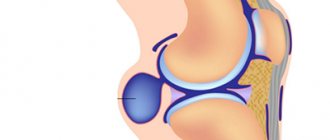
Hygroma in children is a cyst formed by the synovial membrane of a joint or tendon, the contents of which are fluid. The average diameter of the cyst is 0.5 – 3.0 cm. There have been no recorded cases of hygroma degeneration into a malignant neoplasm.
Hygroma in a child is a fairly common disease; the favorite locations on the leg are the knee (the front surface of the knee joint or the popliteal fossa), the ankle joint, and the foot. Being small in size, it does not cause significant discomfort. As the formation increases, restriction of joint movements and pain may occur.
Causes and danger of the disease
A neoplasm can develop due to monotonous loads on the joint - for example, when regularly spending time at the computer, a hygroma forms on the wrist
Even an experienced specialist cannot always accurately determine the true cause of the formation of hygroma in a child. He only manages to find out the factor that contributed to the change in the cells related to the joints.
Most often in children, hygromas form in places that are subject to intense stress for a long time. We are talking about the knee, wrist and ankle joints.
The following unfavorable factors can lead to the development of pathology:
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Joint damage.
- Intense physical activity that is chronic in nature.
- Excessive mobility of the child.
- Passive lifestyle.
This disease affects children who spend a lot of time at the computer. They run the risk of developing hygroma in the wrist area. Without treatment, the disease will lead to the development of carpal tunnel syndrome and decreased sensitivity of the fingers.
Hygroma in children does not pose a serious danger. This is because it is not capable of degenerating into a malignant tumor. But parents still have to think about removing it from their child. Over time, the neoplasm will cause obvious discomfort to the patient and interfere with his usual life activities. The psychological factor is also significant.
If you ignore the development of the tumor, it will continue to grow. Ultimately, the hygroma may burst, and its contents will spread to adjacent tissues under the skin, which should not be allowed.
Prevention and prognosis
It is impossible to completely eliminate the risk of hygromas using preventive measures, but it is quite possible to reduce the likelihood of their occurrence, for this you need:
- do not injure joints, tendons, and tissues above them;
- avoid excessive stress on the limbs;
- do not lead a too passive lifestyle;
- during intense sports, use a tight elastic bandage on the joints and tendons;
- wear comfortable and breathable shoes and clothing;
- promptly and correctly treat fractures, injuries, dislocations, bruises;
- periodically take chondroprotectors;
- consume enough vitamins, protein, calcium;
- Get regular check-ups with your doctor.
After conservative treatment, the probability of hygroma recurrence is more than 80%, after puncture - more than 30%, and after surgical excision - about 5%.
Hygroma never turns into a cancerous tumor, and timely and adequate treatment will avoid complications.
Using these preventive measures, you can avoid the appearance of not only synovial cysts, but also other tumor formations. With timely detection, correct diagnosis and following the recommendations of the attending physician, treatment of hygroma has a very favorable prognosis. The main thing is that this neoplasm does not degenerate into a malignant one; very often in children it regresses on its own and is completely cured, leaving no unpleasant consequences or complications. If the course of the disease is unfavorable, there can be only one consequence - the development of purulent tenosynovitis, which requires separate therapy.
Clinical picture
The tumor hurts when pressed
Hygromas in a child are easily recognized by the signs that this disease has. You need to understand that the progression period can take from a couple of months to several years. During this time, the symptoms of the pathology will gradually increase, which will enable parents and the doctor to suspect a tumor in the child’s joint area.
As the hygroma develops, the child begins to complain of pain at the site of the lesion. You can also notice a seal on his body that can be easily felt.
In the initial stages of the disease, the patient is not bothered by pain. It does not occur even during palpation of the tumor. The following changes appear as it grows:
- Increase in the size of the hygroma up to 6 cm in diameter.
- The appearance of dull pain, which can move to neighboring areas.
- Thickening of the skin that is located above the cyst.
- Difficulty moving the affected joint.
Clinical symptoms of the disease appear in the patient depending on the location of the benign neoplasm. A child may be bothered by the following signs of illness:
- On the foot. The tumor grows in the area of the phalangeal bones or ankle. For this reason, the patient has difficulty moving, as he experiences severe discomfort because of it. Due to the proximity of the cyst to the nerve endings, an exacerbation of the pain syndrome may occur. If the foot is constantly overloaded and injured, this will ultimately lead to inflammation and active progression of the pathology.
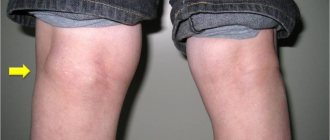
- Near the knee joint. The pathology is accompanied by the development of a compaction that has a spherical shape. It can be seen directly on the kneecap. The child does not notice the growth of the tumor. Discomfort is felt only during a blow to the knee or intense physical activity on the lower limbs.
- Near the popliteal fossa. The tumor in this case is characterized by a slight displacement from above the popliteal fossa. The cyst progresses rapidly, which is why the child begins to experience pain at the site of the lesion, numbness in the leg and cramps.
Similar symptoms are observed with hygroma on the upper extremities.
Hygroma of the knee joint
Hygroma of the knee joint most often develops in athletes with frequent knee injuries. Externally, a spherical formation is determined in the popliteal fossa, which limits movement in the joint and causes pain when moving. The patient may also complain of paresthesia in the knee area.
First, thinning of the joint membrane appears, as a result of which the synovial capsule changes and begins to protrude outward. After the altered bursa is filled with secretion, a hygroma of the knee joint is formed. Hygromas usually take years to form, but in this case the formation can develop instantly, causing severe pain.
For small hygromas of the knee joint, you can begin conservative therapy in the form of electrophoresis, UHF, applications, and punctures. In case of inflammation, antibiotics are prescribed. However, surgical intervention is most likely required, since after it there is practically no relapse of the disease.
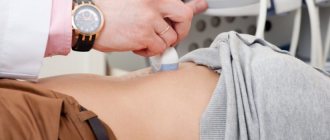
Diagnosis of pathology
A pediatrician can determine a hygroma in a child. If he doubts his diagnosis, he will redirect the patient to a highly specialized specialist who deals with similar pathologies. In both cases, diagnostic measures will be required to confirm the correctness of the proposed diagnosis.
An experienced specialist can identify a hygroma in a child after palpating the problem area. Instrumental diagnostics allows him to become more familiar with the picture of the disease and select an effective method of therapy depending on the indications.
The easiest way to diagnose a benign neoplasm, which has a pronounced character. This is especially true for hygromas, which stand out well under the skin.
To make sure that a child has a hygroma and not another neoplasm, the following research methods will be required:
- Ultrasound examination of soft tissues and the tumor itself.
- Radiography.
- Tumor puncture and histological examination.
These diagnostic methods make it possible to visually examine the hygroma and examine its contents.
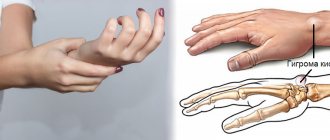
Hygroma on a child's hand
Hygroma in a child can occur on different parts of the body, most often on the arm or leg. In many cases, the hygroma is located on the back of the hand. It is a compacted formation resulting from the filling of some tissues with fluid. This tumor most often develops from the joint capsule, less often from the tendons. Pediatrics does not have clear explanations for the reasons for the appearance of such neoplasms in children. The tumor can be the result of an untreated hand injury, inflammation of the joint, systematic physical activity, as well as a hereditary predisposition.
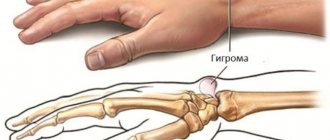
Hygroma on a child’s hand is mainly localized on the palm or back of the wrist. This is essentially a cyst with a cavity containing a gelatinous mass. Over time, this mass accumulates, forming a compaction that can be easily felt when pressed. Sometimes a hygroma appears on the flexor muscles of the child’s fingers (finger hygroma).
By its nature, hygroma in a child differs from other tumor-like formations - atheroma, lipoma, fibroma, and never develops into a malignant form. Quite often, cyst-like lumps appear in the area of the child’s wrist joint. As a rule, this process occurs due to a fracture, frequent impacts or dislocation of the radius, as well as as a result of improper treatment of injuries of this kind.
In any case, if a hygroma is detected on a child’s hand, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor in order to promptly begin treatment of the disease.
Treatment of hygroma in children
Therapy is selected based on where the lump is located, the patient’s age and other factors
Benign neoplasms in children must be treated, as the famous pediatrician Komarovsky has repeatedly said. The treatment option directly depends on the location and size of the tumor.
Conservative therapy
Conservative treatment is offered to children whose hygroma reaches a small size. In such circumstances, surgery can be avoided.
If the cyst does not cause inconvenience or pain, then there is a chance of its successful resorption. To do this, it is enough to use topical medications that help slow down the growth of hygroma.
The treatment option for a benign neoplasm is selected based on the indications identified in the child. The location of the cyst and the age of the patient are also taken into account.
It often happens that hygroma grows due to intense physical activity that is applied to the diseased joint. In this case, the problem can be dealt with by easing constant pressure on the affected area.
If there is no need for surgical removal of the hygroma, then it will be enough for the child to undergo a course of treatment with medications. For this disease, local medications that are used to treat the affected area are relevant.
If the hygroma does not exceed 3 cm in volume, then ointments will help eliminate it. Preference should be given to local drugs that have anti-inflammatory, analgesic and disinfecting effects.
The doctor must warn the patient's parents that conservative therapy does not guarantee the absence of relapse of the disease. In 80% of cases, hygroma appears again.
In some cases, doctors recommend agreeing to drug therapy, which is combined with puncture. This is the name of a medical procedure that allows you to remove the contents of a tumor using an endoscope and a needle. At the end of the therapy session, it is necessary to treat the tissues with an antiseptic and antibacterial agent to prevent them from becoming infected.
Surgery
The most effective treatment method is radical removal of the hygroma. At the moment, there are three main options for eliminating benign neoplasms in children:
- Puncture.
- Surgical excision.
- Endoscopic removal.
The most accessible method of radical treatment is surgical excision of the hygroma. This treatment option is prescribed if the child has appropriate indications:
- Large tumor size.
- Rapid growth of the cyst.
- Cosmetic discomfort.
- Pain when touching the cyst.
- No signs of tumor shrinkage within 2 years.
- Limited mobility of the hygroma.
- Relapse of pathology.
- Development of inflammation.
Puncture is considered the most painless. During this procedure, fluid is removed from the hygroma. The capsule itself is practically not damaged. Agents that belong to the group of sclerosing and anti-inflammatory agents are introduced into the empty cavity. Unfortunately, this treatment option does not provide such a pronounced effect as surgery.
A modern method for removing hygroma in a patient of a younger age group is endoscopic therapy. With its help, it is possible to eliminate the tumor. To do this, you will need to make a small incision in the skin, which will not injure adjacent tissues that are not affected by pathology.
At the time of surgical excision, the tumor is removed along with its contents. This method of treatment gives excellent results if the doctor does not make mistakes during the operation.
Radical therapy is carried out mainly under general anesthesia. Doctors may suggest local anesthesia if the child is over 10 years old. The surgical intervention takes no more than 30 minutes. After this, the patient should be under constant supervision of a specialist for a couple of hours.
Treatment with folk remedies
The prepared ointment should be used only warm
Not all parents welcome traditional treatment methods. Some of them try to cure their child with the help of folk remedies made from natural ingredients.
Experts allow the use of unconventional means in the treatment of hygroma. But their list must be consistent with them. The doctor should make sure that the traditional method is safe and appropriate and only then include it in the course of therapy.
You can try to partially cure hygroma with the help of such unconventional remedies that are offered by traditional medicine:
- Cabbage juice. To prepare it you will need a head of fresh cabbage. The vegetable must be twisted using a meat grinder to make a paste. The mass is carefully squeezed through cheesecloth to obtain juice. It is recommended to drink 1/3 glass before main meals. This course of treatment should be followed for a month.
- Tea mushroom. An effective remedy in the fight against benign neoplasms. The natural product must be applied to the affected area, in this case, to the area where the hygroma is localized. Additionally, the mushroom is fixed with a bandage. Regular use of this folk remedy can speed up the process of tumor resorption.
- Cabbage-honey mixture. It has a pronounced antitumor effect. To speed up recovery, you need to apply a cabbage leaf to the hygroma, onto which a portion of natural honey has previously been applied. The finished compress is kept on the joint throughout the night.
- Honey and aloe. Based on these components, you can prepare an effective remedy against hygroma, approved for children. Products must be mixed together in equal proportions. You should also add a little rye flour to the general mixture. The end result should be a mass that resembles dough in consistency and appearance. A small cake is formed from it, which is applied to the sore spot for the whole night. It is best to fix the folk remedy with cellophane and a warm cloth, for example, a woolen scarf.
- Copper plate. Oddly enough, this product helps in the treatment of hygroma in young children. You will need a plate with a diameter of 2-3 cm. It should be applied to a benign tumor and fixed with a regular bandage. You can remove the compress only after 3 days. The used plate is burned with fire, washed thoroughly and applied again to the hygroma for the same period.
The folk recipes listed above have been time-tested. They are safe for the child’s health and at the same time allow you to get good results. You just need to remember that the positive effect of alternative treatment is achieved only when combined with modern methods of therapy.
Conservative treatment
At the initial stage, treatment of the ganglion can be conservative.
Observation . Because a ganglion is a non-tumorous growth that may disappear over time, if it's not bothering you in any way, your doctor may suggest that you just keep an eye on it to make sure there's nothing unusual going on with it.
Immobilization . Ganglia often increase in size with physical activity, which can put pressure on nerves and cause pain. Immobilization of the wrist joint can relieve these symptoms and reduce the size of the ganglion. After pain relief, the doctor may recommend a set of exercises aimed at strengthening muscles and restoring range of motion.
Puncture and aspiration of contents . If the ganglion is the source of severe pain and limitation of movement, fluid from the ganglion can be removed. This procedure is called aspiration.
The skin around the ganglion is numbed with local anesthetic, the cyst is punctured with a needle and the fluid is removed with a syringe.
Aspiration usually brings only a temporary effect, since the “root” of the cyst or its connection with the joint or tendon sheath does not disappear. The ganglion in this respect resembles a pesky weed that constantly grows back because its root remains in the ground. Therefore, after aspiration, the ganglion appears again in many cases.
Aspiration is most often performed for ganglia located on the dorsum of the wrist.
During aspiration, the fluid filling the cyst is removed.
Surgery
If conservative measures do not cure the problem, your doctor may recommend surgical treatment. The operation involves excision of the ganglion.
Together with the ganglion or hygroma, a part of the altered joint capsule or tendon sheath, which is the root of the cyst, is usually removed. However, even after complete removal of the ganglion, there is a small chance that it will form again.
Excision of a cyst or hygroma is usually an outpatient operation, i.e. patients go home on the day of surgery after a short period of observation in the recovery room. After the operation, you may experience some pain and discomfort, and there may be some degree of swelling in the area of the operation. You will be able to return to normal physical activity 2-6 weeks after surgery.
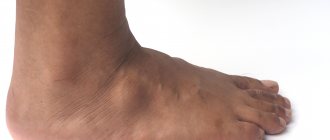
Hygroma under the knee in a child
Hygroma in a child is a kind of cystic formation that suddenly appears in different parts of the body, including on the leg, namely? under the knee. In modern medicine, such a tumor is called a “Becker cyst.”
Visually, hygroma under the knee in a child appears in the form of a dense subcutaneous lump-shaped tumor localized in the upper part of the popliteal fossa. Such a tumor is characterized by a slight displacement of the convexity to the inside of the knee. As a rule, the occurrence of a Becker cyst in a child is not associated with any specific disease of the knee joint. Most likely, the development of such a pathology is provoked by physical activity, as well as excessive mobility of the child, or a knee injury. However, medicine currently does not know the exact causes of this disease.
Localization of the tumor under the knee causes a number of negative symptoms in the child, primarily? compression of the neurovascular bundle, resulting in trophic disorders, pain, and paresthesia. In addition, cosmetic defects occur, and if the disease is neglected, complications such as inflammation of the joints are possible. Therefore, at the first detection of a hygroma under the knee in a child, it is necessary to consult a doctor in order to decide on further treatment.
Hygroma of the foot in a child
Often, active games cause various injuries in children, in particular, severe bruises, dislocations of the foot or fingers. As a result of such injuries, hygroma of the child’s foot may occur. Mostly this tumor develops on the back of the phalangeal bones or in the ankle area. It develops very quickly, while causing discomfort to the child while walking.
Acute pain syndrome is associated with hygroma of the foot, since the tumor is localized near the nerve endings. The child complains of pain and refuses to wear shoes. In addition, in this case, there is a risk of injury when wearing tight shoes: the tumor increases and provokes compression of blood vessels and nerve endings. Injury to foot hygroma leads to the development of an inflammatory process, so the tumor must be removed as quickly as possible, otherwise a pathological exacerbation of the disease is possible.
Hygroma in a child that occurs in the foot area is treated conservatively and through surgery. The first method of treatment is to crush the hygroma or pump out its puncture. It is marked by recurrent manifestations of the disease due to the complete preservation of the capsule producing synovial fluid. Surgical treatment of foot hygroma includes excision or laser removal of the tumor. A successful operation aimed at complete excision of the hygroma capsule significantly reduces the number of recurrent manifestations.
Pediatricians do not recommend treating hygroma in a child at home. Indications for complete tumor removal are factors such as cosmetic defects, rapid tumor growth, discomfort and severe pain, and the development of complications in the form of suppuration, swelling and inflammation.