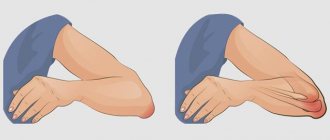
What is osteoarthritis?
Treatment of osteoarthritis should begin in a timely manner, when the first pain occurs
Osteoarthritis is a common disease characterized by joint damage and breakdown of cartilage tissue. Unfortunately, every year the disease not only becomes more widespread, but also “rejuvenates”. The disease is increasingly occurring in young people. Now joint pathologies are the third most common in the world and most often occur in women. As a rule, the disease develops gradually and in the first stages may be invisible or appear during sports or excessive stress, and is detected at a time when serious processes deforming the joints are already underway, so treatment for osteoarthritis may not always begin on time.
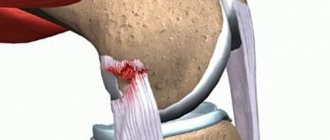
Gonarthrosis (arthrosis of the knee joint)
Despite the commonality of symptoms, the consequences of the disease vary depending on the location of the lesion. Therefore, let us dwell in more detail on the types of arthrosis.
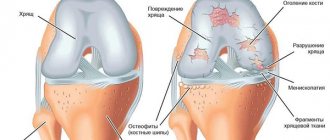
One of the most common forms of arthrosis. The knee joint is under attack. Most often the disease manifests itself after 45 years. Additional provocateurs are excess weight, injuries or bruises.
The risk group also includes athletes: football players, track and field athletes, weightlifters, etc. At the same time, according to statistics, more women fall ill. The disease can affect both legs or one. In this case, painful sensations may appear only on one leg.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis - clinical manifestations
Symptoms of osteoarthritis must be detected promptly in order to consult a doctor to confirm the diagnosis and begin treatment. So, you may have osteoarthritis if the following symptoms are present:
- • You feel pain in the joints (in the first stages it occurs only in case of stress),
- • You observe swelling in the joint area,
- • Have you noticed that your joints are crunching strangely?
- • You feel stiffness in the joint,
- • You feel like you need to “wind up” in the morning to regain your usual mobility.
Over time, all these symptoms of osteoarthritis begin to intensify, and the interval of absence of manifestations begins to decrease.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis, as a rule, are pain in the joints, which is rarely acute, more often aching or dull, subsiding over time. Symptoms of osteoarthritis are intermittent and may subside even without treatment. But, of course, it is worth understanding that if you ignore the symptoms, the disease will progress, which can lead to serious consequences and a significant deterioration in life.
3. Symptoms, diagnosis
The first and leading symptom of deforming osteoarthritis is pain in the affected joint when it is loaded (for example, when trying to raise an arm or walk down the stairs). Mechanical pain syndrome has a number of specific features: for example, it subsides at rest, occurs during the first morning movements, goes away when the joint is “developed,” and intensifies again, as daily stress accumulates, in the evening. As the disease progresses, the joint gradually loses its mobility and natural shape (which leads to characteristic curvature and thickening, for example, of the finger flexures), and mechanical pain sometimes becomes unbearably intense. Starting from this stage (and osteoarthritis deformans progresses, as a rule, quite slowly and reveals four clinically different stages in its course), the changes become irreversible, and all that remains is to relieve the pain syndrome. Usually, more and more new joints are gradually involved in the pathological process, especially those that take on increased load due to the failure of the initially affected joint.
The diagnosis, at least tentatively, is usually established after an initial consultation with a vertebrologist, orthopedist or rheumatologist. Clinical laboratory tests, ultrasound and radiographic examination of joints are prescribed as additional diagnostic methods.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Causes of osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of joint disease. This disease accounts for 60 to 70% of all rheumatic diseases. Osteoarthritis affects those joints that are most often subject to physical stress and mechanical damage - these are the knee joint, hip, and shoulder. There are many causes of osteoarthritis, let’s look at the most common ones:
- age-related changes in joints,
- genetic predisposition,
- injuries: dislocations, fractures,
- infection,
- excessive physical activity,
- hypothermia,
- overweight,
- metabolic disorders,
- osteoporosis,
- menopause,
- arthritis.
It is also worth mentioning that the chance of developing osteoarthritis in athletes increases significantly due to constant stress on the joints. The joint tissue wears out and wears out, and there is not enough time to recover on its own, so the use of special drugs is required.
1.General information
Of all the joint diseases known in rheumatology, deforming osteoarthritis is the most common. According to international statistical and epidemiological data, this pathology in the general population of earthlings occurs with a frequency of about 15%. Women over 45 years of age are more likely to suffer; in older age (60+), deforming osteoarthritis is found to one degree or another in almost any person.
We are talking about a degenerative-dystrophic process in the cartilaginous tissue of the spinal column and joints of the limbs, i.e. about the degeneration and “ossification” of articular cartilage due to pathological changes in the trophism of these tissues (supply of necessary nutrients).
Primary and secondary osteoarthritis differ significantly. Primary is an independent disease, the etiopathogenetic mechanisms of which science has yet to explore and clarify; secondary develops as a consequence of external and/or internal unfavorable or provoking conditions.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Treatment of joint osteoarthritis
Drug treatment is mandatory for osteoarthritis of the joints
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the joints is a labor-intensive and systematic process that cannot be abandoned at the first signs of improvement. How to treat osteoarthritis? Treatment of osteoarthritis is not short-term and has the main goal: to stop or slow down the process of destruction of the affected joint. Most often, inpatient treatment for osteoarthritis includes:
- • drug treatment,
- • diet,
- • therapeutic exercises,
- • massage,
- • physiotherapy,
- • surgery (in extreme cases).
Treatment is always prescribed by a doctor and in no case independently. You need to understand that the effect of treatment will not occur in the first days. For faster results, you must follow all recommendations for nutrition and physical therapy.
If you are overweight, the patient will have to fight the extra pounds. It will be necessary to eliminate physical activity and use devices to reduce the load on the joints.
Drug treatment of osteoarthritis of the joints
Drug treatment for joint diseases is mandatory. How to treat osteoarthritis? As a rule, the doctor prescribes drugs of three categories:
- • Painkillers. Due to the fact that patients consult a doctor at the stage of severe joint pain, the primary task when prescribing treatment is pain relief. To eliminate pronounced pain, psychotropic substances are prescribed, for which a prescription from a doctor is required.
- • Anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs (NSAIDs) This group of drugs has anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. Due to the fact that this group of medications has a detrimental effect on the mucous membranes and stomach, their long-term use is impossible. NSAIDs, of course, quickly relieve pain, but they have too many side effects.
- • Chondroprotectors Chondroprotectors are designed for long-term use and serve to protect and restore cartilage tissue. They need to be taken in long courses and on an ongoing basis. In recent years, numerous studies and trials have proven their effectiveness. One of the most effective chondroprotectors is glucosamine. For example, based on glucosamine, the drug Artracam was developed, which not only relieves symptoms, but also slows down the progression of joint disease. Thanks to chondroprotectors, joint fluid improves and the cartilage surface is restored. The first effect of treating joints with glucosamine-based drugs will be noticeable after 2-3 weeks.
This type of medication is required for use during heavy sports activities.
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee joint
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint affects 30% of the population
The knee joint is the most susceptible to osteoarthritis due to heavy load. With grade 1 osteoarthritis of the knee joint, only minor pain in the knee is observed. At 2, cartilage destruction is already diagnosed, and stiffness is observed when moving. Grade 3 is accompanied by irreversible deformation of the knee and its destruction. For the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee joint, NSAIDs are prescribed to reduce acute pain, chondroprotectors to restore cartilage tissue, vitamins, electrophoresis, ultrasound and magnetic therapy.
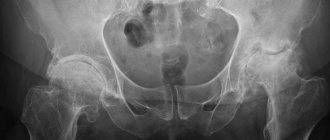
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the hip joint
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint is considered an age-related disease
At stage 1 of the disease, crunching and discomfort appear during prolonged activity. At 2, deformation of the head of the hip bone occurs, gait may change and lameness may appear. At stage 3, complete destruction of cartilage tissue occurs. For the treatment of osteoarthritis of the hip joint, a doctor usually prescribes a novocaine blockade, vitamins, chondroprotectors and warming ointments; in extreme cases, surgical intervention is required.
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the hands
Osteoarthritis of the hands occurs in 60% of cases after 65 years
The hand is a unique tool of the human body that allows you to accurately grasp objects, regulate the use of force, and much more. But if your hands are sick, then the usual way of your life is disrupted. More and more often, people turn to doctors with complaints of numbness, pain, crunching even at rest, without even suspecting that most often this means that they have been developing osteoarthritis for a long time. Unfortunately, the disease is not completely curable, but it can be stopped and slowed down with proper treatment. Typically, NSAIDs, vitamin injections, electrophoresis, physical therapy and, of course, chondroprotectors are used to treat osteoarthritis of the hands, which will become the main assistant in the fight against the disease.
Lifestyle during the treatment of osteoarthritis
Ostearthrosis requires a review of your habits and strict adherence to doctor’s orders
In order to prolong the life of joints, patients need to change their lives and develop new habits.
- 1) First of all, it is necessary to reduce the load on the joints. Running, jumping and squats are too much stress for already injured joints. Try to use the elevator instead of the stairs. Don't go for long walks. Forget about carrying heavy objects.
- 2) Compensate for the lack of usual activity with special exercises that do not put stress on the articular cartilage, but force the muscles surrounding the joint to work.
- 3) Wear special insoles and knee pads for osteoarthritis of the lower extremities.
- 4) Now you should not sit on your knees.
- 5) Do not sit on low chairs and armchairs.
- 6) Normalize your diet. Excess weight will negatively affect the course of the disease.
- 7) Do not sit in one position for a long time.
 You can start using a cane to walk.
You can start using a cane to walk.- 9) Forget about heels on your shoes.
Do not allow the disease to develop to stage 3, consult a doctor at the first manifestations and signs. Remember, taking care of your joints in everyday life is the key to successful treatment of osteoarthritis.
Images designed by Freepik
Arthrosis of the interphalangeal joints of the hands
This form most often occurs in women after menopause. A clear sign of osteoarthritis are small lumps - nodules that can be felt on the fingers. Patients feel burning and tingling in their fingers. The functionality of the phalanges of the fingers is reduced. When diagnosing, it is important not to confuse it with rheumatoid arthritis. It also often affects the fingers, but with osteoarthritis these are the “end” joints, located closer to the tips of the fingers, and with rheumatoid arthritis, these are the “inner” joints, located at the base of the finger.
Diagnosis and treatment of osteoarthritis
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital make a diagnosis of osteoarthritis based on the patient’s complaints, information about the development of the disease, and data from instrumental and laboratory research methods. X-ray signs of osteoarthritis depend on the cause and type of joint inflammation. To visualize changes in large joints, arthroscopy is performed - examination of the joint cavity using an endoscope. Inflammatory changes are detected using laboratory tests. To identify the causative agent of the infectious process, microscopic and serological diagnostic methods are used.
Treatment of osteoarthritis at the Yusupov Hospital is carried out using the latest drugs. Doctors select the drug, dose and duration of therapy individually for each patient. Acupuncture has an analgesic, sedative and antidepressant effect, improves microcirculation in the joints. The specialists at the rehabilitation clinic have sufficient knowledge and experience, so the procedure is absolutely safe, reduces the use of medications during treatment, and provides a long-term effect.
Ozone therapy is the intravenous administration of ozonized saline solution and the introduction of an ozone-oxygen mixture into biologically active points around the joints. Ozone relieves pain, relieves inflammation, improves microcirculation. The patient's pain is quickly relieved.
Under the influence of local application of therapeutic mud, the condition of the musculoskeletal system improves and the protective processes in the body are enhanced. Patients experience reduced muscle contracture and pain relief. Baths and compresses reduce inflammation in the joints. Intravenous laser irradiation of blood is a method of photobiological influence on blood cells, as a result of which all body systems are activated to correct existing disorders. Electrophoresis using medications has an analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-edematous effect. All procedures in the rehabilitation clinic are carried out under the supervision of the attending physician. Regardless of what symptoms of osteoarthritis are present, make an appointment by phone with a rheumatologist at the Yusupov Hospital.
Risk factors
- hereditary predisposition to increased traumatism,
- weight gain,
- age-related changes,
- belonging to specific professions that require additional physical stress on the skeleton,
- infectious diseases,
- hormonal imbalance,
- joint injuries,
- process of breakdown in connective tissue.
Fact. Composition of human bone tissue: 52% - water 22% - inorganic compounds 12% - organic compounds 14% - fatty compounds
Bone tissue is regenerated every 7 years.
Reasons for the development of deforming arthrosis
- presence of previous injuries;
- inflammation with pathogenic microorganisms entering the joint;
- inflammatory diseases, in particular, autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis;
- diseases associated with impaired bone formation (Perthes disease, Koenig disease, Schlatter disease).
Fact. The smallest bone of the human skeleton is the stirrup; after birth, only the ear bones remain unchanged. And the largest bone in the human body is the hollow femur.