Gonarthrosis (arthrosis) of the knee joint is a complex pathological process, a characteristic feature of which is disrupted cellular metabolism in the anatomical structures of the knee, leading to irreversible destruction of the articular cartilage with further deformation of the knee joint. Conservative treatment is fraught with difficulties, since existing degenerations are incurable. Therefore, it is possible to conservatively suspend pathogenesis and prevent it from severely disrupting the quality of life only in the early period of development of the disease.
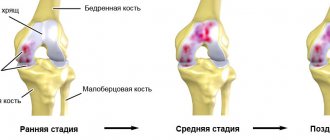
A visual representation of the destruction of cartilage tissue.
The degenerative-dystrophic disease causes gradual thinning, wear and destruction of the cartilaginous tissues enveloping the epiphyses of the articulating bones. As a result of the changes that occur, with each new stage, the functionality of the osteochondral joint located in the knee region is inhibited more and more. The disease of the last two stages - grade 3-4 gonarthrosis - is accompanied by terrible persistent pain, critical limitation of mobility of the lower limb, severe lameness and shortening of the affected leg.
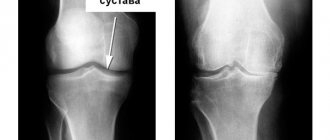
View of a healthy joint through an astroscope, the articular surfaces are perfectly smooth.
The painful syndrome has a pronounced long-term course, even at rest. At the same time, an advanced disease, which is recognized as the most severe, leads to serious deformities of the knee and no less serious curvature of the legs - valgus (O-shaped) or varus (X-shaped) type. The patient cannot move without a wheelchair or crutches. Moreover, he needs constant supervision and assistance. For example, when it becomes necessary to undergo hygiene and toilet procedures, put on shoes, get dressed, and so on, it is problematic for him to do this on his own.
This is what gonarthrosis looks like, find the differences.
According to statistics, people over 40 years of age have the greatest predisposition to knee arthrosis, and it manifests itself especially often in old age. Female patients suffer from gonarthrosis more often than male patients. The reasons for the development of progressive gonarthrosis are quite varied. However, as clinical observations show, the main factors predisposing to pathology are post-traumatic complications, hormonal disorders in the body, excessive physical activity, excess weight, previous local infectious and inflammatory diseases and autoimmune disorders. In rare cases, the nature of the origin of pathogenesis remains unidentified.
Characteristics of the pathology
Arthrosis of the third degree refers to a pronounced degenerative process in joint tissues, including cartilage and bones. Pathological changes developing in the joint are irreversible. At this stage of the disease, a person is assigned a disability, since the function of movement is significantly impaired.
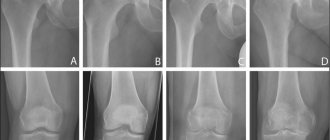
Arthrosis 3rd degree – external development
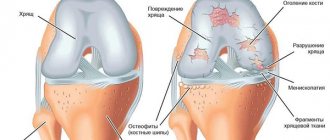
The degenerative-dystrophic process consists of changing the properties of cartilage tissue and destroying it. At stage 3 of the disease, bone tissue is also involved, which leads to the development of joint immobility - ankylosis. The absence of a shock-absorbing cartilage layer causes the bony surfaces of the joint to rub against each other, which causes severe pain.
Interesting!
Most often, the hip and knee joints are affected by pathology. In women, arthrosis of the third degree develops faster than in men.
Is disability granted?
Disability status is given at this stage of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the knee joint, since the disease in this period leads to either partial disability or complete disability. Based on the severity of the clinical picture, disability group 1 or 2 is assigned. In the first case, the group is given when there is no movement in the joint, due to which the person cannot move and cope with basic self-care tasks. The second category of disability is given if movement is still partially possible, but not without assistance, and also if the problematic limb is shortened by 7 cm or more.
Clinical manifestations
Arthrosis of the joints of the 3rd degree has a pronounced clinical picture. The main complaint of patients is pain. Unlike arthrosis of previous degrees, pain occurs not only at the moment of movement, but also at rest. This is due to the constant inflammatory process in the joint. The pain is aching in nature and reaches significant intensity.
Motor function is almost completely limited, not only due to pain, but also due to the fusion of bone surfaces with each other. When the hip joints are affected, a person acquires a duck's gait - he walks, waddling from one foot to the other. When the knees are affected, a person walks with his legs constantly straightened, and there are difficulties when climbing stairs.
Externally, the joints look deformed and enlarged compared to healthy ones. With the development of the inflammatory process, swelling of the soft tissues is noted. When performing movements, a crunching sound is clearly audible due to the contact of bones. Due to the lack of cushioning by cartilage, movements are no longer smooth.
What factors and in which groups increase the risk of the disease?
Gonarthrosis occurs in people who lead a sedentary lifestyle, suffer from obesity, and subject their knees to excessive stress. Its development is often caused by smoking and alcohol abuse, which impair blood circulation in the legs. Gonarthrosis can be provoked by a deficiency in the diet of microelements, fat- and water-soluble vitamins necessary for the full functioning of hyaline cartilage. The risk group includes people whose work involves constantly being on their feet, as well as professional athletes, especially weightlifters.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of third degree arthrosis is made on the basis of characteristic complaints, clinical manifestations, and X-ray data. The x-ray reveals the characteristic signs of stage 3 disease:
- Marked narrowing of the joint space;
- Complete absence of cartilage layer;
- Severe deformation of the bone surfaces of the joint;
- Osteophytes – bone growths – form along the edges of the joint space.
If there is doubt about the diagnosis, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging is performed.
Diagnosis of arthrosis 3 degrees
- Is it possible to cure grade 3-4 knee arthrosis without surgery using medications and folk remedies?
Pharmacological drugs
Almost all medications used in the treatment of grade 3 arthrosis are prescribed to patients to relieve pain. Depending on the general health of the patient, they are used in different dosage forms: in the form of rectal suppositories, tablets, suspensions, ointments, solutions for parenteral administration. The first choice drugs are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Arthrosis is not accompanied by inflammation, but NSAIDs (Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Nimesulide) quickly eliminate severe pain and extensive swelling. The following groups of drugs are also used in therapy:
- glucocorticosteroids (Triamcinolone, Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone) with low clinical effectiveness of NSAIDs;
- narcotic analgesics (Tramadol);
- muscle relaxants (Sirdalud) to relieve painful muscle spasms;
- ointments with a warming effect (Viprosal, Finalgon, Apizartron).
The only group of drugs that can inhibit tissue destruction are chondroprotectors. These are Dona, Teraflex, Structum, Glucosamine Maximum, Alflutop, Chondroitin. The duration of treatment with these drugs is 1-2 years.
Very often, patients need the help of a psychologist. Awareness of the irreversibility of developed complications becomes the cause of neurological disorders, psycho-emotional instability, and severe depressive states. In such cases, antidepressants, tranquilizers, sedatives and sedatives are included in the therapeutic regimens of patients.
| Medicines used in the treatment of grade 3 arthrosis | Name of pharmacological drugs |
| Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in tablets and injection solutions | Diclofenac, Ortofen, Meloxicam, Artrosilene, Movalis, Ketorol, Ketorolac |
| Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of ointments, gels, creams, balms | Voltaren, Fastum, Diclak, Dolobene, Dolgit, Ketorol, Indomethacin, Ibuprofen, Piroxicam |
| Warming agents for local application | Efkamon, Arthro-Active, Viprosal, Apizartron, Finalgon, Revmalgon from the 911 series |
| Chondroprotectors | Dona, Teraflex, Structum, Glucosamine Maximum, Alflutop, Chondroitin-Acos |
| Glucocorticosteroids | Triamcinolone, Kenalog, Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone, Dexamethasone |
| Strengthening and toning products | Pentovit, Milgamma, Kombilipen, Semevit, Centrum, Complivit, Vitrum |
Doctors recommend that patients give up bad habits. Poisonous tobacco tar and ethyl alcohol disrupt blood circulation in the damaged joint, accelerating degenerative processes. This can also be caused by the patient consuming foods high in salt and fat. Harmful cholesterol begins to be deposited in the form of blocks in the blood vessels, and the affected tissues experience an acute deficiency of nutrients and biologically active substances. Only following medical recommendations will help slow down joint damage and improve the patient’s well-being.
Treatment methods
How to treat arthrosis of the 3rd degree - for any degree of the disease, complex therapy is required. Since the third degree is irreversible, the only effective treatment method is surgical. How can stage 3 arthrosis be cured without surgery? In fact, this is not possible, since the tissues of the joint are completely destroyed. To restore movement function, it is necessary to replace the destroyed joint with an artificial one. All other treatment methods are symptomatic.
Medication
Treatment of grade 3 arthrosis with medications is aimed at eliminating pain and suppressing the inflammatory process. For this, different groups of drugs are prescribed:
- NSAIDs. The main medicine to eliminate the symptoms of the disease. They have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. The drugs Ibuprofen, Nimica, Ortofen are used for oral administration. Voltaren and Fastum-gel are used for application to sore joints;
- Analgesics. Indicated for severe pain syndrome. Prescribed drugs such as Dexalgin, Ketorol. They can be taken orally, and in case of severe pain - in the form of intramuscular injections;
- Chondroprotectors. The preparations contain the main components of natural cartilage tissue - glucosamine and chondroitin. In the third degree, the disease is ineffective, since the cartilage is almost completely destroyed. They use Artru, Donu, Cartiflex. Treatment lasts for 3-6 months.
The tactics of drug therapy are determined by the attending physician depending on the prevailing symptoms.
Folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies is only symptomatic and in the third degree of arthrosis does not give a noticeable positive effect. Various tinctures and compresses based on medicinal plants are used. Homemade recipes should never replace treatment prescribed by a doctor.
Surgical
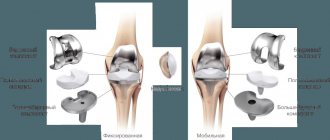
The main and most effective way to treat severe arthrosis. For mild deformities, arthroplasty surgery is performed while preserving the native articular tissues. If the pathological process has completely destroyed the joint, endoprosthetics is performed - replacing the joint with an artificial mechanism.
Physiotherapy
Gymnastic exercises are necessary for constant training of joints and maintaining motor function for as long as possible. Physical activity improves blood supply and nutrition to joint structures, relieves pain. Treatment with gymnastics for the third degree of arthrosis is carried out in a lighter version. Exercises are done in a lying or sitting position, with limited load. A set of exercises is prepared by a specialist in exercise therapy.
On a note!
Water aerobics is useful for severe arthrosis. Exercises in water relieve pain well and are easily tolerated by patients. At the same time, the limbs are massaged.
All methods of treating pathology
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is also symptomatic. The following methods are used:
- Magnetotherapy;
- Paraffin and ozokerite applications;
- Diadynamic currents;
- Ural Federal District.
Physiotherapy helps improve blood circulation and reduce muscle and joint pain. Conducted in courses of 10-15 procedures per year.
- Osteoarthritis of the knee joint: can it be cured without surgery?
Conservative treatment of gonarthrosis
Traditional medicine does not undertake to treat arthrosis in an advanced state using conservative methods. They are used in the first and less often in the second stages. Treatment is aimed at:
- relieve a person from pain;
- eliminate inflammation;
- improve the trophism of cartilage tissue;
- activate blood circulation;
- strengthen the muscles around the joint.
For this purpose, they resort to the following methods of treating arthrosis:
- medications;
- manual therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- cryotherapy - cold treatment;
- laser and magnetic therapy;
- thermal procedures using ozokerite, paraffin, therapeutic mud;
- acupuncture and other methods.
Physiotherapy is ideal until arthrosis reaches the second and third stages
Therapeutic exercises are indicated at the initial stage of gonarthrosis, and will also be an excellent preventative measure if you are at risk. Try this simple set of exercises – it will take about 10 minutes to complete:
Forecast
The last stage of arthrosis is an incurable condition. Patients lose their ability to work and become disabled. It is possible to restore limb function only after joint replacement.
Arthrosis of the joints of the 3rd degree is the final stage of the disease, characterized by irreversible changes. Patients become disabled if left untreated. The only effective way to maintain a healthy lifestyle is endoprosthetics.
Arthrosis of the knee joint 3rd degree (also known as gonarthrosis, osteoarthrosis) is a chronic dystrophic, degenerative condition accompanied by pain, limitation of movement, deformation, change in the axis of the lower limb, leading to a decrease in the quality of life.
There are ways to solve the problem - surgical (operative) and therapeutic (conservative) methods. Each of them has a number of advantages. Most people are afraid of surgical interventions and wonder how to treat grade 3 arthrosis of the knee joint without surgery at home?
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to determine the main symptoms of gonarthrosis.
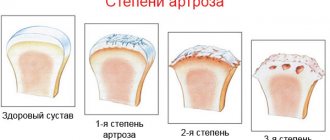
Degrees of arthrosis
Treatment of joint arthrosis depends on the degree of the disease. There are three stages, each characterized by its own symptoms and varying degrees of damage. Of course, therapy should be started at the first stage; ignoring the problem will lead to the need for endoprosthetics. There are arthrosis:
- 1st degree. Symptoms of the disease are weakly felt, slight pain is possible during exercise. At this stage, initial changes are observed in the synovial membrane, and the composition of the fluid changes. There is no modification of the muscles, but they are weakened.
- 2 degrees. The destruction of articular tissue begins, the formation of growths. There are noticeable but tolerable pains, crunching, and disruptions in muscle function.
- 2 degrees. The destruction of articular tissue begins, the formation of growths. There are noticeable but tolerable pains, crunching, and disruptions in muscle function.
- 3 degrees. The most severe stage, which is characterized by deformation of the joints, the axes of the limbs noticeably change. Motor function is greatly reduced, as the joint capsule becomes denser and the ligaments are shortened. There is chronic inflammation and constant severe pain. Trophic changes gradually spread to all tissues of the affected limb.
If rehabilitation is not started in time, after stage 3 the joint is completely destroyed, the only possible solution is endoprosthetics. Arthrosis of the shoulder joint and other types are characterized by complete immobility of the joint or, conversely, atypical mobility.
Causes of the disease
As they studied the problem of deforming arthrosis, scientists put forward various hypotheses to explain the occurrence of this disease.
Constant microtrauma of articular cartilage simply and clearly explains the cause of the development of grade 3 arthrosis of the knee joint. When a knee injury occurs, articular cartilage is damaged. The process of inflammation (chondrosis) begins.
Articular cartilage becomes dull and loses its properties. Damaged areas are replaced with connective tissue. Depreciation is disrupted, and the load is unevenly distributed on both healthy and altered areas of the cartilage.
The femur and tibia gradually change their relationship. Chondrosis is accompanied by changes in the underlying bone beams and the process is already called arthrosis. Chronicity of the dystrophic process and lack of treatment in the initial stages gradually leads to the development of stage 3 deforming osteoarthritis of the knee joint.
- Treatment of deforming arthrosis of the knee joint grades 1, 2, 3, its causes and symptoms
Main reasons:
- Injuries of the knee joint - fractures, sprains, bruises, damage to the ligamentous apparatus.
- Excess weight, which puts excess stress on joint surfaces.
- Physical inactivity leads to disruption of metabolic processes in articular cartilage and stagnation of synovial fluid.
- Poor nutrition, with a high salt content, contributes to changes in the intra-articular environment, disruption of cartilage nutrition, and, as a result, creates conditions for the development of arthrosis.
- Failure to seek medical help in a timely manner when the first symptoms of gonarthrosis occur.
- Inadequate self-medication does not stop arthrosis, but contributes to its further accelerated development.
- Autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatism, gouty arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, have a detrimental effect on the condition of the knee joints.
- Osteoarthritis of the knee joint in 70% of cases has a genetic predisposition.
Reasons for the development of gonarthrosis
When walking, the knee joint suffers the most. With age, cartilage tissue wears out and destructive changes occur in its structure. However, not everyone develops arthrosis of this joint. Those most susceptible to the disease are:
- overweight people (due to increased stress on joints);
- athletes and simply lovers of an active lifestyle;
- those who have suffered a knee injury or fracture in the past, damaged the knee meniscus;
- patients over 40 years of age, especially women during menopause;
- people diagnosed with varicose veins;
- those who have a history of relatives who have already been diagnosed with arthrosis (the hereditary factor also plays a role).
Injured your knee during a scheduled workout? You are automatically at risk for developing arthrosis
Disease prevention
The substantiation and development of a differentiated approach to the selection of methods for the prevention and treatment of grade 3 arthrosis of the knee joint is very relevant. Among diseases leading to disability, arthrosis occupies one of the leading positions.
According to statistics, of all chronic diseases leading to permanent loss of working capacity, patients with arthrosis of the knee joints often receive the 3rd degree of disability.
Measures to prevent arthrosis of the knee joint:
- Daily physical activity (at least 6000 steps per day).
- Swimming is the optimal type of physical activity for gonarthrosis. Visiting the pool 2-3 times a week for 40 minutes;
- See an orthopedist once every six months;
- Perform joint x-rays annually;
- Once every six months, undergo a course of physiotherapeutic treatment.
How to treat
This stage is extremely difficult. The disease completely changes the patient's life and leads to loss of ability to work. After establishing the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes comprehensive treatment for grade 3 arthrosis of the knee joint.
This therapy includes the following components:
- taking medications;
- physical therapy;
- exercise therapy exercises;
- diet.
At this degree of the disease, conservative treatment often does not lead to the desired effect. Then the patient is recommended to undergo surgery.
For different forms of the disease, various operations are performed:
- endoprosthetics (photo) - replacement of a dead joint with an implant;
- arthrolysis - removal of altered membrane adhesions to restore motor function;
- puncture - removal of excess fluid and administration of hormonal drugs;
- arthroplasty - the formation of simplified articular surfaces.
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint grade 3 - indication for surgical intervention
The recovery process after surgery takes place under the supervision of a doctor. In the first days after the intervention, the patient should begin to move the restored joint.
The patient will be allowed to get up 2-3 days after the operation. A specialist will help him develop a gait that is gentle on the joint. First, the patient moves with the help of crutches, then they can be replaced with a cane. The rehabilitation period lasts about 6 months.
Drug treatment
Drug therapy for grade 3 arthrosis pursues symptomatic goals. Internal and external remedies are prescribed that alleviate the situation and improve both the general health of the patient and the condition of the affected joint.
Table No. 2. Medicines for the treatment of arthrosis:
| A drug | Compound | Instructions for use |
| Artra | Glucosamine and chondroitin | Orally, one capsule per day |
| Nurofen | Ibuprofen | One tablet for pain |
| Ketonal Thermo | Ketoprofen | Externally in the form of a patch once a day for 12 hours |
You can buy all these drugs at the pharmacy; their prices vary.
Physiotherapy
Treatment of grade 3 arthrosis of the knee joint using physiotherapeutic methods can bring good results even at this stage. When choosing types of physiotherapy, the doctor takes into account the symptoms and the presence of contraindications.
Preference is given to methods that can help reduce pain, restore soft tissues surrounding the joint, improve blood circulation and nutrition of the joint:
- Magnetic therapy can be local or general. The procedure helps relieve swelling, reduce pain and inflammation. It accelerates tissue regeneration and improves blood circulation.
- Electrophoresis. This method allows drugs to be administered through the skin, directly into the joint.
- Laser therapy will help relieve painful symptoms. It accelerates metabolic processes, dilates blood vessels and improves the nutrition of cartilage tissue.
- Radon and hydrogen sulfide baths are indicated for the treatment of all types of arthrosis. They also reduce pain, improve nutrition and restore blood circulation in the joint.
The use of physiotherapy is also indicated after operations, during the rehabilitation period. In addition, they enhance the effect of drugs, which reduces dosage and side effects. The specialist in the video in this article will talk about the physiotherapeutic techniques used.
Physiotherapy
Even with grade 3 arthrosis, careful exercise has a positive effect on the joint and on the general condition of the patient. Physical exercise is also recommended during the recovery period after surgery.
Therapeutic exercise differs from regular exercise in that all movements are performed slowly, smoothly, with minimal stress. Long pauses are made between approaches. A physical therapy session can only be performed under the supervision of a qualified specialist. Success lies in regular practice.
At the initial stage of training, exercises can be performed without getting out of bed:
- lying on your back, bend your leg at the knee without lifting it from the mattress, then use your hands to pull your leg towards your body and return to the starting position;
- lie on your back and imitate riding a bicycle;
- lift the straightened leg 30 centimeters above the mattress and fix the position for 5 seconds, do the same with the other leg.
It is useful to end physical education with a massage session.
Therapeutic exercises help relieve pain and restore mobility
Diet for arthrosis
Diet is of no small importance in treating the disease. The diet is designed in such a way that the body receives all the necessary microelements and vitamins and excess weight is reduced. Experts recommend avoiding fatty meats, canned and spicy foods, fast food, alcoholic beverages, and fatty sauces.
Preference is given to lean meat, fish, seafood, fresh vegetables and fruits, cereals (except rice and semolina), and fermented milk products. They contain proteins, minerals and vitamins necessary for the human body.
You need to eat small portions up to 4-5 times a day. In addition, you need to establish a drinking regime. Patients with arthrosis benefit from drinking pomegranate and orange juices.
A disease such as grade 3 arthrosis of the knee joint requires long-term and labor-intensive treatment. To prevent the development of this stage, it is necessary to consult a doctor at the first symptoms of the disease. At the initial stage, arthrosis can be successfully treated and the joint can be completely restored without surgery.
Diagnostics
To improve the quality of life and identify the early stages of arthrosis of the knee joint, a comprehensive diagnosis is necessary. Initially, an examination by an orthopedist is required, who will prescribe the necessary diagnostic measures.
Instrumental
- The gold standard for diagnosis is radiography of both knee joints in two projections - anterior and lateral.
- MRI diagnostics, in addition to bone structures, makes it possible to identify changes of an inflammatory or destructive nature in the soft tissues of the knee joint.
- Computed tomography is most often used in addition to the x-ray method when planning surgical treatment.
- Diagnostic arthroscopy of the knee joint has gained wide popularity, allowing to visually assess the intra-articular picture and make the final decision in choosing a treatment method.
Laboratory (Analysis)
- clinical blood test;
- blood chemistry;
- blood test for C-reactive protein;
- clinical urine analysis;
- blood test for rheumatoid factor (if necessary).
Diagnostic methods
To draw up a clinical picture, the doctor interviews the patient: how the disease developed, possible causes, and what symptoms are bothersome. Next, the knee joint is examined and functional samples are taken. But complete information can only be obtained by conducting instrumental research.
These include:
- radiography;
- MRI;
- computed tomography;
- arthroscopy.
At the third stage of disease development, the most informative method is radiography. In this case, photographs are taken in several projections, where you can notice that there is practically no cartilage, the bones rub against each other, and may even grow together. Osteophytes and salt deposits are also visible in the photographs.
Traditional treatment
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint grade 3 has several treatment methods. All of them are described below.
Medication
To relieve inflammation and pain in the knee joint, the most commonly used medications are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as Nimesil, Ketorol, Ketorolac, Diclofenac.
Chondroprotectors - chondroitin sulfate preparations (Chondroxid, Chondroitin-akos) are prescribed in addition to the treatment.
Intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid preparations have become very popular. PRP therapy is relevant - intra-articular injection of centrifuged patient plasma enriched with platelets.
Surgical
Surgical treatment of deforming osteoarthritis depends on the severity of clinical manifestations and diagnostic results.
The main types of operations performed for grade 3 gonarthrosis:
- therapeutic and diagnostic arthroscopy;
- endoprosthetics;
- corrective osteotomy;
- arthrodesis;
- arthrolysis.
Physiotherapy
Exercise therapy for arthrosis of the knee joint should begin after the acute phase of inflammation has subsided. The main goal of treatment is to improve blood supply to the knee joint area, eliminate movement restrictions, and strengthen the leg muscles.
The first 10 days of therapeutic gymnastics classes must be carried out in a physical therapy room with an instructor and under the supervision of a doctor. Next, therapeutic exercises must be done at home every day for 20-30 minutes for 2-3 months from the date of treatment.
The main requirement for physical therapy classes is regularity with a gradual increase in loads. If acute pain occurs, exercise must be stopped.
The first exercise therapy classes include a set of lightweight exercises with self-help to mobilize the knee joint, without additional load. As the intensity of the pain syndrome decreases, it is necessary to include resistance exercises in the complex of therapeutic exercises. Exercise on an exercise bike is ideal for this.
After the complete disappearance of pain and swelling of the soft tissues, classes are carried out, including active exercises aimed at training muscle strength for static and dynamic loads. It is very important to maintain a daily physical activity regimen - take at least 6-10 thousand steps a day.
Gonarthrosis
What happens to the joint during gonarthrosis | Reasons | Symptoms | Treatment of gonarthrosis
Gonatrosis affects the knee joints, destroying their cartilage tissue. And if treatment is not started in time, this can lead to disability and the need to replace the joint with a prosthesis!
Modern methods of tissue restoration will help you do without surgery and a prosthesis: PRP, SVF, Plasmogel and others, available today at the Doctor Ost Medical Center.
Sign up
Half of all cases of knee joint diseases are due to gonarthrosis. According to statistics, this disease occurs in men and women over the age of 45 years. Pain in the knee with every movement, and then at rest - this is how gonarthrosis of the knee joint manifests itself.
Treatment previously came down to one thing: the patient first lived on painkillers, and then was sent for endoprosthetics. Wear of cartilage and bone tissue was previously considered irreversible. The doctors just shrugged: age, natural and inevitable aging of tissues. Even when prescribing chondroprotectors, the specialists themselves are not too optimistic, really understanding the limited capabilities of these drugs in restoring worn-out cartilage. When the destruction of cartilage tissue reached a critical level, the patient was sent to the surgical table. It is clear that a surgical approach to the treatment of grade 3 gonarthrosis is not the best option: you have to recover for a long time after anesthesia and surgical injuries and learn to walk again.
So does gonarthrosis of the knee joint need treatment before surgery? Or are these vain hopes? And how! Today, treatment of gonarthrosis, even in late stages, has more prospects. There is a real chance to restore the damaged joint and avoid disability. The patient’s task is not to miss this chance and seek help from a good specialist in time. And the sooner this is done, the higher the chances of treatment success.
WHAT HAPPENS TO THE KNEE JOINT WITH GONARTHROSIS
Gonarthrosis begins with microdamage to the cartilage tissue of the joint: they become covered with microcracks. Gradually, the cartilage tissue becomes thinner. Treatment of grade 1 gonarthrosis is aimed at restoring the blood supply that nourishes the joint tissue and additionally stimulating the growth of new healthy tissue.
If this is not done, the body will try to cope on its own. As compensation for worn-out cartilage, rapid growth of bone tissue occurs in areas of damage - osteophytes appear (these growths are often called “salt deposition”). But osteophytes do not solve problems; they only complicate the functioning of the joint, injuring surrounding tissues and limiting mobility. Treatment of grade 2 gonarthrosis will be successful only if osteophytes are removed and mobility is restored to the joint.
When the cartilage tissue completely disappears, the bone is exposed and the joint space narrows, the most severe degree is diagnosed - deforming gonarthrosis. Treatment in this case must take into account many factors: the general condition of the body, concomitant diseases, the degree of damage to bone structures and the patient’s readiness for surgery. At the stage of grade 3 gonarthrosis of the knee joint, even the most persistent patients who have previously endured pain for a long time seek treatment. The quality of life is seriously deteriorating. But correcting the pathology is already noticeably more difficult than if it had been treated in earnest earlier.
CAUSES OF GONARTHROSIS
- Increased load on the joint.
- Poor blood supply to the periarticular tissues.
- Disruption of the endocrine system: due to a lack of hormones, the most important proteins - collagen and elastin - do not enter the cartilage tissue. Without them, cartilage tissue loses its elasticity and gradually collapses.
- Violation of water balance.
- Regular hypothermia of the knee joints often causes gonarthrosis.
Often, patients who seek treatment for gonarthrosis also have other pathologies of the musculoskeletal system:
- Flat feet;
- Scoliosis;
- Diseases of the lumbar region.
If you are overweight, your joints have to cope with loads they were not designed to handle on a daily basis. Therefore, competent treatment of joint gonarthrosis cannot be accomplished without weight loss.
SYMPTOMS OF GONARTHROSIS
Symptoms of gonarthrosis appear in increasing order:
1st degree
often not too alarming: rare knee pain occurs after exercise. But it is during this period that it is best to start treatment.
2nd degree
gonarthrosis is accompanied by increased pain. It becomes difficult to squat and climb stairs. Long walking also affects the knee joints: severe pain after exercise does not go away for a long time. Treatment of gonarthrosis with analgesics brings temporary relief, but accelerates the destruction of cartilage and, moreover, affects the gastric mucosa. At this stage, you can still get by with conservative treatment.
3rd degree
gonarthrosis of the knee joint - every movement brings pain. The patient does not put any weight on the sore leg, so lameness, forced postures, and muscle atrophy develop. With bilateral gonarthrosis, the only way to move is a wheelchair. The range of motion is also reduced due to the large number of osteophytes in the joint. An ultrasound will show a reduction in the size of the joint space, a decrease in the volume of synovial fluid and cartilage layer. Upon visual examination: the knee is deformed, contractures and swelling are visible.
TREATMENT OF GONARTHROSIS OF THE KNEE JOINT
The first and most important advice is not to let gonarthrosis progress! At grade 1, treatment of the knee joint has maximum effect. Only tablets and ointments for the treatment of gonarthrosis are an outdated technique: they are designed to restore cartilage tissue, but they do it too slowly and ineffectively. The active substance does not enter the joint in sufficient quantity.
Intra-articular injections of PRP or SVF will work much more productively than ointments and tablets: they stimulate the active synthesis of healthy tissue in place of destroyed ones and have high proven effectiveness even in pathologies previously considered incurable. However, first you need to relieve pain in the knees, especially in the acute stage. Many prescriptions are contraindicated in the acute period. Modern physiotherapy helps to quickly relieve pain, relieve inflammation and swelling.
Treatment of grade 2 knee joint gonarthrosis, among other things, should be supplemented with measures aimed at getting rid of osteophytes that injure surrounding tissues.
To bring gonarthrosis of the knee joint into remission, treatment is completed with strengthening rehabilitation procedures: exercise therapy, massage, kinesiosimulators, lifestyle and nutrition correction. If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, your knees can still be saved.
Treatment of deforming gonarthrosis is the most difficult. In most cases, the patient is referred for endoprosthetics. But don't rush into surgery! Innovative methods for treating grade 3 gonarthrosis, which are already available at Doctor Ost MC, give a chance to restore the native joint without a surgeon’s scalpel!
Expert opinion
Zonova D.P. comments.
traumatologist-orthopedist at Doctor Ost Medical Center in Chelyabinsk. Of course, with severe damage, it is no longer possible to restore tissue to an ideal state.
But surgery is a point of no return. Therefore, it makes sense to stop the destruction, restrain the development of the disease, gain time from it, and push back the threshold for complex surgical intervention. You must understand that the service life of any, even the most expensive, prosthesis is limited. This means that at some point a new operation, a new anesthesia and a new period of post-operative rehabilitation will be required. That is why, before agreeing to endoprosthetics, you need to carefully weigh the pros and cons and make sure that all non-surgical treatment options are used. Only the attending physician can assess the real prognosis for the treatment of gonarthrosis in a particular patient during an individual appointment.
Make an appointment with the orthopedist “Doctor OST” right now to ask all your questions. For your convenience, the website allows you to choose the doctor’s free hours that are most convenient for your visit. An online consultation format is also available. The federal network of clinics "Doctor Ost" specializes in the treatment of joint diseases of varying severity. We work using our own, unparalleled treatment technology, which has already put thousands of patients on their feet and saved them from surgery.
how much does it cost? Gonarthrosis is treated by a neurologist, orthopedic traumatologist, and rehabilitologist. The cost of consultation with a specialist is indicated in the “Consultative appointment” section of our price list. Follow the promotions, don't miss out on the best price!
Our specialists have in their arsenal advanced treatment technologies:
- Intra-articular injections with hyaluronic acid and corticosteroids;
- Plasmolifting and PRP therapy;
- Plasmogel injection - treatment of arthrosis with the patient’s blood plasma;
- SVF therapy – treatment of arthrosis with stem cells;
- Shock wave therapy;
- HILT – high-intensity laser therapy and pain relieving system EPS;
- Pharmacopuncture;
- Acupuncture;
- Magnetotherapy;
- Classes with a rehabilitation therapist on simulators;
- Bioniths of slimness;
- Consultation with a nutritionist.
Therapy and procedures
Physiotherapeutic methods are aimed at improving blood supply to the knee joints, eliminating soft swelling, and improving overall well-being. Each procedure relaxes the muscles, which subsequently makes it possible to walk normally without additional means of support.
Physiotherapy
A course of physiotherapeutic procedures is carried out every 6 months to prevent arthrosis of the knee joint. The best therapeutic effect is obtained in combination with exercise therapy and massage.
Types of physiotherapy used for arthrosis of the knee joint:
- pressotherapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- UHF therapy;
- ultrasound therapy.
Physiotherapeutic treatment has a number of contraindications:
- oncological diseases;
- acute phase of the disease;
- skin damage and diseases;
- infectious diseases.
Nutrition
A balanced diet for arthrosis of the knee joints ensures the prevention of excess weight gain and the intake of minerals and vitamins.
Nutrition Features:
- The plant component should predominate in the diet.
- Reduced salt content in the daily amount of food consumed.
- Daily water consumption is at least 2 liters.
Recommended Products:
- lean varieties of fish and meat;
- cold pressed vegetable oils;
- vegetables, fruits, herbs;
- low fat dairy products.
Traditional treatment
In the age of technological progress, the treatment of stage 3 arthrosis of the knee joint with folk remedies does not lose its relevance. These include tinctures, rubs, baths, ointments, infusions, and decoctions.
Cinquefoil tincture is an excellent remedy for knee pain. Used as a compress on the knee joint. Pour 5 tablespoons of cinquefoil raw material into 500 ml of vodka and leave for 14 days in a dark place at room temperature. Before use, dilute the tincture 1:1 with saline solution. Pour the resulting solution onto a gauze pad, apply it to the knee joint, cover with film and secure. Exposure time is 7 - 8 hours (overnight). Course 10 days.
Rubbing
- Mix apple cider vinegar in equal proportions with olive oil. Rub the knee joint 2-3 times a day. Course 5-7 days.
- Grind fresh birch leaves to a pasty consistency, add 1 teaspoon of ethyl alcohol (40% alcohol-containing liquid). Apply the resulting mixture under the film and secure with a woolen cloth. Exposure time is 7-8 hours. Course 7-10 days.
- Mix turpentine and vegetable oil (sunflower or olive) in a 1:1 ratio, apply to the sore knee joint under plastic wrap and insulating fabric overnight. Course 7-10 days.
Baths
Bath with sea salt. Before performing the procedure, make sure that there are no fresh lesions or scratches on the skin. Pour 1-1.5 kg of sea salt into a bathtub with water. The water temperature is not higher than 40 degrees. Exposure time is 15-20 minutes. Course of 7-10 procedures.
Infusions and decoctions
- Infusion of birch leaves and lingonberries. Take 2 tablespoons of birch leaves, 2 tablespoons of raw lingonberries, pour 250 ml of boiling water. Leave for 30 minutes in a water bath, then cool to room temperature. Drink 50 ml 3 times a day 20 minutes before meals. Course 10 days.
- Decoction of hop cones. Pour 2 cups of hop cones into 1000 ml of water and bring to a boil. Cook over low heat for 20 minutes, then leave to cool. Take 1 tablespoon 20 minutes before meals for 10 days.
Compresses
- Honey with salt. Take 3 tablespoons of honey and three tablespoons of table salt, mix until smooth. Place a tablespoon of the resulting mixture on the joint area under a cotton napkin, and cover with plastic wrap. Exposure time is 3-4 hours. Course 10 days.
- Honey with Aspirin. Take 2 tablespoons of honey, 15 aspirin tablets. Grind aspirin into powder and mix with honey. Apply the resulting mass to the knee joint under a plastic film and under a warming material (preferably made of wool). Exposure time is 7-8 hours. The recipe is relevant during an exacerbation of the inflammatory process with grade 3 arthrosis of the knee joint.
Ointments
- St. John's wort ointment. Grind 3 tablespoons of St. John's wort raw material into powder, mix with 3 tablespoons of petroleum jelly until smooth. Apply to the knee joint area with rubbing movements 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 10 days.
- Ointment from cinquefoil. Grind 4-5 tablespoons of raw cinquefoil into powder and mix with 2 tablespoons of Vaseline. Apply to the knee joint area with rubbing movements during acute inflammation 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 7-10 days.
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint grade 3 is currently not a death sentence. If you consult a doctor in a timely manner and follow all recommendations for prevention and treatment, you can avoid surgery and improve your quality of life.
Bibliography:
- https://nogivnorme.ru/bolezni/artroz/lechenie-artrozov/artroz-3-stepeni.html
- https://revmatolog.net/artroz/kolennogo-sustava-3-stepeni-lechenie-bez-operatsii