation after knee replacement can take up to 2 years, but the patient can often move independently without special aids after 6 weeks. And after 2 months, many are already driving vehicles.
The first stage of postoperative recovery.
Rehabilitation measures begin a few hours after the end of the anesthesia and, if the state of health allows, then the next day the doctor allows the patient to get up. At the initial stage, attention is focused on drug therapy, swelling removal, and correct leg position. While in the hospital, physiotherapy (magnetic therapy, ultrasound, etc.) is prescribed. It is recommended to start with breathing exercises on your own. A day or two after surgery on the lower extremities, simple movements are allowed - sitting, standing and walking on crutches. In this case, leaning on the operated leg is strictly prohibited. All exercises are performed in a supine position with minimal load and may include muscle tension and relaxation, flexion and extension of the foot, and myofascial release.