Traumatologist-orthopedist
Shelepov
Alexander Sergeevich
12 years of experience
Doctor
Make an appointment
Many people mistake a small bulge that appears on the bone as the result of an injury. Education in the early stages does not create any special problems or cause discomfort, so a visit to the doctor is postponed. As a result, patients consult a doctor after the onset of painful sensations, when the osteoma becomes visually noticeable, begins to cause severe discomfort and leads to deterioration of health.
Osteoma is a benign tumor-like neoplasm developing from bone tissue, which is not predisposed to transition to a malignant state. It develops slowly. Osteoma is dangerous because it develops imperceptibly, without pronounced symptoms, so most people turn to doctors when the pathology is severely advanced and long-term treatment is necessary. Osteoma grows slowly, which allows patients to be successfully treated if treated in a timely manner.
Causes
There are two theories for the origin of osteomas: from the remnants of embryonic cartilage or from the periosteum of mature bone. In some cases, the occurrence of osteomas is associated with an inflammatory process or injury Source: Toropova I.A. Features of the clinical course of osteoma of the nose and paranasal sinuses / I.A. Toropova // Bulletin of RUDN University. — Medicine Series. - 2005. - No. 1(29). — P. 95-97. .
It is believed that the development of osteomas is also facilitated by:
- injuries;
- hypothermia;
- inflammation and previous infections;
- some diseases (rheumatism, gout, syphilis);
- genetic predisposition.
Rehabilitation
Image courtesy of kdshutterman on FreeDigitalPhotos.net
Early rehabilitation requires the patient to be in an inpatient setting. In the first few days, proper antiseptic care, monitoring the patient’s condition and postoperative sutures are important.
During this period, a course of antibiotic therapy is prescribed to relieve secondary infectious and inflammatory complications, antiseptic treatment of the wound and regular dressing. Be sure to monitor blood pressure and consult an ophthalmologist or neurologist.
Late rehabilitation includes a gentle protective regime:
- proper nutrition,
- reduction in physical activity,
- prevention of colds, including inflammation of the sinuses during their chronic course.
Typically rehabilitation takes 3-4 weeks.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a tumor depend on where it is located. But a number of clinical signs stand out:
- located on flat, tubular bones, vertebrae, in the walls of the paranasal sinuses, on the surface of the skull;
- immobility;
- density;
- with a smooth surface;
- with clear boundaries;
- does not hurt when pressed.
Osteoma may not make itself felt for a long time and not interfere, but if it grows too large, it begins to put pressure on neighboring tissues and bones, which causes the corresponding symptoms:
- pain;
- if the tumor is in the nasal paranasal sinuses, drooping of the eyelid (ptosis), blurred vision, etc.
- memory problems, epilepsy (if located on the inner surface of the skull);
- lameness (if localized on the bones of the legs);
- nosebleeds, difficulty breathing (if the tumor is located in the maxillary sinus area).
Table of symptoms, depending on the location of the tumor
| Tumor location | Description of symptoms |
| Posterior wall of the frontal sinus | Persistent headaches, increased intracranial pressure |
| Inferior wall of the frontal sinus | Protrusion of the eyeball visible to the naked eye |
| Nasal cavity | Difficulty breathing through the nose, lack of smell, double vision, drooping eyelid, protrusion of the eyeball, blurred vision |
| Paranasal sinuses | Deterioration of vision, pain |
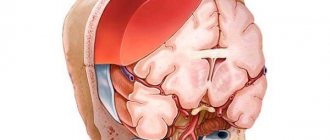
| Frontal bone | Headaches, memory loss, increased intracranial pressure, seizures |
| Occipital bone | Frequent headaches, epileptic seizures |
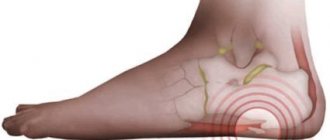
| Femur, talus, tibia | Unusual gait, swelling of the legs, muscle pain while walking |
| Temporal and parietal bones | Only an aesthetic defect, no unpleasant symptoms |
| Knee-joint | The tumor makes it difficult to walk normally |
| Edge | Chest pain |
| Vertebrae | Scoliosis develops |
| "Turkish saddle" | Hormonal disorders |
Classification
Osteoma
Depending on the type of structure of tumors, they are distinguished:
- Hard compact osteoma formed by dense compact bone tissue.
- Spongy osteoma - formed by a porous spongy substance with cavities filled with fibroreticular tissue.
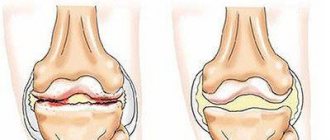
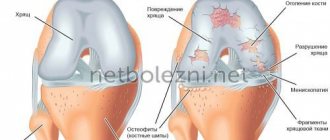
In relation to the bone organ, there are periosteal osteomas, located on the outer surface, and endosteal osteomas, located on the inner surface of the bone (Fig. below).
Osteoid osteomas
Based on localization in the bone (radiologically), several types of osteoid osteoma are distinguished: medullary, cortical, subperiosteal and protruding into soft tissue.
Types of osteomas
Depending on the origin of osteomas, there are:
- Heteroplastic
- formed from connective tissue. This includes osteophytes. They are found not only on bones, but in soft tissues and organs - in the diaphragm, tendon attachment points, lining of the heart, etc. - Hyperplastic
- formed from bone tissue. This group includes osteoid osteomas and osteomas.
Let's look at the subspecies that belong to two main groups.
1) Internal and external osteophytes
.
- The internal ones are called “enostoses”, they grow into the bone marrow canal. Usually solitary, except for osteopoikilosis. They do not produce symptoms and are usually discovered incidentally when a person has an x-ray.
- External ones are called “exostoses”. They grow on the surface of the bones and can appear for no reason or due to certain pathological processes. Causeless exostoses usually appear on the bones of the skull, facial and pelvic bones. They may not cause symptoms and may only be an aesthetic defect or put pressure on neighboring organs. In some cases, a fracture of the exostosis leg occurs and bone deformation occurs.
2) Osteoma
– does not differ in structure from bone tissue, usually found on the facial and cranial bones, including the paranasal sinuses. Bone osteoma is diagnosed twice as often in men, in the area of the facial bones – three times more often. These are almost always single tumors, but with Gardner's disease multiple tumors can grow on long bones. They are painless and do not cause symptoms, but when adjacent structures are compressed, various symptoms appear. Separately, there are multiple congenital osteomas of the cranial bones, which are combined with other developmental defects.
3) Osteoid osteoma
– highly differentiated bone tumor. However, it has a different structure - it consists of vascular-rich elements of osteogenic tissue, zones of bone tissue destruction, and bone beams. Usually there is no pain 1 cm in diameter. It is a common disease, accounting for approximately 12% of all benign bone tumors.
Is osteoma dangerous?
Speaking about the dangers of osteoma, one should note first of all the compression of neighboring organs and symptoms that cause inconvenience to the patient. If the tumor does not manifest itself and does not grow, it can be left in place. A neoplasm of this kind never develops into malignant – there is no need to be afraid of cancer. Tumors on the head should be treated with particular care - they not only cause unpleasant symptoms, but can also lead to a brain abscess. As a rule, they are removed surgically.
Tumor diagnosis
To establish that the tumor is indeed an osteoma, the following procedures are performed:
- X-ray;
- CT scan;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- rhinoscopy of the nose;
- histological examination of part of the tumor tissue.
During diagnosis, the doctor must determine:
- degree of functionality of the affected limb or tissue;
- pain of the tumor when pressed;
- the growth rate of the tumor by the ratio of its size and the duration of the presence of pathology in the patient;
- location of osteoma.
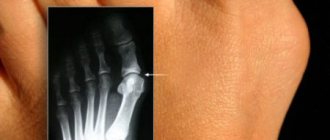
The main method of diagnosis is radiography
. On the image it will look like a homogeneous round tumor with clear boundaries. Osteoid osteoma in the image is a vague defect - a focus of destruction.
- Radiography allows you to find out: the location of the osteoma in the bone, the structure of the tumor, the degree of destruction of the bone on which the tumor is located, and also determine whether the tumor is a single tumor or multiple growths.
- The benign nature of the tumor is confirmed by slow growth, regular structure and geometry, clear contour, and minimal calcification.
- A blood test is also prescribed because the blood formula is of great importance.
- For very small osteomas, radiography is not informative, so computed tomography is performed, which allows one to visualize the smallest details of the tumor structure and measure the size of destruction.
- Differential diagnostics with chronic Brody's abscess, osteochondrosis dissecans, osteoperiostitis, sclerosing osteomyelitis, and osteogenic sarcoma are mandatory. This applies to osteoid osteomas.
Pathogenesis
A pathoanatomical study clearly identifies the boundary of osteoid osteoma against the background of surrounding sclerotic bone tissue containing a large number of vessels. The center of the tumor (osteoid part) consists of interwoven trabeculae/strands of osteoid, which are surrounded by clusters of loose vascularized fibrous stroma and large osteoblasts located along the developing bone beams in the form of a rim. There are mitotic figures. The general appearance of the osteoid is similar to an intricate script. Less common in tumors are single/group osteoclasts.
In relatively “young” tumors, it is the osteoid that makes up the main part of the neoplasm, but as the tumor “aging”, areas of calcification appear, and in fully mature tumors, in addition to osteoids, fibrous bone, which consists of compact trabeculae, is also detected. Cartilaginous tissue is also found in tumors growing under the articular cartilage. This is the structure of the central zone of osteoid osteoma, and around it there is fibrous tissue in the form of a strip of 1-2 mm, which is rich in vessels and the trabecular pattern in it is no longer defined. Further outward there is another layer of sclerotic cortical plate.
Treatment of osteomas
If the tumor does not cause any discomfort to the patient, then medical specialists recommend observational tactics. If a small osteoma stops growing, it does not need to be treated or removed.
Osteoma is treated only surgically. Indications for removal are as follows:
- too big size;
- pain caused by osteoma;
- cosmetic defect.
Removal is carried out if the osteoma compresses neighboring organs, causing pain and discomfort, is an aesthetic defect, changes the shape of bones, causes scoliosis, limits a person’s mobility, and provokes pain. Most often, specialists remove tumors in the sinuses, jaws, ear canals, hip and knee joints.
Preparation for the operation is standard. These include blood and urine tests, ECG, fluorography, consultations with a therapist and anesthesiologist. The intervention is carried out under general anesthesia; you need to spend from 1 to 3 days in the hospital, depending on the extent of the operation performed.
The SM-Clinic employs some of the best maxillofacial surgeons and neurosurgeons who perform minimally traumatic operations using modern techniques and instruments.
During the operation, soft tissues are dissected; access can be external or internal - through the mucous membranes of the mouth and nose. The tumor and part of the soft and bone tissue surrounding it are removed to avoid recurrence.
Basic removal methods:
- curettage – external access, tumor removal, curettage of the tumor focus;
- complete removal – indicated for osteomas in the sphenoid sinus;
- endoscopic removal - is carried out for small tumors and difficulties in accessing them, CT is necessarily used to monitor the progress of the intervention, the duration of the operation is about two hours.
If the removal was not completed completely, then in 10% of cases a relapse occurs. Therefore, it is important to contact a reliable clinic and an experienced surgeon.
Another method for removing osteomas is laser evaporation. A laser beam is directed at the tumor, which actually burns it out. Typically this technique is used for small tumors.
List of sources
- Burdygip I.N. Osteoid osteoma and osteoblastoma of the spine (clinic, diagnosis and surgical treatment): Dis. Ph.D. honey. Sci. M., 1993.- 182 p.
- Zatsepin S.T. Bone pathology of adults. - M.: Medicine, 2001. 639 p.
- Kolesov, V. S. Benign tumors of the face, jaws and oral cavity organs / V. S. Kolesov, A. M. Solntsev. Kyiv: Kyiv University Publishing House. 1985. 168 p.
- Karpenko A.K., Magonov E.P. The role of MRI in the diagnosis of osteoid osteoma / “RADIATORY DIAGNOSTICS” No. 3, 2014. p. 50-52.
- Epidemiology of skeletal tumors: educational manual / Chernyakova Yu.M., Ivanov S.A., Yadchenko V.N. — 2012.
Prevention
There are no special preventive measures to prevent the occurrence of osteoma. Doctors recommend taking an x-ray every year to detect the tumor in a timely manner and, if necessary, remove it.
Specialists of the medical surgical department successfully perform operations to remove various types of osteomas. If you notice a lump on any bone, contact a specialist who will make a diagnosis and promptly prescribe treatment.
There is no special prevention for this disease. The main cause of osteomas is considered to be genetic predisposition.
Some recommendations:
- avoid injury;
- timely cure diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- undergo examination if any neoplasms of unknown origin are detected.
General characteristics of the disease
As a rule, the course of a bone tumor is favorable: its size increases slowly, and negative symptoms are absent for a long time. Sometimes they are found on x-rays ordered by the attending physician for other reasons - for example, to obtain information about the teeth of the upper jaw.
The location of benign bones varies - from the outer surfaces of the skull to the lower extremities, but there may be disturbances in the cellular division of the spine and ribs. Regarding the number of tumors, experts identify single osteomas, while Gardner's disease is more characterized by multiple foci.
Men more often complain to doctors about a lump on the head and leg. Women are more often diagnosed with facial bone lesions.” The causes of the disease were identified as injuries - bruises, a history of fractures and a family predisposition to neoplasms.
Types and code according to ICD-10
Due to its structure, the tumor—compact osteoma—is no different from healthy bone mass. In its external position, the defect is palpable as a local closure with a smooth surface, painless and in most cases small.
There are also the following types of tumors:
- spongy osteomas - formed from loose spongy tissue;
- brain tumors - contain in their structure elements of the brain substance, at the same time they also contain bone cells, but in smaller quantities.
However, most doctors classify the disease according to the origin of the tumor cells:
- hyperplastic form - the lesion develops directly from osteocytes, for example, osteoid osteomas;
- heteroplastic form - the formation of a tumor from connective tissue, for example, from osteophytes.
In accordance with the International Classification of Diseases, which has been revised and supplemented several times, osteomas received a code in accordance with ICD-10 - D16. The third number helps doctors clarify the area of damage. For example, code D16.1 is assigned to tumors of the short bones of the upper extremities, and code D16.2 is assigned to osteoma of the femur. Spinal tumor code D16.6.
Localization
Meanwhile, doctors identify the following neoplasms in body parts:
- rib osteoma;
- damage to the cranial cavity - from the maxillary sinuses to the ethmoid and sphenoid bones;
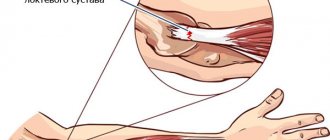
- in long tubular structures, osteoma of the femur is most often diagnosed;
- joint tumors - from the patella to osteoma of the shoulder joint;
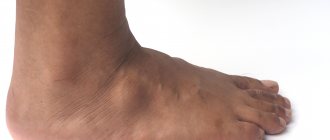
- feet, hands, pelvis, structural neoplasms;
- In dentistry, doctors often encounter lesions of the upper/lower jaw.
Osteoma cells are usually highly differentiated units, which makes it almost impossible for them to develop into a malignant focus - cancer, since healthy bone cells are simply gradually replaced by fibrous tissue. Some doctors believe that this subgroup of osteophytes and exostoses is erroneous - the mechanism of their formation is somewhat different, for example, due to injury or excessive physical activity, as is the case with osteomas of the knee joint.
Danger of disease
As with any pathology of the human body, a spinal osteoma or other bone structure is nothing more than a lesion of a group of cells that requires appropriate treatment. The danger of the disease lies in the potential risk of disruption of the functioning of internal organs and systems and, very rarely, in the transformation of a benign process into a malignant focus.
With the progression of metaplasia - the size of the neoplasm - compression of adjacent tissues occurs, including blood vessels and nerve fibers, sometimes even germination in the cavity and sinuses of the bone, which leads to increased pain and the spread of ischemia. All these manifestations reduce a person’s quality of life and ability to work.
The appearance of pathology in the bone growth zone in children can provoke deformation of the limbs and deterioration of motor function. Such changes can be caused by damage to the tibia and shin bones.
The location of the tumor near the large/small joint causes the accumulation of intra-articular fluid, its subsequent suppuration, and restriction of movement in the leg/arm.
If osteoma forms in the paranatal sinuses of the facial skull, there is a risk of it penetrating into the orbit, which can lead to visual impairment.
The development of osteoma in the temporal bone leads to hearing loss.
Causes
To finally figure out why bone cells suddenly began actively dividing, experts were unable to determine. Their medical research allowed us to establish several basic theories - from negative hereditary predisposition to previously suffered severe infectious diseases in humans.
Main provoking factors:
- congenital anomalies - refusal of bone cell division occurred already at the stage of intrauterine development of the fetus;
- traumatic variant - defective fusion of fragments with local thickening instead of bone calluses;
- poor quality of medical procedures such as puncture of the maxillary sinus;
- various inflammatory processes in bones with a chronic course - from rheumatism to gout, syphilis, osteomyelitis;
- poor nutrition - a minimum amount of fresh fruits and vegetables, fermented milk products with calcium and phosphorus;
- — vitamin D deficiency;
- Radiation - Radiation therapy for tumors elsewhere.
Excessive weight of a person, tobacco and alcohol abuse can provoke osteochondrosis of the hip joint. Among the provoking factors, doctors also point to severe stressful situations, psychological trauma and living in unfavorable environmental conditions.
Symptoms of the disease
The formation time of femoral osteoma is long—several months or even years are required for the tumor to grow. Therefore, symptoms of the disease may be completely absent in the early stages. Sometimes the patient even notices that the contours of the bones have changed, especially if the tumor appears on the forehead and clavicle bone.
Only when the tumor defect puts pressure on neighboring tissues, especially those that are crossed by nerve fibers and numerous vessels, does pain begin to bother people. For example, if the damage is in the paranatal sinuses or on the inside of the skull bones, patients complain of headaches, memory impairment and, less commonly, seizures and mental disorders.
In large spinal osteomas, the spinal nerve roots are gradually infringed by the corresponding symptoms - paresthesia, disruption of the functioning of internal organs, even restrictions of movement, paralysis of the patient.
Causes, symptoms and treatment methods for hygroma
When the tumor multiplies in the orbit, deviations in the visual system become noticeable - deterioration of vision, impaired mobility of the eyeball, deformation of the eyelid, protrusion of the organ from the outside. Osteomas of the ribs, hips, and sternum remain practically “silent.” The detection of neoplasms in them is a diagnostic discovery, the result of diagnostic procedures performed for other indications.
Diagnosis of pathology
Thanks to timely medical care, early diagnosis of benign neoplasms is the “gold standard” in the treatment of all pathologies, including osteoma. Modern advances in oncology make it possible to detect a pathological focus even if it is minimal in size.
You might be interested in: How to drink castor oil to cleanse the intestines: diagram and recipes
The main research methods have been developed:
- X-ray is an accessible way to visualize bone formations, their size and structure;
- computed tomography is a largely significant study that allows differential diagnosis of the disease in the presence of questionable radiological signs of osteoma;
- biopsy - taken from the tumor biomaterial for further examination of cells under a microscope, which makes it possible to eliminate atypia in the cells;
- scintigraphy - allows you to identify several small foci in the bones;
- ultrasound - to clarify the processes of compression of internal organs, nerve fibers, and the causes of functional disorders in their activity.
Laboratory diagnosis of osteoma is meaningless. Blood tests, general and biochemical, as well as cancer markers, are recommended by the doctor to obtain an overall overview of the patient's health. Only after carefully comparing and evaluating all the information about the above procedures, the oncologist will give a qualified opinion and select the appropriate therapy to treat the disease.
Treatment methods for osteoma
After a comprehensive medical examination of the patient and making sure that the osteoma is benign, the doctor will prescribe treatment that takes into account the patient’s age and the characteristics of his body. Therefore, in most cases, a control examination of the pathological focus and a healthy lifestyle is recommended.
Active therapeutic procedures are necessary only when rapid tumor growth is detected. Indications for surgery:
- suspicion of a malignant tumor;
;
- development of functional failure of organs adjacent to the tumor;
- deformation of bone structures.
Usually, osteoma is removed from healthy tissue - truncation. Removal of all or part of the limb is required if cancer is confirmed - bone sarcoma. When the focus is removed from the skull area, another plastic surgery is performed.
If surgical treatment is not possible, doctors decide to use drug therapy to eliminate pain, reduce the severity of other unpleasant symptoms, and improve quality of life. Complex treatment can be supplemented with traditional medicine recipes, such as hawthorn decoction and elderberry tincture. However, they should not replace your own medications from the pharmacy.
Prognosis and prevention
The main task of medical personnel - healing of osteoma - is an appropriate measure when a lesion is detected in the bone at an early stage of the disease. In this case, the prognosis is most favorable - benign bone tumors rarely regress.
However, one should not give up, even if osteoma is detected at a late stage. Advances in medicine make it possible to correct the course of the disease, even in advanced forms, and improve human health.
Specific prevention of osteoma has not been developed, since the main causes of osteoma have not yet been definitively established. Therefore, doctors will recommend methods to prevent the progression of the pathology - proper nutrition, avoidance of injury and radiation, and severe stress. Preventing bad individual habits will also help prevent the development of osteoma.
Popular questions
Can osteoma lead to cancer?
No. Osteoma is a benign tumor. It can cause adverse health effects if it grows into the cranial cavity. But the probability of degeneration into cancer is close to zero.
What causes osteoma?
The causes of the tumor are unknown. The role of hereditary predisposition has been established. If your relatives have been diagnosed with osteoma, you are more likely to develop it than the average population. The trigger for the growth of osteoma can be a bone injury or an acute inflammatory process. There is also a theory of intrauterine developmental defects. The reason for its occurrence was the fact that osteoma most often develops at the junction of the frontal and ethmoid bones, where membrane and cartilaginous tissues develop during embryogenesis.
Is it necessary to remove the osteoma?
The tumor grows very slowly. In most cases it is not dangerous. Only clinically significant osteomas that can grow into the orbit or skull bones are removed. The operation can also be performed for aesthetic reasons.
Sources:
- Kudaibergenova S.F. Osteoma of the nasal cavity / S.F. Kudaibergenova [and others] // Bulletin of KAZNMU. - 2012. - No. 2. - P. 92-93.
- Toropova I.A. Features of the clinical course of osteoma of the nose and paranasal sinuses / I.A. Toropova // Bulletin of RUDN University. — Medicine Series. - 2005. - No. 1(29). — P. 95-97.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
How to make an appointment with a traumatologist
JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) in Moscow offers the services of qualified specialists in the field of diagnosis and treatment of osteoma. If you suspect osteoma, you can make an appointment with a traumatologist in various ways:
- select a doctor in the “Our Doctors” section and make an appointment online;
- call +7 (495) 775-73-60;
- leave a request for a call in a special form on the website.
The clinic is located in the central district of Moscow at 6 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane 10 (Tverskaya, Chekhovskaya, Mayakovskaya, Belorusskaya, Novoslobodskaya metro stations).
Therapy of pathology in children
Osteomas, localized in the immediate vicinity of articular cartilage, provoke the formation of effusion, which often gives rise to an erroneous diagnosis:
Tumors located on the outside of the cranial bones
Modern methods of therapy are good at combating benign formations that appear near the bone growth zone. And in this case, the prognosis of the disease is favorable.
Source sustaw.top
Osteoma of the femur is a benign tumor. Most often, this pathology affects people under 30 years of age. Osteoma of the tibia can reach significant sizes. It depends on its type. The opinion about the etiology of the disease is still controversial. Some experts argue that the tumor occurs as a result of an inflammatory process, which can be infectious in nature, while some doctors refute this theory.
The causes of the disease are considered to be injuries and pathologies of a rheumatic nature. A provoking factor may be a disturbance in calcium metabolism. Sometimes the disease is congenital and occurs in people with genetic mutations.
If parents have osteoma of the tibia, the likelihood of it occurring in children increases several times.
Additional Information
Osteoma of the femur can cause compression of the nerve ending, leading to loss of sensation. Clamping of blood vessels has a particularly detrimental effect on the condition of the joint. This can impair blood flow in the problem area.
There is no treatment for the disease at home. If arthrosis has additionally developed in the causative area, then physiotherapy can be used after tumor removal. Additionally, drugs are used to eliminate degenerative processes in cartilage tissue.
The disease is especially harmful to children during the period of active development and bone growth. Curvature of the spine and other pathologies may occur. In this case, the child begins to experience irreversible changes in the spine at an early age.
Persistent scoliosis may develop. Pain from hip osteoma often radiates to the back, lower leg and buttock. However, painkillers only temporarily relieve symptoms. If the tumor stops growing, then the signs of the disease become erased. The size of the formation often does not exceed 1 cm. Outwardly it resembles a small cherry.
During diagnosis, it is important to distinguish pathology from more dangerous diseases of bone tissue, including cancerous tumors.
Source ortocure.ru
In the past, a number of bone tumors of a traumatic, inflammatory and neuropathic nature were classified as osteomas, but today it has been isolated as a separate disease.
The tumor is benign, does not produce metastases and does not spread to other tissues. Young people under 30 years of age are most susceptible to osteoma.
Among this type of neoplasm, osteoma itself and osteoid osteoma are distinguished. The second is characterized by its small size (usually up to 10 mm) and specific manifestations: the bone becomes spindle-shaped due to periosteal growth and has a focus - a rounded zone of gray-pink tissue, around which a wide sclerotic cortical layer is observed.
- All information on the site is for informational purposes only and is NOT a guide to action!
- can give you an ACCURATE DIAGNOSIS !
- We kindly ask you NOT to self-medicate, but to make an appointment with a specialist !
- Health to you and your loved ones! Do not give up
Osteophytes: reasons for the formation of bone growths and ways to get rid of them
The essence of the operation is the radical removal of the lesion (“nest”) of the lesion along with a thin strip of sclerotic bone tissue.
During the operation, all tissue is removed en bloc. The approach to the area of bone affected by osteoma is most often made through an incision located directly above it. Osteophytes Often this disease is asymptomatic. It can be detected after X-ray examinations.
Osteophytes can form in the cavities of the joints of the extremities, on the surfaces of the arms and legs, as well as on any part of the spinal column. As a rule, they form after a person receives injuries resulting in bone fractures. Sometimes the chronic course of such a disease, occurring in bone tissue, stimulates an increase in bone growths.
Contents of the article: General information and causes Types Symptoms, diagnosis Treatment and prevention
General information
Osteophytes: what is it? These are pathological growths on the bones that are not an independent disease. They usually appear as a compensatory reaction of the body to a violation of the periosteum or bone tissue. They have a variety of shapes and sizes.
The presence of osteophytes worsens a person’s quality of life, causes pain, but is not life-threatening. Therapy for osteophytes usually involves pain relief. In cases where the disease contributes to decreased performance (for example, with a heel spur), doctors recommend resorting to surgical intervention.
How to get rid of osteophytes? They can only be removed surgically, but they may appear again. For this reason, conservative therapy helps to cope only with the symptoms of the disease, but does not significantly affect the osteophytes themselves and their growth.