Spondyloarthrosis of the cervical spine
Spondyloarthrosis of the thoracic spine
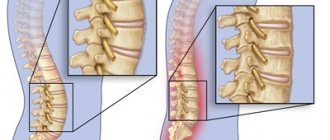
Spondyloarthrosis of the lumbar spine
A pathology such as sponidloarthrosis is one of the forms of osteoarthrosis, which is characterized by degenerative-dystrophic changes in the structures of the facet joint of the spine:
- capsules;
- ligaments;
- joint surface;
- cartilage;
- periarticular muscles;
- bones.
Signs of spondyloarthrosis in the vast majority (up to 90%) of cases appear in people over the age of 60 years. However, the pathology can also be found in young people over the age of 25.
Timely treatment of spondyloarthrosis in a multidisciplinary CELT clinic will provide the desired results and allow you not to give up your usual lifestyle.
Causes
Spondyloarthrosis of the spine can occur due to various reasons:
- spinal injuries, in particular - subluxation in its joints;
- spondylolisthesis;
- abnormalities of the spine;
- osteochondrosis;
- vertebral instability;
- constant intense loads on the spine.
Risk groups susceptible to this disease include:
- elderly people over 60 years of age;
- obese people;
- women after menopause;
- persons genetically predisposed to spinal pathologies;
- patients suffering from diabetes.
Treatment of spondyloarthrosis at SL Clinic
To prevent spondyloarthrosis from causing the development of irreversible complications, it is necessary to diagnose it as early as possible and take measures to stop the process of joint destruction. SL Clinic specialists will help you do this as soon as possible.
The clinic has the best equipment, with which we can quickly conduct a comprehensive examination of the patient and accurately determine the cause of the pain syndrome. The spinal surgeons at our clinic will be able to eliminate it in the most gentle way possible. The high professionalism of surgeons allows us to carry out the most complex operations with a high success rate and achieve a significant improvement in the condition of patients. With our help, hundreds of patients returned to a full life and forever forgot about stiffness of movement and discomfort in the back.
Don't put off taking care of your health until later. Sign up for a consultation at SL Clinic right now.
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms of spondyloarthrosis depend on which part of the spine the pathology is in.
Cervicoarthrosis
Spondyloarthrosis in the cervical spine is called cervicoarthrosis. Its clinical manifestations include the following:
- pain of a constant, aching, shooting nature, localized in the neck and radiating to the occipital, scapular, shoulder regions, as well as to the upper extremities;
- limited movement when tilting and turning the head;
- crunching in the joints of the neck;
- noise in ears.
Treatment of the disease
If you suspect this disease, you should contact a rheumatologist or neurologist, who will tell you how to treat spondyloarthrosis. Treatment of the disease can be divided into several points:
- elimination of pain in the spine;
- destruction of the initial causes of pain;
- normalization of the correct position of the back.
For this purpose, medications are used, as well as other methods:
- Muscle relaxants (Tizanidine, Tolperisone), injections with these drugs will give the best result in reducing muscle tone. They will help relieve tightness in the back and release nerve endings from tight muscles.
- Non-steroidal (Meloxicam, Ibuprofen, Ketonal, Nalgesin - these drugs are used with Omeprazole).
- Local therapy includes creams, ointments, gels (Fastum-gel, Ketonal, Viprosal, Capsicam), which have an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Multivitamins, minerals.
- Using a semi-rigid corset and an orthopedic pillow or mattress (an incorrectly selected pillow or mattress can cause spinal disorders and pain).
After getting rid of the acute stage, it is necessary to treat spondyloarthrosis of the lumbar spine using the following physiotherapeutic methods:
Massage is the most common way to treat the back
Massaging movements can restore the general condition of the patient and reduce signs of pathology. Physical therapy is a fairly important part of therapy. It helps strengthen the muscle corset and restore the spine. Acupuncture - when metal needles are applied to active points, metabolic processes are stimulated and the functioning of internal organs is improved
Acupuncture can eliminate the root of the problem. Spinal traction is used to prevent compression of the vertebrae and regenerate their correct position. Manual therapy is carried out only by a specialist; it helps improve blood circulation and correct the position of the vertebrae. Magnetic therapy – treatment occurs under the influence of magnetic waves on the spine. This procedure will remove inflammation in the pathological area, reduce swelling and pain. Electrophoresis is therapy under the influence of ions, drugs are delivered to the damaged area of the spine. Initially, ions penetrate the skin, then into the body. Surgery is performed if other methods are ineffective and the symptoms of the disease increase. The operation is also possible when a person is paralyzed and lacks mobility. This condition can lead to disability.
Spondyloarthrosis is a rather unpleasant pathology that leads to dangerous consequences (disability, paralysis). To prevent this, you should walk outside more often, move more, and eat right. But, if you still experience back pain, you do not need to self-medicate, but it is better to consult a specialist in time.
Dorsarthrosis
Spondyloarthrosis in the thoracic spine is called dorsartosis. Its symptoms include the following:
- pain localized in the thoracic spine, which initially occurs periodically, but as the disease develops, it becomes permanent;
- a feeling of discomfort and the appearance of aching pain with an increased level of humidity;
- feeling of stiffness in the morning;
- atrophy of the spinal muscles;
- the appearance of a crunch when making sudden movements.
Diagnose spondyloarthrosis
The diagnosis of spondyloarthrosis is made based on a combination of clinical and instrumental data.
X-ray of the spine in direct and lateral projections allows you to diagnose changes in the facet joints, the presence of degenerative changes in the area of the articulation of the ribs to the spine in the thoracic region, the condition of the spinous and transverse processes in the lumbar region, sacroiliac joints, and the presence of osteophytes.
MRI (CT) allows you to visualize not only morphological changes in bone tissue (as with radiography), but also detect changes in soft tissues, the presence of compression of nerve structures, and changes in intervertebral discs.
Radioisotope scanning allows you to diagnose the inflammatory process in the facet joints.
Ultrasound of cerebral vessels is necessary when it is necessary to exclude vertebral artery syndrome.
How is spondyloarthrosis determined on an x-ray?
Before sending the patient for an x-ray, the doctor conducts a preliminary survey, finds out exactly when the pain occurs, where, how often, how quickly it goes away, and how it affects normal movements. The patient also undergoes a thorough examination, palpating the spine, and identifying pain in certain positions. It is impossible to make a definitive diagnosis during an initial visit to a doctor. To confirm or refute the diagnosis, the patient is sent for an x-ray.
The first stage of the disease is not always visible on an x-ray. The joint space and joint height are not so severely deformed. Therefore, the patient is asked to take positions in which the spine is extended and bent. This is the only way to see how correctly the vertebrae lie. If the image shows white areas on the surface of the joints, this indicates a change in the size of the bone tissue.
Polysegmental spondyloarthrosis of the 2nd degree is especially clearly visible on the x-ray:
- The size of the joint space is quite small;
- The connective tissue in the peripheral part of the epiphysis has grown, and grade 2 spondylosis develops;
- Growths appeared on the surface of the affected area of the spine, the length of the process increased;
- The size of the gap and the shape of the holes between the vertebrae were deformed;
- The vertebrae are displaced by about five millimeters.
In this case, for a more accurate diagnosis, a research method using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is used. This method also uses X-rays, but the affected area itself is scanned using a multi-slice detector. The result is a separate image of each layer, the thickness of which can be controlled.
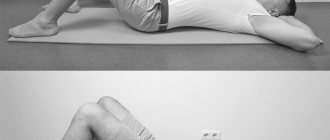
Exercises for the cervical region
Exercise therapy for the cervical region is intended for people who are familiar with the feeling of stiffness in the neck and slight dizziness when moving their head. You cannot work on this part of the body at a time of exacerbation of pain and severe swelling. When you have uncovertebral arthrosis, you need to do exercises especially carefully, gently and calmly, avoiding sudden movements and jerks. This complex is also often recommended for osteochondrosis of the corresponding localization.
- Clasp both hands in your fingers. Place the inside of your palms on your forehead. Perform pressure for 5-7 seconds with the frontal surface on the palm, while creating a strong barrier with them, as if preventing the head from moving forward. You should feel the back of your neck muscles tighten. Number of repetitions – 3-5 times.
- Now we do the same, but from the back of the head. That is, we apply a closed lock of hands to the back of the head, and apply backward pressure with the head. We create a reliable barrier with our hands, not allowing our head to lean back even a millimeter.
- Now we place one palm on the side of the head and carry out the same resistance to the movement of the head, but to the side. We carry out similar actions on the opposite side. For all recommendations on time and frequency of repetitions, see exercise. No. 1.
- Slowly lower your head down, trying to reach the jugular fossa with your chin. Pause after reaching your destination for a few seconds, then calmly return back, while throwing your head back to the maximum you can. Don't force anything! Repeat the exercise 5 times.
- Press your chin to the front wall of your neck. Make turns to the right and left in this position (slowly!). The total number of turns is 10 times. It is also recommended to make regular right-hand and left-hand turns 5 times on each side, keeping your head level. But make sure it doesn't fall down and keep your shoulders straight.
- Tilt your head back, lower it towards your shoulder, trying to touch it with your ear. Do this on the right and left sides for a total of 10 exercises.
It is very important that your physical recovery takes place under the watchful supervision of a professional exercise instructor, orthopedist and physiotherapist. You can’t just take the first example of exercise you come across from the Internet and start doing it; physical therapy is prescribed by a doctor! Along with exercise therapy, the patient’s balanced diet plays a leading role, which will help compensate for mineral and vitamin deficiencies and reduce body weight.
In addition, keep in mind that you are advised to undergo treatment in sanatorium medical institutions 1-2 times a year. Within the Russian Federation, sanatoriums in Karelia have proven themselves well, offering a wide range of procedures for high-quality restoration of the musculoskeletal system.
Medicines
Photo: qtxasset.com
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (meloxicam, ibuprofen) are prescribed to relieve the inflammatory component and for pain relief. The most common side effects include:
- allergic reactions due to individual intolerance;
- dyspeptic disorders in the form of nausea, heartburn, belching;
- erosions and ulcers of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract.
It is important to note that it is not recommended to combine painkillers with each other, since the simultaneous use of 2 or 3 drugs from the NSAID group significantly increases the risk of developing peptic ulcers.
If long-term use of NSAIDs is necessary, drugs that protect the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract (omeprazole, lansoprazole, pantoprazole) are additionally prescribed. A special feature of these drugs is their ability to prevent the formation of duodenal ulcers, but, as a rule, they are ineffective against gastric ulcers.
In case of severe pain syndrome, when NSAIDs do not help either in the form of tablets or in the form of injection, narcotic analgesics are used to help. These drugs are prescribed exclusively by a doctor and not for a long period of time to prevent the development of addiction.
Muscle relaxants are used for spondyloarthrosis to reduce muscle spasm, thereby helping to reduce the severity of pain. In addition, muscle relaxants are able to influence nerve endings and thereby prevent the appearance of pain impulses, which also underlies the reduction of pain.
Chondroprotectors are used to slow down the degeneration of cartilage tissue. Alflutop is one of the representatives of drugs in this group. Prevents the destruction of macromolecular structures of normal tissues, stimulates the processes of restoration of articular cartilage tissue. Its anti-inflammatory effect, as well as the ability to regenerate tissue, are based on inhibition of hyaluronidase activity and normalization of hyaluronic acid synthesis, which underlies the restoration of cartilage tissue. Side effects are rare.
B vitamins (neurobex neo, borivit) are used to generally strengthen the body and improve the conduction of nerve impulses along the fibers. Well tolerated; in rare cases, minor side effects may develop. A contraindication for use is individual intolerance to the drug, which manifests itself as an allergic reaction.
Medical Scientific and Practical Center for Vertebrology and Neuroorthopedics, Professor M.L. Kurganov
Spondyloarthrosis or facet arthropathy is a process of aging of intervertebral joints , during which their anatomy, shape and function changes. The development of the process and the time it begins depends on many factors, which will be discussed below. The facet joints between the vertebrae age and change with age, just like any other joint in the body. This process is called arthrosis. Only the prefix before the term ... arthrosis - determines which particular joint of the body we are talking about. If it is GON arthrosis, then it concerns the knee joint, if it is COX arthrosis, then it is the hip joint, but if it is SPONDYLO arthrosis, then it is arthrosis of the joints between the vertebrae.
Anatomy and mechanisms of spondyloarthrosis.
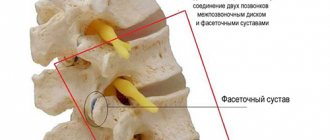
Two adjacent vertebrae connect to each other in several ways.
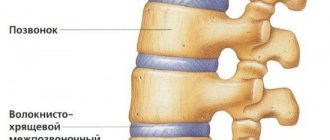
- Connection using intervertebral joints (facets). Their spatial position contributes to the inclination of the vertebrae relative to each other in all directions within a certain physiological volume. Thanks to this, the spine as a whole bends in all directions. But the wedge-shaped position of the joint planes does not allow adjacent vertebrae to move forward, backward, left or right. I draw your attention to this important point!
- Connection using intervertebral discs . As you know, these are “spacers” between the vertebrae. They act as vertical shock absorbers of the spine during movements. It is thanks to the presence of water inside the disk (in the core) that the necessary pressure in it and its height are maintained. If the amount of water in the disk decreases and it “dries out,” then its height decreases. The pressure along the vertical axis on the intervertebral joints increases. This is one of the causes of spondyloarthrosis. We need to dispel the myth about disks “falling out”. The disc cannot fall out - there is NO WHERE! It is very firmly fused with the bone platforms of two adjacent vertebrae! It is bounded on all sides by the most powerful anterior and posterior longitudinal ligaments!
- Connection using a powerful ligamentous apparatus . Movements between the vertebrae are limited by the ligamentous apparatus to a physiological extent. The ligaments are stretched between the spinous processes, the transverse processes of the vertebrae. Moreover, the entire spine is covered in front and on the sides, like a cover, by the anterior longitudinal ligament, similar to a capsule or spacesuit for the spine. It is interesting because it is the only ligament in the body that acts as periosteum. This will be important for understanding the process called spinal spondylosis. There is also another important ligament - the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine. It lines the spinal canal from the inside, protecting the spinal cord from damage by the intervertebral disc during shock-absorbing deformations.
- Connection using many deep tonic muscles . The worm-shaped deep tonic muscles of the back weave around the entire spinal column on the sides and back. They, as it were, fasten all the vertebrae together with their tension so that they become an integral structure - the spine. These muscles also provide a vertical position in space at rest and help during movement, which is provided by other muscles - superficial, related to dynamic ones. Deep muscles do not obey our will and work automatically at the level of spinal cord reflexes. Superficial muscles - obey the human consciousness and control body movements. But they do not affect the static position in space and do not counteract gravity. This is important for understanding the need to perform certain exercises in each specific case.
Let's return to the intervertebral joints . Each joint in the body has its own joint capsule. A durable articular capsule forms a sealed sac filled with synovial fluid around the articular processes. Its function is to moisturize and nourish articular cartilage and reduce friction between contacting surfaces. It is thanks to the joint capsule that the fluid that nourishes the articular cartilage is synthesized.
The life of a joint from the birth of a person until his death can be compared to the life of a tree leaf . When a joint is young, the articular cartilage and joint capsule are elastic, tender and growing. A lot of joint fluid means the joint grows. The range of motion of the joint is increased. That's why children are so flexible and active. When a person reaches a certain age, growth stops and a phase of stable joint function begins. This age is individual and depends on genetic factors given by the parents. Namely, the composition of cartilage and connective tissue, which determines the volume of physiological movements in the joints and overall flexibility. Someone at 25 years old can reach the floor with their elbows, while others can’t even reach their fingertips. Both cases are normal. And not just a norm, but a physiological individual norm. This only says one thing. A person who has a worse bending ability has less elasticity of the ligaments and articular capsules of the joints, and possibly less secretion of joint fluid - lubricant. Often such people early experience audible clicking sounds in their joints when moving. This applies not only to intervertebral joints, but also to all other joints. After all, connective tissue and cartilage tissue are the same throughout the body. It is these people who most often have joints that “dry out” earlier and the range of motion in the joints becomes limited early.
The intervertebral disc is of great importance . If you have taken the time to read the information above, then you understand that the amount of water inside the intervertebral disc can be indirectly judged by the elasticity of the joints. The more elastic the connective tissue and ligaments of the spine, the more movements there are and the more intense the exchange of water in the intervertebral disc. By the way, at the peak of human development, the water inside the disk changes once every 10 minutes. Over the years, this time increases significantly, and the intensity of disc hydration (the amount of water inside the disc) decreases. At the same time, its height and elasticity decrease, it flattens, and the vertical load on the intervertebral joints increases.
And here the process of aging of joints begins - arthrosis . Namely spondyloarthrosis. The axial load on the joint is greater, and the amount of joint fluid - lubricant - is less. The cartilage of the joint does not receive enough nutrition for restoration processes and its surface gradually becomes dull and thinner. This is often accompanied by a shift of one surface of the joint relative to the other. The shift occurs due to an increase in the vertical load on the joint when the intervertebral disc subsides during a sudden movement or lifting of weight. The disc cannot cushion during movement. It doesn't have enough pressure. This stretches the joint capsule, which contains many different receptors, namely stretch receptors. To prevent the capsule from being damaged during sudden movement and stretching, the surrounding muscles sharply spasm (strain) and, as it were, “slam”, fixing the joint in a shifted, incorrect position. We doctors call this a functional block of the intervertebral joint. So, there is less fluid in the joint, it is “dry”, and under axial load it is shifted, fixed and devoid of movement! Where there is no movement, there is no life. Try squeezing your two fingers together... What will happen? The blood will be squeezed out of the fingers and the tissues will no longer receive nutrition. After 2 hours, tissue necrosis will begin. To prevent this from happening, you need to unclench your fingers and restore blood circulation. Now let's apply this knowledge to joints. If there is no joint fluid (like blood) and no movement (compression), what should be done? But more on treatment below.
We are closer to understanding what happens in the intervertebral joint and the spine as a whole as we “grow up.” The joint and intervertebral disc dry out, the elasticity of the ligaments decreases, the range of movements between the vertebrae decreases. Then the joints between the vertebrae can become blocked and stop moving altogether in some overloaded areas. At the same time, the muscles tense and fix the joint. Popularly called - BACKBACK (due to sharp pain at the moment of blocking).
And if at this moment we did not seek help, then the acute period of pain will pass after taking pills or ointment. But immobility of the joints of the spine in any affected area will remain. Other segments of the spine and joints will take on the work of their “lost” counterpart. And this is very important! Because in segments of the spine that are overloaded with work, instability (looseness) occurs, which, in my opinion, is an even greater problem than arthrosis of the joints. It is still possible to restore movement in the joints by seeking help IN TIME! But it is extremely difficult to prohibit excess movement when the cervical or lumbar spine is unstable. And the clinical picture with instability of the cervical spine... – you wouldn’t wish it on your enemy!!!
But let’s say we didn’t ask for help - there was no time . The joints between the vertebrae were blocked and frozen without movement. Just as iron rusts, a joint “rusts” without movement. The muscles fix the joint, as in our example we squeezed our fingers. Pressure on the cartilage surfaces prevents them from properly nourishing and recovering. The surface of the articular cartilage is damaged. In case of disorders of mineral metabolism in general or disorders of uric acid metabolism (which is almost inevitable with age), salt metabolites are deposited in the form of crystals on the surface of the cartilage, causing its inflammation. And the inflammatory process further damages joint tissue due to inflammatory mediators. In many cases, with a long-term chronic course of this process, an autoimmune component is also added. This means that joint tissues damaged and modified by inflammation become foreign to the body. The body does not recognize them as its own, and begins to fight them as foreign and hostile cells. But this process can also be fought. About the treatment below.
A real fire begins in the joints . Add to this fire age-related osteoporosis, in which all the bones and the bony part of the joint become less solid. There is not enough calcium in the bone tissue and it begins to deform under load (we usually get fatter with age). Now let's remember that the planes of location of the articular spaces of the intervertebral joints are of great importance for the correct position of one vertebra in relation to another. When joint deformation begins with osteoporosis, the process becomes deforming spondyloarthrosis. The joint changes spatial position. As the process progresses and there is no medical assistance, a serious complication may occur - spondylolisthesis (vertebral slippage). This problem can only be solved quickly. But, if the patient is old, then what kind of surgery can we talk about? It is necessary to resolve the issue with periodic maintenance treatment.
Symptoms of spondyloarthrosis: With spondyloarthrosis of the spine, patients are bothered by back pain of a predominantly constant aching nature, somewhat varying in intensity, intensifying with load, turning and bending . Sometimes, with prolonged exercise or the presence of a complication - spondylolisthesis, the pain becomes burning due to overstrain of the muscles in this area. The pain is usually localized and, unlike pain caused by a herniated disc, does not radiate to the leg or arm. Not accompanied by numbness and weakness. However, the proliferation of bone tissue in the area of the intervertebral joints with the progression of arthrosis can contribute to the formation of osteophytes, which can lead to the development of spinal canal stenosis and compression of the nerve roots. If this process affects the lumbar region, then symptoms of sciatica (sciatica) may appear, such as pain, numbness and weakness in the leg. This is often caused by concomitant piriformis syndrome.
From all of the above, we can conclude that spondyloarthrosis is rarely the only process leading to back pain . This is always a complex of changes in the structure and physiology of the spine. In the majority of patients who have even mild symptoms of spondyloarthrosis, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans reveal significant degenerative changes in the facet joints and their deformation. To confirm the diagnosis, a diagnostic and treatment procedure is performed: for this purpose, a powerful anti-inflammatory drug is injected into the periarticular tissues once. A significant reduction in pain in the back, lower back or neck after micropharmacopuncture confirms the diagnosis of spondyloarthrosis (facet arthropathy).
Principles of treatment of spondyloarthrosis.
In practice, the patient seeks help at best at the 2nd stage of spondyloarthrosis. At worst - at stage 3. Already with an autoimmune component or complication - spondylolisthesis. In this case, I would like to say... - “Where were you before, when it was still possible to put out this fire and repair your joints, support them in time?”
With timely treatment - at the stage of joint blocking:
Manual correction of blocked intervertebral joints is performed 2 times over 7-10 days. A therapeutic massage is prescribed. Not the kind of massage that leaves bruises and causes pain with persuasion, “This is how it should be, be patient, but then it will be good!” The massage is stretching, myofascial, deep, but gently and gradually penetrating, without bruising or pain. This will help remove the muscular fixation of the vertebrae blocked in movements and prevent re-blocking, relaxing tense muscles. If the doctor detects indirect signs of a decrease in the amount of joint fluid, a decrease in the height of the intervertebral discs, or an increase in cases of blocking of the intervertebral joints, it is recommended to perform an MRI examination of the affected parts of the spine. This will make it possible to qualitatively and reliably determine the degree and stage of the process of disc dehydration in order to adequately prescribe a dose of chondroprotective treatment. This is an important point. Such treatment will lead to an increase in the amount of water in the discs and unloading of the intervertebral joints along the vertical axis. This way the blocking will not happen again. This is a comprehensive and intelligent approach to treatment.
If subsequently a person undergoes preventive examinations by a vertebrologist on time and, if necessary, takes treatment and preventive measures recommended by a specialist, then a good functional state of the spine, even with genetic nuances, will be ensured for a long time.
What if the process has gone further and spondyloarthrosis has already reached the 2nd or 3rd stage ?
In this case, starting with manual correction is like kicking down a locked door. There is reactive inflammation in the joints! There's a fire in the joints! And in the event of a fire, it is useless to rearrange furniture or repair work. That's why:
- We extinguish the fire using all possible anti-inflammatory agents and preferably using the principles of micropharmacopuncture .
- We protect the cartilage and connective tissue of the joint with chondroprotectors .
- We carry out “cleaning up” after a fire before repairs using proteolytic enzymes - enzyme therapy with Karipain .
- We provide anti-arthrosis treatment and carry out repair work using a course of chondroprotectors.
- If anti-arthrosis and anti-inflammatory treatment is successful, manual correction can be performed to the required extent. At the same time, an impeccable sense of proportion is a MUST!
- If there is an autoimmune process, we send the patient to a spa treatment where radon treatment is carried out. Radon inhibits the immune response of the body as a whole and therefore the inflammatory process in joints affected by arthrosis decreases or subsides. But not forever, unfortunately. We observe the so-called stable remission for 1-2 years. Then the immune system is restored after small doses of ionizing radiation (this is exactly how radon works) and the process of arthrosis gradually resumes, requiring further action.
The issue of the need for therapeutic massage . Most often, massage is contraindicated for such patients.
The patients themselves say that they tried to help themselves with massage, but aggravation occurred, the pain intensified and the massage was stopped. In my opinion, in the presence of developed spondyloarthrosis, massage, mechanical beds for massage, procedures for traction of the spine in any part, warming up the affected part of the spine are NOT PERFORMED AND NOT RECOMMENDED!
We advise the patient, depending on the degree of neglect of the process, to receive planned, course-based support for the spinal structures, regardless of the presence of pain and discomfort. We don’t wait for a fire, but preventively and with less effort we control the process of spondyloarthrosis.
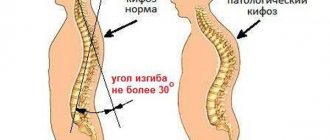
In the fourth stage of spondyloarthrosis , all movements in the affected segments of the spine stop. Ankylosion (immobility and fusion) of the intervertebral joints occurs. Movement in them can no longer be restored. Moreover, it is already very dangerous! The process moves into the next stage - spondylosis. Typically, spondylosis is accompanied by pronounced bone growths produced by the anterior longitudinal ligament. Gradually it changes its structure and becomes ossified. Pain and dysfunction of internal organs, arms and legs arise from the uncontrolled growth of bone tissue, which gradually puts pressure on the nerve roots, closing the holes through which they exit the spine.
The goal of treatment in this case is to strengthen the bone structure in osteoporosis, anti-arthrosis treatment, absorbable procedures, and intermittent anti-inflammatory therapy. Treatment is carried out regularly, as planned. This reduces pain and improves quality of life. The patient can care for himself. Massages are prescribed only during periods of remission in short courses with breaks between procedures individually, with the support of anti-inflammatory drugs. Manual correction is strictly contraindicated.
Which doctor treats spondyloarthrosis?
Most people do not know which doctor to contact for spondyloarthrosis. It all depends on the source and nature of the pain:
- In case of inflammatory and dystrophic nature of joint diseases, you should contact a rheumatologist.
- An orthopedic traumatologist will most fully examine the overall picture of the disease: the root causes or consequences of spondyloarthrosis due to curvature of the spinal column and flat feet.
- If the deformation of the vertebral body has affected the nerve plexuses, a consultation with a neurologist may be required.
At the MART clinic on Vasilyevsky Island
- Experienced doctors (including those practicing in the USA and Europe)
- Prices affordable for everyone
- Expert level diagnostics (MRI, ultrasound, tests)
- Daily 8:00 — 22:00
Make an appointment
Lumbar spondyloarthrosis deformans: description of the disease
The disease occurs with osteochondrosis, and is less often diagnosed as a single pathology. The World Health Organization says that the disease occurs mainly in older people, in 65 percent, and in 20 percent in younger members of the population.
Deforming lumbar spondyloarthrosis has a gradual development. A lot of time passes from the initial to the final stage. This moment plays a big role in the fact that it is possible to make a timely diagnosis and begin timely treatment.
Basic treatment methods
In most cases, when this is not yet an advanced stage, the use of conservative measures is possible in grades 1-2. No matter how strange it may be, the leading role in this pathological development is given to non-medicinal therapy - exercise therapy, therapeutic massage, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, exposure to folk remedies. Naturally, in the initial stages, such methods are the most effective; you can even get by with just this, without using painkillers or non-steroidal drugs.
If pain is still present, painkillers are prescribed - Panadol, Ibuprofen. When diagnosing inflammation, a course of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Diclofenac, Nimesulide - will be required. They are prescribed for oral administration and topical use. When symptoms are accompanied by spasms, it is advisable to use muscle relaxants, the most popular are Mydocalm, Traumeel S, Baclofen. Also, recently the use of chondroprotectors has been actively recommended - drugs that inhibit the process of destruction of cartilage tissue. At the last stages of the process, when the manifestations are pronounced and cannot be stopped with standard drugs, novocaine blockades are performed.
If the above methods are not effective enough, then radiofrequency destruction of nerve endings is recommended. This is a modern technique for destroying nerves, thereby eliminating pain. The procedure lasts no more than 30 minutes and local anesthesia is used.
In some cases, when the deforming process becomes pronounced, more radical methods are needed - surgical intervention. Surgery remains the only option when other methods do not provide the desired result. In particular, the operation is extremely important for young people. The procedure involves installing special implants; in neurosurgery they are called interspinous spoilers.
If we talk about prognoses, they are quite favorable, however, subject to adequate influence and compliance with all doctor’s recommendations, including if surgical therapy is necessary. As a rule, if such conditions are met, it is quite possible to restore the motor activity of the spine and relieve pain, and most importantly, stop the pathological course.
We advise you to study: Marginal osteophytes of vertebral bodies
https://youtube.com/watch?v=h2rgawEcw9I
During treatment, manual therapy is often prescribed or recommended. This is a very good method in the initial stages of the development of spondyloarthritis, when the symptoms and signs are more moderate.
Therefore, it is important to pay attention to the specialist you contact. If the manipulations are performed by an unqualified doctor, simply “anyone”, there is an extremely high risk of not only being left without the necessary therapeutic effect, but also of earning a lot of complications.