The hard base of the foot consists of several small bones connected to each other by many small ligaments. Each of them contains a huge amount of collagen fibers, tightly intertwined. Inflammation of one or more of these ligaments is called ligamentitis. The process can be either unilateral (affecting one leg) or bilateral. Ligamentitis should never be confused with tendinitis. These are completely different diseases that affect completely different structures of the foot. With tendonitis, the tendons, the collagen formations that attach muscles to bones, become inflamed. Plantar fascia ligamentitis is also called plantar fasciitis. With this pathology, the plantar aponeurosis is affected - a long ligament connecting the heel bone to the base of the phalanges of the lower limb. This pathology is the most common type of foot ligamentitis. You can read more about this disease here.
Causes
This disease can be infectious or non-infectious in nature. In the first case, inflammation develops due to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the tissues of the foot, in the second - due to the influence of other provoking factors. The most common causes of ligamentitis:
- recent foot injuries;
- regular foot injury from uncomfortable shoes;
- increased load on the lower limbs;
- inflammatory processes in nearby joints and/or soft tissues of the foot.
Most often, ligamentitis affects people who have to spend a lot of time on their feet or in an uncomfortable position. The risk group includes builders, masons, welders, and professional athletes. People whose relatives also suffered from diseases of the musculoskeletal system are especially susceptible to the disease. Congenital defects in the development of the ligamentous apparatus play a certain role in the etiology of the disease. Ligamentitis can be caused by:
- vascular diseases;
- gout;
- diabetes,
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- thyroid diseases;
- heavy load on the legs during pregnancy.
Symptoms
Painful sensations are usually localized over the inflamed ligament.
The most characteristic sign of ligamentitis is pain that increases with walking and various movements. Most often, painful sensations are localized directly at the site of inflammation of the ligaments, but occasionally the pain can radiate to neighboring areas of the foot. As a rule, a sore leg prevents a person from walking normally and causes him a lot of discomfort. Possible symptoms of ligamentitis:
- the appearance of mild swelling at the site of inflammation;
- feeling of numbness in the foot area;
- increased sensitivity;
- limited mobility of the joint next to which the inflamed ligament is located;
- increased pain after prolonged immobility.
Causes and symptoms of ligamentosis
The disease can be provoked by a number of factors, in particular, constant and repeated microtraumas,
which can occur during intense sports activities or as a result of heavy physical exertion. The cause of the development of the disease can also be chronic degenerative diseases (we can mention, for example, deforming osteoarthritis) or old joint injuries.
In this case, it is difficult to identify any specific symptoms. The main and most striking manifestation of ligamentosis is severe and acute pain.
in the area of the affected ligament. You can also identify secondary symptoms, such as progressive swelling of the soft tissues in the area of damage to the ligaments and joints.
Diagnostics
What does ligament inflammation look like on an MRI?
Diagnosis and treatment of the disease is carried out by orthopedists and traumatologists. At the very beginning, the doctor talks and examines the patient. During the conversation, he finds out whether the person has suffered any trauma, whether he has serious systemic diseases or possible risk factors. After this, the specialist prescribes the necessary studies:
- Radiography. Allows you to see changes in bones or salt deposits in tissues. This method is of great importance in the differential diagnosis of heel spurs.
- Ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging. With their help, you can see the localization of the pathological process. It should be noted that inflamed ligaments are best seen on MRI, but this research method is much more expensive than ultrasound.
- Laboratory research methods. Necessary to determine the cause of ligamentitis. They make it possible to identify infectious processes in the body, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, diabetes and other diseases that lead to damage to the ligamentous apparatus of the foot.
Diagnosis of pathology
The procedure is performed by two doctors: a traumatologist
and
an orthopedist
. Diagnosis of ligamentosis is based on the results of studies such as ultrasound of the affected joints, MRI of ligaments and joints in the pathological area, and radiography. These research methods help the doctor to visualize all structural changes in the ligaments, determine the places of ossification and the zone of deposition of calcium salts.
Using the above diagnostic procedures, diseases that caused ligamentosis or developed after this lesion are identified. It is important for a specialist to assess the consequences of permanent trauma to the joint and adjacent tissues, as well as the degree of progression of the pathology.
Treatment
After conducting the necessary examination, the doctor makes a final diagnosis and prescribes the necessary treatment to the person. First of all, he tries to remove the cause of the disease. That is, if the ligaments are inflamed due to arthritis or gout, he prescribes medications that treat these diseases. Immobilization (immobilization) of the affected leg is of great importance in the fight against ligamentitis. If a person is unable to remain in bed for several days, he can use special orthopedic devices. Prolonged rest makes you feel better and speeds up recovery.
Conservative
The basis of conservative treatment is immobilization of the diseased limb for a period of at least two weeks. Some physiotherapy treatments are prescribed to combat pain and inflammation. Paraffin and ozokerite applications, phonophoresis, ultrasound and shock wave therapy are quite effective. The following drugs are used to treat ligamentitis:
- ointments based on NSAIDs and corticosteroids (Diclofenac, Hydrocortisone ointment);
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of tablets and injections;
- PRP method is the use of enriched autologous human platelet plasma.
Recently, the PRP technique has become increasingly popular. It allows you to quickly relieve pain and reduce the activity of inflammatory processes. Autologous plasma has a pronounced analgesic, wound healing and anti-inflammatory effect.
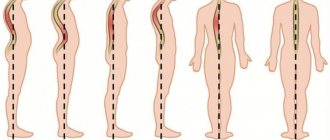
A disease that can immobilize is ligamentosis of the lumbar spine
The danger of this chronic ligament disease is that it progresses, and ultimately leads to loss of mobility of the joints and spine. Usually the disease is detected in older people, but it begins much earlier and, as a rule, without pronounced symptoms.
So what kind of disease is ligamentosis?
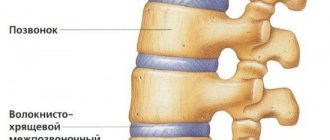
Changes begin in the places where the ligaments of the spinal column attach to the bones. Gradually, as a result of intense loads or microtraumas of the joints, the connective tissue of the ligaments in these places begins to degenerate into cartilage. Subsequent changes lead to the fact that the entire ligament is replaced by bone tissue, and this area loses mobility.
Most often, this disease manifests itself in the knee and ankle joints, but the most serious consequences are caused by ankylosing ligamentosis, a serious disease of the spine.
Why does this spinal disease occur?
The reasons for the appearance of foci of ossification in the ligaments of the spinal column have not yet been precisely established, although the disease has been studied for more than half a century.
The main reasons are:
- excessive stress on tendons and ligaments (this can be intense or prolonged physical exercise, carrying heavy objects, excess weight);
- frequent spinal injuries and their unsuccessful treatment;
- long-term stay in a cast;
- osteoarthritis;
- spondyloarthrosis;
- spondylosis;
- disruption of the endocrine system (in particular, diabetes mellitus);
- the presence of long-term inflammatory diseases (purulent otitis media, tonsillitis, tuberculosis and other infections).
What happens as a result of the development of the disease?
Usually the process begins with the thoracic spine. At first, the painful sensations are absent, or appear periodically, many patients do not even notice it.
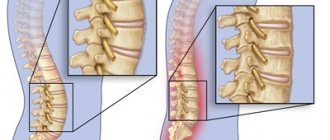
Further changes spread to the cervical region, then to the lumbar region. In this case, calcium salts are deposited in the anterior longitudinal ligament, which is usually elastic. But over time, with this pathology, it is replaced by bone, calcifies, and begins to fuse with the vertebrae. Growths appear that envelop the spinal disc. Then this process can spread to the posterior longitudinal ligament. These growths have different shapes: in the form of spurs, spikes or fringes. When they completely fuse together, the spinal column finally loses mobility.
Patients complain that it is difficult for them to bend or turn, especially in the morning or evening, when fatigue has accumulated. The mobility of the spine is significantly limited.
The difficulty of diagnosis is that many diseases have similar manifestations. And older people generally consider stiffness in movements to be ordinary signs of old age, and, most often, do not consult a doctor.
X-rays begin to show signs of the disease only 10-15 years after its onset, when the changes are already irreversible.
X-rays show areas of ossification (degeneration of cartilage into bone tissue). In the later stages of the disease, the lumbar region has a continuous strip of damage, since the inflammatory process finally changes the state of the ligaments, causing them to ossify.
Therapy: how can we help the patient?
This disease of the spine
has been studied since the mid-20th century, and there are no specific treatments for this disease. Conservative methods are usually used. All of them are aimed at relieving pain, slowing down degenerative processes and maintaining spinal mobility.
To alleviate the condition, there are several treatment options that are combined with each other:
- Symptomatic therapy - NSAIDs. For example: Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Indomethacin, Nimesulide. A good effect is achieved with the combined use of these drugs in tablets and external therapy.
- Applications of anti-inflammatory ointments: Dolgit, Fastum, Voltaren, Nise, and others.
- Chondroprotectors: Alflutop, Teraflex, Dona and others. With prolonged course use, these drugs protect cartilage tissue, stop their further destruction, and prevent complications.
- Pentoxifylline, Eufillin, Curantil - help increase the blood supply to the affected areas of the spine.
- Mexidol or Actovegin can be used to normalize the metabolic process.
- Compress with Dimexide for effective pain relief in painful areas.
- Magnetic and laser treatment.
- Aquatherapy.
- Therapeutic gymnastics, restorative massage.
- Reflexology.
- Diet.
- Folk remedies.
The pain syndrome is relieved by local administration of glucocorticosteroid and anesthetic drugs, therapeutic puncture of articular joints, and applications with NSAIDs.
Of course, degenerative processes with ligamentosis are considered irreversible, but with the help of properly selected treatment it is quite possible to prolong physical activity and save a patient who is at risk of complete loss of motor activity.
Physiotherapy options
Physiotherapy, like traditional medicine, must necessarily complement traditional methods of treatment, because this improves blood circulation in damaged areas of the spine and slows down the process of its destruction.
Thermal procedures and balneotherapy help relieve pain and restore mobility.
The most commonly prescribed ultraphonophoresis is hydrocortisone. Shock wave therapy sessions, magnetic therapy, and laser therapy are effective. There will also be a positive effect from radon or hydrogen sulfide baths, acupuncture, and shock wave therapy sessions. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr