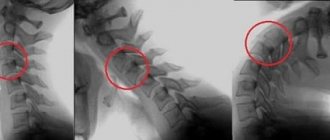
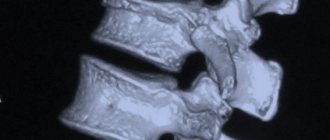
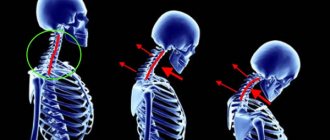
The cervical spine is one of the most vulnerable places in babies. It is not surprising that mechanical impact on it during childbirth often leads to birth trauma.
According to pediatric neurologists (Ratner et al.), more than half of cases of newborn death during childbirth are associated, in one way or another, with the presence of a serious spinal cord injury at the neck level. In this case, extensive hemorrhages under the membranes of the spinal cord, displacement of the cervical vertebrae, and ruptures of the fascia of the neck were observed. If the exposure does not lead to the death of the newborn, then the child remains hidden defects in the development of the nervous system.
Neurological diagnostics of a newborn allows you to quite accurately identify the level of damage to the nervous system (brain, spinal cord, which part), especially if MRI is used to help. However, it is not always the case that when a cervical vertebrae is injured, symptoms immediately appear that would force the doctor to send the child for an appropriate examination.
Osteopathic diagnostics, when used correctly, makes it possible to detect the presence of a birth injury to the neck in newborns much earlier than the first symptoms appear in the form of motor patterns or disturbances in age-related developmental dynamics. Thanks to this, children with birth trauma receive a great advantage in time (on the order of several months) for treatment compared to children who have not been examined by an osteopath. Often these few months can decide whether a child becomes disabled or not.
The main causes of birth injury to the neck in newborns
The main causes of neck injuries are almost the same factors that create the conditions for birth injuries in general. These include rapid labor, discoordinated labor (weak contractions are followed by strong ones, etc.), manual obstetric aids that mechanically affect the head. Cesarean section stands out separately among the reasons, since in general the technique of removing the fetus from the uterus does not cause mechanical damage, but the neck still remains a high-risk place when the fetus is pulled by the head.
Types of Natal Injuries and Causes
The most common natal injuries are due to the use of forceps or suction cups. Often, midwives will use a special suction cup attached to the skull to facilitate the birth of the baby.
Instruments are used to move the soft tissues of the head, which can lead to skull trauma. Blood vessels located below the periosteum are often damaged, causing bleeding.
There are several risk factors that cause RT. In some cases, the rapid passage of the baby's head through the mother's pelvis can cause pathology. Another part of the risk factors is the parietal position.
The term birth injury also includes long-term consequences such as central nervous system disorders or cognitive dysfunction associated with traumatic brain injury.
There are traumatic brain injuries caused by birth trauma and injuries caused by intrauterine asphyxia. In the strict sense of the word, RT refers only to those injuries that are caused by mechanical influences. In RT, damage does not occur due to hypoxia during childbirth.
The effects of a traumatic birth can affect the baby and mother. RTs are considered rare in the Western world compared to corresponding frequencies in the developing world. In the West, birth defects occur in 1.1% of births. Many physical conditions increase the likelihood of birth defects, including:
- discrepancy between the baby's head and the mother's pelvis;
- delayed childbirth;
- incorrect obstetric interventions;
- premature birth;
- multiple pregnancies;
- medications;
- polyhydramnios;
- uterine fibroids;
- tumors in the pelvic area.
In newborns, a number of disorders can occur as a result of trauma. Cerebral palsy occurs in 0.4 to 5.1 children per 1,000 births. Damage to the skull and brain during childbirth can cause pathological conditions, including cephalhematoma and various forms of intracranial hemorrhage. The most common fracture that can occur during childbirth is a clavicle fracture.
Cephalhematoma
Other typical birth defects are: muscle hematoma, torticollis, facial nerve palsy, brachial plexus palsy, nasal cartilage dislocation.
The birth of a person is characterized by physical features that arose in the evolutionary process of hominization. After the development of upright walking, many skeletal and skeletal muscle changes occurred. In the context of childbirth, adjustments to the spine and pelvic girdle are especially important. The pelvic canal, which the fetus must cross at birth, is very narrow. Its internal dimensions are almost identical to the size of a newborn's head. As a result of evolutionary growth of the brain (cerebralization), the human skull has become very large compared to the skulls of other primates. Therefore, a slight deviation from the ratio of the size of the baby's skull to the size of the mother's pelvic floor can cause injury.
During labor, the large head and broad shoulders must move through the relatively narrow birth canal. Although the process of birth remained a normal biological process, due to the mentioned evolutionary features, complex birth mechanics arose. The baby's head must perform complex movements along the mother's pelvis. In this case, the baby may become stuck, especially due to a particularly pronounced discrepancy between the mother's pelvis and the head. The child's sensitive brain is protected by mobile bone plates of the skull. Ossification occurs after birth. The human skull has evolved to be deformable to allow passage through the vaginal birth canal. These deformations likely occur at evolutionary biological limits and threaten the child's brain. The aforementioned possible skull and brain injuries are a result of these anatomical features.
After birth, other physiological changes also occur: the newborn must switch to breathing through the lungs, eat through the mouth, and perceive many stimuli through the senses. This condition is characterized by excessive stress.
Main symptoms and signs of neck injury in newborns
Signs of mechanical trauma to the cervical spine in newborns do not appear immediately. Sometimes 2 or 3 months pass, during which the child behaves quite adequately, without detecting neurological abnormalities. Then the following symptoms may appear in different sequences and combinations:
- Asymmetry of the face and skull, flat back of the head
- Asymmetry of the gluteal folds
- Torticollis
- Increased tearfulness, frequent colic
- Unilateral position during sleep, posture with a strongly extended torso during sleep
- Increased sensitivity in the back of the neck (to touch)
- Absence and abrasion of hair on the back of the head
- Poor appetite
- Problems with breastfeeding, does not eat from the other breast
- Symptom of “head banging” - a child hits his head on the crib
- Trouble swallowing, excessive regurgitation
If a cervical spine injury is not treated when symptoms appear, the child, as he grows up, tries to adapt to it and develop a pattern of behavior that allows him to avoid the onset of pain. If it hurts your baby to lift his head while crawling, he may start walking straight away as part of an avoidance strategy.
How does it manifest?
A birth injury to the cervical spine in a young patient can be noticed immediately after birth. The first signs of injury include: the appearance of swelling and redness in the neck, a too short or too long neck, excessive tension in the muscle tissue and at the back of the head, while the neck itself is in an injured state.
In addition to noticeable symptoms, signs of damage include relaxation of the whole body, although it is normal for the baby to develop hypertonicity after a month of life. The baby’s breathing process is complicated; groans, hoarseness and other extraneous sounds may occur. The nose area may become blue.
We advise you to study - Curvature of the spine in children
The baby may notice excessive anxiety, constant tearfulness, night cries, poor sleep, reluctance to breastfeed, and regular regurgitation. In some cases, a heart rhythm disturbance is detected. The diagnosis of natal neck injury can only be made after a complete detailed examination of the newborn. Ultrasound, radiography and Doppler ultrasound are performed. After the examination, an accurate diagnosis can be made, the degree of injury, the level of severity and the nature of the lesion can be determined.
Consequences of neck injury during childbirth
In older children:
- Poor learning ability, clinical attention deficit disorder mimicking ADHD.
- Developmental delay in any form.
- Headaches, complaints of heaviness in the head.
- Deficient motor skills, up to paralysis and paresis of the limbs.
- Social maladjustment.
In adults:
- Chronic pain syndrome, back and limb pain.
- Headaches, migraines, noise and ringing in the ears.
- Dizziness, loss of coordination, etc.
Is caesarean section a salvation?
According to statistics, birth injuries during cesarean section are rare, but not excluded. It seems that with a planned, well-thought-out operation, any surprises can be avoided, but nature makes its own adjustments here too. Doctors explain this by various factors:
- Strong compression of the child during the passage of the birth canal triggers the work of his cardiovascular and respiratory systems. With a cesarean section, this mechanism is absent; the body is reorganized to function outside the uterus in other, unnatural ways, which subsequently affects the development of the child’s central nervous system.
- The indications for cesarean section themselves can lead to birth injuries.
- The surgical technique does not exclude mechanical damage to the fetus.
So in children, even after cesarean section, doctors diagnose skull injuries, displacement of several cervical vertebrae, hemorrhages in the retina and other injuries. Those young mothers who deliberately insist on undergoing surgery in the absence of medical indications for it should understand that it is not always possible to protect the baby from injury in this way.
Osteopathic treatment of the consequences of birth injuries to the neck
Often, parents of such children first hear about a neck injury from a pediatric massage therapist. However, a neurologist, with a thorough palpation examination, can also detect changes in the bone structure of the vertebrae and muscle tone. Osteopathic diagnosis of neck injuries in infants is most successful.
Treatment of a neck injury in the first days of a child’s life can prevent all negative consequences in the future. An osteopathic doctor, without the help of X-rays or MRI, identifies abnormalities in the bone structure of the cervical vertebrae, their articulation with each other and the bones of the skull. In infants, these connections are very soft, so it is important that the doctor is familiar with pediatric diagnostic techniques.
Elimination of neck dysfunctions is carried out immediately in the first session. The doctor also checks the baby’s entire body and, if necessary, corrects birth injuries. A repeat session is usually scheduled after 2-4 weeks.
Diagnostics
A neck injury in a baby can be detected after birth. It is worth considering some signs:
- redness and swelling of the neck;
- the neck looks either very short or very long;
- muscle spasms appear on the back of the head or neck;
- irregularities of the cervical spine.
Symptoms that are difficult to notice right away:
- the body and limbs of the newborn are very relaxed;
- the baby breathes heavily and hoarsely, groans;
- the appearance of a blue tint in the nose area;
- nervousness in the behavior of the newborn, disturbed sleep and constant crying;
- difficult to agree to feeding, constant regurgitation;
- cardiac arrhythmia.
It is important to correctly and timely diagnose natal trauma.
These signs indicate natal damage to the cervical spine. For accurate diagnosis, it is worth using ultrasound and X-ray examination, Dopplerography. As a result, information about blood flow in the head and neck area is obtained. After the examination, you can find out where birth injuries are located and how severe they are.
Diagnostics
The hematoma is examined immediately after the birth of the child by a pediatrician, midwife and other specialists. Sometimes severe swelling occurs at the site of injury, which can lead to serious consequences if not treated promptly.
If parents seek medical help late, the pediatrician asks the parents when they noticed the hematoma, how much the tumor has changed since its appearance, and how the child reacts to it.
We advise you to study - Hemangioma in a newborn
The next step is a physical examination of the child. The doctor checks the baby for scars on the skull. It also controls the degree of swelling. Also of interest are any neurological symptoms. The child's eyes and hearing are often tested.
Survey
The course of cephalhematoma is usually positive. Although the size of the cephalhematoma increases in the first few days, it disappears on its own in the following weeks and months. A scary but very rare complication is hematoma infection, which can be life-threatening for the child.
Proper nutrition for osteoporosis in women
A factor that prevents the development of osteoporosis is proper nutrition. First of all, your diet should include foods rich in calcium.
The second assistant is vitamin D, it is this vitamin that helps in the absorption of an important mineral.
Doctors urge people to eat only natural products that do not contain preservatives. These substances cause great harm to the body, interfere with the absorption of nutrients, promote the rapid excretion of calcium, and affect the endocrine glands, that is, the glands that are responsible for metabolism and important functions of the body.
Preservatives are added to products to extend their shelf life, enhance taste and give the desired color to products.
So, pay attention to the composition. Unfortunately, now the full composition of products is not always written down.
For longevity, you should receive foods such as milk, cottage cheese, cheese, fish, poultry, fruits, vegetables, cereals, especially legumes. In addition, clean water is important. Of course, most people have all this in their diet, but the quality often leaves much to be desired.
Natural milk contains a large amount of fats; fats are very useful for a healthy body; it’s not for nothing that we used to “get enough” of one mug of milk. In store-bought milk, during its processing, some of the natural fats are removed and preserved, which results in poor absorption of this product by the body.
Natural milk with live bacteria is stored for several hours, and milk in packages is stored for several days. It’s not at all difficult to draw a conclusion on your own which milk is best for a healthy person to drink in order to maintain their health for many years.
Today the market is replete with such dietary supplements. Which one should you choose? We recommend the drug "Osteomed" because it really increases bone mineral density. The calcium contained in it penetrates exactly into the right areas, while other drugs can harm the body, in particular, cause hypercalcemia.
This drug is created on the basis of drone homogenate, which carries calcium and magnesium into bone tissue. Osteomed was developed by Professor, Doctor of Medical Sciences Villoriy Ivanovich Strukov, who is known for developing drugs against osteoporosis.
A woman's body is more vulnerable to osteoporosis; with age, her bones become more fragile. And after menopause, calcium is washed out 2-3 times faster than usual. For this reason, the risk of fractures and dislocations increases.
A woman’s diet after menopause should include foods containing calcium, vitamin D, but another very important component is folic acid, otherwise known as vitamin B9. This substance helps the immune system, promotes the natural deposition of mineral salts, and mineral salts, in turn, maintain normal acid-base balance, the functioning of the glands, and participate in the normalization of metabolism, hematopoiesis, and blood clotting.
Mineral salts play a significant role in building muscles and bones. Sufficient amounts of folic acid are found in salads, root vegetables, grains, fruits and legumes, and in poultry meat.
The cervical spine is one of the most vulnerable places in babies. It is not surprising that mechanical impact on it during childbirth often leads to birth trauma. Neurological diagnostics of a newborn allows you to quite accurately identify the level of damage to the nervous system (brain, spinal cord, which part), especially if MRI is used to help. However, it is not always the case that when a cervical vertebrae is injured, symptoms immediately appear that would force the doctor to send the child for an appropriate examination.
Osteopathic diagnostics, when used correctly, makes it possible to detect the presence of a birth injury to the neck in newborns much earlier than the first symptoms appear in the form of motor patterns or disturbances in age-related developmental dynamics. Thanks to this, children with birth trauma receive a great advantage in time (on the order of several months) for treatment compared to children who have not been examined by an osteopath. Often these few months can decide whether a child becomes disabled or not.
The main causes of birth injury to the neck in newborns
The main causes of neck injuries are almost the same factors that create the conditions for birth injuries in general. These include rapid labor, discoordinated labor (weak contractions are followed by strong ones, etc.), manual obstetric aids that mechanically affect the head. Cesarean section stands out separately among the reasons, since in general the technique of removing the fetus from the uterus does not cause mechanical damage, but the neck still remains a high-risk place when the fetus is pulled by the head.
Main symptoms and signs of neck injury in newborns
Signs of mechanical trauma to the cervical spine in newborns do not appear immediately.
Sometimes 2 or 3 months pass, during which the child behaves quite adequately, without detecting neurological abnormalities. Then, in different sequences and combinations, the following symptoms may appear: • Asymmetry of the face and skull, flat back of the head • Asymmetry of the gluteal folds • Torticollis • Increased tearfulness, frequent “colic” • One-sided position during sleep, posture with a strongly extended torso during sleep • Increased sensitivity back of the neck (when touched) • Absence and fraying of hair on the back of the head • Poor appetite • Problems with breastfeeding, does not eat from the second breast • Symptom of “head banging” - the child hits his head on the crib • Problems with swallowing, excessive regurgitation If when appearing symptoms do not treat the cervical spine injury, then the child, as he grows up, tries to adapt to it, to develop a pattern of behavior that allows him to avoid pain. If it hurts your baby to lift his head while crawling, he may start walking straight away as part of an avoidance strategy.
Consequences of neck injury during childbirth
In older children: • Poor learning ability, clinical attention deficit disorder, mimicking ADHD.
• Developmental delay in any form. • Headaches, complaints of heaviness in the head. • Deficient motor skills, up to paralysis and paresis of the limbs. • Social maladjustment. In adults: • Chronic pain syndrome, pain in the back and limbs. • Headaches, migraines, noise and ringing in the ears. • Dizziness, loss of coordination, etc.
Osteopathic treatment of the consequences of birth injuries to the neck
Often, parents of such children first hear about a neck injury from a pediatric massage therapist.
However, a neurologist, with a thorough palpation examination, can also detect changes in the bone structure of the vertebrae and muscle tone. Osteopathic diagnosis of neck injuries in infants is most successful. Treatment of a neck injury in the first days of a child’s life can prevent all negative consequences in the future. An osteopathic doctor, without the help of X-rays or MRI, identifies abnormalities in the bone structure of the cervical vertebrae, their articulation with each other and the bones of the skull. In infants, these connections are very soft, so it is important that the doctor is familiar with pediatric diagnostic techniques.
Elimination of neck dysfunctions is carried out immediately in the first session. The doctor also checks the baby’s entire body and, if necessary, corrects birth injuries. A repeat session is usually scheduled after 2-4 weeks.
Appointment with an osteopath and treatment - for one treatment price!