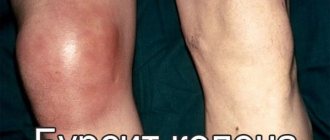
Symptoms of bursitis
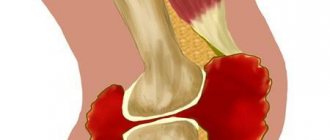
Bursitis is an acute inflammatory disease that manifests itself in inflammation of the synovial bursa of the joint.
Synovial bursae (bursae) are peculiar bags located in places where pressure is expected on a joint, for example, the knee, during physical activity.
Symptoms usually include the following inflammation:
- Soreness. The intensity is determined by the type of disease. Large joints
are more involved in movement, and pain in them will be more pronounced. The chronic stage is less painful. - Swelling and redness. Manifestations of inflammation may be accompanied by swelling, redness and a local increase in body temperature in the joint area.
- Problem with limb control. An advanced disease can cause dysfunction of the limb of the affected joint.
Treatment of bursitis
Treatment can be done conservatively or surgically.
For mild cases of the disease, the patient is observed on an outpatient basis. Treatment is carried out using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for external use.
The course takes 5-8 days, during which time the acute symptoms of the disease subside and the damaged area begins to recover.
In cases where the synovial bursa (bursa) is located deep or the symptoms of the disease are very severe, surgical intervention is used. Traditionally, it is performed using local anesthesia by puncturing the bursa, pumping out fluid and administering anti-inflammatory drugs.
If left untreated, the disease enters the chronic stage.
Types of bursitis
Bursitis is divided according to its form into chronic and acute. It can also be classified according to the location of the lesion.
Elbow bursitis
In the case of inflammation affecting the synovial bursa of the elbow joint, a person notices painful sensations that intensify during flexion and extension of the arm at the elbow, often radiating to the forearm or hand, movements are limited. At the site of inflammation, elastic compaction and swelling of the soft tissues are observed.
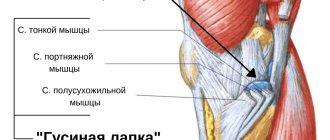
Bursitis of the knee joint
Symptoms directly depend on the form of the disease.
Patellar bursitis is characterized by pain in the anterior surface of the joint. The patient notes a feeling of stiffness while walking. Swelling, redness and a slight increase in local temperature are possible. Palpation is slightly painful; a soft elastic tumor formation is detected.
With popliteal aseptic, the patient notes moderate pain in the knee, which is recorded during prolonged standing or prolonged walking. The joint is slightly enlarged.
Anserine bursitis manifests itself as nagging pain in the joint when bending and straightening the knee, for example, while using stairs.
Symptoms of the purulent form include sharp pain, a feeling of fullness in the joint, and swelling. The patient exhibits symptoms of general intoxication: an increase in body temperature to 38-39°C, headache, weakness.
Bursitis of the shoulder joint
The main symptom of the disease is pain. Its intensity depends on the severity of the disease.
There are several types of inflammatory lesions of this joint:
- Subacromial (subdeltoid) appearance. The peculiarity of this form is the appearance of severe pain at the moment the arm is moved to the side; movement back and forth is not difficult.
- Subcoracoidal (calcified) bursitis manifests itself as severe pain when moving the shoulder back. In addition, there is a throbbing pain radiating to the neck and arm.
- Calcareous (stone) appearance. Pain, swelling and hyperemia are observed in the area of the affected joint.
- Subdeltoid. Features of this variety are swelling, hyperemia and severe pain in the shoulder and arm. Due to the nonspecificity of symptoms, it is difficult to make a primary diagnosis.
- Calculous bursitis is similar in manifestation to subdeltoid bursitis, differing in that the shoulder hurts much more than the arm.
- Subacromial. With this type, the patient has difficulty raising his arm above his head.
- Subcoracoid. Symptoms include swelling, a sharp and significant increase in body temperature, and pain that intensifies when you raise your arm or press on your shoulder.
Bursitis of the hip joint.
Middle-aged and older women most often come for diagnosis with suspected bursitis, the reason for this is the structural features of the female body. Other age groups, including men, may be at risk by leading a lifestyle that puts constant pressure on the femur.
The disease can be classified based on the location of the synovial bursa (bursa), in which inflammation occurs.
Trochanteric or acetabular bursitis is the most common form of the disease. Painful pulling or throbbing sensations in this form should occur on the outside of the thigh. The pain may radiate to the groin area, and this complicates the diagnosis.
With the iliopectineal form, pain is recorded in the groin area and on the inside of the thigh.
The sciatic variety is characterized by pain in the gluteal region.
Diagnostic procedure
If pain occurs in the area where the joint capsules are located, you should immediately consult a doctor. Diagnosis is carried out by a surgeon, traumatologist or orthopedist. They are the ones who treat bursitis. The first step in determining the presence of the disease is palpation of the affected area.
In some cases, an additional puncture of the joint capsule is performed to identify the type of pathology, the degree of bursitis, and to exclude purulent inflammation.
To confirm the diagnosis, the following is used:
- X-ray examination.
- CT.
- MRI.
- Ultrasound.
X-ray diagnosis of bursitis
Bursitis or synovitis - what is the difference?
Detailed diagnostic studies are required to accurately determine the type of pathological process and identify an accurate diagnosis to exclude synovitis. The leading difference between synovitis is the inflammatory process not only in the joint capsule.
The inflammatory process also affects the tendons at the points of attachment to the bones; the inflammatory process during synovitis can also affect large muscles.
Among the differences between diagnoses:
- Bursitis in treatment requires normalization of the condition of several joint capsules . They are treated comprehensively. Synovitis affects only one area.
- With synovitis, exudate accumulates directly in the joint cavities. For bursitis, treatment is required for the entire joint capsule.
- Synovitis leads to inflammation of the entire knee bursa. Bursitis requires treatment of small tendon bursae.
- Externally, inflammation during synovitis is a large single edema. It may be complicated by hematosis. Bursitis is treated by eliminating localized inflammatory foci.
Limitations for bursitis
Is it possible to go to the bathhouse if you have bursitis?
The possibility of visiting a bathhouse or sauna with this disease is determined by a number of factors. On the one hand, under the influence of steam and hot water, the patient’s condition can improve. The bath increases the tone of the body, activates metabolism, improves blood circulation in the area of the synovial bursa, and improves the patient’s mood.
However, all this is true only if a person has no contraindications to visiting the bathhouse. The main contraindication is related to the disease of the joint itself: when the chronic disease is in acute form, visiting the bathhouse is strictly prohibited. You cannot steam the joint in the postoperative period, until complete recovery. In addition, the patient may have concomitant diseases that can cause complications: tuberculosis, oncology, cirrhosis, hypertension, etc.
Is it possible to drink coffee if you have calcific bursitis?
Experts recommend stopping drinking coffee while treating bursitis. Nutrition should be balanced and rational. Alcohol, sweet soda, fast food and processed foods are also prohibited.
Is it possible to play sports with bursitis?
In the acute form of the disease, sports are prohibited. Even a small load can aggravate the course of the disease. And after recovery, the patient must pay attention to his joints: do not exhaust the body with loads, use protective equipment and promptly treat wounds and injuries.
Is it possible to use infrared rays for bursitis?
Physiotherapy has proven itself in the complex treatment of acute and chronic disease. Infrared rays can help relieve joint pain and swelling, improve blood circulation and aid in quick recovery.
However, in this disease there are courses in which physiotherapy is contraindicated, for example, purulent-hemorrhagic effusion in the synovial bursa (bursa) and tissue necrosis.
If you wish to seek treatment with infrared rays, you must consult your doctor.
Which doctor should I contact for bursitis?
Bursitis can be treated by different specialists: a traumatologist, an orthopedist, a surgeon... The choice depends on the course, form and stage of the disease. In order to be referred to the right doctor, you can contact a therapist. After the examination, he will make recommendations.
You can immediately try to get to a specialized doctor, based on the available data about the disease and the cause of its occurrence. If the symptoms of inflammation in the synovial bursa begin to bother the patient after an injury, then it is necessary to visit a traumatologist. The earliest stages of the disease are treated by an orthopedic surgeon. And neglected ones are corrected by a surgeon.
Sorry, there is no such page
The page may have been moved or you entered the address incorrectly. Please go to the site map or use the search
You are absolutely right, but this needs to be monitored from birth. I'm a daughter...
Good article. I’ve been thinking about traditional medicine. In the hospital in...
I have read more than once that you need to do tubage (I think that’s what it’s called correctly...
Good article. Not all antiviral herbs listed are true. I'm flying...
Publications on the site are the personal opinion of the authors and are for informational purposes only.
To practically resolve a particular problem, you need to contact a specialized specialist.
Reprinting is permitted only if an active indexed link is indicated.
2014 - 2021 Health Academy | All rights reserved
Alternative treatment for elbow bursitis
Traditional methods of treatment are acceptable for non-acute and non-infectious disease, after consultation with a specialist.
One of the means to combat this disease is table salt. 1 tbsp salt must be diluted in 0.5 liters of hot water. The resulting solution is moistened with gauze, which is applied to the affected joint and fixed with cling film. The procedure must be repeated daily for 2 weeks.
Another way is a warm compress. The sugar is heated in a frying pan, avoiding melting. The heated sugar is wrapped in cloth and applied to the joint in which the inflammatory process occurs for 2-3 hours. Wrap the top with cling film and a warm cloth.
White cabbage is one of the universal ways to reduce swelling and relieve inflammation. The cabbage leaf must be lightly beaten until the juice is released. The inflamed joint is covered with a small amount of honey, then a cabbage leaf is applied, and the limb is wrapped in cling film and a warm cloth. The compress is kept for about 2 hours.
Unconventional means
Alternative medicine plays a positive role in complex therapy. In the treatment of bursitis, procedures are recommended that further improve blood supply to the affected joint. Such as hirudotherapy or acupuncture.
Using traditional methods and recipes
Traditional medicine offers many recipes that can be used to relieve pain due to bursitis. It is important to consider the inability to treat the disease only on your own and at home.
This dangerous pathology of the musculoskeletal system requires mandatory contact with a specialist at a dispensary or clinic.
Traditional recipes are recommended to be used additionally:
- Applying a cabbage leaf to the sore joint helps relieve inflammation . It is applied for 10-20 minutes, secured with a bandage or plaster.
- The use of Kalanchoe helps relieve symptoms. The leaves of this plant are placed in a cool place overnight, maybe just in the refrigerator. In the morning they are crushed and applied to the site of bursitis in the form of a compress.
- The affected area can be wiped several times a day with a tincture of aloe leaves in alcohol.
- You can add 50 ml of pharmacy bile to a tincture of aloe leaves to enhance the effect. The volume of the 50 ml bottle is enough for 500 ml of alcohol.
- To relieve the inflammatory process, especially in the acute stage, it is recommended to use cold compresses. They use ice crushed in a blender or simply damp cold cloths.
Bursitis in children
At a younger age, the disease practically does not occur. Usually the disease is encountered in adolescence. The main causes of bursitis in children: excessive physical activity, injuries and diseases that provoke the development of inflammation in the joint.
Symptoms are similar to those in adults: swelling, pain, general malaise.
An important point in the treatment of joint disease in a child is timely diagnosis. Children tend to hide the fact of injury and endure pain. Neglected treatment and lack of rest during the acute period of the disease can lead to the need for surgical intervention and more serious consequences.
Prevention and useful tips
Preventive measures play a very important and sometimes decisive role in preventing illness. So, to prevent the disease you need:
- Carry out disinfection after receiving abrasions or scratches;
- Remember about timely treatment of diseases accompanied by inflammatory processes;
- Avoid excessive physical activity;
- Eat properly;
- Play sports, taking into account your health status;
- Use orthopedic products to correct deformed joints.
People whose work involves constant stress on their joints should place soft pillows under their knees or elbows and use protective bandages.
Before starting heavy physical activity, you need to warm up your joints by performing a set of warm-up exercises. It is recommended to jog, exercise with dumbbells, and swim.
Treatment of bursitis in a hospital setting is carried out only if the condition of the joint requires surgical intervention. In other situations, patients are prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures and a set of home activities.