An important role in the treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system is played by physical exercises - specially organized for a specific purpose and strictly dosed movements. They are one of the important factors that support the life activity of a healthy person and stimulate restoration and compensatory mechanisms in the body of a sick person, since all adaptive processes are involved through the system of central regulations to ensure homeostasis.
I. P. Pavlov noted that movement is a natural function necessary for human existence, affecting the entire organism and relating “to the main reactive activity of the body.”
Regular exercise creates dominant foci of excitation in the cerebral cortex, which, through the mechanism of negative induction, leads to the suppression of foci of stagnant excitation, i.e. eliminates “pain points”.
Systematic use of physical exercises in the complex treatment of a patient eliminates the negative effects of physical inactivity on the body and has a multifaceted beneficial effect.
Rhythmic contraction and relaxation of skeletal muscles, tension and relaxation of tendons help improve venous outflow, prevent venous stagnation, and normalize microcirculation in tissues.
Physical exercise prevents the development of atrophy and degenerative changes in tissues and organs.
When choosing a physical therapy technique, it is necessary to take into account a number of factors. The nature and severity of the injury, the stage of the pathological process, the physical and mental state of the patient, his physical fitness. A set of exercises must be compiled strictly individually, taking into account the phase of the process.
Physical therapy is an important method of restoring joint function in arthrosis. The use of dosed physical exercises reduces pain, improves joint mobility, reduces muscle tension, increases the tone of weakened muscles, enhances the nutrition of joint tissues, and improves the patient’s functional abilities.
Physical therapy must be carried out taking into account the nature of the joint damage, the stage of the pathological process, and the general condition of the patient. It is advisable to carry out exercise therapy under the supervision of an experienced instructor, or after consulting a specialist. It should be remembered that in our body in general, and in the musculoskeletal system in particular, everything is interconnected. If one joint suffers, this will certainly lead to changes primarily in the spine and adjacent joints. Therefore, when prescribing a set of exercises to a patient, it is necessary to take these changes into account.
The basic principle of physical education for arthrosis is physical education in the pain-free zone
Otherwise, muscle spasms, painful contractures, spasms of blood vessels, overexcitation of the nervous system develop, and the general condition worsens.
Gymnastics therapy
Effective treatment with exercises begins with a set of exercises. When choosing the optimal option, focus on the sensations both in the foot and in the ankle and knee joints. Consultation with your doctor will help you make a choice in favor of those exercises that correspond to your age, severity of the disease and other individual characteristics.
A few of the most common foot exercises:
- Stretch your legs while lying down. Bend your toes and bring them back. Do it 10 times.
- Without changing your position, make circular movements with your feet clockwise and back. Repeat 10 times in each direction.
- Also in a lying position, bend your knees and place your heels on the floor. Now bend and straighten your legs at the ankles. The number of repetitions is 10-20 times.
- Sit on a chair. Press your toes into the floor first, then your heels. Perform 20 - 30 times.
- Without getting up from the chair, make circular movements with your heel (toes remain on the surface).
- In a sitting position, cross your legs and rotate your feet, first clockwise 10 times, then counterclockwise the same amount.
- Also while sitting, place your toes on the floor and lift your feet up. Quantity 20 - 30 times.
- Perform squats without lifting your heels off the floor. 10 to 20 repetitions.
- Stand on one leg. Bend the other one at the knee, lift it and bring it forward slightly. Stay in this position for about five seconds and return to the starting position. Repeat 10 times with each leg.
On a note. Physical therapy for foot arthrosis should include, among other things, exercises aimed at strengthening the ankle and knee joints. Everything in the body is interconnected, and the condition can only be improved by approaching the problem holistically.
Calf muscle strain
Stand at arm's length from a wall or other fixed support. Hold onto the wall with one hand. Bend the leg you are working on at the knee, and grab its toe with your free hand. Pull your toe toward your heel until you feel a stretch in the front of your shin. Hold the stretch for 15-30 seconds. Repeat 3 times.
Doctor Bubnovsky's technique
Arthrosis requires an integrated approach to solving the problem. The program of one of the most famous doctors, S.M. Bubnovsky, is based on this. He carefully studied the effects of gymnastics on the body with arthrosis and developed his own system not only for the treatment, but also for the prevention of this pathology.
Bubnovsky exercises are a set of exercises aimed at strengthening joints and improving overall health. The essence of the technique is the activation of restoration processes in the human body. The main thing is to come to a strong muscle corset, which will protect sore joints from stress.
General recommendations
In order for the complex to really bring benefits, you must follow certain advice from the doctor:
- start the exercises with a light massage or just stroking - this will prepare the joints and muscles for the load;
- perform therapeutic exercises, starting with a few seconds and gradually increasing the time;
- be sure to drink a lot of water during training - the amount is regulated only by your desire;
- do gymnastics regularly;
- watch your breathing - it should be deep, in rhythm with your movements;
- Complete your workout with stretching to reduce pain after performing gymnastics.
Complex for feet
The exercises are aimed at improving the condition of joints, activating metabolic processes in cartilage, and strengthening muscles:
- Make circular movements with your foot counterclockwise and back.
- Lying on your back (arms and legs not bent), extend your big toe away from you, then toward you. Repeat 10 times.
- Bring your big toes together, then spread them apart as hard as you can.
- Squeeze your toes, then open them as much as possible.
- Bend your knees, straighten (the soles slide along the surface, the heel should touch the buttocks when bending).
- Get on your knees (back straight). Slowly lower yourself onto your heels and sit down. The total duration of the exercise can be up to five minutes. If at the initial stage it is difficult to perform, then place a cushion under your knees.
On a note. Any gymnastic complex does not guarantee an immediate effect. To get results, you need to exercise regularly and listen to your body.
Basic exercises in a lying position
At the initial stage of exercise therapy, it is recommended to perform simple exercises in which the load on the joint is minimal. A suitable option is exercises in the “lying” position:
- Lie on your back. Stretch your legs forward and your arms along your body. Relax your body completely. Make circular movements with your feet to the left. Repeat 5-10 times, then rest for 30 seconds and do a second approach, but in the other direction.
- Stay in the same position. Develop your big toes: bring them together and spread them to the maximum possible distance. Alternate between bending and extending all your fingers. Perform 10 repetitions for each exercise, repeat 2 times.
- Lying on your back, pull your feet up one at a time - first pull your toes towards you, then in the opposite direction. Perform 10 repetitions on each leg. Rest and do the 2nd set.
- Bend your knees. Slowly lift your left leg, gently pull it towards your chest and return it to its place. Repeat 10 times on each leg.
- Sit on a low (about 30 cm) bench, chair or edge of the bed. Extend your legs completely, pressing your feet to the floor. In this position, lift each leg in turn, imitating actions similar to normal walking. Repeat 10 times. Do 2 sets.
On the first day, perform the complex once. If there is no muscle pain the next day, exercise twice a day: in the morning and in the evening.
Massage as an additional method of improving condition
Massage is an especially necessary and important procedure for poor blood circulation in the tissues. It helps activate metabolic processes, improves overall muscle tone and, as a result, alleviates the condition of arthrosis. Spend 5-10 minutes on your feet before going to bed. First apply a light massage cream to clean skin and follow these steps:
- stroking and rubbing, starting from the fingertips, moving to the ankle joint;
- finger rotation;
- flexion and extension of toes;
- stroking with light pressure on the sole of the foot, then the top and sides;
- light pats on the heel area.
Prevention of joint diseases
Arthrosis occupies a leading position in joint diseases. The cause of the disease lies in poor blood circulation and lack of tissue nutrition. The best prevention is walking barefoot on uneven natural surfaces: stones, sand, grass.
Other preventative measures include:
- massage mats - used when it is not possible to walk barefoot on grass or sand;
- a balanced diet rich in substances necessary for joints;
- walks in the open air;
- daily gymnastics.
These activities will help maintain healthy legs and the whole body.
Arthrosis of the feet causes a lot of inconvenience and requires mandatory treatment. It is not possible to completely get rid of the disease. Therapeutic exercises and massage will help reduce pain and slow down the process of destruction of cartilage tissue. It is important to follow your doctor’s recommendations and perform a set of exercises regularly.
We also recommend reading:
Osteoarthritis of the foot is a very common disease. It is impossible to fully assess the extent of the disease. Patients turn to doctors when the pain becomes severe. The disease progresses slowly, but leads to irreversible changes in cartilage tissue. Therapeutic gymnastics in the subacute period and in remission improves recovery processes, reduces the need for painkillers and speeds up the patient’s rehabilitation.
The main causes of the disease
Adequate support for the foot is provided by walking on rough surfaces (earth, grass, sand, pebbles, etc.). When walking on a hard and level surface, the spring properties of the arches are lost: the foot flattens, the heel and toes take the wrong position. Violation of the biomechanics of foot movements entails destructive and degenerative changes in all joints of the spine and lower extremities, leading to stagnation of venous blood. Cartilage destruction and joint dysfunction are caused by many factors:
- Congenital or acquired deformities of the joints and bones of the lower extremities.
- Longitudinal and transverse flatfoot.
- Injuries to the lower extremities, such as fractures, bruises, sprains.
- Chronic metabolic diseases: diabetes, gout and others.
- Chronic autoimmune diseases.
Predisposing factors for the development of arthrosis will be:
- Using the wrong shoes. Wearing shoes with high heels or, on the contrary, with too flat soles, poor fixation in the ankles, uncomfortable lasts, non-breathable materials, shoes that are too narrow or, on the contrary, too wide - this is an incomplete list of factors that contribute to cartilage damage.
- Heavy weight. The joints of the lower limb are supporting. Increasing the load on them can lead not only to fatigue, but also to arthrosis.
- Pregnancy. A pregnant woman's weight increases. Due to the fact that the body is weakened, the ligaments lose their elasticity.
- Professions, especially those associated with vibration, hypothermia, may result in occupational injuries.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Excessive sports activities.
- Poor nutrition.
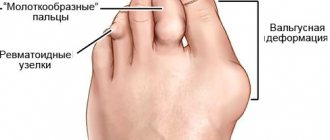
In patients with arthrosis, the disease begins gradually. They may note that there was a period of discomfort in their legs, and then nothing bothered them for a long time. Then there are complaints about the appearance of “foot bunions”, “corns”, Heberden’s nodes (thickenings on the joints), and joint deformation. Poor circulation, trauma and compression of periarticular tissues, muscle spasms cause pain. In advanced cases, the pain becomes constant and bothers you at night due to poor outflow of venous blood.
Treatment of osteoarthritis is complex. Medications (anti-inflammatory, painkillers, chondroprotective) are combined with treatment methods such as a balanced diet, physiotherapy, massage and physical therapy. In cases where joint deformation causes the development of persistent contractures, surgical intervention may be indicated.
Foot surgery
Flat valgus foot
One of the main functions of the foot is to absorb stress when walking and running.
Anatomically, this is solved due to the fact that the foot has the shape of an arch and can flatten under load, softening the blow. In this regard, flat feet are a complex problem, manifested by flattening of the arch of the foot in the transverse and longitudinal direction as a result of changes in the ligamentous-tendon and osteoarticular structures.
The main causes of flat feet include:
- congenital pathology,
- pathology of the posterior tibial tendon,
- inflammatory diseases of the foot joints,
- injuries, surgeries,
- diabetes,
- neuromuscular diseases,
- congenital fusions between the bones of the foot.
In most cases, flat feet are of a so-called “elastic” nature, when the cause is increased mobility of ligaments, joint capsules, tendons, or the structure of the bones themselves, i.e. a congenital condition on which the influence of acquired factors is layered - increased weight, heavy physical activity.
As a result, the musculo-ligamentous apparatus of the foot weakens, its shock-absorbing function decreases, so increased load will be transferred to the ankle joint, hip joint and spinal joints.
The clinical manifestation of the elastic type of flatfoot is the test on tiptoes and when the first toe is extended - in this situation the arch of the foot appears. If during this test the arch of the foot does not form and the heel does not deviate inwards, then a rigid type of flatfoot occurs. Approaches to the treatment of each type of flatfoot have significant differences.
In case of valgus flatfoot in adolescents, when there are no gross compensatory changes in the foot, it is possible to perform a minimally invasive intervention - subtalar arthroereisis (Arthroereisis), when an implant is installed in the subtalar space, blocking the “sliding” of the talus from the heel bone, thereby supporting the medial arch.
A complete cure for flat feet is possible only in childhood; treatment should be comprehensive and aimed at relieving pain, strengthening the muscles and ligaments of the foot, but with the help of rehabilitation measures the development of flat feet can be slowed down. And if the effect of conservative treatment is insufficient, then surgical treatment is necessary.
Pathology of small rays
Pathology of the small rays is the deformation of the small (second to fifth) toes. This condition is the most common reason for visiting an orthopedic doctor; it is most often treated conservatively, however, if the problem persists for a long time, surgical treatment is necessary for a lasting effect.
The main causes of deformation of the small toes are injuries, constitutional features (long second toe), wearing tight shoes, and diseases of the nervous system.
Since the main purpose of the toes is to increase the contact area of the forefoot when the foot is pushed off the surface when walking, stability of the toes is achieved through the plantar fascia. Damage to this connective tissue layer leads to deformities of the small fingers.
There are a large number of types of deformities of the small toes, of which there are hammertoes, clawed toes, mallet toes, elongation, shortening, increase in size, bends in different planes.
The most common deformity, hammertoe , occurs as a result of a rupture of the plantar fascia at the site of attachment to the capsule of the metatarsophalangeal joint, causing the toe to dislocate at the metatarsophalangeal joint.
Clawed toe - most often the cause is a pathology of the nervous system, so several toes on both feet are affected. The difference from a hammertoe is the flexion at the nail phalanx.
Hammer finger deformity occurs due to excessive traction of the flexor finger longus muscle and is a type of hammertoe deformity and is quite easily corrected surgically.
Since the causes of deformation of small rays are varied, treatment should be based on the results of a detailed examination. In particular, hammertoe deformity resulting from hallux valgus should be eliminated simultaneously with the cause. Identification of a clawed toe requires a detailed neurological examination.
Treatment can be conservative or surgical. Often, pain and discomfort can be significantly reduced to the point of disappearance through the selection of shoes, the use of orthotics, and adhesive plaster fixation. Also, conservative treatment of ulcerations and corns precedes the surgical stage of treatment. Surgical treatment includes elimination of the deformity itself and the cause that caused it. After surgery, it will most often be necessary to fix the finger bones with knitting needles in the correct position.
Hollow foot
The basis of the hollow foot is an increase in the arches of the foot, primarily the longitudinal one, and as a result, the arch does not decrease when walking and bends towards the plantar side, especially in the area of the first toe.
The main cause of cavus foot is neurological pathology, because... the basis is muscle imbalance up to the “horsefoot” due to traction of the calf muscle.
With this pathology, conservative measures (orthoses, medications, exercise therapy, massage) help maintain compensation for the disease for a long time, but sooner or later decompensation of the condition occurs when conservative measures no longer help.
When preparing for surgery, the type of deformity (cavus, calcaneal, equinus), elastic or stiff deformity, the degree of neurological impairment, and age are taken into account.
If the deformity is elastic, it is possible to perform joint-saving operations in the form of various osteotomies with subsequent fusion in the required position.
For a stiff type of deformity, arthrodeses of various joints are used.
Since the cause is a neuromuscular imbalance, very often it is necessary to intervene on the tendons, in which case a “strong” tendon is transplanted to a “weak” one, without which there is a high risk of relapse, even if the osteotomy is performed correctly.
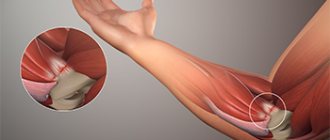
Arthrosis of the ankle joint
The most common type of bone fracture, ankle fractures, results in arthrosis of the ankle joint. This condition is manifested by pain, swelling, and limited movement in the ankle joint.
In the early stages of ankle arthrosis, conservative therapy (orthoses, physiotherapy, drug therapy, including intra-articular) has a good effect, but in advanced cases surgical treatment is required.
For many years, the main treatment method for ankle arthrosis was ankle arthrodesis. The meaning of the method is immobilization (fusion) between the tibia, fibula and talus bones.
As a result of this seemingly simple, but demanding surgical technique, the patient is free from pain for many years. However, the mobility of the ankle joint is sacrificed, and the ability to walk, and in some cases even run, is realized through increased load on adjacent joints, as a result of which the pain syndrome may return.
Therefore, the method of choice for severe arthrosis of the ankle joint is ankle joint replacement. This technology, already a routine practice, although not yet very common, was developed taking into account advances in hip and knee replacement and allows the patient to return to full function of the foot.
More details:
- Ankle arthroscopy
Is it necessary to have surgery?
Conservative methods (selection of shoes, use of insoles, physical therapy, physiotherapy) have their place in the treatment of patients with foot deformities; they bring relief, make the foot more supportable, help to avoid or delay surgery, and in case of surgery, create more favorable conditions. All this allows you to adequately assess the need for surgery and make an informed decision.
What are the features of the operation?
At the present stage, minimally invasive techniques are used, in which access to the operated bones is carried out through punctures up to 0.5 cm under x-ray control. This achieves less trauma to the tissues surrounding the bone, reduces recovery time, and also significantly reduces postoperative pain.
Also, modern anesthetics make it possible to perform operations under peripheral conduction anesthesia, in which only the area of intervention is anesthetized. It also reduces the traumatic effects of anesthesia compared to endotracheal anesthesia and spinal anesthesia.
Unfortunately, in severely advanced cases of the disease open approaches are required, so we recommend that our patients contact us in the early stages of the disease.
What is the guarantee of results after surgery? Will I be able to wear my favorite shoes again?
Successful surgical treatment of foot deformities is associated with adequate selection of the surgical method, adherence to surgical techniques and correct postoperative management.
Taking into account our experience, all this allows us to say that in case of timely and adequate treatment, the patient returns to a full lifestyle, forgets about problems with the feet, and wears ordinary, comfortable shoes.
It is necessary, however, to remember that the foot is a highly loaded part of the body, so there is a possibility of recurrence of deformities, including due to the use of favorite but traumatic shoes, which may have been the cause of the initial deformity.
In this regard, it is necessary to understand that the achieved balance is largely the merit of the patient himself.
Consult with our specialists or request a second medical opinion from an orthopedic traumatologist on the recommendations already received.
Basic principles of physical therapy at home
In order for therapeutic exercises for arthrosis of the foot to be beneficial, follow the basic rules for its implementation:
- Daily and regular execution. Do exercises 2-3 times a day, spend at least 10-15 minutes on it.
- Start with tasks that are simpler and more understandable to you.
- Gradually increase the load.
- Perform movements slowly.
- Watch your breathing, it should be calm.
- Therapeutic exercises are started only after the acute pain syndrome has reduced.
- Perform your first workouts lying down on a hard surface. Then you can begin to perform physical complexes while sitting on a chair. For more complex exercises, gymnastic equipment is used.
- Never do tasks through pain. It is better to reduce the intensity or amplitude of movements, so you will avoid unnecessary tissue trauma.
- Exercise therapy can be supplemented with massage and physiotherapeutic treatment methods.
How to do therapeutic exercises correctly
Like any other treatment method, exercise therapy gives results in cases where the principles of training are not violated.
Doctors recommend following a number of simple rules:
- Increase the load gradually. Start with a small number of approaches and simple exercises. Over time, increase the number of repetitions slightly.
- The goal of gymnastics is to moderate stress on joints and ligaments. Sports training should not cause you significant discomfort. If acute pain occurs, exercise should be stopped immediately.
- Flexibility exercises can be performed only after a warm-up and warm-up complex. If you don't do this, you risk pulling a muscle or tearing a ligament.
- Pay close attention to your breathing while doing the exercises. Take a deep breath at the beginning of the exercise and gradually exhale when finishing. Do gymnastics in a well-ventilated area.
- Choose clothes suitable for sports training. Things should not hinder your movements.
The key to successful therapy with exercise therapy is regular sports training. With light loads, classes can be carried out daily. When the load on the muscles becomes higher, it is recommended to take a short break (1-2 days) so that the muscles have time to recover.
An approximate set of exercises to perform at home
In the initial lying position, the back should be pressed to the floor, the muscles of the neck and back should be relaxed. It is better to perform tasks not in bed, but on a hard surface.
- Legs are bent at the knees. We lift the heel and place the foot on the toe, returning to the starting position, pressing the foot along with the heel to the floor.
- Legs extended. We alternately pull the socks towards and away from ourselves.
- Legs extended. We alternately perform circular movements in the ankles.
- Legs extended. We squeeze our toes as much as possible, as if we are trying to grab something, and then unclench, spreading our fingers.
In the starting position, sitting on a chair, straighten your back and straighten your shoulders.
- Initially, we press our feet to the floor. By alternately raising your heels and toes, we imitate walking.
- We spread our legs shoulder width apart. We tear off the socks from the floor, while keeping the heels firmly pressed to the floor. We repeat the movements, but tear off the heels, the toes remain on the floor.
Osteoarthritis develops in both older and younger people and young children. There are no age-related contraindications to gymnastics. Elderly and old people need to do exercises to prevent the progression of the disease and the development of complications. For children, exercise therapy for the feet is one of the main methods of treatment, since not all medications can be used in pediatrics.
Physical therapy for a child
In children, foot deformities include flat feet and hallux valgus (X-shaped feet). Gymnastics for these pathologies will not only help strengthen the muscles and ligaments of the legs, but will also prevent the development of arthrosis of the feet in the future. It is convenient to conduct classes in a playful way.
For flat feet, it is good to combine training lying on the floor and sitting on a chair with walking alternately on your toes and heels, as well as on an uneven surface (pebbles, sand, ribbed rug).
Below are exercises for hallux valgus in a child (1.5-2 minutes for each set).
Standing
- We rise onto our toes several times and lower ourselves back onto the entire sole.
- We squat with our feet pressed tightly to the floor.
Sitting on a chair
For classes, you need a chair that matches the child’s height and a gymnastic ball with a medium-sized ribbed surface, and you can also use various small objects, rags, and handkerchiefs.
- We put our feet on the ball. Pressing on the ball, we roll it with both feet.
- We squeeze the ball with our feet one by one.
- We stretch our legs forward and use our toes to collect and move small objects. We practice for about 10 minutes.
It is good to supplement the exercises listed above with walking: alternately on your heels and on your toes, on the outer edge of the foot, on sand or small grains, along a straight line (drawn or imaginary), in a bathroom, at the bottom of which a bubble mat filled with warm water is laid (temperature 35 degrees Celsius).
Add vegetables and fruits and foods high in calcium to your diet. Don't forget about good emotions and smile. Do exercises every day and leg pain will not bother you.
7321
Arthrosis of the feet is a dangerous disease that manifests itself in the form of destruction of cartilage tissue in the joints. Without timely treatment, degenerative-dystrophic changes will become irreversible, as a result of which the joint will completely lose mobility. Exercises for the feet with arthrosis are part of a comprehensive treatment. Such gymnastics can also be performed to prevent the development of pathology.
Exercise for osteoarthritis
It is known that physical activity is beneficial for the human body. Sports for arthrosis are necessary. However, any forceful exercise should be avoided. In addition, if exercises cause pain, they should be abandoned. The most suitable sports for arthrosis are:
- calm walking;
- bike;
- skis;
- swimming.
Walking at a calm pace for short distances has a positive effect. During walks, muscles are strengthened and joints are developed. Walking is useful, since in the process there is no additional stress, the functioning of all the main systems of the body (respiratory, cardiovascular, metabolism) is normalized.
Patients need to remember the basic rules:
- to get results you need to walk every day;
- shoes should be as comfortable as possible, insole with arch support, closed heel.
- you can gradually increase the walking time, but only with the doctor’s permission;
- if pain occurs, you need to take a break.
If arthrosis is not too advanced, you can opt for an exercise bike or a bicycle. It is cycling that provides the movements of equal amplitude that the patient needs. This type of riding does not injure cartilage tissue and promotes joint mobility and normalization of blood circulation in the lower extremities. When riding a regular bicycle, you need to choose the road carefully. You should not drive on hilly or country terrain. This can lead to microtrauma of the joints, which will worsen the patient's condition.
Swimming for arthrosis of the joint is the optimal sport. It is used for the prevention and treatment of any diseases of the musculoskeletal system. You can swim even with the most severe forms of pathology. During swimming, muscles relax and pain in the affected joints subsides. There is no load on the musculoskeletal system, while at the same time muscles and ligaments are strengthened.
Is it possible to run if you have joint diseases? A light jog can only be done if the disease is in its early stages. Running with arthrosis of the knee joints of the second degree is prohibited in any form. The fact is that while running, the load on the joints increases 5 times. Thus, with a weight of 80 kg during a run, the damaged tissue will receive a pressure of 400 kg. This leads to even greater destruction of cartilage tissue.
Recently, fitness and aerobics have become very popular. But with arthrosis of the joints, such activities are contraindicated. The following sports are prohibited:
- football;
- tennis;
- hockey;
- volleyball;
- rugby.
An interesting method of physical therapy is Nordic walking. Nordic walking for arthrosis strengthens the spine and reduces the unpleasant symptoms of this pathology. The classes have no contraindications. You can walk at any age, even with highly developed arthrosis of the joints.
Symptoms and causes of the disease
The main symptom of foot arthrosis is pain. At an early stage it is felt only while walking, and at a later stage even at rest. This condition is explained by heavy loads on the joint, poor blood circulation and the negative effects of biological agents. In the morning, the patient may experience slight swelling. The reasons for the development of arthrosis of the foot may be as follows:
- injury;
- excess weight;
- congenital ankle pathology;
- elderly age;
- arthritis;
- pinched nerves;
- metabolic problems;
- hormonal disbalance;
- wearing shoes with uncomfortable heels.
All deformations that are observed during the development of pathology affect gait. After diagnosis, the doctor prescribes comprehensive treatment. It includes not only taking medications, but also performing therapeutic exercises for the ankle.
Principles of physical education for arthrosis.
- “Walking accessibility” - don’t rush things - enjoy the slightest success achieved, the range of movements should be increased very carefully, gradually. Energetic, forced movements are contraindicated
- “Work in the pain-free zone” - stop doing the exercises when pain appears, and under no circumstances “overcome the pain.”
- “Light mechanical load with static unloading” - exercises are best performed in a light state - lying or sitting, movements in the joints should be done slowly, but with sufficient amplitude.
- “Move, but avoid overload” - movements should not be too intense, causing injury to the affected joint.
- “Hardware physical training” - devices help stretch and relax the joint.
- “Physical training in the pool” - there is no vertical load on the joints, mechanical and psychological comfort is achieved.
- “Regularity” of exercises. Repeat the exercises frequently throughout the day for a few minutes
- “Assessment of the arthrosis phase” - exacerbation or remission of arthrosis determines the intensity of exercise
Benefits and features of exercise therapy
In the treatment of pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, exercise therapy occupies a key place. You can start exercising only after relief of acute pain. When performing the exercise correctly:
- strengthen muscles;
- prevent the formation of persistent contracture;
- make ligaments more elastic;
- relieve spasms;
- increase the overall tone of the body;
- activate blood circulation in problem areas of tissue.
For the purpose of treatment, the load on the joints should be minimal. Jerking and excessive tension are unacceptable.
A doctor should be in charge of selecting exercises. It takes into account the general condition of the patient, the stage of the pathology, its type and the cause that contributed to the disease. The purpose of such physical activity is as follows:
- pain reduction;
- improvement of blood circulation in periarticular and cartilaginous tissues;
- formation of correct gait;
- strengthening the muscles and ligaments of the legs.
In order for gymnastics to be beneficial for arthrosis of the foot, it is necessary to adhere to the principles of physical therapy, otherwise you can harm yourself and aggravate the course of the pathology. You can get the necessary therapeutic effect by following these principles:
- Training should be regular. It is recommended to perform exercises for 15 minutes 2-3 times a week.
- You need to start with simple exercises and a minimum number of repetitions. The load should be increased gradually.
- All movements should be performed as smoothly and slowly as possible.
- Breathing should be calm and measured.
- Classes can be carried out only after the acute pain syndrome has passed.
- Training should be regular. It is recommended to perform exercises for 15 minutes 2-3 times a week.
- You need to start with simple exercises and a minimum number of repetitions. The load should be increased gradually.
- All movements should be performed as smoothly and slowly as possible.
- Breathing should be calm and measured.
- Classes can be carried out only after the acute pain syndrome has passed.
The first training sessions are recommended to be done in a lying position. The surface must be hard. After some time, you can begin to perform therapeutic complexes while sitting on a chair and using gymnastic equipment.
It is forbidden to perform exercises while overcoming pain. Strength and range of motion should be continually adjusted to prevent re-injury. To achieve maximum results from exercise therapy for arthrosis of the ankle joint, the set of exercises should be supplemented with massage.
You can start exercising only after you stop taking anti-inflammatory drugs. During menstruation, women should avoid gymnastics. It is important to properly warm up your muscles before the main workout. After finishing the exercises, you need to lie down for a while so that your heart rate returns to normal.
The importance of gymnastics for ankle arthrosis
Performing ankle exercises with arthrosis may seem problematic, painful and even pointless. However, in fact, it is dosed physical activity that helps to achieve progress in treating the disease.
Below we will present to you a number of reasons why exercise therapy really helps with ankle arthrosis:
- During moderate physical activity, blood circulation improves in the affected area. Thanks to this, the necessary vitamins and microelements are delivered to the diseased joint faster.
- Regular training increases the elasticity of the ligaments. This helps prevent frequent injuries and associated pathologies.
- Moderate exercise during gymnastics safely forms the muscle corset and, in combination with diet, reduces fat mass. This helps reduce further pressure on the joints and prevent musculoskeletal diseases.
You can do gymnastics in a medical facility or at home. You can start exercising at a time when the exacerbation has subsided, the pain has become less pronounced, and joint mobility has increased.
Before training, consult your doctor - this simple precaution will help you avoid complications that may arise after training.
Basic exercises
All movements should be smooth and careful, the patient should not feel discomfort. After warming up the muscles, you can move on to rotational movements of the ankle. First, the exercise is performed in one direction, and then in the other.
Next you need to take a sitting position. Socks are lifted from it with legs crossed at the feet and lowered to the starting position. The next exercise is to move your toes. You need to try to squeeze the lying tissue with them.
No less effective are exercises for twisting the feet inward and spreading the heels. They are recommended to be performed while sitting. You can also do the bicycle exercise using your feet. Squats without lifting your heels off the floor give a good effect.
You can do step exercises in the gym. To do this, the toes are placed on an elevation, and the foot remains on the floor. The movements should be upward.
While performing gymnastics, you need to carefully monitor your joints. If pain occurs, you need to stop doing the exercises or reduce their amplitude. The number of repetitions and approaches is determined by the doctor or trainer, who has familiarized himself with the patient’s diagnosis in advance.
What you should absolutely not do
During gymnastics, light exercises are prescribed that provide the necessary load, but do not overstrain the muscles, ligaments and joints. To avoid causing complications, experts prohibit the following:
- Deep squats. They are dangerous because they cause severe tension in the ankle joint and knees in general. It is recommended to replace deep squats with half squats with a smaller amplitude. The angle of inclination should be less than 90 degrees, and the knees should not extend beyond the feet. Barbell squats are also not allowed.
- Rotation of the pelvis (provided that the person is standing on straight legs). To reduce the risk of injury and damage, it is recommended to bend your knees.
- Sharp swings of the leg backwards. Such exercises require great flexibility and, if used carelessly, can cause torn ligaments or pinched nerve roots.
In case of serious violations, any exercise in the gym and experiments with heavy weights are contraindicated.
A safe alternative is swimming in a pool under the supervision of a trainer who knows about your disease and is ready to select a set of exercises in the water.
Evdokimenko complex
A set of exercises developed by Dr. Evdokimenko is effective for the treatment of arthrosis of the feet. The simplest exercise is a deep bend while touching the floor. It is recommended to stay in this position for several minutes. Not everyone manages to touch the floor and stay there the first time, but after six months of training, the elasticity of the ligaments will increase significantly. To begin with, you can make a lightweight version with a bench. To make the exercise as effective as possible, you need to tense the muscles of your lower back and legs as you inhale, and completely relax as you exhale.
The second exercise assumes the following starting position: a straight stance, in front of the patient there is a chair, on the back of which he leans with his hands. You need to rise high on your toes and hold for a minute. You need to return to the starting position smoothly. The optimal number of repetitions is from 10 to 15 times.
Exercise therapy for the ankle with arthrosis involves emphasis on the heel and maximum tension of the toes upward. You need to fixate in tension, and then smoothly move to the entire foot. The repetitions should be quite dynamic. When the foot touches the floor, it should be relaxed.
Bubnovsky's gymnastics
Classes using the Bubnovsky method involve both static and dynamic muscle contraction. Exercises can only be performed with the permission of a specialist and under his supervision.
Starting position: lying on your back. The surface must be hard. Place your arms along your body. You need to spread your legs and pull your toes towards you to feel the tension in your back muscles. In this position, circular movements are made with the toes. First the exercise is performed in one direction, and then in the other. While maintaining the tension, perform the same movements with the entire foot.
The optimal number of repetitions varies from 10 to 20 times. During training, you need to ensure that your heels always remain on the floor. To finish, you need to squeeze your fingers tightly, and then relax and fan them out.
To tune in to the gymnast, you can turn on light music. During exercise, you need to monitor your breathing, since the body must receive the necessary amount of oxygen.