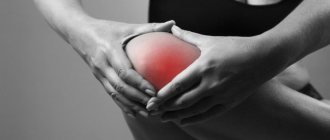
The knee joint rightfully occupies the first place in terms of injury among the joints of the human body. It is no coincidence that he is the leader in the number of damages. It is the knee area that accounts for the overwhelming majority of the static load when moving and carrying heavy loads.
This leads to the fact that people with increased body weight (Quetelet index more than 25) have a significantly higher risk of getting a knee injury.
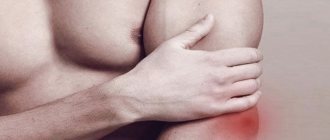
The overwhelming majority of damage to this area consists of bruises of the kneecap, varying in intensity. It is this type of injury that we will talk about in this article.
Injury
What is a bruise and what are the mechanisms of its occurrence?
A bruise is a closed injury to soft tissues while maintaining their integrity and anatomical structure.
However, in clinical practice, the term bruise does not refer to the clinical manifestation of the pathology itself, but rather to the mechanism of its occurrence.
In the vast majority of cases, exposure to a traumatic factor occurs at home or during sports training. A bruise occurs after a fall on the knee, a direct blow to any surface, or after severe compression of soft tissues, for example, in a car accident.
What tests are needed to determine the diagnosis?
No treatment will be prescribed without testing, examination and diagnosis. Therefore, as soon as you walk into the doctor's office, you will be given:
- The question was asked about what happened and when, what treatment was undertaken by you personally, what worries you.
- An examination was carried out, during which the doctor will palpate to determine whether there is internal bleeding, a lump, swelling and redness.
- An ultrasound of the joint was prescribed.
- An x-ray examination was prescribed.
- After receiving all these results, the doctor prescribes treatment.
Classification
The most popular classification among practicing doctors is the ICD-10 classification. The ICD is an international classification of diseases revised in 2010, which systematizes into categories all possible pathologies of the human body.
In the ICD-10 system, a contusion of the knee joint occupies position S80. Further in this classification other superficial injuries of the lower leg are presented.
In addition, knee bruises are divided into two groups:
- Fluid under the skin on the knee after a bruise or injury: symptoms, first aid and treatment
- Complete – in which damage occurs to all components of the joint.
- Partial. Here, due to the damaging agent in isolation: either ligaments, or soft tissues, or muscles and their tendons are injured.
A complete bruise may be accompanied by more severe complications. For example, such as a fracture, dislocation, subluxation, sprain of the knee joint and even separation of the kneecap.
Recovery phase
- If there is a normal bruise, then rehabilitation will take 12 days.
- If hemarthrosis is present, then about two months.
- In particularly difficult cases, mobility is restored after a year.
Experts recommend that 10 days after the injury occurs, start doing therapeutic exercises or swimming. These exercises will speed up the recovery process.
Now you know what a knee injury is. As you can see, without proper attention, possible consequences cannot be avoided. At the slightest suspicion of a bruise, provide assistance to the child and immediately contact the emergency room for advice from a specialist. Strictly follow your doctor's recommendations to avoid unwanted complications.
Clinic
How does a severe knee bruise manifest itself, what symptoms come to the fore here, and how long can the pain syndrome last after the injury?
The severity of clinical symptoms directly depends on several factors: the strength of the traumatic factor, the area of the injured surface, the angle at which the blow was struck and the presence of the accompanying complications listed above.
Symptoms of a bruise are caused by the lightning development of the inflammatory process, which inherently includes 5 components:
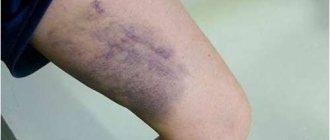
- Rubor – redness or hyperemia in the joint area. Sometimes a pronounced hematoma with a bluish tint, due to the outpouring of blood from the vascular bed into the joint cavity.
- Tumor - swelling in the area of bruise due to the presence of blood or serous fluid in the joint capsules or its cavity.
- Calor is a local increase in joint temperature due to a sudden rush of blood into the area of the damaged area.
- Dolor – presence of severe pain syndrome.
- Functio laesa is a violation of the normal function of the joint and the inability to make full movements.
A severe bruise of the knee joint is always distinguished by the presence of a pronounced hematoma. This is a symptom of the accumulation of copious amounts of blood, which is visible to the naked eye. As a rule, hemarthrosis is accompanied by throbbing pain, which intensifies with any movement in the knee area.
It should be noted that a history of episodes of hemorrhage into the cavity of the knee joint is a risk factor for the development of degenerative pathology such as osteoarthritis. This disease appears after 40 years of age and is characterized by a sluggish and slowly progressive process, as a result of which persistent dysfunction and even the development of disability are possible. Often in these cases they resort to joint replacement.
In addition, severe bruising of the knee joint is often accompanied by rupture of the intraknee ligaments and even separation of the patella.
Severance of the kneecap and rupture of the ligaments are an absolute indication for surgical treatment.
Drugs with venotonic action
It is advisable to apply a venotonic ointment to the site of the injury as soon as possible, preferably immediately after the injury. This will prevent bruising, swelling and redness. Such drugs are available in the form of gels, ointments and creams that have a pronounced antithrombotic effect.
Venotonics contain active anticoagulant substances that effectively thin the blood, preventing the formation of blood clots in the bruised area of the joint. Medicines activate lymph outflow, being considered a good prevention of varicose veins.
Advertising:
Effective venotonics include:
- Heparin;
- Lyoton 1000;
- Troxerutin;
- Troxevasin;
- Hepatrombin;
- Lavenum.
The main active substances in these drugs are heparin and troxerutin. The first normalizes plasma coagulability and activates blood circulation. The second has a broader pharmacological effect. It not only prevents the formation of blood clots, but also strengthens the walls of blood vessels, preventing their permeability and fragility. Troxerutin is used as a prophylaxis for varicose veins.
Treatment
It is important, even at the pre-hospital stage, when the first symptoms appear, to provide the necessary first aid, the purpose of which is not only to eliminate the pain syndrome (which is also a very important component), but also to prevent possible complications.
- Bruise of the elbow joint - symptoms, causes, treatment and consequences
First aid
The first thing you need to do is call an ambulance. Before specialists arrive, you should apply a cold compress to the bruised area, which will not only reduce the intensity of the pain syndrome, but also reduce the severity of signs of inflammation and blood flow to the damaged area. This will reduce the size of the hematoma and swelling.
At the same time, it is necessary to ensure complete immobilization of the injured limb, that is, create conditions for complete immobilization in the joint. It is not advisable to apply splints and tight bandages if there is no bleeding. It is enough to place the injured leg on a hard and flat surface.
Specialized assistance
A doctor or emergency medical technician will numb the patient with medications and even narcotic analgesics for severe pain. This is, for example, Ketonal, Ketanov or Tramadol.
As a rule, these drugs are used parenterally, that is, in the form of intravenous or intramuscular injections, which ensure the achievement of an analgesic effect in the shortest possible time.
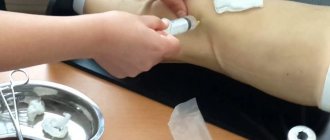
Already in a medical institution, specialized and high-tech medical care is provided. These concepts in this case imply puncture of the joint for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. During this procedure, which is performed under local anesthesia, it is possible to pump out the fluid accumulated in the joint cavity. How much fluid can be removed from the cavity of the knee joint? Typically, the volume of evacuated fluid during arthroscopy is 50–150 ml.
After the fluid is sucked out, Hydrocortisone is injected into the joint cavity, a drug that prevents the development of osteoarthritis and can effectively relieve pain.
When the kneecap is torn off, or when ligaments and tendons are torn, they resort to surgery to suturing these structures. Rehabilitation after such operations can take from a month to six months.
How many days can a joint hurt after a bruise? The duration of pain after a severe injury ranges from several days to two or even three weeks. It all depends on the volume and nature of the damage.
What to do if you are injured
Children regularly experience injuries such as knee bruises. Often such an injury in this age category is accompanied by damage to the integrity of the skin (wounds, abrasions, etc.). What to do if a child has a bruised knee? First aid provided to the child: treat the bruise site with an antiseptic drug to prevent infection, and bandage it.
Lay down, immobilize the leg, place a pillow or folded towel under the knee. If there is no hyperedema, severe hematomas can be treated at home (it is advisable to consult a doctor).
- Knee pain after a fall or old injury
First aid for a knee injury at home for adults:
- Apply cold to the joint
- Lay the victim down, the leg should be slightly higher than the level of the body,
- bandage with an elastic bandage.
At home, you can apply various painkillers and anti-inflammatory creams and gels and at first try to limit the load on the injured leg.
Note! If, after bruising your knee, after providing first aid, your leg swells greatly, you should contact a traumatologist.
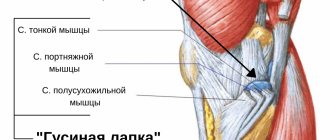
A severe knee bruise is a closed injury, an injury to one of the largest joints in the human body. The knee joint belongs to the group of condylar articulatio, which is how joints are called in Latin. The knee joint is formed by bulges or condyles that arise from the femur, and the structure of the joint also includes the patella and the top of the tibia.
They regulate the dynamic load on the knee by the meniscus - internal and external (lateral). The meniscus is a crescent-shaped cartilage tissue that is located between the femur and tibia bones. The motor activity of the knee is impossible without the ligaments that connect the bones and also help absorb and stabilize the load. Ligaments, in turn, are divided into types:
- Cavity ligaments (located in the articular cavity) - the anterior one, which prevents the tibia from moving forward, and the posterior one, which keeps the tibia from moving backward.
- Collateral external ligament (lateral fibular).
- Collateral internal (lateral tibial).
All bones involved in the functioning of the knee are covered with cartilage tissue, which allows the joint to slide. Inside, the joint is lined with a synovial membrane that secretes lubricant; outside, the joint is enclosed in a specific capsule-bag. The knee joint provides multi-axial movement - rotational and linear. Since the knee is directly responsible for bending the leg, any injury to it, in addition to causing pain, also carries the risk of immobilization.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Advertising:
The first thing to do to eliminate sharp pain in the knee is to apply an ointment from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which is used as a first aid remedy. Such medicines are characterized by rapid action - the active components penetrate into the deep layers of tissue, relieve swelling and pain, and stop the further development of inflammation.
Effective anti-inflammatory drugs:
- Butadion;
- Indomethacin;
- Diclofenac;
- Voltaren;
- Ortofen;
- Finalgel;
- Ketorol;
- Ketoprofen;
- Piroxicam.
Anti-inflammatory ointments begin to act very quickly - within 20-30 minutes after application they relieve pain, relieve muscle tension, reduce swelling and restore joint mobility.
Such drugs improve tissue nutrition, accelerating their recovery after injury.
When using these medications, existing contraindications must be taken into account. Most of these drugs are prohibited for use during pregnancy and breastfeeding, with open wounds on the skin and allergic intolerance.
Severe knee bruise, types of injuries
Simple bruise
Joint contusion is diagnosed by ruling out more serious injuries to the knee. Most often, blows to the straight front surface of the knee or to its lateral part result in a simple bruise. If the blow is tangential and is accompanied by rotation of the hip, as in a fall or jump from a height, the ligaments or menisci are most often injured. Both bruises and other types of knee injuries are accompanied by swelling and pain, so only an x-ray can differentiate the damage.
If the X-ray does not reveal serious damage and the bruise is confirmed, the knee is fixed (immobilized) with a plaster splint for at least two weeks. It also happens that a severe bruise of the knee is accompanied by significant swelling, which indicates possible hemarthrosis - hemorrhage into the joint cavity. In such cases, the accumulated exudate is removed using puncture; after 7-10 days, physiotherapy and gentle therapeutic exercises are indicated. Absorbable ointments and gels based on heparin, horse chestnut extract or containing diclofenac are also well treated for severe knee bruises. The bruise of the knee joint goes away within a month.
Hemarthrosis
A severe bruise of the knee may have a complication in the form of hemarthrosis - minor or extensive hemorrhage into the joint cavity. Clinical manifestations appear very quickly, within a maximum of two hours - intense pain in the knee area and its severe enlargement, swelling. In addition, with hemarthrosis it is almost impossible to step on the injured leg. Hemorrhage, as a rule, continues for a long time, stretching the joint capsule. If you palpate a severe knee bruise, you can feel the movement of accumulated exudate under the skin (fluctuation). The skin of the knee joint stretches, often acquires a bluish tint, the general condition is much more severe than with a simple bruise, and the temperature may rise.
If the patient is not helped in a timely manner, blood begins to saturate the cartilage tissue, forming clots inside it, which leads to inflammatory and degenerative changes in the articular cartilage. As a diagnostic measure, a two-projection x-ray is indicated; in addition, hemarthrosis is easily determined using the patella balloting test (“drowning” of the patella into the exudate and “floating up” on its own). A puncture is required, which aspirates the accumulated fluid, then the knee is fixed with a splint or a pressure bandage. The fixation is removed no earlier than after three weeks. Throughout the course of treatment, the use of chondroprotectors and anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs is indicated. This type of bruise goes away after one and a half to two months, if it is not accompanied by a torn meniscus or sprained ligaments.
Meniscus injury
Injury to the menisci is also one of the common phenomena accompanying a severe knee injury. A severe knee bruise may initially hurt quite a lot, but the person does not lose the ability to move. Only periodic difficulties in bending or straightening the leg, blockage of the knee when climbing stairs and increasing swelling can force the patient to see a doctor. The pain becomes diffuse (“diffused” pain), and internal hemorrhage develops into the capsule cavity – hemarthrosis. Severe knee contusion with suspected meniscal injury is diagnosed using orthopedic tests involving axial loading.
The joint space is also palpated; a characteristic sign of meniscus damage is the presence of isolated situational pain. The diagnosis is clarified using aneumoartography, a special x-ray examination in which air is introduced into the joint cavity. The choice of treatment method depends on the severity of the injury; regular punctures are possible; when they are not effective, surgery is performed. Also prescribed are phonophoresis with the application of hydrocortisone, therapeutic applications to the joint, and gentle rehabilitation exercises.
A severe knee bruise, although it is one of the most common injuries, both domestic and professional, and sports, is a fairly serious injury that can lead to deformation of the articular cartilage, and therefore to loss of physical activity. Therefore, a bruise that does not go away within five to seven days with increasing swelling of the knee should be treated with the help of professionals, that is, trauma surgeons and orthopedists.
Adults and children often suffer different injuries. A knee injury is the most common one. It is so familiar that few people take it seriously. Lack of timely treatment then manifests itself as unpleasant consequences in the form of knee immobility or aching pain.
Diagnostics
A preliminary diagnosis is established by external signs - swelling, bruising.
Further research is needed to rule out more severe injuries that sometimes accompany a knee injury from a fall.
To confirm the diagnosis, the traumatologist may prescribe:
- X-ray – it is used to exclude fractures and cracks of bones.
- MRI, ultrasound or arthroscopy - help to exclude rupture of ligaments, menisci, tendons, and damage to the joint capsule.
- Therapeutic and diagnostic puncture - extraction and analysis of intra-articular fluid for hemarthrosis, synovitis.
Arthroscopy of the knee joint. Click on the photo to see it clearly
A characteristic diagnostic sign of hemarthrosis is a floating kneecap (when a large or medium amount of fluid accumulates, it easily sinks and floats out of the joint).
The patella is located in the thickness of the tendon that extends the tibia. This tendon is formed by the fusion of four muscles on the front of the thigh - the so-called quadriceps muscle. Below the patella begins the patellar ligament, which is attached to the front of the tibia (to the tibial tuberosity). Click on photo to enlarge
Knee injury: causes
Children injure their knees due to their natural restlessness, mobility and curiosity. Adults get bruises when actively involved in unsafe sports, on ice, during an accident or during careless movements. Therefore, the two main causes of bruises in this place are:
- an unfortunate fall on your leg;
- compression of the knee as a result of the mechanical impact of some objects.
The most unpleasant consequence of a bruise can be arthritis and other irreversible changes in tissues that destroy them and render them inoperable.
Characteristic manifestations
If a child hits his knee, one should not exclude the possibility of a bruise. The following manifestations may indicate that your baby actually has it:
- the appearance of swelling, both small in diameter and throughout the entire knee;
- limited mobility;
- painful sensations;
- change in skin color at the site of impact;
- pain when bending;
- the knee becomes hot to the touch;
The following signs may indicate that the meniscus has been damaged:
- severe swelling;
- intense pain;
- when you move your leg, clicks and crunches occur in the joint;
- the pain becomes constant;
- the joint becomes blocked.
How long does it take for a knee bruise to go away and how to treat it?
The knee is the most vulnerable part of the leg, so even a simple bruise should not be ignored. Rehabilitation after a moderate injury takes 2-3 weeks. The main thing is to start treatment immediately, while the bruise is fresh.
Primary care involves the following actions:
- Protection from unwanted load. No weight should be placed on the injured leg. Rest and rest again.
- Cooling. Ice reduces discomfort and reduces swelling. If a hematoma forms, it is very small. Under the influence of cold, small vessels narrow, so less blood comes out. If you don't have ice on hand, you can use an ice water bottle or frozen food.
- Anesthesia. If the victim cannot bear the pain, he should be offered analgin, ketanov or other medications.
- A pressure bandage made of an elastic bandage or scarf. It significantly reduces hemorrhage and tissue swelling. The leg is tightly bandaged in a relaxed and comfortable state for the patient.
After this, it is advisable to take the victim to a doctor so that he can determine the severity of the injury and provide secondary medical care.
We help on our own
Let's look at what to do before the ambulance arrives, which must be called immediately after the incident, or before visiting the emergency room on your own.
- The first thing you need to do is fix your leg. It is important that she is at rest. It is recommended to place the leg higher than the body in order to improve blood flow and reduce swelling on the knee, if any.
- Now you need to apply cold to the knee. It could be ice or some product from the freezer. Just don’t forget to wrap it with cloth first so that your baby doesn’t get a thermal burn.
- The child should be given a pain reliever, especially if the pain is too intense. This could be Nurofen, Panadol or children's Paracetamol.
- If the knee becomes contaminated after an impact, it is necessary to rinse it with running water and then treat it with peroxide and an antiseptic, such as iodine or chlorhexidine. Then you need to apply a bandage. This could be an elastic bandage.
I hurt my knee, what should I do and should I see a doctor?
Secondary therapy is carried out under the supervision of a physician. If a large hematoma has formed, the specialist will perform a puncture to suck out the accumulated blood. The procedure is not pleasant, but it helps to quickly remove discomfort and swelling. Most often, the doctor offers the patient local therapy:
- use of ointments;
- application of compresses;
- traditional medicine.
If no complications arise, after a week you can use physiotherapy, which has a beneficial effect on tissue regeneration. The last stage is physical therapy and special exercises that help develop the knee.
Fractures in the knee joint
Violation of the integrity of the patella is possible if the anterior part of the knee is damaged. In this case, acute pain syndrome occurs, problems with bending the leg, swelling of the soft tissues, and hemorrhage in the middle of the joint. Diagnosis is made using an X-ray of the knee. If the patella fracture is not displaced, then treatment is conservative. The leg is immobilized for 6 to 8 weeks. If there is displacement, surgical intervention is performed. During the rehabilitation period, physical therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures, massages, and pain relief are prescribed. Full recovery is observed within 2 - 3 months.
list
Ointments with a cooling effect
Advertising:
Cooling ointments have a local irritating effect. They effectively reduce pain, soothe and fight the further development of inflammation.
| Medicine | Active substance | Manufacturer | Average cost, rub |
| Gavkamen | Clove, camphor, eucalyptus, mint oil | Tula Pharmaceutical Factory LLC, Russia | 40-50 |
| Phloxal | Ofloxacin | LLC VALEANT, Russia | 130-170 |
| Olfen | Diclofenac | Mepha, Lda. (Switzerland) | 1600-1700 |
| Menovazin | Menthol, novocaine | LLC Hippocrates, Russia | 15-25 |
| Lidocaine | Lidocaine | LLC Biosintez, Russia | 25-40 |
Unlike ointments with a warming effect, cooling preparations can be applied to the site of the bruise already on the first day. They reduce swelling, relieve pain and prevent hematoma.