The most dangerous causes of hip pain in children
Pain in the hip when bending in a child occurs during physical activity or as a result of injury. This can cause damage to ligaments and muscles.
Painful sensations also occur due to:
- congenital dislocation;
- osteochondropathy;
- epiphysiolysis of the head of the bone;
- osteomyelitis;
- hidden fractures
- bone tuberculosis;
- transient arthritis.
Congenital dislocation occurs as a result of a violation of the formation of the hip joint. This pathology is visible immediately after the birth of the child, it can appear in subsequent years.
Osteochondropathy is a pathology that occurs during the period of active growth, from 4 to 14 years. May lead to impaired joint development.
Symptoms of the disease:
- discomfort;
- lameness;
- loss of leg mobility.
Epiphysiolysis of the head of the bone is a disease in which bone growth in a child stops, which leads to asymmetry of the legs. Causes may include endocrine system disorders, hip injury, or active sports.
The head of the bone comes out of the glenoid fossa, this is a very painful condition:
- excruciating pain occurs;
- movements are constrained;
- hip displacement occurs.
The baby must be urgently hospitalized at the nearest hospital.
Boys between the ages of 3 and 14 may develop Perthes disease, which affects the circulation of the femoral head.
This pathology occurs due to:
- infectious diseases;
- birth defects;
- excess load on joints;
- injuries.
The pain appears first in the knee, then moves to the hip joint.
Hidden fractures occur in children when bone formation is impaired due to rickets.
Unpleasant symptoms in the hip area can be observed with cardiovascular diseases, neoplasms and serious infections. Stenosis and occlusion of the aorta and iliac arteries cause pain and claudication.
Malignant neoplasms are quite rare in the hip joint. With metastases, the ilium is affected.
Infections
If a child has leg pain for no apparent reason in the hip area, this may indicate the presence of an infection in the body.
Osteomyelitis is an inflammation of the hip joint that occurs due to an infection affecting the bone marrow.
Young children under 10 years of age sometimes develop bone tuberculosis, which can affect the spine and joints.
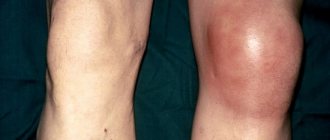
A fairly common cause of hip pain can be arthritis of the hip joint. This disease is viral in nature. The child experiences pain, a swollen knee, possible fever, and a rash.
Inflammation of the synovial membrane - synovitis, a disease of the lining of the hip joint develops against the background of viral infections. The pathology does not require treatment; it is necessary to remove excess fluid from the joint.
Lameness and pain may be felt with other pathologies:
- pelvic abscess;
- complicated appendicitis;
- inflammation of the female genital organs;
- retroperitoneal hematoma.
If a child complains of hip pain and limps, you should immediately consult a doctor. Timely treatment will help avoid serious consequences.
PATHOGENESIS.
The idea of the pathogenesis of osteochondropathy of the femoral head is based mainly on microscopic examination of biopsy material and individual autopsy cases [Sturm V. A., 1935; Kapyatanaki A.L., 1964; Ponseti J., 1956]. At the onset of the disease, an excess amount of yellowish fluid and a thickened and swollen synovial membrane are found in the cavity of the hip joint, which indicates the presence of synovitis. Bacteriological research has not determined its infectious nature.
Since the disease is considered to be avascular in nature, early changes in the joint capsule and its vessels are of particular interest. A. L. Kapitanaki (1964) found an accumulation of plasma cells in the capsule of the hip joint with osteochondropathy, P. Mass (1957) revealed perivascular infiltration with lymphocytes and plasma cells, and G. G. Spiridonov (1959) in the vessels of the fibrous layer of the capsule and adjacent tissue discovered a thickening of the vessel wall with a narrowing of its lumen. Such changes in the capsule resemble allergic inflammation and, obviously, belong to the initial signs of osteochondropathy.
The disturbance of blood circulation in the entire affected limb and microcirculation disorders revealed by radioisotope research in the form of stagnation in the capillaries of the nail limbus of the toes, their expansion and tortuosity, slowing of blood flow, and a stagnant cyanotic background can be secondary in Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease [V. M. Gartanitskaya, 1973; Semenov V. A., Abalmasova E. A., Kryukova N. N., 1972].
In a microscopic examination of the femur in the initial stage of osteonecrosis, R. Mattner (1968) revealed necrosis of osteocyte nuclei, necrosis of bone marrow in the subchondral zones, and areas of detritus in the epiphyseal cartilage. V. A. Sturm (1935) conducted a detailed macro- and microscopic examination of the hip joint of an 11-year-old boy with stage III-IV Perthes disease. Macroscopically it was revealed that when pressed, the cartilage of the head is compressed and flattens the softened bone underneath. A similar softening of the bone is detected in the paraepiphyseal zone of the femoral neck, where the epiphysis, like a cap, is put on the neck. Shortening and widening of the femoral neck, a mushroom head, is possibly formed as a result of this subsidence of the epiphysis. The bone beams of the epiphysis are necrotic and softened, resembling a sponge. Necrosis of the bone beams with fatty bone marrow, poor in cellular elements, is detected in the epiphysis, femoral neck and, to a lesser extent, in the roof of the glenoid cavity and the greater trochanter. V. A. Sturm, based on the prevalence of the process, considered Perthes disease as “osteochondropathy of the hip joint,” and not just the epiphysis of the femoral head. The pathological process in this case has the character of deep dystrophy with necrosis of the spongy bone, partly of the cartilage, especially in the zone of epiphyseal ossification, with necrosis of the bone marrow [Sturm V. A., 1935; Shairo E.I., 1970; Ponseti J., 1956].
Doctors to see
The causes of leg pain in the thigh when walking in a child are often injuries. The child may hit his hip or fall on his leg. Treatment should be carried out by a qualified doctor. He will determine the diagnosis, prescribe therapy and prevent the development of complications.
If you have any complaints about pain, you should contact a specialist:
- osteopath;
- neurologist;
- orthopedist;
- surgeon;
- chiropractor;
- pediatrician;
- reflexologist.
During the examination, the doctor pays attention to the appearance of the leg, stiffness of movement, and conducts a frog test. When lying down, the affected hip should bend in the same way as the healthy one. If the child cannot do this, an examination will be required to determine the diagnosis. The doctor pays attention to the gait.
The following are prescribed as diagnostics:
- external examination of the patient;
- blood tests;
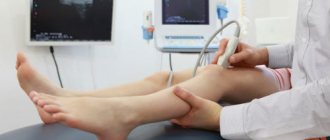
- X-ray of the hip joint;
- ultrasound.
It is necessary to seek help from specialists in a timely manner. You should not hope that the disease will go away on its own. It is important to begin timely therapy aimed at eliminating the pathology.
Injuries are the cause of pain
Disruption of the normal anatomical structure of the hip joint as a result of injury is a common cause of pain.
Dislocations
A fairly rare injury, characterized by severe pain, inability to flex the limb, and unnatural position of the hip. Dislocations are divided into posterior and anterior. Treatment: reduction of the joint, use of osteosynthesis techniques, use of muscle relaxants.
- What to do if a child complains of leg pain for no apparent reason: symptoms and treatment
Injury
The injury is accompanied by moderate pain, which intensifies with movement. Bruising is a common problem that can occur due to a blow or fall. Damage appears on the body in the form of scratches, hematomas, and tumors. The patient is prescribed rest, and a week later a course of physiotherapy is carried out.
Fracture of the femoral neck or acetabulum
Mostly older people are susceptible to injury, but a child can get injured if they have an accident or fall from a height.
Symptoms of pathology:
- acute pain;
- inability to raise the leg in an extended position.
Treatment of hip pain
Children's analgesics
After diagnosing and making an accurate diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a course of treatment. The choice depends:
- from the individual structure;
- causes of pain.
If an injury is detected, movement is limited and a plaster cast is applied to the affected area. If the fracture is complex, then surgery is performed.
Complex therapy methods:
- Severe pain is relieved with analgesics. Pain-relieving injections are especially effective. Anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
- For injuries and inflammations, ice is used; it must be applied for 10–15 minutes.
- If the cause of the pain is arthritis, you can warm the sore area or take hot baths.
- For the first time, bed rest and reduced physical activity are prescribed.
The following are actively used as additional treatment:
- Thigh massage to improve blood circulation and relieve pain.
- Therapeutic gymnastics, swimming.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
It is important to monitor your body weight, as excess weight increases stress on the joints and can lead to the development of diseases.
The main treatment is related to eliminating the cause of the pain.
How to treat Perthes disease?
With a diagnosis such as Perthes disease, treatment depends, first of all, on the stage of development of the disease, as well as on the age of the child at the time of diagnosis of the disease. Treatment is usually complex and long-term. In the early stages, the emphasis is on completely eliminating loads on the affected limb. In addition, the orthopedic doctor prescribes medication, physiotherapeutic procedures and physical therapy courses. During the recovery period, sanatorium-resort treatment in the “orthopedics” profile is of great importance.
In the later stages of the development of Perthes disease, treatment, unfortunately, consists of surgery, during which the doctor corrects the joint abnormalities.
Treatment of Perthes disease takes quite a long time and can last from 2 to 4 years. You should also keep in mind the fact that improper treatment of this disease entails serious complications leading to disability of the child, which is why periodic observation by an orthopedist and implementation of his recommendations are simply necessary.
Folk remedies
Eggshells with sour milk relieve joint pain.
It is successfully used to relieve pain and as an additional therapy in traditional medicine. There are many time-tested recipes:
- Apply a compress of cabbage leaves smeared with buckwheat honey to the sore spot at night and wrap it in a warm towel.
- 50 gr. pour 400 ml of vodka over lilac flowers, leave for 10 days, drink 50 drops before meals.
- White from 2-3 eggs, 50 ml of alcohol, 50 g. mustard powder, 50 gr. Mix camphor until smooth. Rub the product into the sore spot.
- Crush the egg shells, mix with yogurt or milk, apply the paste on the thigh, and wrap with a warm scarf.
It is necessary to monitor your diet, take more vitamins, exercise and spend more time in the fresh air. A healthy lifestyle and good mood are important for proper growth and development.
How does Perthes disease progress?
In the clinical course of Perthes disease, five successive stages are distinguished:
- Stage I - necrosis of the ossification nucleus of the femoral head develops;
- Stage II - due to a violation of the structure and density of the femoral head, a secondary compression-impression fracture occurs;
- Stage III - resorption of necrotic bone tissue and its fragmentation occurs, shortening of the femoral neck;
- Stage IV - connective tissue grows instead of the affected osteochondral structures;
- Stage V - ossification of replacement connective tissue structures occurs due to calcium deposition with the formation of bone tissue.
Diagnostic methods
The diagnosis is made by an orthopedist after a comprehensive examination of the child. To identify the cause of the disease and the stage of its development, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- blood and urine tests to determine the type of pathogen and the presence of inflammation;
- Ultrasound to detect injuries and degenerative changes;
- rheumatic tests;
- fluorography of the lungs;
- Mantoux test;
- X-ray;
- smears from the conjunctiva of the eye;
study of periarticular fluid;
READ ALSO: if the injection site of the Mantoux test is enlarged, what does this mean?
- CT and MRI help diagnose inflammation, circulatory disorders, and the condition of muscles and blood vessels.
Types and symptoms of inflammation of the hip joint in a child
Types of childhood arthritis:
- Rheumatic. The most commonly diagnosed type of arthritis of the hip joint, developing as a complication of sore throat, pharyngitis and other infectious ailments. It manifests itself as swelling, often affects both joints and hinders movement.
- Allergic. It develops acutely, patients suffer from pain when walking, joints swell, and a rash appears on the skin. The body temperature often rises, the baby vomits, and general weakness is observed.
- Psoriatic. The cause of its appearance in children is progressive psoriasis. A characteristic symptom is blue discoloration of the skin around the joint, pain radiating to the spine.
- Purulent. When inflammation occurs, pus begins to accumulate in the tissues; lack of treatment leads to poisoning of the body. The disease at the beginning of its development is manifested by acute pain, increased sweating, and yellowing of the skin. Then the symptoms intensify - weakness, fever, redness, swelling of the joint and sharp pain when pressing on it occur.
- Gouty. It is a consequence of gout. It manifests itself as severe pelvic pain, redness of the area around the affected area and limited joint mobility.
- Spondyloartitis. The child feels stiffness of movement after waking up, and pain and tissue swelling may appear suddenly. The disease is accompanied by redness and tearing of the eyes.
- Reactive. The child complains of stiffness of movement in the morning, pain, and at the same time symptoms of eye damage and infection of the genitourinary system appear. As the disease progresses, a crunching sound is heard while walking, and spots or ulcers form on the skin.