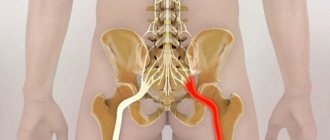
The hip joint is the largest and most powerful joint in the human body, which bears the heaviest load. It is thanks to it that bipedal posture and leg movements in different directions are ensured. Pain in the hip joint seriously impairs its functionality, causing discomfort during any physical activity, sitting, or even lack of movement. This symptom is quite often accompanied by lameness or other gait disturbance, numbness of the limb, shortening of the leg length, and limited joint mobility.
Dysfunction of the hip joint may indicate the development of severe pathologies, so they should not be ignored. Without proper treatment, any of the diseases or injuries of the hip joint can lead to muscle weakness, muscle atrophy, disability, and complete loss of motor activity of the joint.
What can cause pain in the hip joint?
Typically, pain in the pelvic area is caused by the following reasons:
- Bursitis. This is an inflammation of the joint cavity (trochanteric bursa), which is responsible for the lubrication and sliding of the rubbing elements of the bones. Bursitis is called a disease of athletes, especially long-distance runners. It can be acute or chronic; its main symptom is severe pain in the hip joint, often even while lying down.
- Coxarthrosis. The disease is caused by a metabolic disorder in cartilage tissues, which causes them to die. Symptoms of coxarthrosis include pain not only in the hip joint, but also in the entire lumbar region. The pain worsens with physical activity and subsides during periods of inactivity.
- Arthritis. This is an inflammation of the joint tissue that occurs due to a malfunction of the immune system or a viral infection. Arthritis is accompanied by pain and swelling in the hip joint, fever and problems with motor activity.
- Tendinitis. A tendon disease that causes severe discomfort when moving, pain in the hip joint, clicking in the joint area when walking, and changes in gait.
- Infections. The cause of inflammation of the articular tissues can be: tuberculous or purulent arthritis, aseptic necrosis of the femoral head.
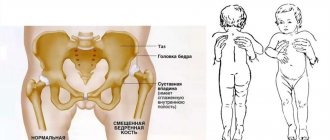
- Osteochondropathies. The most common disease affecting the hip joint is Legg-Calvé-Perthes syndrome, most often diagnosed in children and adolescents. The disease begins to manifest itself with mild pain in the joint area, limping, then the pain increases, and walking becomes difficult.
- New growths of bones and soft tissues in the hip joint area. Tumors, both benign and malignant, undoubtedly also cause pain.
- Injuries. This could be the consequences of a bruise, dislocation, or fracture of the femoral neck.
Types of trochanteritis
Trochanteritis by its nature can be tuberculous, septic and aseptic. The diagnosis is made by a doctor based on palpation of the thigh and movement tests. Additionally, blood tests, x-rays, ultrasound or MRI are prescribed.
Tuberculous and septic trochanteritis occur under the influence of pathogenic organisms. The cause of aseptic trochanteritis can be:
- high physical activity;
- difference in leg length or other deviations in the structure of the pelvis;
- past viral infections - including influenza;
- injuries;
- sudden weight gain;
- hypothermia.
Trochanteritis can be either unilateral or bilateral.
Is it possible to recognize the disease by the degree of pain?
Depending on the intensity of pain in the hip joint, you can roughly judge what triggered it, but this is not 100% evidence. In any case, you must contact a qualified doctor and begin professional treatment.
Pain in the hip joint can be:
- Light. Usually these are the consequences of a bruise. To relieve pain, it is recommended to apply cold, take painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, and limit physical activity. If pain and discomfort do not go away within 2-3 days, you should consult a doctor.
- Moderate. This is most likely a consequence of diseases of the hip joint. Such pain is usually accompanied by limited movement and increased temperature. It is necessary to consult a general practitioner or rheumatologist.
- Strong. They arise due to dislocations and fractures. Usually they cannot be ignored for long because the pain is excruciating and movement is impossible. We need to call an ambulance.
Reasons why hip bones hurt
It is impossible to answer in absentia, without appropriate examinations, the question of why the femur hurts. But there are potential causes and risk factors that can trigger discomfort. So let's talk about them.
Let's start with risk factors in which, with a high degree of probability, a person will begin to develop those diseases that are accompanied by such an unpleasant symptom. These include the following aspects:
- excess body weight, which has a destructive effect on the cartilage tissue inside the hip and knee joints, as a result of which the bone structure may begin to deteriorate;
- maintaining a sedentary lifestyle - muscle fiber degeneration begins, the movement of blood and lymphatic fluid slows down, tissue trophism deteriorates, including the periosteum;
- violation of ergonomic rules when organizing your sleeping and working space (deformation of the pelvic bones and lumbosacral spine occurs, this negatively affects the blood supply and innervation of the lower extremities);
- heavy physical labor, standing for long periods of time, carrying heavy objects;
- incorrectly selected shoes for physical education and constant wear;
- violation of foot placement when walking and running - flat feet or clubfoot;
- smoking and drinking alcohol provoke a narrowing of the capillary bloodstream and the onset of trophic disorders in various tissues of the human body.
Patients with various endocrine pathologies are at risk. For example, a patient with diabetes has a high probability of developing diabetic neuropathy or angiopathy, which will inevitably lead to pain in different parts of the lower extremities. Also, similar symptoms can occur with the development of diseases of the adrenal glands, thyroid gland, etc.
If we talk directly about the reasons that the hip bones hurt, then they are conventionally divided into degenerative dystrophic, ischemic, metabolic, traumatic and inflammatory diseases. Let's look at each group in more detail. Let's start traditionally with injuries.
Here, sprains and microscopic tears of ligament and tendon fibers at a young age and hip fractures in older people come to the fore. The femur itself is rarely subject to fractures and cracks. But dislocations and subluxations both in the plane of the hip joint and in the plane of the knee joint are common injuries at any age.
If on the eve of the onset of pain there was a traumatic impact (fall, blow, unsuccessful landing, participation in an accident), then you must first contact a traumatologist. Using an x-ray, he will rule out the possibility of bone tissue damage. Provide first surgical aid as necessary.
Another common reason for hip pain is osteoarthritis. This is a chronic disease of a degenerative dystrophic nature. It develops in stages:
- first, there is a disruption in the production of synovial fluid, which nourishes and supplies water to the cartilaginous protective tissues inside the knee and hip joint;
- then the cartilaginous synovial layer is destroyed and the head and condyle of the femur are exposed;
- When moving, cracks form on their surface, which are filled with deposits of calcium salts;
- the joint loses its mobility, contracture or ankylosis forms.
This is a very serious disease that can be successfully treated only at the initial stage of its development. When it reaches the 3rd stage, when the cartilaginous synovial layer is already destroyed, treatment is possible only with the help of endoprosthetics surgery.
Next, we will consider a number of potential causes that may be present in people of different ages.
Symptoms
The main symptom of the disease is pain in the thigh while walking, sometimes radiating to the groin area. At rest, pain is usually not observed, but in advanced cases, it can sometimes occur at night when the painful area is compressed - for example, when the patient sleeps on his side.
The risk group is primarily women over 30 years of age. The older a woman is, the greater her chances of developing trochanteritis, since a decrease in the concentration of female sex hormones weakens the musculoskeletal system.
Differential diagnosis
- Coxarthrosis
- Femoral head dysplasia
- Lumbar radicular syndrome
- inguinal or femoral hernia
- lateral femoral cutaneous nerve compression syndrome
- damage to the anterior horn of the meniscus of the knee joint
- marching fracture of the femoral neck
- Juvenile epiphysiolysis of the femoral head
Trochanteritis of the greater trochanter of the femur is a fairly common pathology of the musculoskeletal system, which is characterized by chronic pain, as well as occasional acute attacks. The sensations are localized along the outer surface of the thigh, and some stiffness of movement may also be felt. Specialists at Professor Gorbakov’s Clinic recommend shock wave therapy for the treatment of this pathology. To make an appointment, just call the clinic on the numbers provided.
Based on the causes of trochanteritis, doctors distinguish three forms of the disease:
- Tuberculosis form, in which, as the name implies, bones and joints are affected by tuberculosis;
- A septic form in which tissue damage occurs due to an infection not associated with tuberculosis. This is usually staphylococcus, which can be a consequence of osteomyelitis, sepsis or chronic infections;
- An aseptic form that develops due to hypothermia, increased stress and violations of the correct anatomical structure of the skeleton.
Symptoms of trochanteritis
The main symptom of hip disease is pain. Initially, the pain bothers the patient only during walking or physical activity, however, over time, the pain also appears at rest. An important diagnostic sign is increased discomfort in the patient when lying on his side. Also symptoms of hip diseases are:
- The pain syndrome is more pronounced than the stiffness of movements;
- In the presence of the tuberculosis form, abscesses can form, which externally manifest themselves in the form of swelling;
- The presence of vegetative-vascular symptoms in the limb of the affected joint;
- There is a relationship between pain and physical activity and injuries to the affected joint.
Treatment of diseases of the hip joint is prescribed taking into account the form of trochanteritis and the reasons that caused it.
Treatment of trochanteritis
The need for surgery for trochanteritis occurs quite rarely.
In most cases, the disease can be managed using conservative techniques, which include:
- Drug therapy. Mainly anti-inflammatory and painkillers. Local blockades are used - the introduction of drugs into the painful area. Such manipulations are performed by our Pain Clinic specialists.
- Physiotherapy. For example, laser therapy and magnetic therapy are highly effective.
- Physical therapy after eliminating inflammation and pain.
In the multidisciplinary CELT clinic, the most effective treatment program is selected for each patient, in accordance with modern schemes and individual characteristics.
Trochanteritis of the hip joint: causes
The reasons for the development of trochanteritis are as follows:
- anatomical features of the hip joint;
- intense, constant stress on the femur, hip joint or passive lifestyle;
- hip injury;
- viral and infectious diseases;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- osteochondrosis of the spine and, as a consequence, increased muscle tone in the gluteal region.
Predisposing factors are:
- female;
- age;
- obesity;
- joint diseases;
- systemic osteoporosis.
The disease predominantly affects women - the tendons in women are less strong and resilient than the tendons in men. Most often, the disease affects women during the premenopausal and menopausal periods, when hormonal changes occur and osteoporosis very often develops. Young women rarely get sick; the cause is the long-term effect of factors that provoke the disease.
Trochanteritis of the hip joint: treatment
Diagnosis of trochanteritis begins with examination of the patient and collection of anamnesis. There are no methods for specific diagnosis of the disease. The main clinical criteria for trochanteritis are pain when lying on the side, pain when pressing with a finger in the breeches area, while at the same time maintaining joint mobility. The doctor excludes diseases with similar symptoms after conducting additional studies. Diagnostic tests include:
- x-ray of hip joints;
- Ultrasound of soft tissues of joints and joints;
- MRI or CT;
- blood chemistry;
- rheumatic tests;
- general blood and urine tests.
Treatment of the disease is carried out depending on the cause that caused it. If complications of the disease arise - suppuration, abscesses, surgical treatment is performed. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used to eliminate the inflammatory process and relieve pain. In some cases, hormonal therapy is prescribed.