Elbow bursitis
is an inflammatory process of aseptic or infectious type. The clinical picture of the diagnosed cases indicates the possibility of the disease occurring in both acute, subacute or chronic forms.
The most striking symptom of the presence of a pathological process is local compaction in the articulation area of the upper limb. The chronic form involves systematic pain (minor or moderate).
Diagnosis is carried out taking into account clinical manifestations, the degree of pain intensity, as well as the results of instrumental research methods.
What is elbow bursitis?
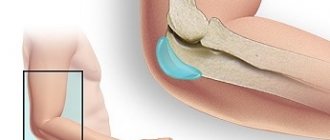
The disease in question is one of the most common types of inflammation of the joint and the accumulation of serous or purulent exudate (effusion) inside its cavity.
The development of most diagnosed cases is provoked by overloads and numerous microtraumas of the elbow. Among the patients there are athletes, people working in conditions of increased complexity (hard work), as well as those who, due to some characteristics, often rest their elbows on the table.
The risk group includes people of different ages, mostly young and middle-aged men.
The treatment plan is determined individually, taking into account the degree of intensity of symptoms, as well as the type of disease and clinical picture of a particular patient.
Causes of epicondylitis
At the bottom of the humerus there are two large protrusions - the epicondyles. They serve as attachment points for the tendons responsible for the movement of the hand. In this case, the tendons of the wrist extensor muscles are attached to the external epicondyle, and the wrist flexor muscles are attached to the internal epicondyle. Decreased elasticity or strength of the forearm muscles, repetitive unnatural movements, and direct trauma damage the tendons and periosteum of the epicondyles. Epicondylitis, or inflammation of the epicondyle, occurs as an acute condition but in many cases becomes a chronic problem.
Overload of the hand extensors leads to lateral, or external epicondylitis. This form of pathology is called “tennis elbow”, as it is often found among tennis fans. Golfer's elbow, or medial epicondylitis, affects office workers when using an uncomfortable keyboard or mouse. In this case, the flexors of the hand and fingers, attached to the internal epicondyle, are most affected.
Pathological anatomy of the disease
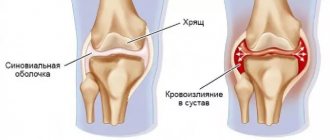
The cause of exacerbation of the symptomatic picture and the need for a therapeutic complex is inflammation of the bursa.
A bursa is a slit-type formation located relatively close to protruding bony areas, within which there is a relatively small amount of fluid.
The key function of the bursa is to cushion and protect the periarticular tissues from excessive pressure or excessive friction.
With systematic microtraumas, as well as increased pressure inside the joint, aseptic inflammation may occur, which will result in the active release of fluid from the bursa membrane. Depending on the amount of fluid produced, local swelling appears, caused by protrusion of the filled cavity.
How is the procedure performed?
In most cases, the affected joint is numbed using local anesthesia, and there is no need to put the patient to sleep. If the doctor determines that the affected joint requires drainage, a small incision is made and the bursa is opened. A small tube is inserted and kept in the bursa for several days to remove fluid. Concomitant antibiotic therapy is also prescribed to prevent infection.
In cases where draining the fluid does not provide relief, the doctor may decide to remove the bursa completely. This is especially important if movement is severely limited and the patient is experiencing debilitating pain.
In this case, the surgeon makes an incision and removes the thickened bursa. However, there are a few cases where the surgeon decides to remove only part of the bursa and leave a small portion intact to maintain lubrication and reduce friction. If this is the case, there is a chance that the bursa will return to its normal size. The incision is then closed with sutures. A modified version, called an arthroscopic bursectomy, is performed on patients diagnosed with inflammation of the bursa in the hip joint.
The surgeon makes an incision in the hip joint and inserts a small camera to guide his instruments towards the bursa. Special surgical instruments are then used to drain the excess fluid. In some cases, the bursa is completely excised from the surrounding muscles and tissues. The incision is then closed.
Classification
Specialists involved in the diagnosis and treatment of elbow bursitis have created a classification that allows you to select the most effective treatment plan. Let us consider the types of inflammation of the hand joint according to various criteria in more detail.
Bursitis is classified according to the location of the pathological process:
- subcutaneous ulna;
- radioulnar;
- interosseous.
Depending on the characteristics of the course of the disease, three forms are distinguished:
- acute;
- subacute;
- chronic.
The type of illness is also determined by the nature of the inflammatory fluid. So, inflammation is isolated:
- serous;
- hemorrhagic;
- fibrinous;
- purulent.
And as the last classification criterion, the type of pathogenic microorganisms is determined, according to which two groups of infected elbow inflammation are distinguished:
- nonspecific (caused by staphylococcus or streptococcus);
- specific (caused by spirochete pallidum, tuberculosis microbacteria, as well as gonococci and other pathogens).
The most difficult to treat is purulent bursitis of the elbow joint, in which it is difficult to avoid surgical intervention.
conclusions
- When choosing a method of alternative treatment for bursitis, you should consult a doctor.
- Home therapies will be especially effective if combined with traditional medications.
- The most effective methods of treatment are compresses, wraps and baths.
- Warming procedures should not be used if there is pus in the synovial bursa or severe swelling of the soft tissues.
- To enhance the effect during treatment, it is advisable to adjust your diet to include as many foods rich in calcium and vitamin D as possible.
Causes of elbow bursitis
Like any other pathological condition of the human body, the disease in question is provoked by various types of reasons.
The causes of bursitis of the elbow joint can be determined by various types of factors and prerequisites, which are usually included:
- previous injury (bruise)
– the negative impact of optimal force on the tip of the elbow can provoke fluid secretion, inflammation and local swelling;
- Providing long-term impact (support on a hard surface, etc.)
– constant pressure can cause swelling, which will provoke the development of pathological processes;
- infection
– in a situation where an infection enters the body through damage to the skin, certain consequences may occur, including inflammation of the joint cavity;
- development of concomitant diseases
– illnesses associated with multiple lesions can cause an unwanted inflammatory process.
Why does inflammation occur?
Bursitis occurs in most cases due to injury to the elbow. If you hit yourself accidentally, you are surprised to find a tumor on the bend of your elbow after some time. The accumulation of fluid under the skin is determined by touch. Bursitis occurs as a result of:
- the elbow is under tension for a long time when performing labor activities;
- salts are deposited in the joint due to non-compliance with nutritional rules;
- are treated with steroid drugs for a long time.
The bursa area becomes inflamed as a result of infection of the bone tissue. An increase in fluid in one of the synovial sacs will be a consequence of arthritis, rheumatism, arthrosis, gout. The pathological process spreads throughout the body, affecting most of the joints.
Risk group
People at risk for developing this type of pathology include:
- who are forced to monotonously repeat mechanical actions characteristic of a certain professional specificity;
- whose life is closely connected with sports activities that involve repetition of movements;
- those suffering from pathologies of the respiratory system, which forces them to lean on their elbows to facilitate the flow of air into the lungs.
Symptoms of elbow bursitis
Before understanding the type of disease present and forming an idea of the upcoming treatment plan, it is necessary to have an idea of the symptomatic picture.
Symptoms of elbow bursitis include:
- local swelling and increased skin temperature
– the first and one of the main symptoms of pathology (“bump” the size of a goose egg);
- pain syndrome of varying degrees of intensity
– the stronger the swelling, the brighter and more intense the pain, which intensifies with pressure on the inflamed area or flexion/extension of the limb;
- visual changes
– with the development of an active inflammatory process, the affected area acquires a reddish tint;
- limited mobility
– the range of motion does not change, but performing a number of them may be difficult due to pain.
It is important to note that acute forms can cause severe pain in a situation where the articulation cavity is transformed in the process of movement. Symptoms may be vague.
When a relapse occurs, there is pain and limited mobility for a period of several days to several weeks.
Bursitis in children
At a younger age, the disease practically does not occur. Usually the disease is encountered in adolescence. The main causes of bursitis in children: excessive physical activity, injuries and diseases that provoke the development of inflammation in the joint.
Symptoms are similar to those in adults: swelling, pain, general malaise.
An important point in the treatment of joint disease in a child is timely diagnosis. Children tend to hide the fact of injury and endure pain. Neglected treatment and lack of rest during the acute period of the disease can lead to the need for surgical intervention and more serious consequences.
Which doctor should I contact if symptoms of elbow bursitis appear?
In a situation where one or several symptoms of elbow bursitis are observed, the time comes to find the answer to the question “Who should I turn to for help?”
Diagnosis and treatment can be carried out by several specialists, which include:
- therapist (primary superficial diagnosis and referral to a specialist);
- orthopedist-traumatologist (initial examination and development of a treatment plan);
- rheumatologist (providing professional assistance if clinical data consistent with inflammatory arthropathy);
- orthopedic surgeon (if, in parallel with the inflammatory process, there is a crack or immediate surgical intervention is required).
Based on the results of seeking medical help, the need for hospitalization in a hospital is determined, indications for which may include exacerbation of septic bursitis, aggravation of the pathology by concomitant infections, as well as the lack of a positive effect from the treatment already completed.
Methods for detecting bursitis
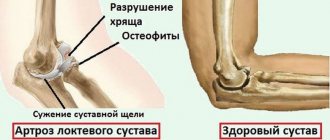
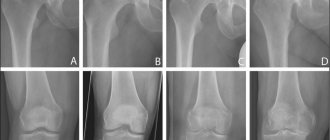
The diagnosis of infection is made on the basis of an x-ray examination. The image determines the presence of fluid in the bursa and its location. Determine whether there are osteophytes on the bone process. The growths are often localized in the fossa of the elbow joint and lead to an increase in degenerative processes in bone tissue.
Taking a puncture will allow you to study the composition of the liquid. The laboratory will determine at what stage of development the disease is. To diagnose bursitis, it is necessary to take blood for leukocytosis and ESR. A serological test of venous blood will be required.
Diagnostic features
The diagnostic process is based on a patient interview, clinical assessment of existing symptoms and, of course, direct examination. To clarify the suspected diagnosis, instrumental research methods are additionally used, including:
- radiographic examination
– the examination results allow us to exclude the possibility of a bone fracture or the presence of foreign bodies, salt deposits, etc.;
- ultrasonography
– forms an overall picture for visualizing the situation, allowing you to fully assess the condition of the walls and the volume of inflammatory fluid;
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
– detailing the results obtained provides the opportunity to confirm/refute the diagnosis and exclude other assumptions;
- puncture
– sampling the contents of the cavity allows you to determine the type of fluid, which is of particular importance when making a diagnosis. It is important to note that during the collection of material for research, therapeutic manipulations may be carried out.
In addition, a number of additional laboratory tests are carried out (clinical and biochemical blood tests, detection of C-reactive protein and rheumatological tests), which makes it possible to verify the accuracy of the diagnosis and makes it possible to assess the severity of the existing pathological process.
Treatment of elbow bursitis
Treatment of bursitis of the elbow joint is determined exclusively on an individual basis, after a thorough diagnosis, taking into account the existing clinical picture and medical history of the patient.
As with any other ailment, the best results in the treatment process can only be achieved with an integrated approach, involving a combination of conservative agents and other techniques.
Let's look at the main methods of treating elbow bursitis in more detail.
Conservative treatment
Involves the use of medication. The impact can be provided by drugs of various forms, in particular, local effects.
Among the most prescribed groups of drugs are:
- NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) – reduce inflammation and relieve pain;
- antibiotics - help fight infections in the septic form;
- corticosteroids - intra-articular injections are especially effective in situations where you need to quickly and effectively eliminate pain;
- chondroprotectors – provide the opportunity to activate the process of tissue restoration.
Chondroprotectors are of particular importance in conservative treatment, promoting the restoration of affected tissues and improving functionality. Their use is also advisable during the period of remission, which gives additional confidence in maintaining a healthy elbow during a chronic disease. Artracam is considered to be one of the best drugs in this category.
Physiotherapy
The use of physiotherapeutic treatment methods accelerates the recovery of the functional abilities of the upper extremities and has a large number of other advantages. Among the most effective and widely used physiotherapeutic techniques are:
- attending massage sessions (course);
- exposure to the affected area with ultrasound/laser/electric current;
- phonophoresis.
The duration of courses of physiotherapeutic treatment is determined by the attending physician, taking into account the characteristics of the patient’s recovery process and the characteristics of the pathology.
Radical methods
Despite the fact that most cases of elbow disease do not require surgical treatment, radical methods of its treatment still exist and are used in situations where conservative therapy and physical treatment do not give the necessary result (more than 2 months of starting treatment or in situations where secondary pathologies form).
The most effective and used method of radical therapy is endoscopic excision of inflamed tissue, which belongs to the category of minimally invasive surgical interventions.
Standard recommendations
In the initial stages of development, bursitis is treated at home. If characteristic symptoms occur, joint immobilization is performed. To do this, you need to apply a bandage made of an elastic bandage and limit the mobility of the joint without doing your usual work. After the diagnosis has been confirmed, the main condition is ensured - no load on the affected elbow. Immobilization is carried out using a pressure, scarf or elbow bandage. A possible option is the use of a special orthopedic device.
If there has been damage to the skin (bursitis of traumatic origin), the wound is treated with antiseptics, and then several layers of sterile bandage are applied.
Acute inflammation or exacerbation of a chronic process involves simple but effective methods:
Advertising:
- Tablets - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, preferably of a new generation (Doloxen, Nimesil, Celebrex, Arcosia - are more effective and have fewer side effects. In most sources you can still find advice to use Ibuprofen or Butadione, but these are just well-known names, since their development which decades have passed.In case of severe pain, you can take aspirin or Analgin, but as a complementary remedy, and not the main means of eliminating the pain symptom.
- The acute process requires the mandatory use of oral medications to supply anti-inflammatory and analgesic compounds from the inside. External agents are used directly at the site of the lesion, but have an external effect without penetrating to the inflammatory focus. The doctor may prescribe both tablets and ointments if quick elimination of an advanced disease is necessary.
- Antibiotics are prescribed provided that the cause of bursitis is a bacterial or microbial lesion, the infection has penetrated into the synovial bursa from another lesion, or has become the result of a systemic lesion. Recommendations for the prophylactic use of such drugs are unacceptable. The pathogenic agent may have resistance to the selected series. It is unacceptable to take them just because the name seemed familiar or someone recommended it.
- It is much better if the selection of medication was carried out by an orthopedist who knows about the infection based on the results of the tests obtained. Immediate antibiotics are prescribed only for purulent processes; common prescriptions are Amoxiclav or Lincomycin. However, these names are not a recommendation for drugs for any source of pus. A doctor’s recommendation is also necessary to determine the dosage and duration of the course of treatment.
- On the first day, when the inflammatory process has just started, simple cold water compresses are used. They are applied often, but for a short period of time.
- Dimexide, in solution or in combination with Novocaine, is used for pain relief and anti-inflammatory action, applying a moistened gauze bandage no more than 3 times a day, according to the standard scheme - the joint is covered with gauze moistened with a diluted drug, then polyethylene is applied, the joint is fixed with natural fabric
The ointment has a good effect and alleviates the patient's suffering. The range of ointments with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory components is wide, the effect on the affected joint is prolonged, but the choice of topical application is also best left to the doctor.
Possible complications and prognosis of patients with diagnosed bursitis of the elbow joint
Like any other disease, ulnar bursitis has certain prognoses, which were formed thanks to a large number of cases of medical practice.
In the vast majority of cases, the development of pathology does not lead to serious restrictions on the mobility of the arms (mostly the joint).
In the absence of an infectious lesion, positive dynamics are observed in the near future after the start of complex treatment (in conjunction with a system of anti-inflammatory drug therapy).
However, it is important to say that in rare cases, a relapse may occur, in which even minor swelling and mild pain can trigger the release of a large amount of fluid.
Refusal of treatment or untimely assistance may aggravate the situation and complicate the treatment process.
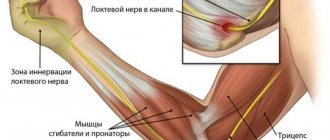
External epicondylitis of the humerus
It is expressed in sharp pain in the area of the outer epicondyle of the humerus - this is a bone protruding from the outside in the area of the elbow joint. If you put your hands on your belt and try to walk through a doorway, these are the bones with which you will hit the frame. The brachioradialis muscle (m.brahioradialis), which is responsible for dorsiflexion of the hand, is attached to this bone. In a non-professional environment, this movement is called extension. Inflammation occurs at the place of attachment to the humerus - the external epicondyle. It occurs due to overstrain of muscle fibers, which can occur due to repetitive movements of the same type: working with a hoe, practicing with a tennis racket or spinning rod.
If such loads occur spontaneously after a long break, this is often the cause of the onset of inflammation. The fact is that during the rest period we often lean on a table top or handrails or hold a smartphone in our hands, so this muscle is in a shortened state. When we begin to work with a contracted muscle, the load on the attachment site increases, which leads to inflammation, accompanied by partial breakage of muscle fibers, which causes even greater inflammation. Since this area is poorly supplied with blood and is often subjected to stress, the inflammation drags on and becomes chronic. In the patient, external epicondylitis causes great discomfort: the pain makes it difficult to pick up a teapot or cup, and sharply intensifies with any muscle tension in the hand and straightening the arm at the elbow joint.
Preventive measures
The best method of treating diseases is their timely prevention. To avoid having to experience the effectiveness of modern treatment methods, it is best to take preventive measures. Let's try to figure out what these include.
Disease Prevention
A number of simple recommendations will help prevent elbow bursitis, compliance with which will ensure the ability to maintain healthy joints and the overall level of quality of life:
- Preventing injuries, ensuring skin protection.
- Providing high-quality first aid for injuries to the skin or joint.
- Timely seeking medical help.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
- Quitting bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol, overeating).
- Attending preventive medical examinations.
- Preventive use of a course of chondroprotectors like Artracam.