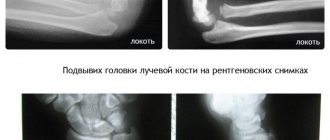
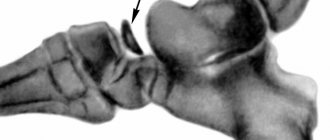
Subluxation of the radial head in children under three years of age is a fairly common occurrence, and it occurs twice as often in girls as in boys. Older children of preschool age are also at risk, but after six years such injury is already rare. The fact is that in children of this age, the head of the radius is a rounded cartilaginous tissue, and even with a slight sudden movement it can freely slip out of the annular ligament. Most often, injuries occur if a child is pulled by the arm while playing, or if he was walking with an adult by the hand, tripped and fell, and the adult tried to support him and pulled his arm. Less commonly, such an injury occurs when a child falls under his or her arm. And sometimes such stretching of the arm occurs when, while playing, a child is taken by both hands and rotated around himself, and even when putting on and taking off clothes with narrow sleeves. In some cases, at the moment of dislocation, you can hear a characteristic crunch. Parents of preschoolers may encounter this problem more than once, but fortunately, once they leave preschool age, the likelihood of such an injury is practically reduced to zero.
Total information
Subluxation of the shoulder joint, among other types of traumatic injuries, is not a particularly frequently diagnosed disorder - according to various sources, it occurs in 2-7% of patients who go to the clinic for any traumatic pathology. But among subluxations it occupies one of the leading positions - according to various sources, it is among the 3-5 most common types of the described pathology.
According to statistical data, this pathology is detected in all age categories - from preschool to old age. In children from zero to three years old, subluxation of the shoulder joint is less common due to the absence of situations fraught with this type of injury - children at this age are injured regularly, but such injuries are caused by mechanisms that differ from those observed with subluxation of the shoulder joint.
The peak of the described pathology occurs in the age category from 25 to 45 years - due to high vital activity. But men do not suffer much more often than women - in contrast to the cases of other injuries to the torso and limbs.
note
In itself, subluxation of the shoulder joint does not belong to the category of pathologies that can threaten health and even life. But after some time, the patient may experience long-term vascular and neurological complications that arise due to insufficient attention to this disorder.
How to make an appointment with a pediatric traumatologist
Our clinic employs qualified doctors who have extensive experience in diagnosing and treating dislocations. Experts will tell you how to significantly reduce risks and protect your child from injury. Modern equipment for diagnosing and treating various types of injuries is available to patients. To make an appointment with a specialist, you can use any convenient method:
- by phone;
- on the clinic website by filling out a special online form.
Also on the website you can find out the cost of the services provided, see a list of available equipment, and choose which doctor you want to undergo treatment with. Contact us, we will always help you and your children!
Articles
20 Oct 2020
In modern society, anorexia has become one of the global problems among adolescents, especially among girls. According to experts, a mild form of the disorder is…
15 Apr 2020
The year 2020 was marked by the pandemic of the new coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. He began his march around the planet from the fish market in the Chinese city of Wuhan at the end of November 2021, covering several…
13 Mar 2020
Inflammation occurring in the small intestine is called enteritis in children.
12 Mar 2020
Glaucoma in children is a whole group of eye diseases, the characteristic features of which are increased intraocular pressure and visual defects that develop against the background of this…
Source
Causes and development of pathology
The immediate cause of subluxation of the shoulder joint is a traumatic agent, under the influence of which the head of the humerus is displaced, but does not completely leave the glenoid cavity of the scapula. Subluxation occurs when the force is not enough to break the integrity of the humerus (fracture) or complete dislocation.
The described disorder can appear in situations of any nature - the same ones in which more pronounced damage occurs, the difference lies only in the intensity of the impact of the traumatic agent. This can be domestic, industrial or sports damage. Sometimes patients are referred for subluxation of the shoulder joint after fights, and very rarely it is diagnosed during road traffic accidents, as well as large-scale disasters (man-made and natural).
In everyday life, subluxation of the shoulder joint occurs during actions that entail a sharp displacement of the upper limb. Some examples could be the following:
- the owner of a large dog tried to keep her on a leash when she ran with acceleration, seeing the cat, and sharply pulled the leash;
- the child made an attempt to catch a vase falling from the cabinet in order to avoid punishment from his parents, bent forward and sharply extended his hand;
- an amateur athlete, playing golf, swung his club too sharply to hit the ball;
- a passenger was riding in public transport, holding the handrails, and it suddenly braked, as a result of which the passenger, holding the handrail, suddenly shifted
and others.
In almost all such cases, subluxation of the shoulder joint was preceded by any of the possible pathologies of the joint capsule and ligaments (the role of these disorders in the development of subluxation will be discussed below).
Quite typical is the occurrence of subluxation of the shoulder joint due to alcohol intoxication, in which a person loses his balance and falls rather awkwardly without having time to react and make attempts to reduce the severity of the damage. In this case, the described pathology seemed to arise under circumstances that should not be fraught with serious injuries - when falling from a stool, a low tree, a ladder, or even one’s own height. In children, subluxation of the shoulder joint often occurs when falling from a swing.
Subluxation of the shoulder joint in people employed in industry or agriculture is diagnosed when basic safety rules are not followed. In agriculture, it often occurs due to inability to handle large animals - for example, among grooms who care for restive stallions.
Often this pathology occurs in novice athletes who do not take into account their level of training during physical activity. The circumstances surrounding the occurrence of such an injury are as follows:
- falling on the shoulder. This often happens in equestrian and cycling sports, as well as in team games during competitions in football, volleyball, basketball, hockey and others;
- a strong, sharp blow to the shoulder joint. This mechanism of the described type of injury is observed in athletes who engage in boxing, taekwondo, and so on;
- performing exercises on sports equipment - rings, parallel bars, goat, horizontal bar;
- exercises on simulators associated with pronounced loads on the shoulder joint - for example, lifting a barbell while lying down
and so on.
Sometimes shoulder subluxation is diagnosed in motorcycle and car racers after minor accidents.
The described type of damage can occur during a fight - in particular, with the use of any objects used to strike (a pry bar, a piece of reinforcement, a bat). Often, a subluxation of the shoulder joint occurs when a person is knocked to the ground and kicked in the area of the shoulder joint.
During road traffic accidents, this type of damage usually develops when:
- falling from a bicycle;
- sudden braking of a vehicle;
- pedestrian falling when hit by a car.
Subluxation of the shoulder joint can occur when one half of the body is injured - thus, the victim simultaneously experiences subluxation of the shoulder joint, injury to the chest, hip joint and other structures on one side.
During man-made and natural disasters, subluxation of the shoulder joint rarely occurs; in such circumstances, more severe types of damage (fractures and dislocations) appear.
note
The occurrence of subluxation of the shoulder joint during polytrauma is considered unfavorable - in these cases, the attention of the victim and doctors is concentrated on more serious injuries with severe pain, against the background of which subluxation of the shoulder joint may not be diagnosed in a timely manner.
Often, in the occurrence of subluxation of the shoulder joint, a major role is played not by the severity of the traumatic agent, but by the weakness of the articular capsule and ligaments, which normally hold the head of the humerus in a certain position, preventing it from extending beyond the boundaries of the glenoid cavity of the scapula. The causes of such weakness may be pathologies:
- congenital;
- acquired.
Congenital disorders of the joint capsule and ligaments of the shoulder joint, which can lead to their weakening and become a prerequisite for the development of subluxation, occur in the fetus:
- at the stage of laying the elements of the articular capsule and ligaments (namely during embryogenesis - the early period of intrauterine development);
- at the stage of intrauterine development itself.
The reasons are the same as the reasons that provoke the development of other intrauterine disorders. These are aggressive factors that affect the mother’s body, and therefore the fetus’s body:
- physical;
- chemical;
- somatic diseases;
- bad habits of the expectant mother;
- endocrine pathologies
and others.
All groups of factors are standard causes of the development of intrauterine anomalies in the fetus.
Physical factors include various types of radiation, injuries to the pregnant woman’s abdomen (severe bruises), too low or too high temperatures.
Chemical factors are any aggressive compounds that, having penetrated the tissues of the fetus at various stages of its development, negatively affect interstitial metabolism, thereby disrupting the development of tissues, and therefore the organs of the unborn child. Such aggressor compounds are divided into two groups:
- coming from outside;
- produced in the pregnant woman’s body itself.
In the first case, these are chemical compounds used in industrial processes, agriculture, and also in everyday life.
In the second case it is:
- toxins of pathogens, products of their vital activity and decay of dead microbial bodies;
- products of impaired cell metabolism, pus and products of the processing of dead tissue.
Bad habits of the expectant mother are one of the most dangerous causes of intrauterine anomalies (in this case, from the shoulder joint, which contributes to the development of its subluxations). You should be equally careful about smoking, drinking alcohol and using drugs.
Disruption of the intrauterine development of tissues of the joint capsule, ligaments and other elements of the shoulder joint can be observed against the background of various somatic diseases of the mother. This is especially often determined in chronic, protracted diseases of the following systems:
- cardiovascular;
- respiratory;
- digestive;
- blood systems.
What role do endocrine disruptions of the expectant mother play in the occurrence of intrauterine anomalies (in particular, disruption of the development of shoulder joint structures)? In this case, metabolic processes in the tissues of the fetus are disrupted, which entails anatomical disorders. As a rule, anomalies in the intrauterine development of the structures of the shoulder joint develop against the background of diseases of the expectant mother, such as diabetes mellitus (failure of carbohydrate metabolism due to insulin deficiency) and pathology of thyroid hormones, since they regulate tissue processes. In the latter case, it is hypothyroidism (lack of thyroid hormones) or hyperthyroidism (excess).
Of the acquired disorders, the most common causes of subluxation of the shoulder joint are:
- systemic connective tissue disorders, which also affect the connective tissue structures of the shoulder joint;
- hormonal imbalances;
- previous injuries to the shoulder joint.
note
Among systemic connective tissue disorders, the impetus for the occurrence of subluxation of the shoulder joint, as a rule, is a violation against the background of autoimmune processes - pathologies that arise due to the fact that the body ceases to correctly recognize structural elements and, mistaking its own tissues for foreign ones, begins to fight them.
Among hormonal pathologies, the most common contributing factors are the patient's diabetes mellitus and disruptions of thyroid hormones.
Due to previous injuries to the shoulder joint, the normal structure of the shoulder joint is disrupted, which facilitates the occurrence of subluxation of the shoulder joint even with mild traumatic effects.
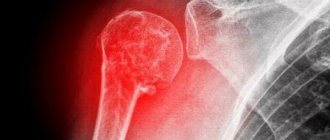
Symptoms of shoulder subluxation
The main clinical symptoms of subluxation of the shoulder joint are:
- pain;
- swelling of soft tissues;
- disruption of the functional activity of the joint.
The characteristics of pain will be as follows:
- by localization - in the area of articulation;
- in terms of distribution – irradiation is not typical;
- by nature - aching;
- in terms of severity – weak or medium intensity;
- by occurrence - appear at the time of injury, increase when attempting active and passive movements in the shoulder joint.
Tissue swelling is insignificant and occurs as a reaction of the body to a change in the configuration of the joint.
Impaired functional activity of the shoulder joint is observed due to:
- disturbances in the mechanics of movement - even a slightly displaced head of the humerus cannot slide freely in the glenoid cavity;
- pain syndrome - this factor can have a greater impact on the function of the joint.
Rehabilitation of dislocations in children
The rehabilitation program for children with congenital hip dislocation is divided into 4 periods:
- The preparatory period involves the appointment of individual physical therapy sessions, which are general strengthening and help stabilize the hip joint;
- Postoperative period. After the operation, a plaster cast is applied to the leg, which covers the belt and healthy thigh. Three days after surgical treatment, physiotherapy is prescribed, the purpose of which is to eliminate pain and inflammation. At the same time, breathing and therapeutic exercises are carried out, which includes exercises that stimulate the cardiovascular system, increase the tone and reactivity of the body;
- The next period of rehabilitation begins from the moment the plaster cast is removed, instead of which a “boot” is applied to prevent the rotation of the limb. To unload the joint, a system of blocks with loads of different weights is installed. During this period, it is important to ensure that all movements are careful and smooth, so passive gymnastics is prescribed, after which they begin to develop their own movements in the hip joint;
- The final period begins 9-10 months after surgical treatment. It coincides with the removal of metal fasteners that were installed previously. Rehabilitation activities are aimed at learning to walk. First, additional means are used (walkers, canes, etc.) without support on the sore leg, then partial support is allowed and, at the end of rehabilitation, full support without the use of additional means.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of subluxation of the shoulder joint is made based on the patient’s complaints, anamnesis (history) of pathology, and the results of additional examination methods.
The following is important from the anamnesis:
- what was the mechanism of injury;
- whether there have been previous injuries to the shoulder joint;
- whether the patient was diagnosed with non-traumatic pathologies of the shoulder joint or systemic connective tissue diseases (primarily autoimmune);
- how much time passed from the moment of injury to the visit to the clinic.
A physical examination reveals the following:
- upon examination - in the early period there are no features, then swelling of the tissues in the area of the shoulder joint is noted, as well as the fact that the patient tries to support the injured arm with his uninjured hand, and sometimes cannot give the upper limb the correct position to alleviate his condition. Sometimes upon examination, reactive hyperemia (redness) of the skin covering the joint is determined;
- upon palpation (palpation) - unexpressed swelling and pain in the joint area are noted.
During the physical examination, the range of active and passive movements in the shoulder joint is also determined. In the first case, the doctor asks the patient to perform a series of movements in the joint - raising the upper limb, rotating around an axis, bringing it to the body. In the second case, the doctor fixes the shoulder girdle with one hand (between the shoulder joint and the neck), the other covers the elbow and carefully tries to make movements. Such functional testing is carried out with caution so as not to transform the subluxation into a full-fledged dislocation.
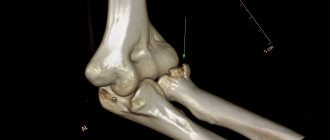
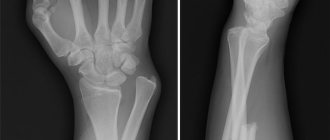
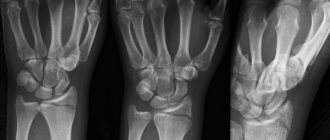
Of the instrumental diagnostic methods, X-ray examination in two projections is informative - during it, the fact of displacement is revealed and the degree of deviation of the head of the humerus from the normal position is clarified.
Other examination methods (instrumental and laboratory) may be prescribed to identify diseases that can lead to weakness of the connective tissue and dysfunction of the articular capsule and ligaments that normally hold the head of the humerus in the glenoid cavity of the scapula.
Important
If vascular or neurological symptoms appear when a subluxation of the shoulder joint occurs, you will need to consult a neurologist or neurosurgeon, as well as a vascular surgeon - they will prescribe an examination of the vessels and nervous structures of the shoulder joint.
Clinical picture
It is quite difficult to recognize an injury right away, especially if the baby is capricious and cries too often. General signs that accompany injury:
- The shoulder or the entire arm, depending on the severity of the injury, partially or completely loses its mobility. The baby, making chaotic movements, waves only one hand.
- Visual deformation, asymmetrical position of the shoulder girdle. The injured arm may be higher or lower in relation to the healthy limb.
- The injured arm is in an atypical position.
- Any movement of the injured limb is accompanied by a characteristic crunch or sound similar to a click.
- Changes in mood - the baby almost always cries, sleeps poorly and loses appetite. Crying intensifies if the shoulder area is touched.
- The site of injury swells and the skin takes on a bluish tint.
All of these signs are highly likely to indicate that the baby has a dislocated shoulder. In this case, you need to show it to a doctor without delay: the more time passes from the moment of injury, the harder it will be to cure it and prevent possible complications.
Differential diagnosis
Differential (distinctive) diagnosis of subluxation of the shoulder joint is carried out, as a rule, with such pathologies as:
dislocation of the shoulder joint - complete displacement of the articular surfaces of the head of the humerus and scapula;- fracture of the head of the humerus - a violation of its integrity;
- separation of its small or large tubercle (anatomical protrusions);
- fracture of the anatomical neck of the humerus - a violation of the integrity of the location between the head and its tubular part;
- fracture of the surgical neck of the humerus - a violation of the integrity of the location between the head of the bone (below its tubercles) and the tubular part.
Dislocations in children
Dislocation is understood as a persistent separation of the articular surfaces of bones, which occurs under the influence of mechanical force (trauma) or diseases that are accompanied by the destruction of cartilage (arthrosis, arthritis). With dislocations, the joint capsule may be damaged or remain intact. If there is complete separation of the articular surfaces of the bones, then they speak of complete dislocation. If the separation is incomplete and the articular surfaces have points of contact, then a diagnosis of “subluxation” is made. In addition, congenital and acquired dislocations are distinguished.
Treatment of shoulder subluxation
Treatment of shoulder subluxation is conservative. The appointments are as follows:
- reduction of the head of the humerus using various methods (according to Hippocrates, Kocher, Dzhanelidze, and so on);
- functional rest;
- painkillers – if the patient’s pain threshold is low (that is, pain occurs even with a slight displacement of the head of the humerus).
If pathologies have been discovered that contribute to the occurrence of subluxation (in particular, connective tissue disease), then they are treated.
If necessary, the reduction procedure is performed under anesthesia.
The effectiveness of reduction is determined by the following criteria:
- during manipulation, a click is heard - the sound that occurs when the head returns to the glenoid cavity of the scapula;
- the patient immediately after the reduction notes relief of pain;
- the patient can perform movements in the shoulder joint.
In some cases, the shoulder joint may need to be immobilized after the reduction procedure. For this, a scarf bandage is used. The appropriateness of such fixation is determined by the doctor. Indications for it are:
- weakness of the joint capsule and ligaments due to recurrent subluxation;
- pathology of connective tissue, due to which subluxation occurred.
During immobilization, the patient is allowed to make any movements with his fingers or hand to prevent disruption of local circulation.
In uncomplicated cases, no special appointments are required after reduction of the joint. If immobilization with a bandage was prescribed, then a short rehabilitation is carried out, which is based on:
- exercise therapy;
- massage.
Note:
After realignment of the shoulder joint and rehabilitation measures, the patient is already allowed physical activity on the affected upper limb in the early period - first dosed, then usual.
When to see a doctor
Only a doctor can accurately determine the type and severity of damage. Therefore, if a child receives an injury and the symptoms described above appear, it is necessary to immediately consult a traumatologist.
When a patient comes in, the doctor conducts a diagnosis. The initial stage of diagnosis is visual inspection and palpation. During palpation, the traumatologist determines the degree of hand mobility and skin sensitivity, and measures the pulse. This method also makes it possible to identify changes in the shape of the composition and the location of the articular endings. The next stage is hardware research. Most often this is an x-ray. With its help, you can identify damage to internal tissues that was caused by a dislocation.
Prevention
Measures to prevent the described disorder are basically all those methods that can be used to prevent the development of many types of damage. This:
- avoiding household, industrial, sports and other injuries in which the head of the humerus may become displaced;
- use of personal protective equipment;
- regular physical activity to strengthen the shoulder joint;
- preventive examinations with a therapist and other specialists - to prevent pathologies of connective tissue, which may damage the structures of the shoulder joint.
There are no specific methods for diagnosing congenital pathologies that may cause subluxation of the shoulder joint. The risk of their occurrence can be reduced if the pregnant woman is protected from the influence of aggressive physical, chemical and other factors.
Congenital dislocations in children
This group includes dislocations that are the result of various congenital disorders. An example is dysplasia (underdevelopment) of the articular cavity of the femoral head. The most common congenital dislocations of the hip joint are detected, less often - the knee joint and patella. You can notice a dislocation in a newborn child by the asymmetry of the folds on the inner surface of the thighs, a decrease in the amplitude of limb abduction, etc. If the child begins to walk, then with a dislocation, lameness, a specific “duck” gait, etc. may be observed. Attentive parents may notice different limb lengths. With congenital dislocation of the patella, pain, immobility of the knee joint, inflammatory manifestations, and hemarthrosis develop. The child has difficulty moving and often falls.
Treatment of congenital dislocation should be as early as possible. The best results can be obtained if specialized care begins before 3 months of age. Treatment can be carried out at a later date, but its effectiveness will be less. At the initial stages, conservative methods are used - reduction, splinting and plaster casts). If these measures are ineffective, as well as if the injury is long overdue, surgical treatment is used.
To prevent congenital dislocations, you must follow a few simple rules:
- It is mandatory to conduct an orthopedic examination of the newborn;
- Avoid tight swaddling;
- Do not put the child on his feet until he begins to stand;
- Do not forcefully straighten your legs.
Forecast
The prognosis for shoulder subluxation is generally favorable. Sometimes incomplete displacement of the head of the humerus can lead to disruption of the innervation and blood supply to this area, but this most often occurs with an abnormal arrangement of blood vessels and nerve branches.
The prognosis worsens if the patient presents to the clinic late. Thus, already 6 hours after the occurrence of subluxation of the shoulder joint, tissue ischemia (oxygen starvation) may be observed due to compression of the vessel, which can further provoke a violation of the functional capabilities of the upper limb.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical observer, surgeon, consultant doctor
12, total, today
( 56 votes, average: 4.95 out of 5)
Comminuted fracture of the humerus: symptoms and treatment
Laryngeal injuries: causes, symptoms, treatment