- home
- /
- Articles
- /
- Symptoms of intervertebral hernia
It is not for nothing that intervertebral hernia is considered a “worldwide” disease. Because this disease can affect anyone: people of any age, gender and financial income. This disease does not go away on its own. Under no circumstances should it be left to its own devices. At the first suspicion, you should immediately consult a doctor. What are the symptoms of intervertebral hernia?
Causes of the disease
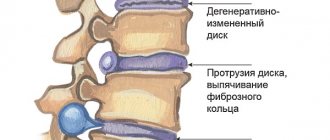
To begin with, externally, intervertebral discs are a kind of combination of a soft, jelly-like center, which is surrounded by many thin, but strong, dense fibrous membranes. The older a person is, the less he moves his spine throughout his life, the greater the load on the spine when lifting heavy objects, the less fluid there is in the intervertebral discs, they become less “elastic”, and begin to lose their shock-absorbing properties. And if it happens that the outer membrane ruptures, then a hernia appears. A pinched nerve occurs and pain or numbness appears in the legs or arms, depending on where the hernia occurs - in the lower back or in the neck.
At that very moment, as soon as you feel unpleasant pain, you need to go to the doctor and get diagnosed. Otherwise, it may happen that the nerves will be unnecessarily compressed. And then the consequences will be completely sad. Up to and including disability.
Treatment of leg numbness due to spinal hernia
If numbness in the legs occurs due to a hernia, treatment should be started immediately. To do this, you should consult a neurologist or vertebrologist as soon as possible. These doctors will conduct all the necessary examinations and decide on conservative treatment or recommend surgery. As a rule, surgery to remove the disc is required if the nucleus pulposus has separated and penetrated into the spinal canal. In this case, there is a high probability of paralysis of the patient’s body and even death due to a total dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system. Therefore, emergency surgery is indicated.
In all other cases, treatment of leg numbness due to spinal hernia is carried out using conservative methods. For example, in our manual therapy clinic the following methods of influence are used in this process:
- manual traction of the spinal column in the lumbar region - allows you to remove pressure from the nerve fiber and restore sensitivity;
- osteopathy restores the integrity of the disc (reduction of the hernial protrusion occurs), triggers impaired microcirculation of blood and lymphatic fluid in the lesion;
- massage improves the elasticity of muscles and soft tissues, relieves their hypertonicity, improves blood supply, enhances diffuse nutrition of cartilage tissue;
- reflexology (acupuncture) – by influencing biologically active points on the human body, the processes of regeneration of damaged cartilage tissue are launched;
- physiotherapy enhances metabolism at the cellular level, increases tissue aggregation and accelerates the recovery process;
- kinesiotherapy and therapeutic exercises restore motor activity and improve the condition of the muscular frame of the back, which ensures the absence of relapses in the foreseeable future;
- laser vaporization allows you to restore the integrity of the fibrous ring.
The course of treatment for numbness of the legs due to a hernia of the lumbar spine is always developed individually. Therefore, we recommend that you consult a doctor. Sign up for a free initial appointment with a vertebrologist or neurologist right now. To do this, use the form located further on the page.
Symptoms of the disease
Let's talk in more detail about how you can recognize the signs of an intervertebral hernia. And let’s say right away: there is good news - you can recognize the symptoms of the disease at the very beginning.
In a word, if you have the following signs, you need to be on alert. These include:
- Stiffness of movement in the morning;
- Dull pain in back when standing up;
- The muscles became flaccid;
- Unreasonable pain appears in the arms or legs;
- Numbness in fingers or toes.
Features of the disease
There are a number of features of an intervertebral hernia that are also recommended to be taken into account. This should include:
- Concentration of pain in the sacral and/or lumbar regions. It occurs because the disc begins to exert excessive pressure on the root of the nerve and presses it against the spinal column.
- The pain can radiate to the legs or arms, as well as to the chest, shoulders, perineum, back of the head or rectal area.
- Painful sensations often appear when performing physical exercises, when bending the body forward and backward, or bending to the sides.
- Most often, the disease manifests itself most acutely in the morning, because the spinal discs have been in one position for a long time (all night), the movement of fluids is disrupted, and stagnation occurs.
Forms of the disease
The nature of the numbness that occurs may also indicate what form of intervertebral hernia the patient has. So, the following forms of this disease are distinguished:
- If the hernia is lumbar, then pain will occur in the buttocks, on the back, outer side of the legs.
- If there is a pinched nerve in the sacral region, you will feel a decrease in sensitivity in the calf muscles or feet. In parallel with this, numbness may appear in the buttocks, lower back or legs.
- If the disease occurs in the thoracic region, then the pain will be localized specifically in the chest, and it may radiate to the ribs, or you may experience discomfort when turning your body, as well as between the shoulder blades.
- If the pathology is cervicothoracic, then headaches may begin, which will become stronger when turning the head or bending. At the same time, memory may deteriorate or dizziness may occur. There will be a feeling of numbness in the fingers or weakness in the muscles of the hands.
Why does leg numbness occur?
Numbness of the leg due to intervertebral hernia can be caused by several pathogenic factors. These are mechanical compression of the nerve fiber, compression of the spinal cord, stenosis of the spinal canal, swelling due to an inflammatory reaction due to irritation of the surrounding soft tissues by proteins of the nucleus pulposus, excessive muscle strain in the area of damage to cartilaginous tissue, etc.
In order to understand the mechanism of development of neurological syndrome, it is worth delving into the mechanism of development of this pathology:
- the intervertebral disc consists of the fibrous ring and the internal nucleus pulposus;
- it does not have its own circulatory network, it receives nutrition through diffuse exchange with the surrounding soft tissues, including muscles;
- if the muscular frame of the back is not subjected to regular physical activity in the required volume, then the fibrous ring begins to be neutralized and loses its strength and elasticity;
- then it begins to take fluid from the cells of the nucleus pulposus located inside it, thereby provoking the development of the protrusion stage (decrease in the height of the intervertebral disc and loss of its physiological shape);
- in this condition, the intervertebral disc cannot fully perform its functions, therefore, with a sudden movement, emergency compression or traumatic impact, the fibrous ring ruptures and part of the nucleus pulposus emerges through the crack - this is an intervertebral hernia.
Since the intervertebral disc is primarily designed to ensure the safety of the radicular nerves extending from the spinal cord, when this ability is lost, they are compressed by neighboring vertebral bodies. Some radicular nerves are involved in the formation of the femoral, sciatic, lateral saphenous and other nerves responsible for sensitivity and motor function of the lower extremities. When compressed, these nerves become inflamed. If sensory types of axons are affected, then sensitivity is lost, which is felt as numbness of the skin. The situation is worse when both motor (motor) and sensory (sensory) types of axons are affected simultaneously. In this situation, the leg loses not only sensitivity, but also mobility.
The main causes of numbness of the lower extremities due to a herniated disc:
- an inflammatory process that occurs when the proteins of the nucleus pulposus irritate the soft tissues surrounding the spinal column;
- swelling and infiltration of soft tissues, resulting in compression of large nerves, roots and their branches at the site of rupture of the fibrous ring;
- excessive muscle tension in the lumbar region for a compensatory purpose - they compress large nerve structures and provoke displacement of the vertebral bodies, which can lead to stenosis of the spinal canal;
- infringement of large nerve plexuses (cauda equina, lumbar and sacral), as a result of which numbness of the lower extremities can be combined with dysfunction of the internal organs of the abdominal pelvic cavity;
- stenosis of the spinal canal due to the prolapse of a dorsal intervertebral hernia into its lumen.
Numbness of the toes with a spinal hernia may be associated with instability of the position of the vertebral bodies against the background of a decrease in the height of the cartilaginous disc. In this case, one branch of the radicular nerve, which is responsible for the innervation of one or another lower limb, is affected.
Only laboratory diagnostics will help to establish the exact cause and localization of herniated protrusion of the intervertebral disc. It is necessary to take an x-ray, contrast myelography, CT and MRI. All these examinations will allow an experienced doctor to make an accurate diagnosis and develop an effective course of treatment.
Dissociation of sensitivity
Dissociation or splitting of sensitivity is the preservation of some types of sensitivity with a decrease or complete loss of others. This situation is typical for compression of the spinal roots, one of the causes of which is intervertebral hernia.
Most often, tactile and pain sensitivity worsens or disappears. At the same time, the reaction to temperature and conductors of deep sensitivity is preserved. This can be explained by the scattered arrangement of the conductors and the direction deep into the body, characteristic of a disc herniation, which corresponds to the position of the nerves of tactile and pain sensitivity. If a defect with equal pressure put pressure on all nerve conductors, then all types of sensitivity would suffer, including temperature and joint-muscular. In practice, this is extremely rare.
Sometimes spinal hernias are accompanied by the occurrence of hyperpathy, in which the patient feels only a gross effect, and the subtle is not perceived at all. In such situations, the sensations will be sudden, poorly localized and, one might say, explosive. But this picture is more typical of neuropathic pain.
With hernias, the phenomenon of causalgia, characteristic of injuries to peripheral nerves, i.e., causeless burning pain along its course, is almost never observed.
Prevention
To prevent lumbar hernia, our doctors recommend:
- walk more, play sports - swimming, yoga;
- watch your posture, keep your head and back straight when walking;
- when working at a computer, lean on the back of a chair;
- When sitting for a long time, take breaks and do exercises - for example, 10 bends of the body in different directions. In this case, you need to keep your hands on your lower back;
- before lifting weights, bend your knees and keep your back straight;
- distribute weight in both hands;
- sleep on an orthopedic mattress;
- eat chicken, beef, fish, dairy products;
- Avoid fried foods, canned foods, and spicy seasonings;
- no smoking.
Conservative therapy
The basis of treatment is the elimination of the aseptic inflammatory process and the resulting swelling in the area of the affected disc. As a result of reducing the volume of soft tissue surrounding the nerve roots, it is possible to reduce the pressure on it, which will lead to self-elimination of neurological disorders. Moreover, the sooner treatment is started, the higher the likelihood of full recovery.
Patients are prescribed a set of measures that are selected for each individual. Typically this is:
- drug treatment;
- physiotherapy;
- manual therapy;
- Exercise therapy.
In general, the nature of the therapy does not differ significantly from treatment aimed at eliminating pain. But if, despite all efforts, sensory disturbances persist, patients are recommended to undergo a more thorough examination, since their causes may lie not only in a hernia, but also in the presence of diabetic, alcoholic polyneuropathy, or even in the onset of multiple sclerosis.
Drug therapy
Almost all patients without exception are prescribed:
- NSAIDs – have analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties;
- muscle relaxants – have a relaxing effect on overly toned muscles, which leads to an improvement in the quality of transmission of bioelectric impulses and a reduction in the severity of sensitivity disorders;
- corticosteroids – have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect, therefore they are used for severe inflammatory processes;
- vitamin and mineral complexes, especially those containing B vitamins, help normalize the quality of signal transmission along compressed nerves and spinal roots.
Additionally, other drugs may be prescribed that are necessary to eliminate the negative effects of basic medications. That is why drug therapy is developed individually for each patient. For example, patients with gastritis and similar diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are advised to use proton pump inhibitors simultaneously with the use of NSAIDs to protect the mucous membranes.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy methods are aimed at restoring normal blood circulation in the affected area, which can effectively combat soft tissue swelling. Most often, patients are prescribed a course of procedures:
- electrophoresis with vitamins and aminophylline;
- UHF;
- magnetic therapy;
- phonophoresis.
Traction therapy or spinal traction is recommended for most patients. The procedure involves the use of a special apparatus that creates a tensile load on the spine. The patient is placed on a special couch or in a bathtub (with underwater traction), and special belts are attached to his body.
By selecting the optimal load, it is possible to increase the distance between the vertebral bodies, which immediately leads to a decrease in pressure on the affected disc and decompression of the compressed nerve.
Exercise therapy
Therapeutic gymnastics plays one of the main roles in the conservative treatment of sensitivity disorders and numbness. Correctly selected exercises help restore normal mobility not only of the legs, but also of the back. With their help, it is possible to improve blood circulation and strengthen the muscle corset, which will create adequate support for the spine and minimize the risk of progression of intervertebral hernia.
But exercise therapy is allowed only after acute pain has been eliminated. For each patient, the complex is developed individually, taking into account the patient’s level of physical fitness, location, size and type of hernia.
Exercises are performed daily at a calm pace, without sudden movements. It is recommended to conduct the first classes under the supervision of a specialist in order to fully master the correct technique for performing each exercise.
Manual therapy
Skilled manual pressure on the back muscles and spine can eliminate excessive muscle tone, activate blood circulation and even normalize the position of the vertebrae. As a result, it is possible to significantly improve microcirculation and provide the affected intervertebral disc with the necessary nutrients, as well as eliminate the prerequisites for further aggravation of the situation and pinched nerves. Therefore, after a course of manual therapy, patients note a significant improvement in their condition.
Sensation in legs is normal
Sensitivity is the final process of awareness of irritation that affects receptors, is carried along sensory nerves, enters the central nervous system and is recognized by the sensitive parts of the cortex. There are several specific types of sensitivity. Which of them will be important when considering the pathology of intervertebral discs?
First of all, it is tactile sensitivity, or touch. This is the feeling of touching the skin, its intensity, localization. Pain is also one of the specific types of sensitivity, but, as a rule, it is assessed as a separate symptom. It is important to assess temperature sensitivity by alternately assessing the ability of the skin of the foot to distinguish between hot and cold shades. There is a discriminatory feeling, that is, the ability to distinguish between two simultaneous touches. This is done with a special compass. The distance at which two touches feel like one is considered the minimum discriminatory distance. These are all types of superficial sensitivity. They are determined by specific receptors located in the skin.
But there are also deep types of sensitivity. This is a joint-muscular feeling, or a sense of the position of a limb in space. Deep are the feelings of vibration, the sensation of pressure, the feeling of weight on the limb. Many of these types of sensation are impaired in the presence of herniated intervertebral discs.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of sensory disorders, first of all, involves a thorough neurological examination. After the neurologist has assessed all types of sensitivity and their disorders, assessed the strength and tone of the muscles, examined the reflex sphere, volume and amplitude of movements, he can make a preliminary diagnosis taking into account the history and palpation of the back muscles.
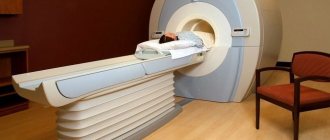
Then, a mandatory step is imaging diagnostics, with magnetic resonance imaging being preferable to X-ray computed tomography (X-ray CT). This is due to the fact that MRI shows soft tissue formations, including cartilage tissue, much better. But RCT, for example, has an advantage in the emergency diagnosis of stroke in the first hours, since, unlike MRI, it reacts very well to free blood. In order to confidently diagnose not only the presence of a hernial protrusion, but also its localization, as well as the degree of compression of the roots, a resolution of at least 1.5-2 Tesla is required on the tomograph magnets.
Finally, once the diagnosis has been made, the extent of peripheral nerve damage can be assessed, if there is evidence for this. Electroneuromyography (ENMG) is performed. It allows you to assess the degree of nerve degeneration and make a differential diagnosis between radicular symptoms caused by a hernia and, possibly, the presence of underlying compression-ischemic neuropathy. This disorder does not directly affect the root, but a nerve, and can simulate a hernia.