Spina bifida is the Latin name for spina bifida or cleft spine, or an open defect of the spine, accompanied by a malformation of the spinal cord and its membranes. Another name for this disease is spina bifida (SMH).
Spina bifida is a severe malformation of the spinal cord that occurs as a result of disruption of the formation and closure of the medullary plate into the medullary tube. In addition, the development and closure of the vertebral arches, which normally, together with the soft tissues and meninges, close the spinal canal, are disrupted. To date, there is no scientific data that would indicate the hereditary nature of this pathology. The likelihood of having a child with spina bifida again in one family is negligible. At the same time, many researchers associate the development of this defect with a deficiency of folic acid in the body of a pregnant woman and recommend taking it as a dietary supplement before pregnancy, as well as in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy.
Disorders in children with spina bifida
Children with spina bifida develop a whole range of different disorders:
- neurological disorders (paresis and paralysis of the lower extremities, sensory impairment, hydrocephalus and shunt failure, symptoms of a fixed spinal cord);
- movement disorders;
- cognitive and perceptual impairments (difficulty planning your movements and determining the correct sequence of actions, incoordination of motor responses, may look like general slowness, memory impairment, difficulty concentrating, easily distracted and quickly get tired, there may be problems with communication, reading, writing);
- orthopedic problems (clubfoot, contractures, deformities, dislocations and subluxations of the hip, scoliosis and other curvatures of the spine);
- osteoporosis;
- urinary and fecal incontinence;
- urological problems (urinary tract infections);
- soft tissue disorders (burns, bedsores and other lesions due to sensory impairment)
Some of these disorders are detected in early childhood, while other complications develop later. The severity of these problems is determined by the level and extent of damage to the spinal cord. Quite often, spina bifida is combined with other developmental disorders of the central nervous system, for example, with structural disorders of the corpus callosum (in 70-80% of cases) or disorders of the formation of the frontal cortex of the brain.
It is important to mention that about 80-95% of children with SMH have problems with the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the cavities of the brain and intrathecal spaces, resulting in external or internal hydrocephalus or a combination of both. For the treating specialists of such a child, the issue of timely shunting is very important, and for parents and rehabilitation team specialists, the issue of monitoring the condition and functioning of this shunt and timely detection of its failure.
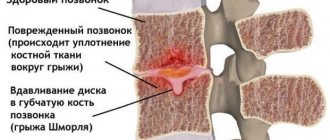
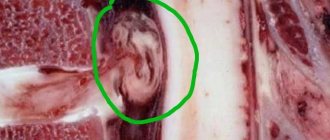
Schmorl's hernia
Schmore's hernia can be posterior, anterior, central or lateral
With a Schmorl's hernia, the protrusion does not affect the nerve fibers, so pain is rare. The pathology affects the endplates that separate the disc from the adjacent vertebral bodies. With such a hernia, the cartilage of the plates penetrates the vertebral body, which consists of spongy tissue. This fundamentally distinguishes it from other types of disc herniations.
The pathology usually affects the lumbar or thoracic region. It is hereditary. Formed when a child begins to grow rapidly. Soft tissues have time to stretch, but bone tissues lag behind. Because of this, voids appear in the spongy body of the vertebra, into which the endplates are pressed.
A Schmorl's hernia of the lumbosacral region can be caused by trauma when the disc becomes displaced, forming a defect. Another reason is degenerative diseases of the spine (osteoporosis, osteoarthritis), when cartilage loses its elasticity, forming a knot.
This hernia usually has no symptoms. It is dangerous because the intervertebral disc can fall into the vertebral body, disrupting its function. At the same time, the nodule is the weakest point of the vertebra and can cause damage to it during heavy physical exertion or a strong blow.
Each type of intervertebral hernia has serious complications, so you should not delay treatment.
See how easy it is to get rid of a hernia in 10 sessions
Signs of shunt failure
Signs of shunt failure that anyone around a child with SMG should know:
- lethargy, absent-mindedness, changes in gaming behavior;
- dizziness;
- headache;
- nausea, vomiting;
- increase in head volume (it is necessary to regularly measure head circumference).
Until the 70s of the 20th century, most children with spina bifida died from complications associated with hydrocephalus and kidney damage. However, due to the introduction of early closure of the defect, shunting and catheterization into the standards of management of such patients, their survival rate has increased sharply since the late 60s.
Spinal cord malformation results in structural defects in motor and sensory neurons.
To date, unfortunately, there is no way to restore the structural integrity and function of these neurons, which means there is no way to cure spina bifida. That is why the rehabilitation of such patients from a very early age, during which we do not expect miraculous healing and recovery, but develop what can be developed and maintain even minimal muscle activity, becomes vitally important.
Classification of hernias by location
The annulus fibrosus often ruptures in the lumbosacral region. Less often - in the neck area, very rarely - in the chest.
Hernia of the lumbosacral region
The intervertebral discs in the lower back not only cushion the impacts of the vertebrae against each other, but also help support the upper body. They also provide the ability to move in a wide range (in all directions).
The main causes of protrusion in the lumbosacral region are heavy loads and disc degeneration. A common symptom is dull pain in the lower back, which is accompanied by joint stiffness. When moving, the discomfort intensifies and occurs after standing or sitting for a long time, or walking a short distance. Leaning forward, laughing, sneezing, or other sudden action may make the symptom worse.
The pain can be so excruciating that a person is unable to straighten the spine normally or even move. A tear in the annulus fibrosus causes sciatica, leg discomfort along the sciatic nerve at the back of the leg.
Other symptoms of intervertebral hernia in the lumbar region:
- Pain in the legs is worse than discomfort in the lower back. (But if it spreads down the leg along the sciatic nerve, it is sciatica).
- Burning, sharp, electric, or stabbing pain.
- Discomfort occurs in different places, depending on the location of the protrusion. It can be felt in the lower back, buttocks, thighs, lower legs, and even the feet and toes.
- The pain usually affects one side of the body.
- Neurological symptoms – numbness, tingling in the leg, foot, fingers.
- Problems lifting the foot when moving.
If a herniated disc is caused by muscle spasms in the lower back, it can be relieved by:
- Spend 1-2 days in bed, placing a pillow under your knee;
- apply heat or ice;
- sit, leaning on a comfortable backrest.
The fibrous ring often ruptures in the lumbosacral region
Thoracic hernia
The middle part of the back is the most immobile part of the spine, so hernias rarely appear here. The main reasons for their occurrence are disc deformation, trauma, cracks, and changes in the shape of the vertebrae. Sometimes scar tissue forms between the disc and the spinal cord, which can cause an anulus fibrosus defect.
Common symptoms of a thoracic hernia:
- pain in the upper, middle part of the back;
- “compression” of the heart, tingling, shooting in the chest;
- headaches when a person sits or lies in a certain position;
- numbness, pins and needles or burning in the legs;
- problems with walking, it hurts to move the lower limb;
- weakness in arms or legs;
- problems with urination or bowel movements.
Cervical hernia
The main causes of cervical hernia are disc deformation, scoliosis, and osteochondrosis. The pain can be mild, aching or acute.
Symptoms of a cervical hernia:
- The pain radiates to the right or left shoulder, between the shoulder blades. It spreads throughout the arm and can reach the hand and fingers.
- Numbness, tingling in the shoulder, arm, hands.
- Weakness of the arms and hands.
- Certain positions or movements of the neck increase pain.
- Stiffness in the neck, difficult to bend or turn to the side.
Treatment and Rehabilitation of Children with Spina Bifida
Rehabilitation tactics for spina bifida are implemented in close partnership between parents and specialists of the rehabilitation team and are determined by:
- the severity and severity of symptoms, which in turn depends on the level and extent of damage to the spinal cord;
- prevention of secondary orthopedic complications, which are easier to prevent than to treat (correct positioning and verticalization, wearing a corset, orthotics, etc.). For example, scoliosis in SMG is very specific and pronounced, and when formed early, it is difficult to even undergo surgical correction;
- careful monitoring of the child in order to prevent the development of life-threatening complications (shunt failure, fixed spinal cord, progression of urological problems);
- adequate selection and use of technical means of rehabilitation, without which the rehabilitation program will not be complete;
- the need to develop the maximum possible number of movements for each baby, excluding those that are dangerous for him;
- the need to ensure the stability of unstable parts of the body, taking into account the correct position and correct distribution of body weight;
- preventing problems that can significantly affect a child's motor abilities, such as obesity.
To solve these problems, within the framework of the rehabilitation program for children with spina bifida, the following activities are carried out in our center:
- consultation, active observation, planning and adjustment of the rehabilitation program, management of hydrocephalus, monitoring the occurrence of neurological and neurosurgical complications by specialists from an interdisciplinary team (pediatric neurologist, orthopedist, pediatrician, doctor and exercise therapy instructor, neuropsychologist, occupational therapist);
- individual exercise therapy classes aimed at increasing muscle strength, developing motor strategies and skills necessary to maintain posture, implement motor transitions, move, verticalize, use technical means of rehabilitation, improve the function of the upper extremities, develop movement planning, etc.;
- on-site group classes in adaptive physical education;
- training parents in correct positioning and active movement of the child;
- children's massage;
- selection and production of orthopedic products (shoes and insoles, orthoses, corsets);
- selection and training in the use of technical means of rehabilitation;
- classes with an occupational therapist, including at home, development of social activity;
- individual sessions with a neuropsychologist (work on cognitive and perceptual impairments);
- performing control laboratory tests, monitoring problems associated with incontinence and urological management by a pediatrician;
False hopes, attempts to teach a child diagnosed with spina bifida to walk like ordinary people walk, sooner or later lead to disappointment for parents, and most importantly, to the loss of your child’s precious time. Therefore, it is very important for every parent to accept their child as soon as possible for who he is, start solving pressing problems day by day and step by step achieve even small but real goals, adhering to the basic principles:
- Preventive approach. Any complications are easier to prevent than to treat.
- Early development of activity, mobility and participation.
- Early involvement of the child in the problems of his own health (teaching catheterization for a child from 5-8 years old, monitoring the condition of his skin, monitoring his weight, maintaining the level of physical activity).
- Age-appropriate social activity.
Classification of hernias depending on size
The larger the size of the protrusion, the worse the state of health. The smallest formation appears in the neck area, the largest in the lower back. The classification of intervertebral hernias by size is as follows:
- Small (from 1 to 5 mm).
- Medium (from 6 to 8mm).
- Large (from 9 to 12 mm).
- Huge (from 12 mm).
Small, medium, and large formations are treated using traditional methods. Huge protrusions require surgery if they severely compress a spinal nerve, causing urinary and fecal incontinence, paralysis, and in men - impotence.
What types of intervertebral hernias are most difficult to treat?
4 stages of treatment for intervertebral hernia
Types by degree of protrusion
Another classification distinguishes hernias according to the degree of their extension beyond the intervertebral space and the integrity of the fibrous ring. There are such types - protrusion, prolapse, extrusion, sequestration.
Protrusion
A type of minor spinal hernia, when only the internal fibers of the fibrous ring are damaged, the ring itself does not rupture. The reason is deformation and dehydration of the intervertebral disc, which reduces its elasticity. Cracks appear in the ring, and the fixation of the vertebrae with each other deteriorates.
Bulging occurs under vertical loads. Therefore, if the patient was lying down during the examination, the defect may not be noticed. The formation often occurs in the lumbar spine, less often in the neck and chest. The compression of the nerve endings disappears quickly. The nature of the pain depends on the location of the protrusion:
- thoracic region
- the heart, lungs, and other organs inside the sternum ache; - lumbar zone
- discomfort in the back, numbness in the legs, groin area; - cervical spine
– neck pain, decreased blood pressure, headache, tinnitus.
Prolapse
Prolapse is a medium-sized hernia of the spine, which is characterized by partial release of the nucleus into the spinal canal. The ring may simply stretch too much or tear. The nucleus compresses the nerve roots, causing inflammation and swelling of the tissue.
The appearance of a protrusion is accompanied by chronic pain, impaired sensitivity in the lower back, neck, legs and arms. Discomfort intensifies with sudden movements (coughing, sneezing), and can put a person to bed for several days.
Prolapse usually appears in the lower back. The main reason is spinal injury due to heavy lifting, sudden straightening and turning, working in an awkward position, hypothermia, and stress.
Extrusion
Extrusion is a hernia in which the fibrous ring is torn, but the longitudinal ligament remains intact. Discomfort appears if the nucleus pulposus touches the nerve roots.
Pain symptoms may vary, depending on the size and displacement of the protrusion. With a strong shift, a dull spasm occurs in the neck, which moves to the head and shoulder. Possible numbness, tingling, and loss of skin sensitivity. With breast extrusion, the heart, ribs, stomach, and intestines hurt. When the lumbar region is affected, problems appear in the lower back, groin, and legs. The development of pathology is fraught with impaired urination and erection in men.
Protrusion, prolapse, extrusion, severstration - types of hernias according to the degree of their extension beyond the intervertebral space
Severstration
Sequestration is a severe form of hernia, which is characterized by the formation of a sequester - the prolapse of the nucleus or part of the disc into the spinal canal. Due to rupture of the longitudinal ligament, the nucleus pulposus is completely or partially separated from the disc. It falls into the canal, squeezing the nerves. The mass may remain in place or migrate up or down, simulating a herniation of another vertebra.
The diagnosis is usually made in older people. A striking symptom is lumbago in the back, which radiates to the legs or arms, followed by numbness, sometimes paralysis.
Approach to the treatment of different types of hernias at the Paramita clinic
If lumbago occurs frequently, buy an anesthetic ointment (Indomethacin, Diclofenac). You can apply a piece of ice to the affected area, after wrapping it in a towel, to avoid damaging the skin. Keep for 15 minutes, then remove. But, if the intervertebral hernia is not treated, the pain will last for several weeks and may become permanent. Depending on the dislocation, the patient is unable to bend normally, turn his neck, raise his arm, leg, stand, or sit.
Don't ignore the pain. Paramita Clinic specialists use in their work:
- exercise therapy exercises;
- proven methods of alternative medicine - acupuncture, manual therapy, massage, reflexology, etc.;
- physiotherapy - electrophoresis, Darsonval, laser therapy, shock wave therapy.
We use non-surgical hernia treatment techniques
Read more about our unique technique
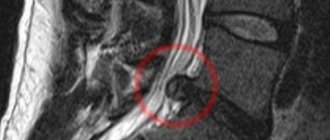
Before prescribing treatment, the doctor prescribes diagnostics - x-rays, CT, MRI. They allow you to assess the condition of soft and bone tissues, the size and location of the hernia, and accurately determine its type.
Surgery for any type of hernia should be resorted to only if the analysis shows the impossibility of another solution - severe constant pain from a spinal hernia, the risk of paresis, paralysis.
Themes
Intervertebral hernia, Spine, Pain, Treatment without surgery Date of publication: 09.17.2020 Date of update: 01.12.2020
Reader rating
Rating: 5 / 5 (2)
Prevention of spina bifida
Since spina bifida is a congenital developmental anomaly, the prevention of this disease is the elimination of its causes even before conception. The primary measure is to provide the unborn child with all the necessary microelements and vitamins. Even if the pregnancy is unplanned, the use of medications and appropriate foods can be started after conception - the sooner the better. In the specific case of preventing spinal cord herniation, the emphasis is on vitamin B9 (folic acid). It is interesting that this substance can enter the fetus’s body not only from the mother, but also from the future father, since it is transmitted through the seminal fluid, having a significant effect.
Any expectant mother should contact a gynecologist and consult about diseases that develop during the fetal development stage. The doctor should talk about ways to ensure a favorable pregnancy. To begin, stop taking most pharmaceutical drugs for at least the first eight weeks while the neural tube forms in the embryo. Also, don’t get carried away with cosmetics; the same goes for any household chemicals.
Author of the article:
Volkov Dmitry Sergeevich |
Ph.D. surgeon, phlebologist Education: Moscow State Medical and Dental University (1996). In 2003, he received a diploma from the educational and scientific medical center for the administration of the President of the Russian Federation. Our authors