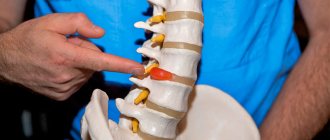
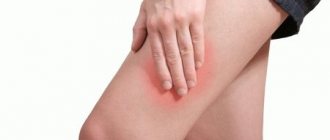
Complaints about pain and numbness in the hips are often received from patients suffering from various pathologies of the lumbosacral spine. Osteochondrosis, accompanied by protrusion (decrease in height) and hernial protrusion of the intervertebral disc, comes to the fore during diagnosis. The more the fibrous ring of the disc is destroyed, the higher the likelihood of developing radiculopathy and disruption of the process of innervation of the soft tissues of the lower extremities.
The hip also becomes numb due to the development of carpal tunnel syndrome. Anatomically, it is arranged in such a way that the so-called sensory types of axons are responsible for sensitivity. They arise from the corresponding root nerve emerging from the spinal canal. Sensory (sensitive axons) are responsible for collecting the necessary information and transmitting it to special motor centers of the brain. The signal is transmitted along the nerve fiber to the structures of the spinal cord, and then to the posterior structures of the brain.
If there is an obstacle along the path of nerve signal transmission that compresses the axon, then the information will not reach the center of analysis. The patient will experience a feeling of numbness.
Disruption of nerve fiber conduction can be observed at various levels of the autonomic and central nervous system:
- nerve endings located in the thickness of the muscle and connective tissue layer, in the epidermis;
- conductive nerves (femoral, sciatic, hypogastric, obturator, etc.);
- the radicular nerve, which subsequently enters into the formation of the lumbar or sacral plexus;
- spinal cord;
- medulla;
- pyramidal cerebral tracts;
- motor cerebral centers.
If any of these structures are affected, you may experience a feeling of numbness in the hip area or other areas of the lower extremities. Therefore, the patient is unlikely to be able to independently diagnose himself. It would be much more correct to contact a neurologist. During the appointment, the doctor will conduct an examination and a series of diagnostic functional tests. This will allow him, by comparing the data of an objective examination and the patient’s subjective complaints, to make an accurate diagnosis. Then additional examination will be recommended (if necessary). An individually developed course of therapy will help you get rid of the feeling of hip numbness quickly and safely.
If you have numbness in your hip, you can schedule a free appointment with a neurologist at our chiropractic clinic. Call the administrator and agree on a time convenient for your visit.
The main reasons why thighs go numb
There are a variety of reasons why thighs become numb, and they can include a huge list of pathologies. We will consider only the main factors under the influence of which such a symptom occurs. The first reason why the hips become numb is the development of lumbosacral osteochondrosis with various complications. In modern humans, dystrophic degenerative disease of the spinal column is the leading cause of impaired innervation in almost all parts of the body.
Why are the lower extremities more affected:
- by the age of 25 years, a person experiences physiological deformation of the spinal column with a change in the process of distribution of shock-absorbing load - all the vertebrae of the sacral region are fused together;
- transformation of the spine due to fusion of the sacrum leads to the fact that an increased shock-absorbing load begins to be placed on the intervertebral disc located between the last lumbar and first sacral vertebrae;
- the process of degeneration of cartilage tissue begins;
- with prolonged development, an intervertebral hernia occurs, which puts pressure on the outgoing radicular nerves;
- This is how the primary symptom complex is formed, indicating radiculopathy.
This is why the thigh becomes numb with the development of osteochondrosis. But this is not the only potential disease. This is followed by instability of the position of the vertebral bodies. This pathology is characterized by “subsidence” not only of the intervertebral discs, but also of the vertebral bodies. The cause may be osteoporosis (usually occurs over the age of 50) or endplate sclerosis (can develop at a fairly young age).
As a result of a decrease in the height of the spinal column, instability in the position of the vertebral bodies develops, since the longitudinal ligaments maintain their length for a long time. This is also facilitated by partial dystrophy of the muscular frame of the back. Those who suffer mainly are those engaged in sedentary mental work and who do not pay due attention to the development of their physical fitness.
Numbness of the thigh can be a consequence of the development of tunnel syndrome, traumatic disruption of the integrity of soft tissues, tumor growth, etc. We'll look at the potential causes in more detail later in the article.
Numbness in the thigh of the leg on the left side (reasons)
The main reason why the left thigh goes numb is osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine. At the level of the lumbar and thoracic vertebrae, the radicular nerves L1, L2, L3, Th12 and L4 arise. They form the lumbar nerve plexus. It is responsible for the innervation of the soft tissues of the lower extremities. The root nerves are paired - they depart from the spinal cord symmetrically: on the left and on the right side. If there is a decrease in the height of the intervertebral disc on the left side, then a disruption of the innervation of the lower limb on this side occurs.
If the left thigh is numb in the groin area and along the inner surface, then pathological changes affect the iliohypogastric nerve. if unpleasant sensations appear in the anterior surface area, damage to the femoral nerve should be excluded. It is often subject to compression from the round inguinal ligament. In men, numbness in the anterior thigh may be associated with a prolapsed inguinal hernia. the outer surface of the thigh most often experiences numbness when the conduction of the lateral cutaneous nerve is disrupted. It is a branch of the sciatic nerve and is responsible for normal blood supply to the tissues of the epidermis.
In a situation where the thigh of the left leg goes numb, the following reasons should be excluded:
- development of tumors in the lumbosacral spine and in the pelvic cavity;
- hernial protrusions in the groin area;
- disruption of the blood supply to soft tissues and pelvic organs;
- lumbosacral osteochondrosis;
- cauda equina syndrome;
- traumatic effects, as a result of which the integrity of the nerve pathways was disrupted;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases that lead to the formation of scar fibrous tissue in the areas where nerves pass;
- tunnel syndromes, including those caused by destruction of the bones of the hip joint.
If you have numbness on the left side of your thigh and there is headache, dizziness, and muscle weakness, you should urgently seek medical help. In this way, a developing brain stroke may manifest itself. This is a dangerous disease, often leading subsequently to paralysis of the upper and lower extremities.
Neuropathy of the external cutaneous nerve of the thigh
Neuropathy of the external cutaneous nerve of the thigh is a tunnel syndrome of peripheral nerve damage. In the medical literature you can find several synonyms for the name of this disease: meralgia paresthetica, lateral cutaneous nerve syndrome of the thigh, Roth syndrome, Roth-Bernhardt disease.
Development mechanism
The nerve and its branches extending to the knee joint innervate the outer and partially anterior femoral surfaces. The most vulnerable part of the nerve is where it exits the pelvic cavity: above the anterior superior iliac spine or under the inguinal ligament. It is there or in the tunnel formed by the connective tissue membrane of the thigh muscles that it is compressed, causing the development of the syndrome.
Neuropathy manifests itself as numbness, tingling, pain in the area of the anterolateral surface of the thigh, with increased load and intense pain - impaired walking. Roth-Bernhardt disease occurs mainly in middle-aged and elderly people, and the incidence in men is three times higher than in women.
Why does meralgia paresthetica develop more often after 50 years of age? This is explained by age-related degenerative changes in nervous tissue due to:
- obstructed venous outflow;
- inferiority of the capillary network;
- metabolic disorders.
Provoking factors
Complaints begin to appear when the compressive effect of the provoking factor becomes critical. Compression in the groin area or at the level of the iliacus muscle can occur as a result of:
- wearing a corset, a tight belt, excessively tight underwear;
- excess fat deposition in the lower anterior abdominal wall and hip area;
- retroperitoneal hemorrhage;
- tumor process;
- inflammatory infiltrate of the abdominal cavity;
- surgical intervention on the abdominal organs.
Reasons why the thigh on the right side goes numb
The answer to the question of why the right thigh is numb will not differ much from listing the reasons for the appearance of unpleasant sensations in the left leg. More often the right thigh goes numb after various traumatic effects. It should be understood that for most people, it is the right leg that bears the main load when jumping, running, etc. This is due to the fact that this lower limb is more physically developed. But, since a person prefers to land on his right leg after making a jump, the likelihood of injury increases proportionally.
The main reason why the right thigh is numb lies in a dystrophic degenerative change in the fibrous ring of the L5-S1 intervertebral disc. it bears all the main physical load during human movements.
In some cases, the right side of the thigh becomes numb due to poor posture. The habit of slouching leads to deformation of the lumbar spine. This entails a disruption of the process of innervation of the lower extremities.
Do you need medical attention?
It doesn’t matter whether the thigh of the right leg is numb on the outside or inside, the patient is advised to see a doctor. Recurrent paresthesia is rarely physiological in nature; it is a manifestation of pathological processes occurring in the body. We need to find out which ones exactly.
The exception is pregnant women. The situation when the right leg from the hip regularly goes numb is not regarded as a disorder - this is a feature of the restructuring of the body. Blood circulation priorities change - the fetus is supplied with blood first. Blood flow through the umbilical artery is restarted; during moments of addiction, many parts of the body tingle and sensitivity is lost.
The outer thighs become numb
In some patients, the outer thigh becomes numb, but the skin sensitivity on the inner side is completely preserved. For a neurologist, this clinical sign indicates that the iliohypogastric nerve is affected. most likely this condition was provoked by the development of osteochondrosis in the thoracolumbar spine.
Very often, the thighs on the outside become numb with the development of vascular pathologies, such as atherosclerosis, varicose veins of the lower extremities, diabetic angiopathy, etc.
Numbness of the external projection of the thigh may be associated with intoxication of the body. But the most dangerous disease that manifests itself with a similar clinical symptom is spinal canal stenosis. It can be caused by prolapse of an intervertebral hernia, traumatic deformation, the appearance of scar tissue in the dural sac, displacement of vertebral bodies, etc. If such a symptom appears, you should consult a neurologist as soon as possible. The specialist will conduct an examination, make an accurate diagnosis and provide the necessary medical assistance.
Part of the thigh goes numb: muscle and skin on the surface
In most cases, part of the thigh becomes numb, and the rest of the lower limb retains its innervation in full. This is typical for damage to individual branches arising from the radicular nerve or plexus. Complete numbness of the entire limb is an extremely unfavorable clinical symptom that requires emergency medical attention.
Usually, a certain thigh muscle goes numb, the innervation of which is supplied by the nerve fiber that has been subjected to compression. The stronger the compression on the nerve, the higher the intensity of the manifestation of the clinical sign. With complete paralysis, we can say that there is no conduction of the nerve fiber. With slight compression, sensitivity may disappear for a while and return.
The localization of the pathological process indicates which nerve is damaged. So, if the skin on the thigh becomes numb, then with a high degree of probability the lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh, which is formed by the root nerves L2 and L3, is damaged. A similar clinical symptom appears with osteochondrosis, herniated disc, compression fracture, subluxation of a vertebra, displacement of its body towards the spinal canal, destruction of the uncovertebral joint between these vertebral bodies in the lumbar spine.
At the initial stages of the development of such pathologies, the surface of the thigh becomes numb, then the disruption of innervation begins to spread to the muscles and blood vessels. In the absence of properly provided medical care, the process of trophic damage to soft tissues may begin. Due to a total disruption of innervation, aseptic necrosis of the femoral head often occurs.
The thigh goes numb: what to do, treatment
If your hip becomes numb, the first thing to do is see a neurologist. The doctor must make an accurate diagnosis based on objective examination data. When compared with the patient's complaints and the results of radiographic images, the correct diagnosis can be made and effective treatment can begin.
If the thigh becomes numb, treatment should be aimed at eliminating the cause of this symptom, and not at relieving the sensation itself. There is a huge difference between symptomatic and etiological treatment. In the first case, the doctor’s efforts are aimed at eliminating the patient’s discomfort. At the same time, the disease continues to develop safely, increasingly worsening the health of the sick person.
The second approach, etiological, is to eliminate the disease that causes the feeling of numbness. In this case, the doctor treats the patient, relieving him not of discomfort, but of existing health problems.
In our manual therapy clinic we practice an etiological approach. The following methods are used in practice:
- traction traction of the spinal column allows you to eliminate compression of the radicular nerve and completely restore the impaired innervation of the lower extremities;
- massage and osteopathy improve blood supply to damaged tissues and accelerate the process of outflow of lymphatic fluid, which quickly reduces the intensity of the inflammatory reaction;
- reflexology starts the process of natural tissue regeneration;
- Therapeutic gymnastics and kinesiotherapy strengthen the muscular frame of the body and increase its functionality.
If you have numbness in your thigh, we recommend that you make an appointment with a neurologist. In Moscow, you can get a free consultation with a doctor at our manual therapy clinic.
Treatment
A prerequisite for achieving a positive effect in the treatment of chronic paresthesia is the elimination of the immediate cause that led to its development. It is necessary to treat comprehensively, using medication, physiotherapy and reflexology methods. Achieving results is facilitated by:
- balanced diet;
- normalization of body weight;
- to give up smoking;
- exclusion of alcohol;
- therapeutic physical exercises, especially swimming and walking.
The sooner the patient seeks qualified medical help, the more successful and cheaper the treatment will be.