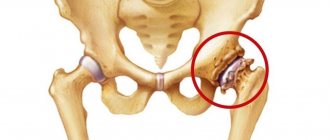
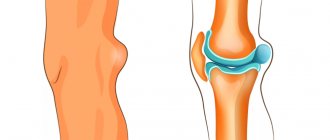
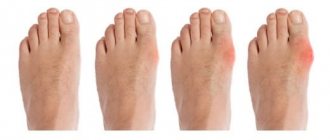
Gouty arthritis is a pathology that occurs against the background of a metabolic disease such as gout. It is known for its long course and often causes severe destructive processes in the joints.
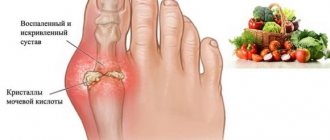
Symptoms of gouty arthritis occur due to the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints. These crystals not only destroy the tissue around it, but also do not bypass the hyaline cartilage. Infrequent pathologies such as:
- gouty arthritis of the ankle;
- gouty arthritis of the knee joint;
- gouty arthritis of the elbow joint.
The disease practically does not affect the pelvis and shoulders, but is fully manifested in other joints, on the fingers of the upper and lower extremities, most often on the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint of the foot. You can learn about the symptoms and undergo a course of treatment for gouty arthritis at the CELT multidisciplinary clinic.
At CELT you can get a consultation with a traumatologist-orthopedic specialist.
- Initial consultation – 3,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
Clinical manifestations
The first clinical manifestations of gouty arthritis are pronounced:
- pain localized in the area of the affected joint;
- redness of the skin;
- increased pain during movement;
- increase in body temperature.
After a few days, the above symptoms practically disappear, but others appear:
- subcutaneous formations in the area of the affected joint, which sometimes burst;
- increasing the duration of attacks and decreasing the time period between them.
At this stage, cartilage is destroyed and the disease becomes chronic. If treatment for gouty arthritis is not started at this stage, the following symptoms are observed:
- roughening of the skin in the area of the affected joints;
- restriction of movements of the arm or leg;
- deformations of bones and cartilage.
Examination for gouty arthritis:
- general blood test (possible leukocytosis, accelerated ESR);
- biochemical blood test (determination of C-reactive protein, fibrinogen, uric acid, etc.);
- urine analysis to determine the concentration of uric acid;
- detection of uric acid crystals in synovial fluid or tophi contents;
- X-ray examination of the osteoarticular system to identify bone defects - “punches”
- Ultrasound of joints - reveals the presence of inflammatory fluid in the joint, unevenness of bone structures due to the presence of marginal osteophytes, uneven thickness of bone structures due to the presence of tophi, visualization of uric acid crystals in the synovial fluid in the form of a “blizzard”;
IMPORTANT: It is more advisable to take tests during the interictal period and several times because A test for uric acid at the time of an attack will usually be negative, due to the fact that large amounts of uric acid accumulate in the joints!
Diagnostics
If gouty arthritis of the knee is suspected, the patient is referred for consultation to a urologist and rheumatologist. The primary diagnosis is made based on the patient’s complaints, external examination, and medical history. Differential diagnostics must be carried out to exclude arthritis, gonarthrosis, and injury to the joint. A general blood test is informative, the results of which do not change during the remission stage. During a gouty attack, there is an increase in the concentration of band neutrophils, which indicates the occurrence of an inflammatory process. The parameters of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate and the content of uric acid, alpha-2-globulin and fibrinogen in the blood increase.
To make a final diagnosis, an x-ray examination is prescribed. The resulting images clearly visualize signs of gonarthrosis of varying severity:
- foci of clearing in the epiphyseal region measuring 2-3 cm;
- destruction of the epiphyses of bones, their replacement with urate masses.
Puncture of the knee joint.
A puncture of the knee joint is performed to take a sample of synovial fluid. The results of microscopic analysis show the presence of crystals of sodium salts of uric acid. They are also found in the punctate of tophi. Patients are shown an ultrasound examination of the kidneys to identify deposited urate stones in them.
Clinical picture
Gout first affects the small joints, usually the phalanges of the fingers. If the patient does not seek medical help or does not follow medical recommendations, the disease spreads to large joints. Gout is often diagnosed in the ankle and knee joint, which leads to limitation of movement. The periarthrial form of the pathology is characterized by damage to the synovial membranes and tendons at the initial stage of development. Then, signs of gouty polyarthritis gradually begin to appear, affecting almost all joints of the legs:
- defiguration, stiffness of joints;
- deformation of articular tissues;
- proliferation of the edges of bone plates, formation of osteophytes;
- contracture (limitation of passive movements in the joint);
- crunching in the knee joint when flexing or extending, the intensity of which increases during movement;
- increasing sprains of fingers.
The development of gouty status is possible, especially against the background of constant relapses of the pathology. A person suffers from unabated exacerbations of arthritis of the knee joints. Mineral salts begin to be deposited in the paraarticular tissues, and a chronic inflammatory process develops. Severe attacks of gout reduce motor activity and lead to loss of performance.
If the patient does not consult a doctor to prescribe treatment, then after a few years specific symptoms of gout of the knee joint appear. Gouty nodules form in its cavity - deposits of crystals of uric acid salts in soft tissues, usually in the subcutaneous tissue. When the disease worsens, the tophi are opened, and their whitish contents are brought out. At such moments, the severity of pain decreases somewhat, but the risk of tissue infection by pathogenic bacteria or pathogenic fungi increases. After the wounds heal, urates again begin to be deposited near the knee joint.
Crystallization of uric acid salts also occurs in the kidney structures, disrupting the processes of filtration, concentration and excretion of urine. This provokes frequent, sharp jumps in blood pressure, the formation of edema, and painful renal colic. There have been cases of gout affecting the heart muscle.
Treatment of gout of the knee joint
During an acute attack of gout, it is advisable to immediately seek medical help: this will allow a correct diagnosis. The easiest option would be to visit your local physician, but it is much better to consult an experienced rheumatologist.
During the diagnosis, the following studies are carried out:
- lab tests;
- X-ray;
- MRI;
- CT;
- joint puncture.
These tests allow you to determine the level of uric acid. X-ray, MRI and CT images show damage to bone and cartilage tissue, changes in the size of the joint space and other pathological changes. The treatment plan for knee gout depends on what symptoms the patient is experiencing. If tophi are present or the joint is severely damaged, surgery may be required. But in most cases, complex conservative treatment is indicated, and the development of a treatment plan often requires the participation of several specialists: a rheumatologist, an orthopedist, a cardiologist, a urologist and a nutritionist. The complex course of treatment includes medication, a therapeutic diet, exercise therapy and physiotherapeutic procedures.
The patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory and painkillers, as well as drugs to normalize metabolism, hormonal levels and urea levels. You may need to take diuretics and some other medications. Diet is necessary to reduce urea levels and normalize weight. Therapeutic gymnastics improves metabolic processes, helps reduce weight, promotes the proper functioning of joints, strengthens muscles, prevents tissue destruction and prevents the deposition of urates. Physiotherapy relieves pain and muscle strain, stops the development of inflammatory processes, promotes tissue regeneration and normalizes blood flow. If you suspect you have gout of the knee, contact any of the clinics in the Hello! network. A comprehensive examination using modern equipment will allow you to accurately determine the causes of swelling and pain. Once the diagnosis is established, an individual treatment plan will be developed with the participation of all necessary specialists. Experienced and highly qualified medical staff provide careful care for each patient. All clinics are located close to metro stations, which is important for visitors who have difficulty walking.
What kind of knee pain is there?
Acute knee pain occurs suddenly and is most often caused by external influences (injuries) or an acute inflammatory process. It can be cutting, stabbing or bursting, depending on the cause and mechanism of the lesion.
Chronic knee pain occurs gradually and persists for more than 3 months. The cause is most often degenerative diseases or chronic inflammatory processes. It can be aching or bursting. During physical activity, the pain intensifies. In some diseases, it occurs during the first steps, then gradually subsides.
Pain may be accompanied by:
- swelling of the joint;
- redness;
- crunch;
- limited mobility;
- joint deformation.
Why do my knees hurt?
The most common cause of acute knee pain on one side is injury. Damage can occur during sports, unsuccessful falls, or sudden movements. Common types of knee injuries:
- bruise – accompanied by pain, increase in size, bruising;
- ligament rupture due to sudden twisting of the leg or thigh;
- meniscus tear – occurs under heavy loads, impacts, falls;
- fractures – accompanied by unbearable pain and pathological mobility of the joint;
- dislocations of the knee joint and patella;
- cartilage damage – a torn fragment of tissue in the joint cavity causes severe pain.
An experienced orthopedist can diagnose some types of injuries based on the appearance of the joints.
Another common cause of knee pain is diseases of the joints and periarticular tissues:
- arthritis – inflammation of the joint, can be infectious, post-traumatic, autoimmune, metabolic;
- bursitis - inflammation of the joint capsule, sometimes with accumulation of fluid in it;
- periarthritis - damage to muscles, tendons and ligaments in the joint area;
- osteomyelitis – inflammation of the bones;
- chondropathy – degenerative diseases of articular cartilage;
- tumors and cysts - compress adjacent tissues, causing pain and impairing function;
- Osteoporosis is a metabolic disorder in which calcium is washed out of bone tissue.
Knee pain may be a sign of a neurological disorder:
- neuritis is an inflammatory disease of the peripheral nerves.
- pinched nerves – can occur due to trauma, compression by a tumor.
One of the causes of joint pain may be depression and other psychological problems (so-called psychosomatic disorders).
Causes
Louis XIV, Dickens, Turgenev, Renoir, Beethoven, Cromwell, Caesar, Macedonian and many other famous writers, scientists, and composers suffered from gouty arthritis, “the disease of kings and geniuses.” In 1927, G. Ellis even wrote a book where he tried to explain genius by the presence of gouty joint damage. Indeed, there is some kind of relationship. With gout, the level of bioactive compounds similar in action to theobromine, a powerful stimulator of cerebral circulation, increases in the systemic circulation.
In the Middle Ages, representatives of high classes - aristocrats, merchants, landowners - more often suffered from this pathology. Every day they consumed large amounts of fatty foods, washed down with alcoholic beverages of various strengths. Along with the products, many purine compounds came in - sources of the formation of uric acid, and then its salts. This compound is synthesized in the body itself as a result of biochemical reactions between nucleotides. In a person leading a healthy lifestyle, the processes of uric acid synthesis are balanced. The body receives as many purine bases as necessary for full metabolism, and the excess is quickly eliminated. But under the influence of negative factors, this balance is disrupted, and the processes of crystallization of harmful salts in the knees are accelerated. The causes of hyperuricemia are:
- increased consumption of foods containing purine bases;
- increased biosynthesis of purines in the body;
- intensification of the processes of decomposition of nucleoside phosphates;
- a combination of these factors.
The deposition of uric acid crystals in the knee joints can be provoked by taking cyclosporines, diuretics, acetylsalicylic acid, and some antibiotics. Excess weight, diabetes mellitus, intoxication with lead compounds, and coronary heart disease predispose to the development of gouty arthritis.
Excess weight provokes the development of gout.
There have been cases of disturbances in the biosynthesis of uric acid after organ transplantation, administration of contrast agents, surgical interventions, and injuries. Joint pathology sometimes occurs against the background of metabolic syndrome, chronic renal failure, and psoriasis.