Tibia fracture
A fracture of the tibia occurs due to the impact of great force on the body of the bone and occurs at different levels. This often happens during road traffic accidents. Of all fractures of the musculoskeletal system, tibial fractures account for 23% of the total number of musculoskeletal injuries.
Classification of tibial fractures
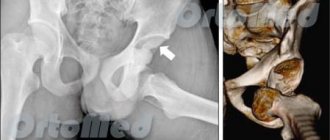
Fractures of the bone diaphysis are classified into transverse, oblique, comminuted, fragmentary and intra-articular. Intra-articular fractures of the tibia include fractures of the tibial condyles and fractures of the medial (inner malleolus). The medial malleolus is the medial bony stabilizer of the ankle joint and fractures occur during twisting (rotation) of the leg with a fixed foot. Also often, a fracture of the inner (medial) malleolus occurs with a sharp, non-physiological rotation of the foot.
Indications for testing
X-ray of the lower leg
can be carried out in the presence of various indications and can be prescribed by different specialists.
In traumatology
Fractures of the leg and foot can have a very diverse location, size, and complexity. An x-ray will help identify the features of the fracture, see if there are bone fragments and how they are located. X-rays are also used after the broken bones have been connected and cast. In this case, it is important to observe in dynamics how the fusion of bone tissue occurs.
In oncology
Oncological foci, as is known, can arise not only in internal organs or soft tissues, but also in bone tissue. Bone cancer most often affects areas near the knee joint, such as the lower leg. It is worth clarifying that we are talking about primary cancer, that is, cases when cancer cells first originate in the bone, and are not a consequence of metastasis of a soft tissue tumor. There are three main types of cancer that can affect the ankle joint:
- Osteosarcoma. This pathology is the most common, and the risk group includes mainly adolescents who are in the stage of active growth and physical development. Osteosarcoma begins in new, developing bone tissue.
- Chondrosarcoma. This pathology most often originates in the cartilage of the joints and affects people aged 40 to 60 years.
- Ewing's sarcoma. This disease mostly affects young children. It is characterized by the appearance of small cancerous foci in the child’s bone marrow. If such a pathology is detected in the early stages, then it responds quite well to treatment.
In purulent surgery
The bones of the lower leg can also be affected by purulent diseases. The most common of these is osteomyelitis. This pathology can affect all elements of the bone: bone marrow, periosteum and bone tissue itself.
Osteomyelitis can be acute, that is, occurring for the first time, or chronic. In both cases, an x-ray of the leg helps to accurately determine the focus of the pathology, assess its size, and the degree of bone damage. An x-ray is also necessary if surgery on the lower leg is planned to eliminate foci of osteomyelitis.
Treatment of tibial fractures
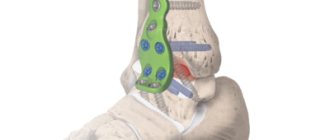
Currently, treatment of a tibial fracture is usually performed through surgery. Due to the anatomical structure of the lower leg, the tibia along its main length is located superficially (not covered by muscles along the medial surface), which often leads to secondary perforation of the skin with bone fragments during a fracture. To immobilize fragments of fractures of the tibia, hospitals use skeletal traction on the heel bone. This method is used for preoperative preparation and improvement of the condition of the skin on the injured lower leg.
In our center, traumatologists and orthopedists use the most modern methods of conservative and surgical treatment of tibial fractures. The use of the latest methods of extraosseous and intramedullary osteosynthesis allows us to speed up the recovery and rehabilitation of patients with fractures of the tibia . As a rule, the patient can put weight on the injured leg the next day after surgery. In most cases, the use of osteosynthesis for intra-articular fractures in the early stages allows for the most accurate restoration of the articular surfaces, which eliminates the risk of early development of arthrosis of the damaged joint.
What will an X-ray of the shin bones show?
An X-ray of the shin, like a black and white photo, shows the location of the bones of the ankle joint. Their connection, cartilage tissue, is also visualized. Joint fractures will be visualized as shadows on the white background of the bone. Tumor-like malignant neoplasms are also defined as opacities, but have unclear boundaries.
Sometimes, in order to get a clearer picture of the pathology, pictures of the lower leg are taken of two legs at once, even if only one is affected. When comparing images and their symmetry, it can be easier to find a deviation and make a diagnosis. Osteomyelitis of the leg has special signs on x-ray:
- Thickening of the bone at the site of inflammation.
- Foci of necrosis may be visualized on bones and muscles. They look like dark circles on bones or light circles on soft tissues that have an irregular shape.
- In osteomyelitis, the bone marrow canal is not visualized in the image.
Decoding the results
After development, the images need to be decrypted. For this, certain indicators are used and compared with standard values:
- The arrangement of bones in relation to each other, as well as their shape and size. In cases where the bones increase when receiving load, a diagnosis of hyperostosis is made, that is, an increase in bone substance. Reduced bone size occurs with atrophy due to limited physical activity and nerve diseases.
- Condition of the surface of the shin bones. In case of oncological diseases in the lower leg area, foci of destruction of the upper layer of bone tissue are observed. The opposite situation may also occur, that is, there is ossification of the periosteum tissue, detachment.
- Structure of the bones of the lower leg. When images show shadowed areas in the white areas of bone structures, osteoporosis may be diagnosed. At the same time, the outer layer of bone is thinner, and the medullary canal is expanded. With increased bone density, osteosclerosis is diagnosed.
- The size of the gap between the joints. Uneven narrowing of this gap indicates the presence of arthritis or arthrosis.
- Foot angle. Normally it should be 130˚. Deviation from the norm is a sign of flat feet, the degree of which will be determined by the doctor.
How is the procedure done?
X-ray of the ankle takes little time and does not require special preparation. The patient's body, with the exception of the area being studied, must be protected at the time of filming with a special apron that shields ionizing radiation.
An x-ray of the lower leg is taken in two projections: direct and lateral. If these projections are not enough to make a diagnosis, an x-ray is taken in oblique projections (at different angles), as well as an x-ray of the foot with a load
.
Varieties
Traumatology classifies all fractures of the fibula, dividing them into several types:
- fracture - a small crack formed in a vertical or horizontal plane;
- comminuted fracture - injury with the formation of bone fragments;
- closed - an injury in which the broken bone does not extend beyond the soft tissue;
- open - a fracture with a visible violation of the integrity of the skin and the bone coming out;
- fatigue - a characteristic injury to the tibia as a result of traumatic overstrain of that part of the skeleton that already had small cracks.
Interesting! The latter type of injury is most often diagnosed in professional athletes - gymnasts or basketball players.
First aid
When the tibia is fractured, it is very important to take care of first aid in a timely manner, and to do it competently and carefully.
This does not eliminate the need to call an ambulance, but while you wait for it, you need to do the following:
- Pain relief. Whether it is an open or closed fracture, the victim will experience severe pain. You can suppress them with any painkiller - Analgin, Nimesulide, Ketorol and the like.
- Immobilization of the injured limb. To do this, you will need a tire in the form of a pair of ordinary boards or similar objects that are at hand. The first is applied on the inside of the limb, and the second on the outside. You can secure the splint with any cloth or bandage.
- With an open fracture, it is important to wash the wound and treat it with an antiseptic to avoid infection. After this procedure, the injury is covered with a sterile bandage.
- If there is severe bleeding, apply a tourniquet to the thigh.
Delayed fracture consolidation - what is it?
What is delayed consolidation of fractures (bone non-union). Most bone fractures heal (consolidate) within 3-6 months. If the fracture has not healed by this time, then doctors talk about delayed consolidation of the fracture or delayed healing of the fracture. Pseudoarthrosis (false joint, non-union fracture) is a complication of a bone fracture when the healing process of the fracture is interrupted. Fibrous or cartilaginous tissue forms between the main fragments of the fracture and therefore, even after 6-8 months, the formation of bone callus and healing of the fracture does not occur.
Causes of injury
- injury during sports activity;
- falling from height;
- accidents, traffic accidents.
During a car accident, hitting your feet on the front seat or dashboard is of great importance. if the legs are bent at the knee joint, a condyle fracture is more likely to occur. With strong impacts, the direction of the force also plays a role; this injury is characterized by a direct action in the lateral projection of the knee.
Low-energy trauma occurs from a minor impact or a normal fall. The main role here is played by a violation of the structure of bone tissue, which occurs with osteoporosis or as a result of age-related changes.
If an isolated fracture of the lateral condyle occurs, the most likely cause is a forced outward deviation of the tibia. If it moves in the medial direction, the fracture will occur in the area of the medial structure.
How to recognize a fracture of the femoral condyle?
- The main syndrome with this injury is pain. Localization of pain is the knee joint, which becomes smoother and loses its usual contours;
- Internal hemorrhage leads to tissue protrusion, swelling, and pain on palpation;
- Pressing on the patella makes it possible to feel its unusual position and how it “springs” under the pressure of the blood collected inside the joint;
- If the condyle is displaced, this is reflected in the deviation of the tibia to the side;
- The patient cannot make active movements, and passive ones cause severe pain.
Similar symptoms accompany fractures of the patella, tibial condyles, as well as sprains of the knee ligaments and damage to the meniscus. Therefore, additional diagnostics are required to make an accurate diagnosis. The difference between fractures of the femoral condyles and damage to similar structures of the leg is the fact that in the first case the pain is localized above the joint space of the knee, and in the second - below it.
How is shock wave therapy performed to treat delayed fracture consolidation?
In case of delayed consolidation of the fracture (non-union of the bone), the procedure is performed once every 7-10 days. At the Avatage Medical Center, doctors use special attachments that stimulate the formation of callus (stimulate osteogenesis). The impact is applied to the fracture area. Doctors at the Avatage Medical Center use their own patented methods for treating and preventing delayed fracture consolidation, based on the use of Storz Medical equipment. As the famous scientist Professor G. Ilizarov said: “Tensile tension is a powerful factor that activates tissue growth. According to this pattern, it is possible to stimulate the formation of new structural units of fibrous tissue, blood vessels, skin, and bones.” Taking this into account, we force muscles to contract and stretch using biomechanical stimulation (directed local vibration therapy), which trains the muscles and makes them work without making movements. This effect complements shock wave therapy and accelerates the process of bone healing.
Review of Key Symptoms
Finding out that it was part of the tibia that was damaged by a fracture is not so difficult if you know the list of main symptoms characteristic of this injury.
So, it is necessary to seek first aid if the following manifestations are observed:
- aching and dull pain at rest;
- sharply manifested pain when trying to lean on the injured limb;
- swelling in the damaged area or hematoma, which occurs a short period of time after injury;
- obvious deformation of the limb, for example, unnatural mobility of the bone in the place where the fracture occurred;
- rarely - decreased sensitivity of the foot, pale skin and decreased local temperature. This is a direct sign that there is serious damage to blood vessels and nerves.
If a closed fracture can make the victim doubt what kind of injury he had to face, then an open type injury immediately makes itself known. An open wound, bone protruding, and bleeding are obvious signs.