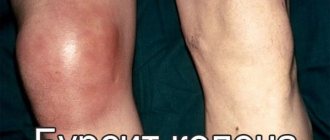
The knee is a large joint with a large and constant load. It is not surprising that injuries often occur here and the risk of knee joint diseases is high. Periodic knee pain bothers almost 50% of people at the age of 40, and by the age of 70 it becomes a constant companion. One of the common pathologies of this joint is bursitis of the knee joint. In this case, the periarticular sac becomes inflamed and fluid accumulates in it. Movement becomes limited and painful. Doctors at the Kuntsevo Medical and Rehabilitation Center know how to recognize and treat bursitis. The clinic’s specialists are ready to help with acute and chronic forms of the disease using the most modern, safe and effective methods.
Knee bursitis and its types
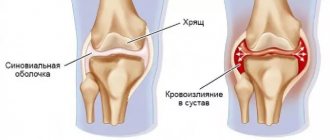
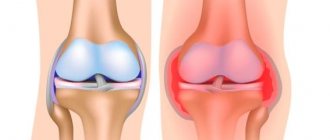
The term “bursitis” is applied to the inflammatory process that occurs in the anatomical structure of the joint – the bursa.
This is a kind of hydraulic airbag - a cavity made of dense connective tissue that protects the joint from external damage. On the outside, it consists of dense tendons and ligaments that provide a durable outer covering. Inside is a layer of cells that produce synovial fluid. This is a special joint lubricant that facilitates the sliding of bone heads in it, protects tendons from friction, nourishes and moisturizes joint tissues. When moving, cartilage, like a sponge, absorbs this liquid along with nutrients.
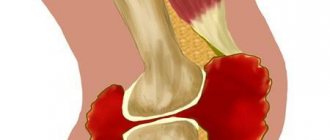
The knee is a complex joint, in which there are several synovial bursae: above, below and in front of the kneecap, on the lateral ligaments, tendons, heads of the gastrocnemius and popliteus muscles. Inflammation can appear in each of them or in several at the same time.
Bursitis occurs at the site of inflammation:
- Anterior kneecap - prepatellar - inflammation and swelling occur as a result of diseases such as rheumatism, gout and from constant injury. For example, when working specifically with frequent support on the knee. Maid's or priest's bursitis is what they call this type of pathology, in which the front of the knee swells.
- Popliteal – the tendon bursa in the lower part of the kneecap becomes inflamed. A typical cause for this type of pathology is falls and strong impacts to the knee, injuries and tears of the meniscus. Traumatic bursitis of the knee joint is common in people with arthritis or excess weight.
- Goose - or Baker's cyst. Inflammation occurs in the inside or back of the joint. It manifests itself as pain in the knee when moving, walking up stairs, and more often affects overweight women.
Knee bursitis is classified according to its course:
- Acute – occurring suddenly, with noticeable and intense symptoms and lasting up to a month.
- Subacute.
- Chronic – lasts up to a year.
- Recurrent - periodically worsens.
According to the type of cause, bursitis occurs:
- Aseptic is a non-infectious pathology caused by injuries (post-traumatic bursitis of the knee joint), gout, and autoimmune diseases.
- Septic – caused by bacteria or infections (tuberculosis, syphilis and others).
According to the type of accumulated synovial fluid: serous, purulent and others.
An accurate classification of bursitis is needed to understand its cause and which treatment methods will be effective.
Osteoporosis
The seemingly harmless diagnosis of “osteoporosis” is actually very insidious. In old age, this disease poses a serious threat to life, along with heart attacks and strokes. Osteoporosis is a pathological decrease in bone density that threatens fractures from minor injuries, which leave a person bedridden for months and years, or even for life. Its main cunning is its imperceptible asymptomatic development.
From the section on osteoporosis you will learn:
- Are there effective methods for strengthening damaged bone tissue?
- Why osteoporosis should be treated before it makes itself felt.
- How to avoid fractures if osteoporosis has already developed.
- How to eat properly with this disease.
- What habits increase the risk of osteoporosis complications.
Symptoms
General signs of bursitis of the knee joint (they will appear when different joint capsules are affected) include:
- Pain – bothers you at rest or when moving: running or walking up the stairs. Pain with bursitis of the knee joint most often occurs in the morning and gradually increases with increasing strength or intensity of exercise.
- Swelling – of the knee as a whole or of a specific joint capsule.
- A rise in temperature – both local (a feeling of heating appears in the knee) and in body temperature as a whole.
- Limitation of the possibility of movement - from slight stiffness and pain (the leg bends and unbends worse) to the complete inability to transfer body weight to the leg and walk normally.
- Signs of general intoxication during infections and purulent inflammation.
- Local symptoms of bursitis of the knee joint: swelling and pain in the area of the inflamed bursa.
General information about the disease
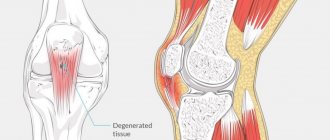
Suprapatellar bursitis is an inflammatory lesion of the suprapatellar bursa, which is located at the junction of the knee cartilages. This joint structure plays the role of a kind of shock absorber. The suprapetellar bursa protects the tendon from excessive mechanical stress, such as friction or compression. Normally, there is always a small amount of liquid in it. With bursitis, its production increases so much that a tumor-like compaction forms in the knee area. The liquid presses on the inner walls of the bag, which leads to the development of an acute inflammatory process.
Causes
The main causes of knee bursitis:
- Knee injuries range from severe (from falls, impacts) to microtraumas due to regular physical activity on the knees.
- Excessive physical activity due to obesity, carrying heavy objects, and playing strength sports.
- Diseases in which salts are deposited in the joint in the form of microcrystals.
- Arthritis of various natures (rheumatic, psoriatic and others).
- Spread of bacterial infections.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Arthrosis of the knee joint (gonarthrosis).
- Malfunctions of the endocrine system.
Rehabilitation process
As a result of any surgical intervention, the body requires some time to fully recover. When making an incision, the wound must be sutured, always several times. To significantly improve its healing, a brace may be applied to the knee. It must be left on the leg for up to 5 days.
If no problems arise as a result of wearing the retainer, then this is an indication for its removal. Then you can engage in therapeutic restorative exercise.
In the future, the patient can perform such safe exercises at home without medical supervision. If you follow all the specialist’s recommendations and receive proper treatment, almost all patients return to their normal, full-fledged lives in a minimum amount of time. But it is not recommended to carry out work with loads on the damaged knee joint for another couple of months.
Diagnostics
Consulting a doctor will help confirm bursitis. Inspection of the joint, palpation and a series of tests will be required. Moreover, with bursitis of the right knee joint, you need to pay attention to the left knee (and vice versa). An orthopedic traumatologist evaluates pain, swelling and other signs, asks you to make some movements to understand what exactly causes the most pain and where the inflammation occurs.
Instrumental diagnosis of bursitis:
- Ultrasound – for visualization of periarticular tissues, the meniscus, the amount and nature of intra-articular fluid, the location and boundaries of inflammation.
- MRI is the most informative method for diagnosing soft tissues.
- X-ray (an alternative to computed tomography) - assessment of bone structures - the presence and foci of their degeneration and destruction.
- Diagnostic puncture - collection and laboratory examination of fluid.
Laboratory diagnostic methods:
- Tests to look for diseases that could cause bursitis.
- A blood test for general and specific indicators that will indicate the autoimmune nature of bursitis.
- Analysis of joint fluid.
When to make an appointment and see a doctor
If you have symptoms of knee bursitis, bursitis of the elbow joint, finger, or shoulder, you should immediately contact the clinic. The sooner the diagnosis is made, the greater the chances of a complete cure of the disease.
We recommend that you make an appointment immediately if you experience:
- joint pain when walking or at rest;
- swelling;
- chills and fever;
- mobility restrictions.
Remember that treatment of joint bursitis is a long process that requires an integrated approach. We do not recommend using the advice of other patients from thematic forums, since each case has its own treatment algorithm. It depends on the causes of the disease, the stage of its development and concomitant chronic diseases.
Treatment of knee bursitis
Both conservative methods and surgical interventions are used.
Conservative treatment:
- Medicines – for the treatment of bursitis of the knee joint, taking into account its cause, the following can be used: anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers, antibiotics (in tablets, gels and ointments or injections). The course of taking prescribed medications is 5-7 days. If the clinical picture remains without positive changes, the drugs are changed.
- Puncture - a puncture is done to remove accumulated intra-articular fluid and rinse the cavity of the bursa with anti-inflammatory drugs. In case of purulent inflammation, drainage is installed for the internal cavity of the joint in order to remove the accumulating pus out.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures - techniques such as laser, ultrasound, magnetic, electro-, shock wave therapy activate blood circulation and lymphatic drainage, reduce inflammation, swelling and pain, accelerate healing processes, and “break up” salt deposits. One effective way to relieve swelling and pain is to apply a cold compress.
- Therapeutic physical education - classes using an individual set of exercises (and preferably under the supervision of a doctor or exercise therapy instructor) speed up recovery.
The operation is the opening and even removal of the inflamed bursa if conservative procedures are unsuccessful and an abscess or phlegmon develops (spill of purulent contents beyond the bursa and “melting” of its walls).
Exactly how to treat knee bursitis will differ depending on the type of pathology. So, in case of acute bursitis, which has developed for the first time, it is necessary to ensure temporary immobility in the joint (at least reduce the load). This will be helped by supporting bandages, wearing an orthosis, taping, temporary refusal or reduction of physical activity.
With chronic inflammation, joint immobility is less important. In this case, more attention is paid to an individually selected set of physical therapy exercises and the prescription of anti-inflammatory drugs.
In case of septic inflammation, it is necessary to act on the causative agent of inflammation. You cannot do without antibiotics and (in many cases) without drainage of the joint cavity.
Experts' forecast
When a patient seeks medical help with complaints about the appearance of the first signs of bursitis, the prognosis is favorable. Timely conservative treatment allows you to fully restore all functions of the knee. If complications develop, the prognosis is less favorable, especially if surgical intervention is necessary. Despite the proper execution of the operation, areas with rough fibrous tissues form in the joint cavity, so in the future there may be a disruption in the functioning of the knee.
Where to treat bursitis in Moscow
A quick and accurate diagnosis of diseases of the musculoskeletal system (including joints) will be carried out at the Kuntsevo Treatment and Rehabilitation Center. For this we have all the necessary equipment and doctors with extensive experience.
We are ready to offer the safest and most effective treatment methods. The clinic has a specially equipped day hospital for minimally invasive procedures and a physical therapy room with all the necessary exercise equipment. Classes are held in small groups or individually.
Book a consultation by phone.
Complications
With timely diagnosis and treatment of joint bursitis, doctors give a favorable prognosis. This disease responds well to treatment, so the patient, if its acute form occurs, has every chance of a full recovery. To do this, you must not delay it, but immediately contact an orthopedic traumatologist. Doctors of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) in Moscow conduct consultations at the address: 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane, 10.
If the disease is brought to an advanced form, the consequences of this may be:
- infection with accumulation of pus;
- deposition of salts in the cavity of the synovial bursa;
- myositis;
- dysfunction of the joint.
Prevention
Treatment of bursitis is a complex and lengthy matter. To prevent relapse, it is necessary to follow general recommendations for preventive purposes. To do this you need:
- limit heavy lifting;
- visit the pool;
- refuse strength training, visit the gym only under the supervision of a trainer with a medical education;
- monitor your body weight (every kilogram of excess weight increases the load on the supporting joint 10 times);
- undergo regular diagnostics;
- take complexes of vitamins and minerals to strengthen bone tissue;
- increase immunity and body resistance.
How to make an appointment with an orthopedic traumatologist?
Bursitis is treated by a professional specialist - an orthopedic traumatologist. Carry out a diagnosis of bursitis, get a consultation with a doctor at JSC "Medicine" (clinic of Academician Roitberg) in the center of Moscow at the address: 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya Lane, 10. From the Mayakovskaya metro station you need to walk 5 minutes.
To make your first appointment with a specialist, please call. Calls are accepted 24 hours a day.
You can also submit an application through a short electronic form on the website. Don't forget to include your name and contact number for communication. The clinic administrator will call you back and make an appointment for you at the next available time.