In our clinic you can get an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment for a march fracture.
For more detailed information and to schedule a consultation, call us by phone.
Features and diagnosis of a fracture.
There are two types of such injuries - the “Deuchlander” and “Jones” marching fractures (the latter is localized over a wide area of the base of the fifth metatarsal bone). First of all, radiography is used as a diagnostic method, which makes it possible to establish the clinical picture characteristic of a given pathology.
The main symptoms of the disease are:
- Pain of varying strength in the front side of the foot (especially when walking while rolling);
- Painful lesions on the back of the upper foot (may be accompanied by small tumors about two centimeters in diameter);
- The edematous area resembles bone upon palpation in density;
- In some cases, the swelling is larger and may spread to the entire back of the ankle;
- Sharp pain in the metatarsal bone, arising due to its restructuring and changes in load;
- Painful syndrome when standing on half toes (in the final stages – inability to stand on them).
Diagnosis can be difficult because the problem is not easily identified on an x-ray. Often patients are treated for other diseases - tendonitis, bruises, and so on. In repeated photographs, the march fracture is easier to see - over time, the bone becomes deformed, and the fracture lines become more obvious. In general, the ability to recognize such fractures depends on how long ago the pathology began.
If the diagnostic situation is difficult, the doctor will:
- X-ray ¾ projection;
- Tomography.
At-risk groups.
The following are susceptible to the disease:
- Gymnasts;
- Ballerinas;
- Active tourists and travelers;
- Women who wear high heels;
- Athletes performing exercises after a long break;
- Sellers, waiters, nurses, hairdressers and representatives of other “standing” professions.
The procedure for reconstruction of the second metatarsal bone often has relapses, as well as complications in the form of a fracture with the presence of displacement of detached pieces, a slight dislocation of the proximal Lisfranc articular part.
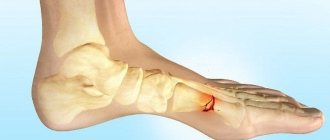
Metatarsal fracture
Metatarsal fractures are one of the most common foot injuries. Fractures of the 5th metatarsal bone occur most frequently. Fractures of metatarsal bones are more common in socially and economically active ages, 2-5 decades of life.
Typical mechanisms of injury are direct – falling of a heavy object, crushing, or indirect impact of force – rotation of the leg with a fixed forefoot. Other possible mechanisms include excessive plantar flexion - the equivalent of a Lisfranc injury, with multiple fractures of the bases of the metatarsals, as well as stress fractures (marching fractures), due to constant repetitive microtrauma.
The classification takes into account the location, type of fracture, degree of displacement, angle, involvement of articular surfaces - all standard criteria for classifying fractures of long bones. In addition, we can distinguish acute fractures associated with a single exposure to excessive traumatic force, and stress fractures associated with functional overload and constantly repeated microtraumas.
Depending on the location and type of fracture, the first symptoms are pain and the inability to fully bear weight on the leg. During examination, you should pay attention not only to the presence of swelling and bruising of a certain location, but also to the general anatomical features of the structure of the foot (normal, cavovarus, planalgus). When assessing the range of motion, the degree of rotation of the toes and their crossing are also assessed. In the case of chronic fractures, changes in the arch of the foot are possible in the form of collapse of the arches compared to the uninjured side.
For diagnosis, an examination by a specialist and radiographs in frontal and lateral projections are usually sufficient. In the case of stress fractures, additional examination methods such as CT and MRI may be necessary.
For isolated fractures of the 2-3-4 metatarsal bones without displacement, conservative treatment in a brace or short plaster cast is indicated with a gradual increase in load as the pain syndrome regresses.
This is possible thanks to the many transverse ligaments that act as stabilizers of fragments, thanks to splinting with intact metatarsal bones. If more than one metatarsal bone is damaged or there is a significant displacement (more than 4 mm), surgical treatment becomes the method of choice. For surgical treatment, intramedullary wires, screws or rods can be used (in the case of rotationally relatively stable fractures), miniplates (both compressing and locked), or the use of compression screws (2-3) without a plate. In the postoperative period, walking in the orthosis without load is required until signs of consolidation appear.
Fractures of the 1st metatarsal require surgical treatment. This is due to the fact that during walking, the first metatarsal bone accounts for 40-60% of the load, and also through it the force of the plantar push is transmitted, in addition, it is the shortest and is connected with the longest of the metatarsal bones, and in the gait cycle it has the greatest amplitude of movements . This type of fracture rarely occurs in isolation.
For osteosynthesis, compression screws and plates are most often used.
Fractures of the base of the 5th metatarsal are covered in a separate article. For fractures of the diaphyseal part, neck and head of the 5th metatarsal bone, the approach is not much different from the 2-3-4 metatarsal bones; for transverse fractures, it is possible to use intramedullary pins, screws, rods, compression plates; for oblique fractures, compression screws; and for comminuted fractures – lockable plates. Combinations of these methods are possible depending on specific cases.
Stress fractures of the base of the 2nd and 3rd metatarsals are “march” fractures. Often the diagnosis cannot be made in a timely manner, since radiological diagnosis in the early stages is difficult. Fractures often occur against the background of a sharp increase in physical activity or a change in the nature of the load. The pain in the foot is initially dull and aching, gradually becoming more acute and localized in the area of injury.
Treatment is predominantly conservative. In addition to the immobilization period of 6-8 weeks, the patient's attention should be drawn to the need to change the training regimen, and often the diet (often such fractures occur in very thin patients with severe dietary restrictions, as well as osteoporosis). In the case of a professional athlete, early surgical treatment using a compression intramedullary screw with or without bone grafting has shown better results in terms of speed of fusion and return of the patient to professional sports.
Treatment.
As a rule, they resort to a conservative method of treatment, which involves avoiding physical activity, as well as keeping the foot at rest. In addition, they use:
- Kinesio taping;
- Wearing plaster overlays;
- exercise therapy;
- Myostimulation;
- Other physiotherapeutic procedures.
Recovery takes up to six months. Rehabilitation is accompanied by wearing optimal shoes and custom-made orthopedic insoles. High-heeled shoes are excluded due to excessive pressure on the toes and the front of the foot, and, accordingly, on the site of injury. Periodically, such fractures lead to the detachment of pieces of the bone body and their displacement, damage to the Lisfranc joint. Then surgical intervention is indicated.
Advantages of osteosynthesis for tibia fractures
The main advantage of installing a plate for osteosynthesis of the tibia is the provision of conditions for rapid, complete fusion of bones, which are organized using two conditions:
- Possibility of reliable, precise fixation of all bone fragments in the required areas.
- The ability to launch rapid tissue regeneration. This is done by improving blood flow and speeding up recovery.
The bones are securely fixed by a plate, and the limb itself is relieved of the pressure of the applied plaster.
This method of treatment is carried out in the treatment of complex fractures, when a fracture is diagnosed on both bones at the same time. Osteosynthesis surgery on the lower leg is recommended if the ankle joint is involved in the traumatic process, fragments are displaced, or surrounding tissues are injured.
Conservative therapy
If the fracture is open, or there is significant displacement of the metatarsal bone fragments, then surgery is performed. Uncomplicated injuries are treated with the following methods:
- When the base of the fifth, fourth, third, second or first metatarsal bones is fractured without displacement, plaster is not applied. But, if a child is injured, then you cannot do without a cast, since it is difficult to explain to the child why you cannot step on your foot.
- In case of traumatic fractures, it is allowed to walk by stepping on the heel or using crutches.
- In case of stress fractures of the metatarsal bone, the recovery process takes place under mandatory loads, but with the use of orthopedic insoles, thanks to which tension is relieved from the damaged area.
- If there is displacement, the patient will have to walk in a cast.
Diagnostic methods
X-ray of a foot with a fracture of the 5th metatarsus
First of all, in case of a fracture of the metatarsal bone of the foot, a specialist conducts a visual examination of the leg to determine the mechanism of injury. Symptoms such as hemorrhage, swelling and deformation of the foot appear almost immediately when a metatarsal bone is fractured in children and adults.
Next, an x-ray is taken in two projections, which is enough for the doctor to determine a displaced fracture, but if a stress fracture of the metatarsal bones of the foot without displacement occurs, then even a specialist with extensive experience will not be able to accurately make a diagnosis. X-rays are repeated after 2 weeks, when callus begins to form, which is visible in the pictures.
If it is difficult to determine a fracture of the 5th metatarsal bone, as well as the fourth or third, second or first, an MRI or CT scan is prescribed.
The ointment is a good pain reliever and relieves inflammation of the injured area.
Simple fractures are treated by applying a fixative - a cast or a cut, and complete rest for 4-6 weeks, since the damage takes a long time to heal. To speed up the recovery process, it is recommended to apply the following painkillers and anti-inflammatory liniments:
- "Diclofenac";
- "Dolobene";
- "Voltaren";
- "Fastum";
- "Deep Relief".
If the fracture occurred in children, you can use children's medications:
- balm “Rescuer”;
- "Troxevasin";
- "Bruise Off".
Types of osteosynthesis
Osteosynthesis operations on the bones of the legs during fractures can be performed using the following techniques:
- intramedullary, using rods and pins that are inserted into the bone marrow canal;
- extramedullary, when the plates are secured to the bone with screws.
The use of Volkov-Oganesyan and Ilizarov extrafocal fixation structures has a huge impact on the quality of treatment and rehabilitation. Their use is based on compression-distraction osteosynthesis. These devices subject one area of the limbs to pressure and others to stretching.
The technique for installing a shin plate is constantly being improved. Among the devices used today there are wire and rod designs for external fixation. They are used for urgent surgery and for complex surgical fractures. They are implemented effectively and minimally invasively. The choice of surgical intervention is influenced by the severity of the injury, type of fracture, and the presence of complications.
A very important factor influencing the quality of the surgical intervention should be considered the experience of the doctor, the availability of modern equipment for diagnosis and operations, and the availability of materials for implantation. With the proper qualifications of the surgeon, the patient quickly recovers; an unsuccessful operation leads to repeated interventions and improper fusion of bones. High-quality implantation of a plate for a tibia fracture will ensure a quick return of the patient to normal life.
Surgery
Depending on the complexity of the injury, several types of surgical intervention are offered.
The most popular treatment method. First, the surgeon, in a closed mode (without an incision), correctly positions the fragments; then, taking into account the nature of the metatarsal bone fracture, they are drilled and fixed using knitting needles.
Negative sides:
- the needles remain visible above the surface of the skin, which allows them to be removed after some time;
- there is a risk of infection entering the wound;
- The bandage needs to be worn for one month, which causes inconvenience.
The positive aspects of this procedure: low cost, quick implementation and low trauma, no postoperative scar.
During the operation, a surgical incision is made to gain access to the damaged area of the metatarsal bone. Tendons, nerves and vessels are retracted, debris is collected, and displacement is eliminated. Using a plate and screws, the bones are fixed in the correct position. After the operation, the doctor allows the patient to walk, but for 1 month. You can only step on your heel.