Anterior cruciate ligament rupture: symptoms
- clicking sound coming from inside the knee
- feeling like the knee is moving
- sudden, sharp pain in the knee
- immediate swelling, inflammation, redness and bruising
A sprain or tear of the anterior cruciate ligament usually occurs during sports (for example, playing football or hockey, skiing, snowboarding, etc.), as well as due to unfortunate falls or accidents. Women are more at risk of ACL injury when playing sports than men, which is due to differences in physiological structure.
ACL rupture occurs when there is a blow to the knee area or severe twisting.
Not every ACL injury requires surgery. Treatment tactics depend on the extent to which the ACL is injured. Early symptoms of injury, such as pain, swelling and muscle spasms, can make it difficult to diagnose and determine the extent of ligament injury. For a more accurate diagnosis, special tests may be required, as well as MRI and X-rays.
Anterior cruciate ligament tears are usually diagnosed based on severity:
- A grade 1 ACL injury to the knee includes some types of minor ligament injuries that involve spraining the fibers of the ligament. The patient usually feels pain and swelling, but this injury can resolve on its own with rest, the use of ice and anti-inflammatory drugs, and special therapeutic exercises (rehabilitation).
- A grade 2 ACL tear involves tears in the fibers of the knee ligament. This injury is usually called a "partial injury" of the anterior cruciate ligament and in some cases requires surgery.
- A grade 3 ACL tear is the most severe injury to the anterior cruciate ligament, where the fibers are completely torn in half. This tear of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee almost always requires surgery.
A peculiarity of the injury of a complete rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament is that it itself almost never heals. There are two ways to treat this injury: The first is radical. A complex surgical operation is performed, everything that interferes with fusion is removed, injured tissue is cleaned out, the femur and tibia are drilled and an implant is inserted. Surgery is an additional injury, especially since bone damage occurs, which significantly impairs blood circulation and creates a risk of inflammation. . After which the knee is rigidly fixed in a crooked, deformed position with a plaster cast for several weeks or months. Contracture develops (stiffness of mobility). And the patient is waiting for a miracle.
Usually, you have to use painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs for the entire period you are in a cast to relieve congestion in the knee. Movements are sharply limited, all physical indicators decrease. Excess weight is gained and depression often occurs. After removing the plaster, long-term rehabilitation is carried out (gymnastics and physiotherapy, massage).
The advantages of this operation are that the operation is widely used for a long time and gives acceptable results. After a few months a person can already walk, and after a course of rehabilitation he begins to live a full life in a gentle manner. The downside of this method is that during an injury, not only the joint, but the entire body is deformed and becomes crooked, and surgery and then a cast practically reinforces this stereotype, which in the vast majority of cases never returns to normal. And therefore, pain, swelling, tight mobility and uncertainty in the knee often remain, and often with repeated extreme situations, a re-rupture occurs. By the way, surgery on crosses can only be done twice.
But few people know that in addition to the main 4 ligaments, there are also small ligaments of the joint capsule + muscles. And this is a team game. Not all surgeons even know that the main 4 ligaments provide only 30% of the fixation of the knee joint. Small ligaments and the joint capsule provide another 30% of stabilization. The Fascia muscles surrounding the joint contribute another 40%. That is, the loss of one main ligament is a maximum of 7% of the stabilizing functions that can be covered by muscles (https://www.physio-network.com/blog/acl-surgery-no-longer-kneeded/). After all, if we wish, we can develop muscles, fascia and ligaments (strengthen, increase in size), remove deformation of the joint and the whole body; this is what Doctor Popov’s method is based on. In this case, quite often it is possible to do without surgery at all. With this method, the knee is fixed with an open semi-rigid bandage. This allows you to fix the injury site and at the same time maintain mobility in the joint. Open access allows constant monitoring of the injury site and surrounding tissue. It also makes it possible to carry out massage and other restorative procedures from the very first days of injury or surgery. The structure of the semi-rigid bandage does not interfere with rehabilitation exercises. Due to all this, abundant blood supply to the injured area of the body, especially the ligaments, is achieved, neighboring tissues receive motor load, which together allows the knee to actively recover. The advantages of this method are that the likelihood of recovery, including complete recovery, increases significantly. The duration of treatment and rehabilitation is reduced to four to six months. Disadvantages of this method: firstly: if you have a complex injury, surgery will still have to be performed. Secondly, the technique is proprietary and can only be carried out by Dr. Popov and his specialists.
General information about ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURY
The body, when a traumatic situation arises, uses the entire complex of ligaments, tendons, fascia, connective tissue and muscles to try to the limit to maintain the integrity of the joint. At this time, the deep reserves of the body are activated (people in this state can run with a broken leg, jump to a height and length that is unrealistic even for athletes, or lift a huge load). The body seems to freeze at the moment of injury, instantly creating protective armor around the endangered area. That is, in a split second the usual position of the soft skeleton changes (the definition of the soft skeleton was given by Nobel laureate Ilya Mechnikov) - these are ligaments, tendons, cartilage, fascia and blood. The entire body was deformed, most of all in the place of possible injury, in this case the knee. The knee has changed shape, the surface of the joint no longer moves... But the muscle movement remains the same.
And there are two ways out of this situation.
Or restore the correct shape of the knee, the tissues around it, the whole body, and strengthen the soft and hard skeleton. Return the knee to its rightful place by strengthening it with ligaments, tendons and fascia, restore blood circulation impaired by injury and make the joint stronger, faster and younger than before the injury.
Or insert an implant into a deformed knee, adjusting it to a changed, curved body. But in the next extreme situation, the injury will repeat, but it will be more serious than the first time. Subsequent treatment with surgery, plaster cast and rehabilitation will restore the functionality of the knee to some extent, but the destructive process will develop and ultimately lead to arthrosis, and possibly joint replacement.
Fixation in a plaster cast.
Usually, immediately after surgery, the leg is immediately fixed in a cast. Crutches are prescribed. However, a plaster cast cannot change shape and when the body changes (swelling subsides, muscles atrophy), the degree of fixation sharply decreases, blood circulation worsens especially at the site of injury and surgery, coordination of movements is impaired, abrasions and even bedsores may appear, the condition of the injury site is poorly controlled, the functioning of the cardiovascular system and respiratory organs decreases, athletes quickly get out of shape. A knee covered in plaster is not available for massage and rehabilitation procedures. Forced inactivity leads to muscle atrophy, a particularly strong change occurs in the calf muscle, osteoporosis develops, loads are sharply limited, the body bends and becomes inactive, lymphostasis may appear, and depression often occurs. We must remember that fixation with a plaster cast is only the beginning of treatment, after which many months of intense rehabilitation lie ahead.
Semi-rigid fixation.
Developed on the basis of a historically accepted method of treating meniscal injury, Dr. Popov’s method uses new knowledge acquired in recent years in research medical centers, as well as supplementing it with “folk methods” and his personal developments.
According to Dr. Popov’s method, a special semi-rigid bandage is immediately applied instead of plaster. It is lighter and more convenient than plaster. The dressing is changed frequently (every day in the first days, then less often, once every 1-3 days). This allows for much better fixation of the injury site and at the same time maintaining mobility in the joint.
You can more accurately monitor changes in the site of injury and neighboring areas, as well as carry out massage and other procedures almost from the very first days of injury or surgery.
This method allows you not only to recover very quickly, but also to control the recovery process itself almost continuously. Control examinations are regularly carried out by leading specialists in specialized trauma centers using tomographic and ultrasound equipment, and if necessary, a consultation with the best traumatologists who are familiar with the system of treatment and recovery of injuries using the methods developed by Dr. Popov is organized as soon as possible.
The methods developed by Dr. Popov make it possible to reduce the time of recovery and rehabilitation due to the fact that treatment, rehabilitation and restoration of shape are carried out simultaneously, which is especially important for athletes and artists.
According to Dr. Popov’s method, patients begin micro-gymnastics classes from the very first days to improve blood circulation, restore coordination and prevent contractures (stiffness), ointments are used to improve blood circulation and nutrition of ligaments, cartilage, periosteum, bone, bone marrow and stem cells. A special, proprietary intra-articular massage, massage of muscles, ligaments, tendons, and bones is performed. Special nutrition and medications are prescribed.
Stagnant blood is removed from the injured area using the vortex method (a combination of myofascial massage according to Travel, osteoreflexotherapy according to Yankovsky, the Arabic hijama technique and periosteal massage). Immediately after the procedure, pain goes away or noticeably decreases, range of motion increases and becomes easier, nutrition inside the bone improves and bone marrow and stem cells are stimulated, blood circulation in the injured area noticeably improves, mood and sleep are normalized.
Various devices are used in treatment and rehabilitation, including BIOM-VOLNA devices for the recovery of astronauts. Treatment procedures are monitored using a thermal imager and by comparing the temperature distribution in tissues before and after the session, you can clearly track the dynamics of changes in blood circulation at the site of injury and surrounding tissues, constantly adjusting the treatment process. The thermal imager detects foci of the inflammatory process characterized by elevated temperature, areas with stagnant blood, low temperature and tissues saturated with fresh blood at natural body temperature (usually 36.6 C).
Patients report positive results almost every day: pain decreases, range of motion increases, swelling decreases, coordination, reaction, and endurance improve. Confidence in a good and quick result appears and grows. Patients work several hours a day, the workload and pleasure from activities increases every day (they work from one to eight to nine hours a day).
Thanks to Dr. Popov’s method, recovery is several times faster than according to accepted regulations in the world’s best centers. And it is very important that after recovery the patient feels better than before the injury, and the injured place becomes the most reliable in the body. Athletes, after recovery using Dr. Popov’s methods, have repeatedly improved their personal records. Their general condition improves, the functioning of the cardiovascular system, the functioning of the lungs, their reaction, coordination, endurance, stress resistance improve, and they gain faith in themselves and their capabilities. It is also a powerful injury prevention tool. Injuries become less frequent, and if a re-injury occurs, recovery is even faster and easier.
Anterior cruciate ligament rupture: treatment
Conservative
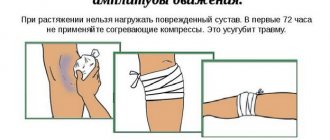
If the patient does not experience instability in the knee with an ACL injury and does not stress it with serious sports activities, physical therapy may be sufficient for recovery. Developing an effective treatment strategy takes into account the patient's age, age of injury, and the types of activities they engage in. General recommendations for first aid for an ACL injury are the following 4 points:
- The knee should be at rest, without the load of body weight. If walking is necessary, you must use crutches.
- Ice (cold) on the knee
- Compressing the knee with a pressure bandage (elastic bandage)
- Raising your leg
Surgical
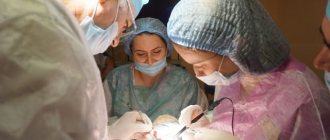
If more than one knee ligament is sprained, or if the ACL is completely torn, and if there are progressive signs of instability, pain, and swelling, the patient may be recommended for ACL reconstruction. In most cases, if the patient leads an active lifestyle and plays sports that place stress on the knee (for example, football, hockey, alpine skiing, tennis), the surgery eliminates the damage caused by the injury and the athlete can return to sports. In these cases, ACL reconstruction is the best solution.
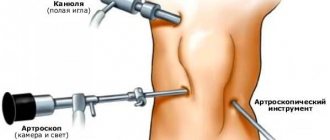
An ACL repair is a surgical procedure in which a doctor removes pieces of a damaged ACL and replaces them with another ligament called a graft. The procedure is performed using arthroscopy using one or two incisions. The patient’s own implanted tissues recover faster, reducing the risk of complications. For older patients or those who have previous knee injuries and those who do not have enough native tissue for implantation, a donor implant (allograph) may be used. There are many ways to attach an implant to the bone. For example, interference screws, endobattom, pins. Some are made of metal, others are organic and dissolve over time. The type of fixator and fixation technique depends on the method of the procedure. ACL reconstruction can be performed on an outpatient or inpatient basis. Find out more about ACL plastic surgery