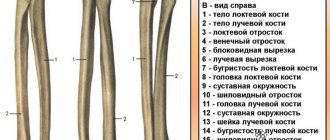
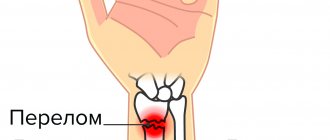
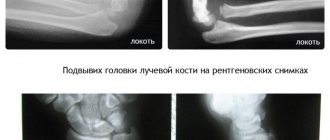
The radius bone is part of the forearm and consists of several parts that can be damaged. According to statistics, a fracture of the styloid process of the radius accounts for approximately half of all injuries. Often the damage is combined with a trauma to the radius in a typical location. In order for this type of fracture to occur, there must be specific reasons that are worth understanding in more detail.
Causes of injury
First of all, you need to look at the position in which the person falls. Most often, this can happen when falling on an outstretched arm; a person instinctively extends it forward. This feature is the most common cause of damage. In some cases, a fracture of the styloid process of the radius is the result of a direct blow to the bone. In the latter situation, the fracture is often open, and there is a wound of various sizes.
The frequency of such damage increases sharply in winter. On ice, older people become especially vulnerable; osteoporosis is an additional factor. Injury can also occur when:
- hobbies of cycling, roller skating, skateboarding;
- professional sports;
- road accident;
- unsuccessful jump;
- active games.
Falls in such conditions cause the victim to instinctively stretch his arm forward and this leads to serious damage to the styloid process. In view of this, in addition to an open or closed fracture, compression or avulsion damage can be encountered.
Arthroscopic findings
The articular disc has a yellowish-white surface resembling the cartilage of the radius. Often, a feeler gauge must be used to determine the location of the radial attachment of the disk. The ulnar and dorsal attachments of the disc are homogeneous. As a result of complex disc avulsion in the dorsal-ulnar region, the small prestyloid volvulus on the ulnar side of the disc may expand.
The consistency and elasticity of the disc, as well as its dorsal and radial attachments, are assessed by palpation with a probe.
The degree of damage to the disc varies from local compaction and superficial fibering to flap-like ruptures of various sizes. With widespread degenerative changes and relative elongation of the ulna, complex injuries are revealed during arthroscopy, in which only the palmar and dorsal thickenings of the disc remain intact.
If the disc appears intact, it should still be instrumented to look for hypermobility due to an old rupture. Peripheral dorsal-ulnar tears are quickly covered by synovial tissue and functional tests are necessary to detect avulsion.
Classification
Several classifications of disk damage have been proposed. A more practical classification is Ostermann (1990), which distinguishes three types of disc damage:
- Type 1 – Traumatic radial tear .
- Type 2 – Central degenerative perforation .
- Type 3 – Traumatic peripheral rupture .
Unfortunately, this classification does not take into account structural changes in the disc. Careful palpation is required to identify disc damage. In many cases, the tear is not noticeable because the edges touch or overlap. This is common in central degenerative lesions that become symptomatic after trauma or normal movement. In contrast, identification of central perforation is usually not difficult.
To confirm or exclude rupture of an apparently unchanged disc, the following sequence of instrumental palpation has been proven effective:
- Elimination of the central gap.
- Rule out peripheral rupture or hypermobility.
- Assessment of disc tissue (softening, hardening, surface fibering).
- Exclusion of impingement syndrome caused by the head of the ulna.
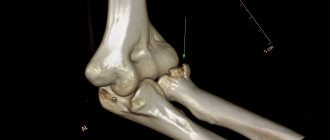
Compression fracture
In the photo, such an injury appears as a small crack. The mechanism of injury is associated with an impact of a nearby area of the wrist on the styloid process; as a result, due to the force of the impact, the radial process is pushed outward and somewhat backward. Often the force of an impact is transmitted through the nearby scaphoid bone, which can also be damaged.
Symptoms of damage
A person is bothered by several characteristic symptoms at once, all of which, with additional examination methods, allow us to put an end to the issue. The clinic is represented by:
- pain at the site of injury;
- crunching of fragments, which is called “crepitus”;
- due to pain, movements in the wrist joint are severely limited;
- the fracture site is swollen;
- a hematoma forms under the skin;
- As the hematoma grows, a feeling of skin tension in the joint area is felt.
The last symptom is not characteristic and is not detected in all cases.
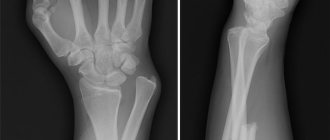
Diagnostics
Before any action is taken to treat or correct the displacement, an accurate diagnosis must be established. Initially, an x-ray must be taken and always in two projections. If in doubt, a CT scan is indicated; if cartilage damage is suspected, an MRI is indicated.
First aid
Immediately after receiving an injury, a cold object or ice, previously wrapped in cloth, should be applied to the injury site. Cold will help reduce pain and reduce tissue swelling. Duration is from 15 to 20 minutes, after which a break is taken and the procedure is repeated several times. The limb must be immobilized using a special splint or any available means.
First aid
In any case: a bruise, sprain or rupture of ligaments, dislocation or fracture occurs, immediately after the injury and for 48 hours after it, the application of dry cold is indicated.
Do not bandage your hand to the splint too tightly, and do not forget about the cushion under the hand
If a fracture is suspected, the injured arm must be immobilized by any available means. If possible, then it is necessary not only to “hang” the hand like a scarf like Deso, but also to fix the wrist joint using available tools and materials. These can be branches, a book, a piece of plywood, pieces and strips of fabric, belts.
Advice. It is advisable to fix the hand in such a way as shown in the figure above, and then additionally fix the arm, immobilizing the elbow joint, in the position of the arm - with the palm facing the stomach. The victim must sit during transport.
Avulsion type of fracture of the styloid process of the radius
This type of damage does not occur as often as previously described. The cause of an avulsion fracture is tension on the radial collateral ligament, resulting in damage to its attachment site. A similar type of injury can occur after a person falls on an outstretched arm, causing subluxation of the wrist joint medially. At this point, the wrist is displaced inward, at which point the radius may fracture in the typical location, but the styloid process is torn off.
Symptoms
Immediately after receiving an injury, a person is bothered by characteristic symptoms. Based on their complex, an avulsion fracture of the styloid process of the ulna can be diagnosed. Characteristic is:
- severe pain at the site of injury;
- increased pain when trying to move;
- the area of the wrist joint is deformed;
- crunching of fragments when trying to move;
- numbness of fingers;
- increased pain when tapping on the base of the palm;
- the pain intensifies when walking or while moving the upper limb.
Diagnosis of damage
Knowledge of the medical history, the nature of the injury and a simple medical examination are sometimes not enough to make a correct diagnosis. To make a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to take an x-ray, always in two projections. If the doctor has doubts about the x-ray, a CT scan is indicated.
Treatment of avulsion fracture
The subtleties of first aid and the reduction of displaced fragments have already been described above. For such an injury, a cast is applied for about a month with mandatory x-ray control 3-5 days and two weeks after the injury. When the fracture line passes through the articular surface of the radius, surgical treatment is indicated. The surgical option is chosen by the doctor depending on the degree of displacement and the presence of fragments. Fixation is carried out with screws or using a plate.
Diagnostics
X-ray image of a compression fracture of the styloid process of the radius
After questioning, examining and palpating the site of injury, the doctor will definitely send you for an x-ray, which will be performed in 2 projections.
Pictures will help:
- accurately determine the type and severity of the fracture;
- decide on the method of comparing bone fragments - closed or open manual reduction, osteosynthesis;
- predict subsequent treatment tactics and time until full restoration of performance.
If the images appear blurry, you may need to take either a repeat image(s) or a CT scan. For severe open wrist injuries in a typical location, with extensive damage to soft tissue, blood vessels and nerves, you may need to undergo an MRI examination.
Recommendations for nutrition and medication
Regardless of whether the fracture is without displacement or with displacement, recommendations on nutrition and taking medications are relevant. The diet should include foods containing calcium, chonroitin and hyaluronic acid. Similar substances are found in:
- cottage cheese;
- sour cream;
- milk;
- aspic;
- gelatin products;
- hard cheeses;
- seafood.
Additionally, the body needs protein, its source is meat. Low-fat varieties of veal, rabbit, and poultry will be beneficial for the body. You can supplement your diet with legumes, herbs, dried apricots, and figs. The source of vitamin D for humans is fish oil.
Medications can also help speed up fracture healing. In particular, calcium supplements, especially in combination with vitamin D, for example, the drug “Calcium D3 nycomed”. The following drugs are also used: “Structum”, “Osteogenon”, “Kalcemin”. Such drugs are prescribed for the entire duration of treatment until the fracture completely heals.
Recovery
Rehabilitation begins immediately after applying a plaster splint. In the early period of rehabilitation, finger movements are indicated. This will avoid stiffness in your fingers and develop your forearm muscles. Despite the plaster cast, physiotherapeutic procedures are indicated. During this period, magnetic therapy and UHF are indicated, which help improve blood flow and activate bone cells.
After four weeks, the plaster must be removed after X-ray control. During this period, the range of rehabilitation opportunities expands significantly. For the first time after removing the plaster cast, it is recommended to wear an orthosis. The purpose of therapeutic exercises, which is performed under the supervision of a physical therapy instructor, is indicated. Flexion and extension of the wrist joint, abduction and adduction of the hand are performed. Then circular movements are added.
Gymnastics are initially performed without load, which is gradually added as recovery progresses. It is recommended to use a regular sponge as a load, which is compressed and unclenched. As the hand is trained, it is developed using a manual expander; it can have varying degrees of rigidity.
Massage, which is also carried out under the supervision of an experienced specialist, can speed up recovery after a fracture. Also, massage will tone the muscles, reduce tissue swelling, and improve blood flow.
Physiotherapy procedures are shown, the list of which is significantly expanding. Shown:
- magnetic therapy;
- UHF;
- diodespeaker;
- shock wave therapy;
- Ural Federal District;
- ultrasound.
Anesthetic gels help reduce pain during the recovery phase. You can apply them several times during the day to washed skin. Can be used: “Ketorol gel”, “Diklak gel”, “Flamidez gel”, “Voltaren”, etc.
Complications
Complications can be divided into early and late, depending on the time of occurrence. The early ones include:
- Purulent-septic complications (with an open fracture).
- Secondary displacement (if the cast is removed early).
- Vascular disorders at the site of injury.
Late complications include:
- Neurotrophic disorders.
- Deformations of bones and articular surfaces after fracture healing.
- Post-traumatic deforming osteoarthritis.
When the fragments of a fracture are set incorrectly or the joint is untimely and can become deformed, the styloid process protrudes under the skin. In some situations, after an injury, a person is bothered by pain at the fracture site.
Incorrectly healed fractures cannot always be corrected even with the help of surgery. To prevent a similar situation from happening again, after receiving an injury, a person should seek medical help from a traumatologist and undergo an examination. The condition for the occurrence of complications is the early removal of the plaster, after which the fragments are displaced.