01.12.2020
Tendinitis is an inflammation that affects tendon tissue. The development of inflammation can occur in any part of the body, and if left untreated, it can become chronic, which makes the disease serious.
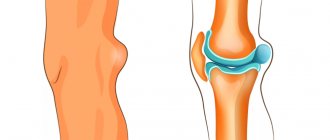
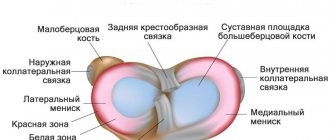
Knee tendonitis is characterized by inflammation of the tendons in the knee area. The knee joint consists of three parts:
- hips;
- tibia;
- patella
A powerful tendon is attached to the patella from the thigh muscles. It is constantly exposed to physical stress during sports, and therefore is at constant risk of microtrauma.
Knee tendonitis most often affects the patellar ligament. This inflammation is considered to be an occupational disease of athletes. Moreover, according to research in the field of sports medicine, overweight men are more likely to have knee joint damage than others.
Causes
If the load on muscles and ligaments during active sports training is so strong that the muscles and tendons do not have time to rest and restore micro-damage caused by stress, then they are destroyed - a so-called chronic (fatigue) injury is formed.
The most common of these injuries is tendinosis - progressive dystrophy, areas of degeneration in the tendon area.
The most common causes of tendinosis:
- microtrauma of tendons,
- excessive, increased motor load on the tendons.
The result is the formation of areas of necrosis, fatty degeneration of tendons and cartilage, and deposition of calcium salts. As the process progresses, the tendon ossifies, loses elasticity and leads to dystrophy and inflammation.
Tendinosis is evidence of excessive load on these muscles, very hard training.
Causes of knee tendinitis
As a rule, knee tendonitis begins to develop in professional athletes and people over forty years of age. It is excessive physical activity and age that increase the likelihood of inflammation in the knee joint.
Jumping on hard surfaces is considered a trigger for knee tendonitis. Other factors predisposing to inflammation are:
- uncontrolled training order;
- shoes that cause discomfort when worn;
- joint injuries;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- foot pathology;
- poor posture;
- spinal injuries.
In the process of rheumatic, infectious or endocrine diseases, secondary tendonitis may develop.
Symptoms of tendinosis
Common symptoms of tendinosis include:
- pain during movement, which goes away with rest,
- passive movements of the limb are practically painless,
- palpation of the affected tendon is unpleasant, painful,
- it is compacted, redness is visible on the surface, an increase in temperature over the affected area,
- When moving, you can hear a crunching or crackling sound.
Depending on the location, there are characteristic features of tendinosis.
Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis)
- damage to the wrist extensors. In this case, pain occurs in the elbow area and radiates upward, into the shoulder, along its outer part and along the forearm. There may be weakness in the hand, difficulty in lifting cups, shaking hands or wringing out clothes.
Golfer's hand , baseball player's hand (medial epicondylitis)
– damage to the extensors and muscles that rotate the forearm. It manifests itself as pain in the inner part of the elbow, pain when bending the hand down, pressing on the hand.
Querwen's disease
– tendinosis of the tendons of the thumb, manifested by pain when extending and abducting the thumb. Pain when palpating the base of the thumb, as well as pain when connecting the pad of the thumb to the little finger.
Patellar tendinosis (jumper's knee)
– pain in the knee area, tendon swelling, swelling. Untreated tendinosis can cause patellar tendon avulsion.
Quadriceps tendinosis
resembles a patella problem, but usually occurs in older athletes.
Post-tibial tendinitis
with damage to the tibialis muscle it gives pain in the tendons, pain in the heel, in the arch of the foot. May lead to flat feet and heel spurs. The pain intensifies when running and carrying heavy objects.
Local lesions and symptoms of connective tissue formations
A similar picture emerges with tendonitis of the lateral collateral ligament. In terms of incidence, inflammation is equated to meniscus injury. The anomaly occurs:
- after a fall on the ski slope;
- with a direct blow to the leg;
- sharp twisting movements in the joint.
After an impact, the joint space opens and the collagen fibers are partially or completely torn. With strong drinking, the frontal cruciate fasciculus is damaged and tendinitis of the medial collateral ligament occurs. At the moment of impact, many people hear a click or squeak. The process is accompanied by bleeding into the cavity, hematoma and other classic signs.
Orthopedic surgeon Eduard Viktorovich Zhezherya comments:
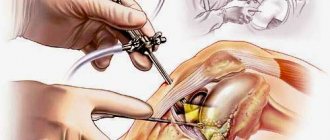
If no action is taken, the joint will lose stability. The leg will turn inward and sink with each turning movement. After a blow or fall in young people, the fibers usually remain intact, but the bundle comes off with a bone fragment. Surgery is indicated to treat tenosynovitis of the knee joint.
Problems with the external lateral and dorsal cruciate bundles occur less frequently. This happens when the leg is twisted, the shin is strongly deviated from the straight axis. In this case, the dislocation may be accompanied by a fracture of the fibula.
Treatment of tendinosis
Orthopedic traumatologists treat tendinosis.
Conservative or surgical therapy is prescribed. In the early stages, conservative measures of a primary and secondary nature are indicated.
The primary ones include:
- ensuring complete peace,
- cold and rest the tendon,
- applying tight or supportive bandages and placing the limb in an elevated position.
Secondary measures for conservative treatment of tendinosis include the use of:
- physical therapy and physiotherapy,
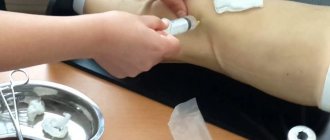
- drug injections,
- rehabilitation methods,
- anti-inflammatory drugs.
All methods of therapy at all stages are prescribed by a doctor; special bandages and bandages are used based on the specific location of the injury and type of injury. Sometimes it is necessary to use a special type of fixing bandages.
Anti-inflammatory gels and ointments are used in the first three days of injury, then they will be most effective.
For advanced tendinosis, surgical treatment is used - areas with altered tissues are excised, followed by plastic surgery to restore the tendon.
Diagnosis of tendinitis
Diagnosis begins with examination of the patient and analysis of the affected limb. This is usually done by an orthopedic traumatologist. Based on an analysis of the symptoms and causes of tendinitis, the doctor refers the patient for additional studies.
The examination includes the following procedures:
- X-ray of the knee joint - to exclude pathologies that have similar symptoms. In rare cases, images may show increased soft tissue volume.
- Ultrasound, MRI and CT - to visualize the knee joint and the tissues around it. The deformation of the structure, the location of tendon tears and the source of inflammation are determined.
- laboratory tests - general analysis of urine and blood. Signs of tendonitis appear in the blood if there is an infection, and if there is a metabolic disorder, the test may show increased levels of creatinine and uric acid.
Signs of tendinitis can easily be confused with other joint diseases, so diagnosing the inflammation yourself is not recommended.
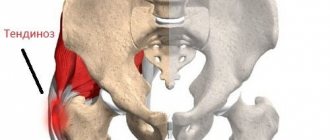
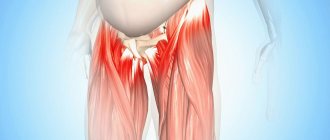
Tendinosis of the hip and thigh
Let's figure out what it is - tendinosis of the hip joint and what negative changes the disease can lead to if you do not pay attention to its development. Hip tendinosis often affects the abductor tendons. These are the gluteus minimus and medius muscles, the tendons of which are located in the area of the greater trochanter. Pain in this type of pathology is localized in the trochanteric area. In the absence of timely treatment, a destructive process begins in the area of cartilage tissue. After 12–18 months, deforming osteoarthritis of the hip joint may develop, which will result in the patient’s disability.
Tendinosis of the thigh muscles can damage the adductor muscle groups. This entails a violation of the ability to make rotational movements with the hip, move the leg to the side and bring it back. If the short tendon that attaches the iliopsoas muscle is affected, pain may occur on the inner thigh and lower abdomen.
The treatment is carried out by an orthopedist. Diagnosis includes ultrasound, x-ray and MRI examination.
Clinic
Clinical manifestations increase gradually and progress slowly. First, pain on the front surface of the knee occurs at peak loads. Further, dull, periodically paroxysmal pain bothers you during normal exercise, and quickly disappears after stopping training. Gradually, pain and discomfort progress, not disappearing after 4-8 hours of rest. As a result, a tear or rupture occurs in the pathologically altered tendon.
A characteristic clinical symptom of tendinitis is pain when palpating the tendon, when pressing on the tibial tuberosity, or patella. Sometimes local swelling and hyperemia of the adjacent skin, limited range of motion, and creaking and crunching when flexing and extending are characteristic.
Important! Untreated tendonitis reduces resistance to physical activity, interferes with training, and can put an end to a sports career.
Classification
Taking into account the location, the following types of tendinosis are known:
- Elbow joint. Tennis players and golfers are susceptible to pathology.
- Wrist joint. It is observed in patients whose work involves active motor activity of the wrists. Pain sensations are concentrated in the area of the injured finger and radiate to the forearm.
- In the ankle area. Often considered to be the result of frequent tendon strain or increased muscle tension in the lower leg.
- Knee joint. Pain sensations are formed in the patella, through which the femoral muscle is attached to the bones of the leg. Discomfort is formed in the lower part of the meniscus only during movement, and is absent in a calm state.
- Hip joint. It is noted in a situation of constant injury to the tendons connected to the hip joint. Unpleasant sensations appear in the pelvis during physical activity.
Tendinosis of the knee tendons
Damage to the meniscal ligament, which is connected to the quadriceps femoris tendon, is often recorded. In addition to the patellar ligament, the ligaments of the knee include lateral, posterior and intraarticular ligaments. Each of them is capable of undergoing dystrophy.
Tendinosis of the knee ligaments is called “jumper’s knee”, since a similar pathological process is often observed in athletes involved in athletics. Unpleasant sensations are concentrated below the patella, appear during walking, flexion and extension of the knee and are not observed in a calm state.
Stages of pathology development
The disease is conventionally divided into 4 stages, during which the symptoms intensify. A preliminary diagnosis is made based on these:
- At first, discomfort and pain occur only under high loads, and disappear after rest;
- Aching sensations appear in the popliteal ligament and around the knee joint after exercise and persist even at rest;
- Painful sensations occur both during activity and during rest, they can only be eliminated with the help of medications;
- The tissues become inflamed and swollen, and the knee tendon is destroyed.
Slow tissue inflammation or unexpected injury can lead to grade 2-3 tendinosis of the knee joint.
Prevention
Tendinosis in the pelvis, hips and other anatomical structures can be prevented by following certain preventive measures:
- before physical activity, you need to do exercises for a quarter of an hour, stretching your muscles and joints;
- the weight should be lifted without sudden movements, carefully;
- in case of muscle strain or joint damage, it is imperative to rest, apply a cool compress or apply a cooling ointment;
- after injury, sprains and bruises, excessive stress should be avoided for 15-20 days until the tissues are fully restored;
- physical activity should alternate with rest.
The rehabilitation period lasts up to 3 months or more, stretching techniques are used. The prognosis is mostly positive, but recurrence is likely.
Tendinosis involves pathological changes, the symptoms of which suggest dystrophic damage in the tendons of large muscles. The disease can also manifest itself as significant discomfort and impaired motor activity in the damaged joint. Discomfort is expressed during the period of movement, in a calm state it is virtually absent. Tendinosis is dangerous due to the separation of injured tendons from the place of attachment to the bone. Injury to any tendon is associated with pronounced painful symptoms and can significantly worsen the quality of life. In addition, therapy for the disease in question is long and difficult. Before treatment, you must consult with your doctor regarding possible contraindications.
Pathogenesis
As a rule, inflammation occurs at the site of attachment of the patellar ligament to the bone. With excessive loads, microdamages with local hemorrhages occur in the tendon tissue, which cause aseptic inflammation. The outcome of the inflammatory process is necrosis of collagen fibers and replacement with scar tissue.
A tendon with many scars is fragile, inelastic, and therefore vulnerable and easily injured again. New microbruises, aseptic inflammatory process and scar, long-term sluggish course, leads to degeneration and thinning of the tendon-ligamentous structures of the joint.
Complications and consequences
Without timely treatment, pathology can cause complications, which include:
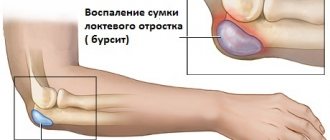
- Tenosynovitis. Acute or chronic inflammatory changes in the joint and nearby tissues, which is accompanied by intense pain.
- Ossifying tendinosis. It suggests the accumulation of salts of various metals in injured tissues, caused by impaired blood flow and lymph flow in this area.
- Tunnel syndrome. Compression of the nerve processes in the wrist due to significant swelling in the tissues.