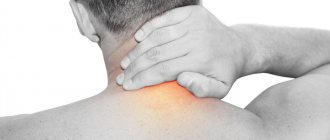
A shoulder injury is a fairly common consequence of a careless fall. When landing, a person involuntarily puts his hand forward, trying to soften the blow. In this case, the shoulder joint experiences significant overload, which leads to injury.
Knowledge of anatomy will help you understand the characteristics of the injury. The human shoulder has a complex structure. It is a spherical joint of the humerus, collarbone and scapula, held together by muscle fibers, tendons and ligaments.
All of these structures can suffer from a fall. The shoulder joint has the greatest mobility and range of motion of any joint in the body. This mobility further increases the risk of injury. On top of the shoulder is the acromioclavicular joint, which is also easily damaged by a fall.
Symptoms of a forearm injury
Signs of this injury are:
- pain in the hand and forearm area during palpation and movement;
- the occurrence of a hematoma in the area of impact;
- edema and swelling.
The motor activity of the hand is preserved, however, the patient may complain about its limitation. Painful sensations can appear suddenly and also disappear unexpectedly. The severity of pain and nature may also vary.
If pain after an injury persists for a long time, this indicates more serious problems than might initially seem.
In patients with high capillary permeability, even a minor bruised wound of the forearm and careless touching it can lead to the formation of a significant bruise. With a severe injury, there may be no external hematoma at all.
Prevention
To prevent forearm bruises, doctors advise following simple rules:
- observe safety precautions at work;
- choose the right shoes in the cold season - with anti-slip soles;
- do not forget about protective equipment during potentially dangerous sports;
- Closely monitor children playing - stop visiting construction sites, quarries, etc.
A forearm bruise is an injury that resolves on its own in most patients. Experts recommend not delaying contacting a trauma center - only an instrumental examination will allow you to distinguish a fracture from a bruise. Ignoring pathology over time can lead to arthrosis, deformation changes in the tendon-ligamentous apparatus, and degeneration of muscle tissue.
Bruised forearm in a child
Children are at risk. Due to increased physical activity, carelessness, and curiosity, it is this category of people who often receive forearm bruises due to falls or blows.
The clinical picture is varied. There is pain on palpation, discomfort when moving (turning, raising the arm). Often a bruised forearm wound in children is accompanied by swelling and rupture of capillaries (hematomas). Complicated injuries can be characterized by damage to ligaments, muscles, and tendons, so it is advisable to seek medical help as soon as possible. This will help determine the type of problem, select the right treatment for a speedy recovery and shorten the rehabilitation period of the little patient.
Symptoms
Common clinical signs of a forearm injury include:
- severe swelling of tissues in the affected area;
- ruptures of capillaries with further occurrence of hematomas;
- pain syndrome - intensifies when touching or moving the affected upper limb;
- complex injuries provoke damage to joints, muscles, tendons, ligaments - with them the pain is stronger and can persist for a long time;
- if at the time of injury soft structures are between the bones and a hard object, then there is a possibility of a necrotic process;
- when the articulation area is damaged, there is a risk of subsequent development of post-traumatic arthritis: blood entering the cavity of the articular apparatus leads to an aseptic inflammatory process.
Pain syndrome occurs against the background of increasing swelling - accumulated blood puts pressure on the nerve endings. If discomfort in the injured arm persists for a long time, then this is the first signal of more serious injuries than a simple bruise.
The area of hematomas is proportional to the volume of ruptured vessels: bleeding from capillaries stops within a few minutes, from venous-arterial lines it can continue for over 24 hours. Extensive bruising can occur under certain conditions:
- hemophilia, complex liver diseases;
- autoimmune diseases, therapy with fibrinolytics, anticoagulants.
In the presence of these parameters, large hematomas are formed when the integrity of the capillary bed is disrupted. With bruises in the forearm area, the bruises retain their bluish or purple tint for 72 hours, then begin to acquire a yellowish color.
First aid for a bruised forearm
If symptoms appear, the patient must be given first aid. This can be done at home. To do this, apply a cold compress to the bruised area. You can make it yourself using cotton cloth and ice, which is wrapped in it.
Cold helps reduce pain, swelling and minimizes the risk of hematoma.
It is important not to overexpose the ice compress to avoid skin necrosis due to frostbite. The maximum time to use a cold compress is 15 minutes. It is also not recommended to apply ice to the bruised area without using a cloth, i.e. You need to wrap the cold or frozen object in a towel or purchase a special ice pack from the pharmacy.
The hand itself must be immobilized; for this you can use a scarf. You should not massage the bruised area; this can lead to even greater damage to the soft tissue. The patient may be given a pain reliever to relieve pain. This has virtually no effect on further diagnosis, since more informative methods are used to make an accurate diagnosis than simple visual and manual examination.
In this case, taking aspirin should be avoided. Acetylsalicylic acid thins the blood, which may increase bleeding. To stop it, you will need medical care in a hospital.
After providing first aid, the patient must go to a medical facility.
When a doctor's help is needed
The consequences of a bruise can be assessed by the nature of external symptoms and sensations. Due to shock, the victim may not immediately understand the severity of the injuries. If the movements are accompanied by unbearable pain, the arm cannot be raised, it is better to immediately seek help from a doctor. Here are some questions to help with self-diagnosis:
- Does the arm rotate freely in all positions?
- Can you bear the pain?
- Do you have enough strength to carry out daily activities with your injured hand?
If you answered “no” to any of these questions, you should seek help from an emergency room or orthopedic surgeon. Timely X-ray diagnostics will help to identify the severity of the problem, which is hidden behind a banal bruise. If adequate treatment is not started on time, there is a possibility of developing post-traumatic arthrosis in the future.
Classification of injuries
Doctors divide shoulder injuries into the following categories.
Soft tissue bruise
From a medical point of view, “bruise” is not a very good term, defining not so much the essence as the mechanism of injury.
It reflects the method of injury, that is, during a fall, there was a collision of the body with a hard surface.
As a result of the impact, superficial damage occurs in the form of hemorrhages, abrasions, as well as various pathological processes in the shoulder muscles, ligaments, tendons, joints, and bones.
An uncomplicated injury has a favorable prognosis with treatment. Its symptoms are:
- pain that increases when turning the arm or body;
- dull pain symptom at rest;
- presence of hematoma;
- swelling, edema, which can spread to the elbow.
If the bruise affects nerves or blood vessels, numbness, tingling, and weakness are felt in the shoulder girdle. Bruises are caused by rupture of capillaries under the skin due to twisting or direct impact. Blood enters the tissue, causing the skin to turn blue-black, turning purple, green, and yellow as it heals.
Fracture
Most often, an unsuccessful fall on an outstretched arm breaks the collarbone. This bone has a thinned part and is not designed for extreme loads. Diagnosing a clavicle fracture is not difficult.
The person’s hand does not rise; a crunching sound is heard. Upon external examination, a protruding deformity of the shoulder is noticeable. A fracture is accompanied by sudden and severe pain.
The final diagnosis is made after radiography in 2 projections.
If a fracture is suspected, emergency care is as follows. You need to bend the injured arm and place it on your chest. Tie the humerus to the body with a bandage or clean cloth.
Shoulder dislocation
Sometimes one of the shoulder joints moves or is pushed out of its normal position. This condition is called instability and can cause one of the joints in the shoulder to dislocate. People suffering from instability will experience pain when raising their arm. They may also feel as if the shoulder is moving out of place.
The symptoms of a dislocation are:
- strong pain;
- the shoulder is in an unnatural position;
- a person tends to press his hand to his body;
- the hand goes numb.
If the bruise is accompanied by a dislocation of the shoulder, the victim should not be moved until the ambulance arrives. You can apply cold to the sore spot. The victim is advised to limit his hand movements. It is prohibited to reset a dislocation for people without specialized medical training.
Rotator cuff injury
The rotator cuff is one of the most important components of the shoulder. It consists of a group of muscles and tendons that hold the bones of the shoulder joint together. The rotator cuff muscles give people the ability to raise their arm above their head. After injury, it is sometimes not possible to completely restore the function of shoulder rotation. Surgeon intervention is necessary.
Muscle inflammation
Sometimes sharp compression of the muscles during a fall causes inflammation, which doctors call myositis. Its characteristic symptoms:
- It's a dull pain;
- skin hyperemia;
- swelling;
- fever.
Inflammation is dangerous due to complications. If left untreated, muscle atrophy may develop, leading to loss of performance.
Shoulder sprain
In this case, partial rupture of the tendon fibers occurs. A sprain has similar symptoms to a dislocated shoulder: pain, swelling, and the arm cannot be raised. Due to different approaches to treatment, both conditions must be differentiated by a specialist.
Bruised rib hurts to breathe
How to treat a shoulder after a bruise
Treatment of a bruise may include first aid measures, physical therapy, drug therapy, and in rare cases, surgery is indicated.
What to do immediately after a fall
If, after an injury, there is limited mobility of the shoulder joint, the first step is to immobilize it. This is necessary in order to give rest to damaged tissues after injury, reduce pain symptoms and eliminate complications. The victim's limb must be suspended in a sling in a bent state.
After this, doctors recommend cooling the bruised area: applying ice, a towel soaked in ice water, or any cold object. Frostspray works great at home. It helps to quickly relieve pain and prevent bruising. Coolants lead to vasospasm, which prevents blood from leaving damaged capillaries.
If the pain is unbearable, you can take the painkiller tablet in your medicine cabinet. Treatment with cold and rest should be continued for several hours after the fall.
Important! Do not apply products such as ice or snow directly to the skin for more than 15-20 minutes. This can cause tissue frostbite.
To speed up the resorption of a fresh hematoma, a lead lotion is applied to the bruised area. After the formation of subcutaneous hemorrhage in the body, the natural healing process begins.
Special leukocyte cells get down to business, breaking down hemoglobin to form various pigments and remove it from the tissues.
Medicinal ointments and gels increase blood circulation, which attracts more leukocyte cleaners to the problem area. Thus, the hematoma disappears faster.
On days 2-3, heparin-based ointments are used to treat bruises, which tone and restore blood vessels. A noticeable effect is obtained by applying an iodine lattice to the affected area.
Vodka compresses, as well as lotions made from a decoction of coltsfoot leaves, calendula, and burdock, help get rid of a bruise faster. To activate regeneration, you can take a course of vitamins C and K.
Eat more red fruits.
For large hematomas, the doctor may prescribe UHF therapy procedures. In some cases, the surgeon may perform a puncture to remove the collection of blood.
Resolving a bruise is not a quick process. Depending on the size and intensity of the hemorrhage, this may take from one to three weeks.
Sprain Treatment
It is necessary to treat the ligaments of the shoulder in a comprehensive manner, using techniques that restore the integrity of the tendons and prevent the formation of scar changes. Necessary:
- To relieve pain and swelling, immobilize the arm with a support for one to three weeks, depending on the severity of the sprain.
- Apply cold to reduce pain and swelling for the first two days after the fall. You cannot keep ice constantly, so as not to provoke the development of inflammation in the joint. Use a cold compress for 15-20 minutes every 2-3 hours.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used as prescribed by a doctor. It is recommended to smear the bruise site with external preparations based on ibuprofen and diclofenac in the dosage specified by the doctor. They relieve pain and prevent inflammation of the joint and tendons.
- Try to avoid painful movements. Limit heavy lifting or strain until your shoulder pain subsides.
- If your condition does not improve after these steps, your doctor may inject a corticosteroid (hormone) directly into the joint to reduce swelling and pain.
Treatment of forearm bruises
When an accurate diagnosis is established, the patient needs conservative treatment, which is mainly aimed at restoring the function of the affected arm and eliminating existing symptoms.
It is not much different from first aid.
So, how to treat a bruised forearm:
- Apply cold for 15 minutes 3-4 times during the first 6-12 hours;
- Apply a bandage, thereby creating peace and limiting movements (in case of severe bruises and severe pain);
- Painkillers (NSAIDs), for example one of these: Movalis, Nise, Nurofen, Ketorol, 1 tablet up to 2 times a day, no more than 5 days;
- Anesthetic ointments, for example: Dolobene gel, Traumeel, Voltaren, apply topically 2-3 times a day until the symptoms stop (disappear);
- Physical therapy may be prescribed to help reduce swelling and pain.
Almost all bruises pass without a trace, but with serious bruises there may be some consequences.
Diagnostic measures
When contacting a local trauma center, the patient is sent for an instrumental examination in order to identify the type of injury present. Differential diagnosis allows you to distinguish a bruise of the forearm from fractures, dislocations, sprains, and ruptures.
To clarify the pathology, the patient undergoes:
- X-ray images - allow you to exclude the fact of a fracture, show where exudate accumulates;
- Ultrasound is a technique necessary to study the condition of soft and bone tissues;
- CT or MRI - give a detailed picture of the condition of the upper limb, showing hidden bleeding, hematomas, cracks.
After confirmation of a forearm injury, the patient receives a regimen of the necessary therapy.
Consequences of bruises
Usually everything goes away without consequences. In particular, this applies to injuries that are not accompanied by complications. Most often, symptoms disappear within 2-3 weeks, depending on the severity of the bruise.
However, in rare cases, serious consequences of such an injury can occur. For example, calcification of a hematoma. In this case, the compaction in the soft tissues does not resolve and causes pain.
If the hematoma does not resolve on its own, a compaction forms in its place, and the patient may require surgical intervention. The operation is performed on an outpatient basis and does not take much time.
In rare cases, in patients the injury is accompanied by myositis ossificans, that is, inflammation of the muscle. In this case, small areas of ossification appear in the thickness of the muscle.
Sometimes severe forms of bruises are accompanied by trauma to the periosteum, and bone growths may form. All these consequences require longer treatment and rehabilitation.
First aid algorithm
Symptoms of the injury will gradually appear after the injury. In order to alleviate the victim’s condition as much as possible, it is necessary to perform the first actions in case of a bruise of the forearm as correctly and competently as possible.
The assistance algorithm implies the following:
- Immobilization of a limb . Regardless of whether a person has broken his arm or just received a bruise, complete rest of his injured limb should be ensured. First of all, it will reduce pain. If a more serious injury is suspected, it is recommended to apply a fixing bandage; this will provide rest to the damaged soft tissues and prevent complications in the future. For this purpose, you can use an elastic bandage. If it is not available, you can use suitable available means. The injured person should take a position in which he does not experience severe discomfort.
- Cooling the injury site . According to the instructions, ice should be applied to the injury site. Cold will help prevent increased swelling and bruising. If you don't have ice cubes on hand, you can fill a heating pad or empty bottle with cold water. This should be done in the first quarter of an hour after falling or receiving a blow. This procedure will help dull the pain, which will significantly alleviate the general condition of the injured person.
- Pain relief . If an injured person complains of sharp pain, it is recommended to give him a tablet of any analgesic. After this, care should be taken to ensure that the victim receives professional medical care.
- Medical consultation . Regardless of the extent of the injury, a traumatologist must examine the injured person. It is imperative to call an ambulance and take the victim to the emergency room so that he can be examined by a doctor and, if necessary, prescribe a diagnostic examination. You should not try to differentiate a bruise from a sprain or fracture on your own. This should be done by a specialist.
When a forearm is bruised, first aid is important, since severe bruises are often accompanied by sprains or cracks in the bone. Such an injury can cause unpleasant consequences.
Rehabilitation after a forearm injury
Recovery is aimed at restoring full motor function of the right or left hand. To do this, 10-12 days after the lesion, a course of exercise therapy is prescribed. Usually, no further rehabilitation procedures are prescribed.
Also, one of the serious consequences of a forearm injury is a violation of the integrity of large vessels, the formation of blood clots and even blood clots, with the subsequent occurrence of a serious disease - thromboembolism, which, in turn, leads to heart attacks, strokes and other serious consequences.
Despite the apparent simplicity of the injury, forearm bruises should not be underestimated. If symptoms occur, you should seek help from a medical facility.
| Shoulder bruise | To the list of articles |
Sources of development
The leading sources of development of forearm bruises include:
- injuries associated with falls on a straight upper limb;
- contact with hard objects;
- falling things with a lot of weight onto the forearm area.
The complexity of the pathological process depends on the type and weight of the traumatic object and the speed of its fall. Bruises can be combined with many injuries, which include open wound surfaces, violation of the integrity of bone tissue, and dislocations. Lesions may be accompanied by inflammatory reactions in the joint apparatus, muscle tissue, and ruptures of the tendon-ligamentous apparatus.