Compression fracture of the thoracic spine
Compression fracture of the lumbar spine
Compression fracture of the cervical spine
The vertebrae that form the spinal column can be damaged (broken) as a result of a sharp blow when jumping, an unsuccessful fall, or incorrectly calculated physical activity - just like any other bone structure. A compression fracture, which occurs as a result of compression of the vertebral body, is considered a serious injury and can be localized in the lumbar, thoracic and cervical spine. If you encounter such an injury, hurry to seek professional medical help at the CELT clinic. In order to undergo diagnostics and treatment with us, it is not necessary to have a residence permit in the capital or to be a citizen of the Russian Federation. We provide assistance for spinal compression fractures to everyone who needs it.
At CELT you can get advice from a neurosurgeon.
- Initial consultation – 3,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
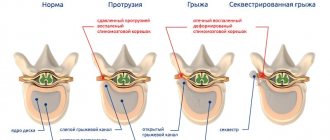
Types of fractures and classification
The degree of vertebral compression fracture is usually determined depending on the degree of deformation of the vertebral body:
- a 1st degree fracture is characterized by a decrease in vertebral height by no more than 30%;
- a 2nd degree fracture is characterized by a decrease in vertebral height by no more than 50%;
- A grade 3 fracture is characterized by a decrease in vertebral height by more than 50%.
Depending on the presence/absence of complications, these pathologies are:
- uncomplicated - characterized by pain in the damaged area, often occurring in a latent form;
- complicated - in addition to pain symptoms, they are characterized by a number of neurological disorders that arise due to damage to the nerve roots by bone fragments.
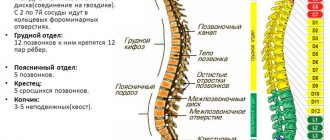
Depending on the location of the fracture, there are:
- thoracic injuries - the eleventh and twelfth vertebrae are the most vulnerable, since they are subject to the greatest load;
- lumbar injuries - most often the body of the first vertebra is destroyed, which leads to compression of the nerve roots;
- cervical spine injuries are rare, usually in patients between 30 and 50 years old due to road accidents, heavy objects falling on the head, or strong blows to the head.
Forecasts
In most cases, simple compression injuries can be successfully treated. The complete recovery process takes no more than 6 months. The patient may experience moderate back pain throughout the recovery period.
After completion of treatment, the following phenomena are observed:
- Persons who have suffered a compression injury, which is accompanied by neurological symptoms, may at times experience minor pain. This is due to the fact that the deformed cartilage affects the spinal cord and root;
- with the pathology in question accompanied by infections of bone tissue, the prognosis is also overwhelmingly favorable. Persons who have suffered a fracture due to purulent osteomyelitis can count on a high chance of recovery provided timely treatment;
- If the fracture occurred against the background of puncture tuberculosis, unfortunately, the prognosis is unfavorable. Such patients become disabled.
As for a fracture caused by latent osteoporosis, after proper therapy the patient’s condition stabilizes within 2 months. Complete recovery is possible only if the pathology is detected in a timely manner and therapy is started on time.
Complications
Timely seeking professional medical help plays an important role, as it helps prevent the occurrence of complications such as:
- instability of the injured area;
- curvature;
- development of osteochondrosis;
- development of radiculitis;
- narrowing of the spinal canal and the development of neurological disorders;
- sensory disturbances in the hands and feet;
- paralysis;
- hump formation.
Transportation
The patient is transported on a rigid stretcher with straps to securely secure the entire body. It is also necessary to carry the patient to the ambulance or reanimobile using a hard surface. As a last resort, you can place the victim on a soft stretcher. But this makes it much more difficult to control vital functions and reflexes. Because the patient with this method of transportation should be face down (on his stomach).
Fixation of fractures
When transporting a person with a spinal fracture, it is also important to consider the following points:
- If a person on a stretcher lies on his back, a cushion of rolled up clothing or any fabric must be placed under the lumbar area. In a face-down position, such a cushion is placed under the chest and pelvic area.
- The minimum number of people to carry a patient with signs of spinal injury is three. The optimal number of assistants is five or more.
- While moving the patient, it is necessary to carefully hold the head to prevent additional trauma and displacement of the vertebrae and bone fragments.
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms of a compression fracture of the spine depend on the part in which the pathology appears. In general they include the following:
- pain symptoms - mild, moderate or severe (depending on the degree);
- pain when moving;
- a feeling of weakness and numbness in the legs and arms, which becomes more pronounced over time.
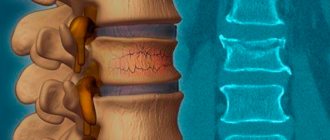
An X-ray examination reveals the following:
- deformations of the affected vertebrae;
- changes in the intervertebral space;
- displacement of the posterior part of the vertebra into the spinal canal;
- the presence of subluxation in the intervertebral joints.
A compression fracture of the spine in children may have virtually no symptoms; it can be detected by a doctor during palpation. If the injury is serious, then the symptoms are much more noticeable:
- limited mobility in the spine;
- muscle tension in the area of pathology;
- pain radiating to the abdomen or surrounding it.
Symptoms
With fractures of the thoracic vertebrae, especially from 1 to 10, the symptoms are not as acute as with injuries to other parts of the spine. This is due to significantly less mobility of the components of the thoracic region; they are little involved in performing usual everyday activities and experience less stress.
Damage to the 12th thoracic vertebra is associated with severe symptoms, since this part of the spine is very mobile. This also leads to frequent occurrence of signs of damage to nerve structures.
The main symptoms of a fracture of the vertebrae of the thoracic spine are:
- pain in the chest, back and upper abdomen, which tends to intensify with movement, breathing and changing body position;
- irradiation of pain in the groin, abdomen and a significant decrease in their intensity when taking a supine position;
- back muscle tension;
- limited mobility;
- change in posture;
- swelling of soft tissues in the affected area;
- formation of hematomas;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract and urinary system.
Compression fractures of the thoracic region are often accompanied by the formation of a small hump in the projection of the injured vertebra. It is formed by the tops of two spinous processes of adjacent vertebrae, which, as a result of a decrease in the height of the anterior part of its body, have shifted from their normal position.
If a spinal fracture causes nerve damage and compression of the spinal cord, you may experience:
- difficulty breathing;
- dizziness, fainting;
- impaired sensitivity and decreased muscle tone of the limbs.
Diagnostics
Operations for diseases of the spine
- Cost: 100,000 - 250,000 rubles.
- Duration: 40-60 minutes
- Hospitalization: 2-3 days in hospital
More details
Since pain is not specific in this case, CELT specialists conduct diagnostic studies to differentiate compression fractures from other pathologies. To do this, the patient is given a referral to:
- radiography of the spine in direct and lateral projections;
- computed tomography;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- densitometry;
- examination by a neurologist.
- examination by a neurosurgeon
- examination by a traumatologist
What procedures can be performed at home after a spinal fracture?
The following procedures can be performed at home:
- exercise therapy;
- Kinesiotherapy;
- Mechanotherapy;
- Massage;
- Certain types of physiotherapy (myostimulation, magnetic therapy, phototherapy);
- Occupational therapy;
- Classes with a psychologist;
- Consultations with specialists (surgeon, urologist, neurologist, rehabilitation specialist).
Occupational therapy
Kinesiotherapy
Photodynamic therapy (PDT)
Myostimulation (electrical stimulation)
The presence of bedsores, epicystostomy, catheter, tracheostomy is not a contraindication for rehabilitation at home.
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment methods are aimed at:
- elimination of pain syndrome;
- rapid healing of the fracture;
- minimizing axial load on the spine.
In order to avoid complications, it is necessary to correctly fix the damaged part of the spine. The patient must remain in bed and wear a reclinator or orthopedic corset. The use of painkillers can minimize or eliminate pain symptoms. In order to prevent the formation of bedsores and strengthen muscles during prolonged bed rest, professional massage is used.
What causes vertebral fractures?
The most common cause of vertebral fractures is traumatic injuries resulting from:
- Falls from a height onto the lower limbs, buttocks, head;
- Sports activities;
- Road traffic accidents;
- Gunshot wounds.
It is worth noting that vertebrae break not only under strong energy impacts. If the patient suffers from pathological conditions characterized by decreased bone strength, he may be injured even during his usual daily activities.
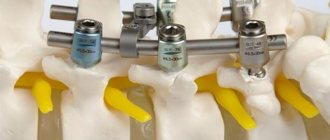
Surgery
Surgery may be required for complicated compression fractures. Modern techniques involve the use of the following minimally invasive methods:
- kyphoplasty – aimed at restoring the height of the vertebral body;
- Verteboplasty – allows you to relieve pain symptoms and strengthen the damaged vertebra.
The use of verteboplasty is advisable for unstable fractures with a high risk of neurological complications. It involves a puncture through which a special solution is injected into the vertebral cavity. The latter plays the role of “cement”, ensuring the strengthening of the vertebra. Verteboplasty is performed under local anesthesia and lasts no more than one hour and requires bed rest for one to two hours and the exclusion of physical activity for 24 hours after surgery.
Depending on the damage to the spinal cord, there are:
- fractures with spinal cord damage;
- spinal fractures without damage to the spinal cord.
Initial consultation with a rehabilitation specialist
+8
Record
By nature, spinal fractures are divided into:
- compression (as a result of vertical compression of the vertebral bodies;
- crushed (fragmented);
- combined compression-comminuted;
- fractures combined with dislocations (fracture-dislocations).
Reviews of doctors providing the service – Compression fracture
In 2000, Andrei Arkadyevich performed spinal surgery on me.
Four days in the clinic and I have been living a full life for 20 years without restrictions on movement and I remember with gratitude Dr. A.A. Khodnevich. God bless him. And in 2000 he could walk no more than 10 meters. Read full review Viktor Alexandrovich
20.05.2020
Low bow to Alexander Semenovich Bronstein and Andrei Arkadyevich Khodnevich. I arrived at CELT on July 2, 2021 with extreme pain that I endured for 10 days. Hernia C6-C-7. I was given two blockades in Ivanovo, about 9 complex IVs, I lost 6 kg in a week and was in a panic, I didn’t see a way out and nothing happened to me... Read full review
Elena Nikolaevna L.
20.10.2019
What are our advantages?
- More than 7 years of experience in outpatient rehabilitation;
- Necessary equipment for rehabilitation at home;
- Individual approach to each patient;
- Own training center for employees and relatives of patients and volunteers;
- Rehabilitation techniques recognized as effective throughout the world;
- We actively participate in the lives of our patients and support the volunteer movement.
Thanks to all this, we offer you a clear rehabilitation system with clear goals and objectives of treatment and joint monitoring of its results.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation measures play an important role in the treatment of spinal compression fractures. They consist of performing physical therapy exercises under the guidance of a specialist. The stages of exercise therapy are as follows:
- During the 1st week after injury, exercises are performed to stimulate the functioning of the respiratory system, gastrointestinal tract, heart, as well as exercises that prevent a decrease in muscle strength;
- Over the next thirty to sixty days, exercises are performed to strengthen the muscle corset. The load gradually increases by adding new exercises, increasing the duration of classes and repetitions;
- As the patient is ready, preparation for vertical loads is carried out, exercises with weights and resistance are performed;
- As the patient is ready, exercises are performed in a standing position, i.e. vertical loads.
Timely seeking medical help is the key to successful recovery after a compression fracture of the spine.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Results of our work
- Woman
; - Age:
56 years old. - Diagnosis:
compression-ischemic myelopathy.
Patient with spinal fracture. Compression-ischemic myelopathy. At the time of admission, the skills of independent movement and positioning are absent. She cannot turn over in bed on her own and does not get out on her own. completely dependent on care. Video of getting up and taking the first steps after 2 months of treatment.
- Man
; - Age:
42 years. - Diagnosis:
spinal fracture.
Let's sum it up
A fracture of the lumbar spine is a serious injury that can cause serious complications. The risk of getting it increases with age as bones lose strength. Self-treatment is strictly contraindicated. Diagnosis is carried out exclusively using instrumental studies. Restoring the position of the vertebrae depends on full treatment and rehabilitation, which are carried out in a hospital setting. Correctly provided first aid and the chosen tactics of therapy and recovery guarantee a complete recovery.