Treatment of foot arthritis, symptoms and detailed photos
The development of foot arthritis occurs when there are changes in the synovial fluid (the elastic mass that fills the joint cavity and protects the joint from damage), as well as when inflammation develops in it.
If inflammation occurs in one of the joints of the foot (subtalar, talocaleonavicular, calcaneal-cuboid or sphenavicular), the volume of synovial fluid in the articular joint increases significantly. It begins to compress the synovial membrane, and that, in turn, due to the presence of a large number of nerve endings, begins to respond almost instantly with an inflammatory reaction.
Causes
The causes are divided into primary, which arose due to direct damage to the joint, and secondary - from complications of concomitant somatic diseases. The primary causes of foot arthritis include:
- injuries;
- anatomical deformations of the foot, an example is a disease such as flat feet;
- weakened immune system;
- hard physical work;
- pregnancy;
- hypothermia.
The last four reasons are not only the causes of arthritis. But also factors that aggravate its course and contribute to the development of complications. Secondary causes of foot arthritis:
- Infections. They can be either specific (tuberculosis, syphilis, gonorrhea), which is characterized by damage to the joints by microorganisms, or nonspecific (streptococcus, pneumococcus), which causes purulent arthritis.
- Rheumatoid arthritis. This type is due to its autoimmune nature. This disease is very difficult to treat, as it tends to recur. The body's struggle with its own cartilage tissue can be provoked by the patient having flat-valgus feet, excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages, and excess nicotine.
- Psoriasis lesions. One of the stages of manifestation of this chronic disease is psoriatic arthritis, which affects the joints of the hands and small joints of the feet.
- Gouty arthritis can be caused by a metabolic disorder, due to which excess uric acid salts settle in the joint cavity of the big toe. The disease is characterized by suddenness and acute attacks of pain, which block movement and paralyze the usual way of life of the affected person.
Many factors can be avoided by treating your health correctly and leading a healthy lifestyle. Timely consultation with a doctor can prevent the development of the disease.
General symptoms of arthrosis
- freezing feet (a symptom of poor circulation in the lower extremities);
- “crunching” while driving;
- “ache” due to the weather;
- discomfort and limited joint mobility when walking;
- aching pain, which can be replaced by sharp pain;
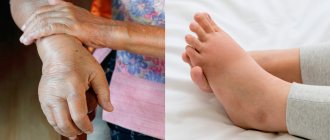
- swelling and hyperemia around the inflamed joint;
- painful calluses in areas of primary stress;
- Heberden's nodes (tumors the size of a pea at the level of the interphalangeal joints of the foot; can periodically rupture);
- deformation and destruction of joints (especially the thumb).
This is a common set of symptoms. The full picture of arthrosis can only be described taking into account one or another stage of the disease.
Symptoms of Foot Arthritis
As a rule, patients come to the clinic after the onset of stage 2 arthritis, when the disease begins to affect the quality of life. In this case, the symptoms of foot arthritis can be divided into two main groups: specific and nonspecific (see photo).
Specific signs characteristic exclusively of such a disease as arthritis of the joints of the foot:
- stiffness of movement in the morning;
- inflammation is one of the signs of foot arthritis
- severe pain in the foot area;
- valgus changes in the feet;
- multiple lesions (with an infectious nature of the disease);
- rash and hyperemia.
Nonspecific symptoms are characteristic of a number of different conditions, including arthritis:
- violation of joint functions;
- specific, crunching sound when moving;
- acute pain;
- swelling and redness;
- general intoxication: weakness, chills, increased body temperature, lack of appetite.
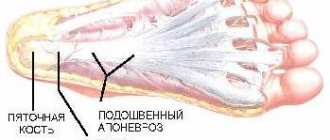
What joints are affected by arthrosis of the feet?
- metatarsal bones of the foot;
- phalanges of the toes;
- tarsal joints;
- heel bone.
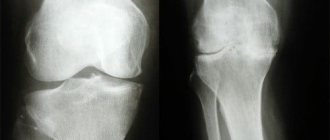
Radiographs show arthrosis of the ankle joint.
You should know!
Most often, the disease affects the joint of the big toe, so patients can notice a characteristic “nomad gait” when, when moving, the main burden is transferred to the outer part of the foot.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of arthritis in most cases does not cause difficulties - the characteristic external signs are striking, and the patient’s complaints do not raise any doubts in this regard.
It can be much more difficult to identify the cause of foot arthritis and the degree of movement disorders. The severity of inflammation can be indirectly judged by the number and changes in leukocytes in a routine general blood test. In this regard, rheumatic tests and blood tests for C-reactive protein are more informative.
The severity of movement disorders is indicated by specific functional tests. Among the instrumental methods, computer and magnetic resonance imaging are used. However, radiography of the foot in 3 projections is still effective. Diagnostics of internal organs (heart, lungs, gastrointestinal tract, kidneys) is mandatory.
How to treat foot arthritis?
For each type of foot arthritis, specific treatment regimens are used to combat the catalysts of inflammation. However, there is a standard course of treatment for this disease, including:
- Nonsteroidal drugs. The ankle joint is subject to constant increased load. Therefore, the inflammatory process immediately affects the patient’s mobility: the leg swells and the slightest movements can cause a severe attack of pain.
- Antibiotics. Acute arthritis begins suddenly, usually with a sharp increase in body temperature. The patient experiences chills, severe fatigue, and pain. It is almost impossible to relieve pain using improvised means. In its acute form, the pathology is best treated. To begin with, a course of antibiotics is prescribed.
- Heel arthritis is especially painful. With arthritis, shooting pains are observed in the heel, which can radiate throughout the leg. Heel arthritis can appear as a consequence of flat feet. To relieve swelling and swelling, NSAIDs are prescribed. The course of therapy ranges from 7 to 10 days.
- If, after completing the course, it hurts the patient to step on his foot, corticosteroids are additionally used. Relief occurs after 2-3 injections.
- Specific drugs. Treatment for post-traumatic ankle arthritis may require a course of medications to repair damaged muscles and tendons.
- Gout requires the use of medications that help remove uric acid.
- Ointments for rheumatoid arthritis have a local analgesic effect. Ointments gently warm the tissues and help reduce swelling. The ointment must be used carefully. The ointment only relieves symptoms, but does not eliminate the cause of inflammation.
- Rheumatoid arthritis of the top of the foot and small joints requires the use of medications that block the immune system.
- Chondroprotectors are used as restorative therapy. Chondroprotectors are especially effective at the initial stage of disease development.
If symptoms are severe, drug blockade may be required. The blockade brings relief from pain after the first injections, provided that the therapist conducting the injection is highly qualified.
Stages of damage
1st stage. The feet often react to changes in weather with aching joints; joint mobility is impaired, aching pain appears. In the absence of stress, it can be asymptomatic for a long time.
2nd stage . Pain occurs more often, intensifying as the disease progresses. The first metatarsophalangeal joint becomes inflamed and increases in size, which leaves its mark on the gait and tightens the requirements for wearing shoes.
3rd stage. Pain becomes a constant companion. The level of deformity of the joint limits the movement of the foot. The thumb curls and moves down. Degenerative processes spread to soft tissue and bone, depriving the patient of the ability to move freely.
Additional therapy measures
In the acute phase of the disease, a plaster splint may be applied. Auxiliary methods of treating the disease are:
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- special gymnastics;
- massage;
- mud therapy;
- amplipulse therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- Hirudotherapy is used in case of metabolic disorders.
- Wearing special shoes also gives positive results.
In advanced stages of arthritis, surgical intervention may be required: arthroplasty or joint replacement. If there is significant deformation of the thumb, resection is advisable.
During the acute period of the disease, it is necessary to reduce the load on the damaged joint as much as possible and apply a fixing bandage to avoid an increase in the inflamed area.
Treatment
Treatment of arthritis is aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease and risk factors that contribute to the development of inflammation, relieving symptoms, improving metabolism in the affected joint, and preserving its function.
This can be achieved through the use of medications, physiotherapy, physical therapy and massage. In advanced cases, with purulent processes, dislocations and subluxations, surgical intervention may be required. If the joint is completely destroyed, it can be replaced with an artificial one - endoprosthetics.
Conservative therapy, depending on the form of arthritis, includes the use of tablets, ointments and injections of various groups of drugs:
- antibiotics for bacterial infections;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and hormones;
- chondroprotectors – agents that improve the quality of joint tissue;
- painkillers;
- vitamins, microelements and amino acids.
Author:
Pugonina Tatyana Alekseevna, Therapist
Exercise therapy
Treatment of foot joint disease is impossible without performing a set of physical exercises. This point is a prerequisite in any therapeutic regimen for arthritis. For the treatment of foot joints, the complex is selected individually.
However, there are several universal exercises that can be performed by everyone without exception:
- It is performed lying on your back with your arms and legs extended. Then you need to raise your legs and try to stretch your toes as far as possible. After that, lower your legs back, and only then stop stretching them.
- Sit on a hill, such as a table. Lower your legs down and stretch your toes, trying to reach the floor with them.
- Bend and straighten your toes.
- Lie on the floor, but on your side. Move the extended leg to the side and return it back.
You need to start training during the period of remission of the disease, so as not to provoke increased inflammation. For the first time, it is best to train under medical supervision, so that the doctor makes sure that the patient is performing all the exercises correctly.
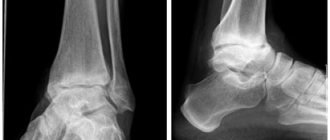
What is ankle arthritis?
Ankle arthritis is inflammation of the joint without previous injury. It occurs mainly against the background of other diseases or as a result of infection. The latter include dangerous types, such as purulent, the treatment of which may require surgical intervention.
Although the vast majority of arthritis sufferers are elderly, young people and even children are often affected. To prescribe the correct treatment, a thorough diagnosis and an established diagnosis according to ICD 10 are necessary.
Folk remedies
A lot of traditional medicine recipes for the treatment of foot arthritis have been accumulated, but any of them can only be considered as a useful addition to the main therapy prescribed by the doctor.
- Mix approximately 100 ml of the juice of one lemon with 50 ml of hot water, moisten multi-layer gauze and apply to the joint overnight, fixing the compress with cling film and putting a woolen sock over it;
- Mix ground equal parts of radish, turnip and horseradish leaves and rub the resulting mixture on the affected area. Repeat the procedure for 7 days.
- Apply a mixture of warm sea salt with a few drops of fir essential oil to a joint heated in a warm bath, wrap the foot in gauze, film and also insulate it with a sock.
- Measure out 100 g of finely chopped cinquefoil, pour in 1 liter of vodka and leave to steep for two weeks. Take the resulting mixture one tablespoon at a time, be sure to dilute it with a small amount of water. In addition, you can apply liquid in the form of a compress to joints damaged by arthritis. After the tincture runs out, take a break of 30 days before the next course.
- Cabbage compress. Cut a washed cabbage leaf to release the juice, wrap the painful, inflamed area, and bandage it. Change the cabbage after an hour (or earlier), when the juice is absorbed and the leaf becomes dry and warm. Harmless, proven product.
The prognosis depends on the degree of neglect of the disease, as well as the correctness of the chosen course of therapy. If it was possible to start treatment in a timely manner, the prognosis is generally favorable. If the joints are severely inflamed and a serious deformity of the feet has developed, then the treatment will be very painful and may not lead to the desired effect - there is a risk of lameness, gait disturbance and even disability.
Post-traumatic arthritis: causes, mechanism of development
The cause of post-traumatic arthritis is damage to the joint, as well as periarticular tissues - muscles, ligaments, tendons, bones, blood vessels, nerves. The cartilage itself suffers quite rarely due to its deep location, but nearby foci of inflammation affect the density and thickness of hyaline cartilage and the rate of its wear.
Due to inflammation and swelling after a joint injury, tissue conductivity deteriorates, nutrients do not enter the joint, and innervation is observed. As a result, the cartilaginous lining of the joint loses its elasticity, and wear of the supporting surfaces appears (at first, in the form of foci of erosion). Since cartilage no longer absorbs the shock, vibration and pressure that our bones experience from walking and other stress, the heads of the subchondral bones, which were not designed for this, take on them.
The body's attempts to compensate for the degeneration of cartilage tissue lead to subchondral osteosclerosis (thickening of bone tissue) and ischemia (insufficient blood supply to the affected area).
At the same time, along the edges of the joint, around its supporting surfaces, there is a growth of cartilage and bone tissue, and the appearance of protrusions - osteophytes. This process blocks the joint and impairs its mobility.
Damage may occur due to:
- domestic or work injury;
- sports injury;
- injuries sustained in road accidents, animal attacks, etc.;
- surgical intervention, resuscitation and other medical measures
Often, post-traumatic arthritis of joints occurs against the background of bruises, dislocations and subluxations, sprains or ruptures of ligaments, tendons, ruptures or damage to the meniscus. The pathological process is not always triggered by a serious injury - sometimes it can be a series of minor injuries (hit with a hammer, pinched fingers, constantly hurting yourself on the corner of furniture) or a single re-traumatization of an already damaged area (for example, a wrist injured in sports received additional stress during everyday activities) .