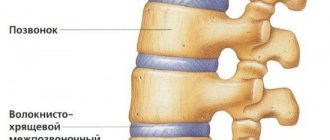
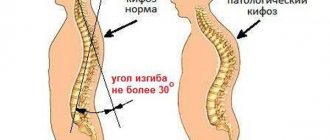
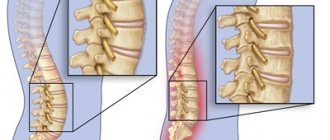
Spondylolisthesis is a spinal condition in which one vertebra is displaced horizontally relative to the underlying vertebra. The most common case is listhesis of the lumbar spine; listhesis of the cervical spine is less common and almost never of the thoracic spine. Complex cases require surgery. Important! Any manual therapy techniques are contraindicated and dangerous to health.
There are a huge number of reasons for such displacements, but the most important thing with listhesis is maintaining the stability of the spinal segments. A specially designed exercise program is aimed at strengthening the deep muscles of the back and abdomen. Do not start exercising without first consulting your doctor!
To rehabilitate the cervical spine, you need to use Exercises to strengthen the neck muscles.
To increase blood circulation and eliminate muscle blocks, it is recommended to undergo 3-5 sessions of massage and muscle stretching from a qualified specialist.
Clothes should be loose, it is advisable to remove shoes. Perform all exercises (especially the first days) smoothly and gradually. Remember the important principle: “Endure mild pain, do not allow severe pain.”
Do these exercises daily for at least 2 weeks.
Beetle movement
Lying on your back, legs bent at the knees, arms along the body.
Tighten your abdominal muscles. While maintaining tension, lift one bent leg a few centimeters from the floor and hold it for 5 seconds, then lower it. Repeat the exercise with the second leg. Then raise your arm above your head and hold it for 5 seconds. Then lower and repeat the exercise with the other hand. Repeat 5 times with each arm and leg. As soon as the exercise ceases to be difficult for you, begin to lift your leg and the opposite arm at the same time. Hold also for 5 seconds. 3 sets of 5 reps on each side.
Diagnosis of the disease
Spondylolisthesis treatment involves long-term treatment, but it cannot be started without certain examinations.
Spondylolisthesis sometimes does not show its symptoms right away. Initially, the specialist talks with the patient, focusing on approximately the following questions:
1. How long ago and after what did back pain occur?
2. What does the pain feel like and is it related to movement?
3. Is there a feeling of numbness in the lower extremities and weakness?
4. Are there any problems with stool and urination?
During the dialogue, the doctor may have additional questions that will coordinate the further treatment plan.
After a conversation and filling out the patient’s information card, he is prescribed to undergo some examinations. Necessary tests to make a diagnosis:
- CBC and general urinalysis;
- two-plane x-ray;
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging);
- EMG of the lower extremities.
You will also need consultations with a vertebrologist (a specialist in dysfunctions of the musculoskeletal system) and a neurologist.
Interpretation of X-ray data:
- a maximum of 25% of the degree of slipping of the vertebral body with the arch - I degree of the disease;
- recorded limits of 26 - 49% - II degree of the disease;
- degree of slipping from 50 to 74% - III degree of pathology;
- indicators from 75% to final displacement - IV degree of the disease.
Separately, it is worth highlighting the most critical parameters, when the vertebrae are completely separated from each other and spondyloptosis is diagnosed.
Twist
Lying on your back, legs bent at the knees, arms along the body. Tightening your abdominal muscles, lift your shoulder blades off the floor and stretch your arms towards your legs. Hold the achieved position for 3 seconds. Do not hold your breath. 2 sets of 15 times. If you clasp your hands behind your head and spread your elbows to the sides, the effectiveness of the exercise increases significantly.
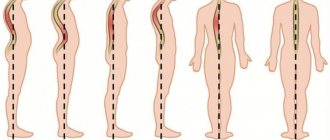
Classification types of pathology
Vertebral spondylolisthesis is divided into four categories: depending on the direction of the shift, the reasons for the formation of the pathology, the position of the person’s body at different moments of his activity and the duration of the disease.
First qualification group (by direction of shift):
- antilisthesis with forward displacement of the spinal column element;
- retrolisthesis with deformation-slipping of the vertebra backwards;
- lateral displacement.
The direction of pathological sliding can also vary, because the shift can occur along an angular or linear trajectory.
Second qualification group (for reasons of pathology):
1. Dysplastic. The reason for the violation of the integrity of the vertebral row is a deviation in the development of the sacral spine or its lower lumbar region. The disease can occur in childhood, causing trouble for a person for many years. The first sign of the dysplastic form is detected by the age of 11-12, and as the 17-year mark approaches, the terminal stage of the pathology begins.
2. Spondylolysis. The main reason for the occurrence of this type of spondylolisthesis is problems of various types with the vertebral arch. The voiced form occurs without age restrictions, but its diagnosis is complicated. The reason for the difficulty in making a medical diagnosis is the unclear clinical picture of the course of the disease.
3. Degenerative. The source of the pathology is overactive mobility of the vertebrae due to destructive joint dysfunctions. Women aged 50+ with existing osteoporosis are most susceptible to degenerative spondylolisthesis. Accompanying diagnoses for this type of vertebral displacement are lordosis and kyphosis.
4. Traumatic. The main provoking factor for such spondylolisthesis is a severe bruise or fracture.
5. Pathological. The reason for its occurrence is a complication of serious joint pathologies with arthrogryposis, Albers-Schönberg and Paget's diseases.
Third classification group (according to the position of the human body):
1. Stable. With this type, during a change of position, the integrity between the displaced and the underlying intact vertebrae is not violated.
2. Unstable. The relationship between the voiced vertebrae changes when the position of the body changes.
Fourth classification group (by disease duration):
1. Lingering. A significant term for the course of spondylolisthesis is due to the fact that it arose due to dysplasia and pathological transformations in the arches.
2. Spicy. This rapid development of the disease is justified, because it is provoked by a serious dislocation, bruise or fracture.
Some tips ↑
You should start doing a set of exercises with just one exercise.
If it does not cause pain, then after about 3-4 days you can try the following.
So, gradually, adding one exercise at a time, perform the entire complex every day.
You should only perform exercises that do not cause pain. If it does occur, then they are not suitable for you and you should choose others.
In order to avoid exacerbation of the disease, it is necessary to observe the correct motor mode, from which carrying heavy objects or at least their even distribution is excluded. You also need to watch your posture.
If cyclic training is necessary, then you should give preference to simple cycling, exercise bike and swimming.
Unlike other sports, they do not cause impact on the vertebrae.
Do not engage in physical therapy or yoga during an exacerbation of the disease.
Physical therapy for spondylolisthesis is not a panacea that will help completely cope with the problem, but it is still the main method of maintaining the spine in normal condition.
To do this, it is necessary to perform a set of exercises for a long time and not let the disease take its course.
Treatment of spondylolisthesis
In many cases, conservative therapy for listhesis is used. It includes:
Relieving tension in the spine (absence of physical activity for a certain time, prohibition on flexion or extension of the spine);
Exercise therapy - thanks to this treatment, the spine becomes mobile, the muscle corset is strengthened;
Drug treatment consists of taking NSAIDs. After a short time, the patient’s inflammation stops and the sensation of pain decreases. In some cases, an epidural steroid is used.
For isthmic spondylolisthesis, it is advisable to use a special corset.
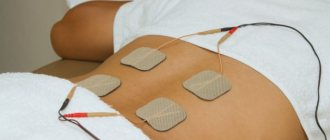
Physiotherapy reduces pain, eliminates swelling and inflammation.
Surgical therapy is indicated for grade 3-5 listhesis, as well as the presence of severe neurological symptoms. These treatment methods are aimed at strengthening the vertebrae and reducing pressure on the spinal structures.
Symptoms and possible consequences
Displacement of a vertebra leads to consequences such as spinal deformation, narrowing of the spinal canal, and compression of the nerve roots. Such consequences of spinal displacement cause pain in a person, which intensifies after physical exercise, in particular, stretching exercises for the lumbar region. In addition to pain in the lower back, symptoms of spondylolisthesis include tightness and stiffness in the lower back, and tightness in the hamstrings. A person experiences a change in posture, weakness and increased fatigue, and dysfunction of internal organs, which quickly becomes chronic.
If, as a result of a slipping vertebra, compression of the nerve occurs, the patient feels numbness, weakness in the legs, and tingling. The development of the disease leads to complications such as loss of bowel and bladder control - these symptoms require immediate treatment, as they greatly complicate life activities.
A set of effective exercises
The lesson plan is usually drawn up by a physical therapy methodologist. It determines what exercises can be done, the volume of load and the number of approaches, as well as the duration of the course. This takes into account the patient’s age, the main factor in the development of the disease and the severity of the lesion.
Gymnastics for spondylolisthesis of the lumbosacral spine involves, at the first stage of exercise, movements at a moderate pace and with a small amplitude in order to avoid pain.
Why is exercise therapy so necessary?
Physical therapy remains the main method to help stop the development of spondylisthesis. It is impossible to completely correct mechanical damage to the vertebra, but strengthening the muscular system will ensure a healthy physical shape and prevent possible complications of the disease from appearing.
Exercise to help stretch the spine
A complex of exercise therapy performed for spondylolisthesis actively helps to reduce the unnatural curvature of the spine. Strong abdominal and back muscles can maintain an even posture for a long time. With even fixation by the muscles of the spine, further displacement of the vertebrae and a negative effect on the nervous system are prevented.
Prevention of spondylolisthesis
The development of spondylolisthesis cannot be completely excluded. Some physical exercises increase the load on the spine, thereby increasing the likelihood of the disease.
Spondylolisthesis is a disease that requires immediate medical attention. If initial symptoms of the disease are detected, treatment should not be delayed. Only timely therapy will avoid adverse consequences in the development of the disease. The doctor will be able to prescribe a complex treatment method to the patient only after conducting the necessary medical examination.
Wearing a corset
To prevent damage to the lumbar region after surgery, special corsets are worn. They are also prescribed to patients who are getting rid of the problem using a conservative treatment method.
Types of orthopedic structures based on rigidity:
1. Hard. The ribs of the structure are made of plastic or metal. The purpose of rigid corsets is to use them after surgery in the spinal column and for the need to undergo rehabilitation after a serious injury. The design is necessary to fix the body in a position in which displacement of damaged vertebrae is impossible. When used, the rehabilitation period is significantly reduced.
2. Semi-rigid. In this case, we are talking about protecting a sore back for people whose work activity involves either sedentary work or physical activity. This risk group includes athletes, loaders, office workers, programmers and drivers. An additional advantage of a semi-rigid corset is the ability to warm and relax the back muscles.
3. Elastic. It can be called a lightweight version of semi-rigid corsets. The functions of such a bandage are to reduce pain in the back and relax its muscles.
Types of orthopedic structures by location on the body:
1. Lumbar. This is the shortest model of all corsets because it covers and protects only the top of the pelvis, the bottom of the chest and the lower back.
2. Thoracolumbar. You can purchase a semi-rigid or rigid version of this design. It is most suitable for people after spinal surgery due to the shift of its components.
3. Lumbosacral. This model implies the presence of a back wall and is suitable for people from the already mentioned professional risk group.
Tips for choosing a corset after the doctor has determined its model:
1. Selection of material. The fiber of the belt should not cause skin rashes. You should check in advance if you are allergic to a particular material, because in some cases you will have to wear the corset for quite a long time.
2. Product quality assessment. The product must have high-quality ribs and fasteners without any defects.
3. Fit to size. The presence of a dynamic fixation in a corset is not a reason to buy an orthopedic product that will press or will not ultimately support your back in the desired fixed position.
When choosing a size, you should remember that for different manufacturing companies such an indicator as M means different parameters. In this case, a measuring tape will come to the rescue, which you should stock up on before visiting a specialized store.
The corset is worn no more than ¼ of the day, and taken off at night. The general term for its use is prescribed by the doctor.