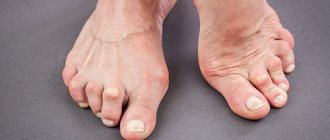
Wandering arthritis.
Wandering arthritis is an inflammatory, infectious-allergic systemic pathology that affects connective tissue structures. The cause of the development of the disease is a combination of these factors: infection with β-hemolytic streptococci, hereditary predisposition, disruption of the immune system. Wandering arthritis is diagnosed upon re-infection in approximately 3% of people who have had a common sore throat. The leading symptoms of the pathology are migrating joint pain, increased body temperature, swelling and stiffness of movement.
To identify wandering arthritis, radiography, MRI, ultrasound are performed, and, if necessary, arthroscopy. The most informative laboratory criteria are positive C-reactive protein and elevated levels of streptococcal antibodies. Treatment is conservative: bed rest, a course of pharmacological drugs, physiotherapeutic procedures.
What is wandering arthritis?
Wandering arthritis is difficult to recognize
The specificity of the disease lies in its name. Wandering arthritis is characterized by temporary pain in different joints, which sometimes worsens and sometimes subsides. The pain has no precise localization, which makes diagnosis difficult. First of all, migratory arthritis is dangerous because the patient does not understand the causes of periodic discomfort and simply postpones a visit to a specialist. At this time, the disease progresses, acquiring more and more pronounced symptoms.
Specifics of the pathology:
- “walking” pain throughout the body;
- periodic impairment of joint mobility;
- rapid progression;
- damage to one or more joints at the same time;
- deterioration in the patient's quality of life;
- risk of complications.
Treatment of wandering arthritis requires a long period of time, so it is important to consult a specialist in a timely manner. The earlier therapy is started, the more favorable the prognosis.
Classification
Arthralgia varies in location and depth, the number of joints involved, the nature and intensity of the pain syndrome, its daily rhythm, duration of existence, and connection with a certain type of movement.
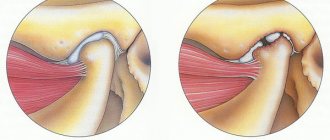
If there is pain in a single joint, we talk about monoarthralgia; if there is simultaneous or sequential pain in several joints, we talk about oligoarthralgia; if 5 or more joints are involved, we talk about polyarthralgia syndrome. According to the nature of the arthralgic syndrome, acute and dull pain are distinguished; by intensity - from weak and moderate to intense; according to the type of flow - transient and permanent. More often, arthralgia occurs in large joints - hip, knee, shoulder and elbow, less often in medium and small ones - wrist, ankle, interphalangeal.
The occurrence of pain in the joints is facilitated by irritation of the neuroreceptors of the synovial membranes of the joint capsules with inflammatory mediators, products of immune reactions, salt crystals, toxins, and osteophytes. In rheumatology, it is customary to distinguish the following types of joint pain:
- caused by toxic syndrome during acute infections;
- primary episode or intermittent (intermittent) arthralgia in acute or recurrent arthritis;
- long-term monoarthralgia of large joints;
- oligo- or polyarthralgic syndrome accompanying the involvement of synovial membranes or progressive degenerative changes in cartilage;
- residual post-inflammatory or post-traumatic arthralgia in the joints;
- pseudoarthralgia.
Causes of the disease
Hormonal and metabolic disorders can trigger wandering arthritis
The main reasons for the development of walking arthritis are age-related changes in connective tissue. According to statistics, this form of the disease is most often encountered by people over 50 years of age.
The reasons for the development of this pathology also include:
- decreased immunity;
- history of joint inflammation;
- genetic predisposition;
- congenital pathologies of the musculoskeletal system;
- infectious factors;
- overweight;
- hormonal and metabolic disorders;
- chronic diseases.
Decreased immunity often causes the development of inflammatory joint damage. This occurs against the background of previous infectious and viral diseases. HIV-infected people and people with autoimmune disorders are prone to arthritis.
Systemic diseases such as lupus erythematosus and scleroderma play an important role in the development of the disease. Arthritis can develop against the background of diabetes. In this case, infectious forms of pathology are most often diagnosed, associated with the spread of bacteria or fungi throughout the body through the bloodstream.
The risk of developing arthritis increases in the presence of congenital anomalies of the structure and disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Thus, people with severe kyphosis, scoliosis, and flat feet face various arthritis, including vagus arthritis. This is due to improper distribution of body weight on the spine and lower limbs when walking.
Pathology may have an age-related nature. In people over 50 years of age, there is a deterioration in the nutrition of cartilage tissue, as a result of which the cartilage loses its elasticity, becomes thinner and becomes covered with microcracks. Particles of this tissue can penetrate the synovium of the joint and cause inflammation due to irritation of the capsule when walking.
Separately, the presence of excess weight and metabolic disorders are identified as probable causes of the development of arthritis. This is due to the increased load on the joints, as a result of which the nutrition of the cartilage tissue deteriorates and the friction between the joints increases.
Despite the large number of provoking factors, wandering arthritis is often associated with infectious causes rather than lifestyle. Pathology often develops in the presence of a chronic source of infection, which can be caries, tonsillitis, diseases of the genitourinary system and respiratory tract.
Wandering arthritis may be associated with infection with syphilis, gonorrhea or tuberculosis, if pathogenic agents spread to the joints.
OSTEO-VIT. Vitamins for bone health
Over the years, the musculoskeletal system wears out, which is why joint diseases
are increasingly persecuting older people, and given the significant decrease in physical activity, one of which is sedentary work, it is increasingly common for young people to seek medical help.
The cause of joint weakening is inflammatory and degenerative-dystrophic processes in cartilage tissue. A frequent treatment among cases of joint diseases is arthritis, one of the acute forms of which is wandering arthritis
.
The main symptom of wandering arthritis
is inflammation and
pain in the joints
, which does not have a specific area of localization, the cause of which can be either a genetic predisposition or joint injuries, excessive stress on the joints, past infections (fungal, viral, bacterial), hypothermia, poor diet, hormonal age-related changes, as well as excess weight.
Treatment of wandering arthritis
takes a long period and has a favorable outcome, provided that treatment for the disease is started promptly and preventive measures are followed, otherwise the severity of this form of
joint disease increases, which can further lead to disability and the only solution to the health problem will be surgical intervention.
Symptoms of wandering arthritis.
Symptoms of wandering arthritis
, are not much different from the manifestations of reactive arthritis, when inflammation can cover several joints, with characteristic
joint pain
, which is accompanied by swelling, redness, and a local increase in temperature.
The peculiarity of wandering arthritis
is that the clinical picture of arthritis is persistent, does not have a permanent localization, manifests itself for no longer than three days in one or more areas, changing its localization.
Moreover, against the background of the main manifestations, other symptoms of wandering arthritis may be observed: fatigue, stiffness in the joints, limiting motor ability, sleep disturbances due to night pain in the joints, muscle weakness and weight loss.
symptoms of wandering arthritis are detected
there is no need to delay visiting a specialist, because with a correctly carried out diagnosis, including laboratory (blood tests) and instrumental examination, it is possible to identify
joint disease
in the initial stages, when
the treatment of wandering arthritis
can have a favorable prognosis.
Treatment of wandering arthritis.
An integrated approach to the treatment of wandering arthritis
includes drug therapy, physiotherapy, physical therapy and nutrition control and gives a favorable prognosis for recovery, provided that treatment is started in a timely manner.
In the presence of pain, anti-inflammatory drugs and muscle relaxants, chondroprotectors and drugs that restore blood microcirculation are prescribed; in the event of symptoms of wandering arthritis of infectious etiology, antibacterial therapy (antibiotics) is prescribed.
With severe arthralgia of the joints, which is with wandering arthritis
does not have an unambiguous localization, drugs with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects are prescribed.
Currently, along with drug therapy, specialists prescribe vitamin D, since its significant role in eliminating foci of inflammation has been proven. In addition, its immunosuppressive activity makes it an indispensable tool in the treatment of diseases of autoimmune origin (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, etc.). joint diseases often associated with vitamin D deficiency, which often affects older people and fairly young people during periods of reduced solar activity, which causes articular meteopathy and the development of acute forms of arthritis, one of which is vagus arthritis
.
It is quite difficult to obtain the daily requirement of vitamin D from food, so on gloomy autumn days and frosty winters, with a lack of sunlight and short daylight hours - the main supplier of valuable vitamin for the health of bones and joints, the required amount for normal body function can be obtained using a vitamin supplement. complexes containing it. Osteo-Vit vitamins contain the necessary dose of vitamin D, represented by its active form - D3 (cholecalcifelor), the combined action of which with vitamin B6, which takes part together with vitamin D in mineral metabolism in the body, which has an analgesic property that helps reduce joint pain .
An important component of the Osteo-Vit vitamin complex is drone brood (a donor of entomological prohormones), which influences hormonal levels, the decrease of which during menopause and postmenopause in women provokes joint diseases (arthritis, arthrosis), spinal dorsopathy, bone diseases (osteoporosis, osteomalacia, osteopenia). Get rid of symptoms of wandering arthritis
is impossible without taking chondroprotectors, the action of which is aimed at stopping the degenerative process of cartilage and controlling the regeneration of cartilage tissue, but also having a restorative effect on cartilage tissue.
A natural remedy for chondroprotective action is dandelion root, on the basis of which, for ease of use, the herbal preparation Dandelion P is produced, the action of biologically active substances in which is enhanced by vitamin C, which promotes the absorption of microelements, recommended in the prevention of diseases of joints
, ligaments and bones.
In the treatment of wandering arthritis,
dandelion root is also used as a natural venotonic, normalizing the outflow of venous blood and preventing the formation of stagnation that provokes disturbances in blood microcirculation in the joint structures.
Restoration of capillary blood supply in joint tissues is ensured by antioxidants, therefore in the treatment of wandering arthritis
Antioxidant vitamin complexes are indicated.
Positive dynamics in joint diseases
is shown by taking dihydroquercetin - a natural antioxidant, recognized as a reference, which is part of the Dihydroquercetin Plus vitamin complex, acting together with vitamin C and vitamin E, which are also powerful antioxidants.
To reduce night pain in the joints, it is recommended to take muscle relaxants, which have a relaxing effect on spasmodic muscles located in the periarticular area. Valerian officinalis is a natural muscle relaxant that helps relieve muscle spasms, on the basis of which the drug Valerian P is produced.
Physiotherapy (laser, shock wave, magnetotherapy), mud treatment, acupuncture, which can only be done after passing the acute period, physical therapy for joints, specific yoga exercises for joints, swimming, massage will help you get rid of joint stiffness.
wandering arthritis requires special attention
, requiring the refusal of different groups of products, and the introduction of a significant amount of products containing calcium and vitamin D. It is also recommended to use dietary supplements containing calcium.
The biologically active complex Osteomed will help you protect the body from calcium deficiency and normalize its metabolism, disturbances of which often cause wandering arthritis
and other
joint diseases , frequent bone fractures due to falls or minor injuries (osteoporosis).
Do not forget about preventive measures, including not only physical exercise and proper nutrition, but also timely prevention and treatment of infectious diseases that cause wandering arthritis
. Avoid excess body weight, which puts additional stress on your joints. Eliminate bad habits.
Treatment of wandering arthritis
must be timely, in the initial stages when the first signs appear, otherwise this advanced joint disease can lead to disability and the only solution to the problem can be surgery.
We recommend reading:
What is arthrosis-arthritis? Causes, symptoms, treatment.
How and why do your hands go numb at night while sleeping? Treatment for hand numbness at night.
Arthritis of the toes: causes, symptoms, treatment.
Arthritis of the ankle joint. Causes, symptoms, treatment.
Elbow pain is one of the symptoms of elbow arthritis. Causes and treatment of elbow arthritis.
What is joint arthropathy? Symptoms and treatment of arthropathy.
← Vitamin D for strong bones. How to protect yourself from fractures in winter?
What are the grades of knee arthritis? Causes, symptoms and treatment methods for arthritis of the knee joint. →
Symptoms of the disease
The main symptom of wandering arthritis is migrating pain in different joints
The symptoms of arthritic inflammation in wandering arthritis are not specific enough, so the symptoms of the disease are often ignored in the early stages of the development of the pathology.
The pain characteristic of arthritis migrates in the wandering form of the disease; there are practically no specific manifestations, signs and symptoms of the pathology, which significantly complicates treatment at an early stage.
Symptoms can be divided into general and articular. Joint symptoms of wandering arthritis include:
- migrating pain in one or more joints;
- sudden loss of mobility;
- swelling of the joint.
The peculiarity is that these symptoms arise spontaneously, last from several hours to several days, and then also suddenly disappear.
Vagal arthritis can manifest itself as pain in one joint or several at once. In this case, the localization of pain changes from attack to attack.
Common symptoms of the disease include:
- general malaise;
- morning sickness;
- loss of appetite;
- apathy;
- dizziness;
- sudden increase in temperature.
These symptoms are caused by an inflammatory reaction, in which specific substances are released that cause signs of intoxication.
Clinical picture
The signs of wandering arthritis are polymorphic, that is, the disease manifests itself with numerous articular and extra-articular symptoms. Its intensity depends on the activity of the inflammatory process, the stage of its course, and the involvement of other organs. Wandering arthritis develops approximately 10 days after a sore throat, scarlet fever or pharyngitis. The man took antibiotics, followed all medical recommendations and recovered. But, despite the fact that he was able to completely get rid of the respiratory pathology, he could not avoid damage to the joints. Its characteristic clinical manifestations are:
- body temperature rises to subfebrile values (37.1-38.0 °C), and sometimes overcomes them;
- weakness, fatigue, drowsiness occur;
- periodic headaches appear;
- sweating increases.
Headache is one of the symptoms of wandering arthritis.
But the main symptom of wandering arthritis is multiple symmetrical arthralgias, or joint pain. Its exacerbations occur after hypothermia and excessive physical exertion, with influenza and ARVI.
Articular signs
Initially, pain occurs in the large hip joints, knee, and shoulder joints. They are then felt in the ankles and elbows. And last of all, the radiocarpal and metatarsophalangeal joints are involved in the pathological process.
| The form of the course of wandering arthritis | Characteristic features of the flow |
| Acute | Sharp severity of symptoms, polysyndromic lesions, high activity of the inflammatory process |
| Subacute | Moderate clinical manifestations, joint wandering pain is felt for several months, inflammatory activity is less pronounced |
| Protracted | Arthralgia has been observed for more than 6 months, the activity of the inflammatory process is low, the dynamics are sluggish, only one of the syndromes is clinically manifested |
| Latent | The heart defect has already formed, which makes it possible to make a diagnosis in the absence of any biochemical, serological, or instrumental data |
| Recurrent | An undulating course with acute painful relapses followed by short-term remissions, polysyndromic manifestations, rapid damage not only to joints, but also to internal organs |
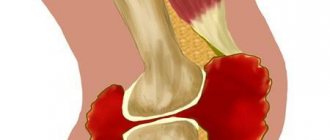
With wandering arthritis, the pain is fleeting. At first they are felt in some joints, and then gradually subside in order to arise with new intensity in others. Since they are provoked by acute or low-grade inflammation, patients experience swelling of the joints regardless of the time of day. The skin turns red, becomes hot to the touch and seems to smooth out.
Joint swelling, pain, redness are signs of inflammation in the joint.
Movement in the joints is severely limited for several reasons. Firstly, their flexion and extension is made difficult by the formed inflammatory edema. Secondly, the person himself deliberately avoids making movements that cause him severe pain. Severe joint symptoms usually disappear after a few days, but moderate pain persists for quite some time.
If the nervous system was involved in the pathological process, then minor chorea develops, manifested by hyperkinesis. Individual muscle groups begin to twitch involuntarily and muscle weakness occurs.
Extra-articular symptoms
Approximately 10-20 days after the onset of migrating joint pain, rheumatic carditis begins to clinically manifest. It is precisely this complex symptomatology that distinguishes wandering arthritis from infectious or gouty pathology. Its development is indicated by the combination of volatile arthralgia with the following extra-articular signs:
- asthenic syndrome, or chronic fatigue syndrome;
- pain in the heart area;
- increased heart rate;
- heart rhythm disorder.
Heart pain is one of the symptoms of rheumatic carditis.
The reason for such symptoms is damage by β-hemolytic streptococci not only to connective tissue joint structures, but also to individual membranes of the heart. Most often, the inflammatory process develops in the endocardium, myocardium, and pericardium. In most cases, patients experience cough, shortness of breath, and a feeling of lack of air after intense physical activity. But sometimes the pathology provokes circulatory disorders, cardiac asthma, even pulmonary edema.
Clinical manifestations of the epidermis are diagnosed even less frequently. Ring-shaped erythema develops - the skin is affected by ring-shaped pale pink rashes.
This is what ring-shaped erythema looks like.
Specific rheumatic nodules also form. They are dense, round, single or mobile. When pressed, they move slightly, and no discomfort occurs. The nodules are usually localized on the skin over medium or large joints.
Sometimes (very rarely) wandering arthritis is accompanied by damage to internal organs. Dry or exudative pleurisy and pneumonia develop in the lungs. Damage to the kidney structures is indicated by the appearance of proteins and red blood cells in the urine, and symptoms of nephritis also occur.
When the abdominal organs are involved in the pathological process, abdominal syndrome develops - abdominal pain, vomiting, increased tone of the abdominal muscles.
Abdominal pain and increased tone of the abdominal muscles indicate the development of abdominal syndrome.
Diagnosis of the disease
A biochemical blood test is done first
With wandering arthritis, symptoms and treatment depend on the stage of the disease. At the same time, it is important to make a correct and timely diagnosis, which is often complicated by the vague symptoms of the disease.
Necessary examinations:
- general and biochemical blood test;
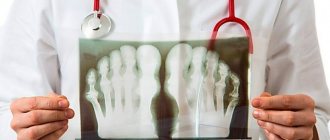
- X-ray of diseased joints;
- MRI;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and heart;
- liver examination and respiratory tract examination.
The first thing you should do is take a blood test. This allows us to establish the very fact of a hidden inflammatory process. Rheumatoid factor, a special antigen that is released only during rheumatoid arthritis, can also be detected in the blood.
X-rays help identify the exact location of inflammation and assess the condition of bone tissue. An MRI must be done to visualize the cartilage tissue, the destruction of which is characteristic of wandering arthritis.
Additional examinations of the internal organs help to exclude disturbances in their functioning, which could presumably be the cause of migrating pain in the joints. It is also recommended to be tested for hidden infections and undergo a comprehensive examination by a therapist.
Treatment of infectious arthritis
Treatment of infectious arthritis depends on several parameters: the form of the disease, the causative agent and concomitant diseases. If necessary, treatment of complications is carried out.
Self-medication for this disease is strictly contraindicated, since it is impossible to determine the cause of arthritis without special laboratory tests - highly specialized drug therapy is required.
Diagnosis of infectious arthritis
Diagnosis relies on symptoms of infectious arthritis (eg, pathological changes in the tissue around the affected joint). Why does a doctor determine whether the infectious agent is actually in the joint, blood or adjacent tissues, and determines the infectious agent. This is necessary for the correct choice of antibiotic: if the bacterium or a specific strain turns out to be insensitive to the drug, precious time will be lost.
For example, an ultrasound examination of a joint helps a specialist determine the presence of effusion in the joint and lesions.
To identify the causative agent, leukocyte and bacteriological analysis of the joint fluid is performed, which makes it possible to determine the presence or absence of pathogenic microorganisms. After laboratory culture, with a high probability, the type of pathogen will be established - unless it is gonococcus, Borrelia spirochete or treponema (the causative agent of syphilis), since they are difficult to detect in joint material.
A general blood test (helps to detect bacteremia), ESR, PCR, and, less commonly, examination of urine, sputum or cerebrospinal fluid are also performed. To achieve this, minimally invasive interventions are performed - for example, taking blood from a vein or puncturing a joint. An x-ray is prescribed last - it allows you to evaluate the destruction of the joint and bone heads caused by the disease, determine the narrowing of the joint space and other deformities.
Taking an anamnesis plays an important role in determining the symptoms and treatment of infectious arthritis - it helps to establish the possible cause of the disease at the pre-laboratory stage and eliminate unnecessary studies.
Taking antibiotics to a patient (for self-medication or treatment of a primary disease) can significantly complicate diagnosis.
Drug treatment of infectious arthritis
Sometimes treatment with broad-spectrum antibiotics is prescribed even before the pathogen is identified (usually penicillin, cephalosporins). For children under 3 months of age, initial therapy is with antibiotics active against gram-positive bacteria.
The drugs are administered intravenously (2-4 weeks) and then orally (another 2-6 weeks). In urgent cases, injections directly into the diseased joint are possible. A combination of various antibiotics is possible (for example, for tuberculosis), as well as intravenous and oral use of various drugs simultaneously. With the correct selection of antibiotics, improvement is observed already in the first 2 days of treatment.
In case of fungal infection, antimycotic agents are prescribed. In case of parasitic - antiparasitic. For some diseases, special chemotherapy or antiallergic treatment is performed.
If the cause of arthritis is a viral infection, instead of specific treatment, symptomatic treatment is carried out, aimed at eliminating fever, pain (analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), maintaining cartilage tissue (chondroprotectors and other similar drugs). Immunostimulating therapy is possible only as prescribed by a doctor and is completely contraindicated in rheumatoid arthritis.
Non-drug treatment
In the presence of a purulent process, the accumulated exudate is removed using a drainage tube or pumped out through a needle once a day, sometimes rinsing with saline solution is carried out. In difficult cases, when it is impossible to remove pus in this way (for example, due to bone growths), surgical intervention is possible. If the joint is severely damaged, prosthetics are performed. In some cases, arthroplasty, arthrolysis, and synovectomy are prescribed.
To ensure that the joints do not lose mobility, patients undergo physical therapy (for example, medicinal electrophoresis, compresses, amplipulse, magnetic therapy), and are prescribed therapeutic exercises - strictly under the supervision of an instructor. The complex includes active and passive exercises that help avoid contractures. Strength exercises shouldn't hurt.
In the acute stage of the disease, massage and physical therapy are contraindicated. In the early stages of the disease, it is recommended to limit joint mobility using a splint or splint. Clinical recommendations for infectious arthritis include timely treatment of systemic and local infections, chronic diseases, as well as compliance with the rules for surgical interventions.
You may be interested in:
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint Osteochondrosis of the knee joint, or what to do when your knees hurt? Reactive arthritis is a disease of young people Osteochondrosis of the lumbar region Osteoarthritis of the elbow joint
Drug treatment
In the treatment of wandering arthritis, medicinal and non-medicinal agents are used. Drug therapy is aimed at normalizing nutrition and restoring cartilage tissue. For this purpose, medications from the group of chondroprotectors and vasodilators are prescribed.
Chondroprotectors improve the elasticity of cartilage, protect it from loss of elasticity and destruction. Vasodilator medications are indicated to improve metabolic processes in the affected joint, as they improve blood microcirculation.
To relieve pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in tablets and ointments are prescribed. They reduce the inflammatory response and relieve pain. They should be used when the symptoms of the disease worsen.
Vasodilator ointments containing Ibuprofen or Diclofenac are often prescribed. Such drugs simultaneously relieve pain, reduce swelling and improve local blood circulation.
Additionally, taking medications to strengthen the immune system, vitamins and dietary supplements for joints may be indicated. For arthritis, it is useful to take B vitamins and Omega-3 capsules.
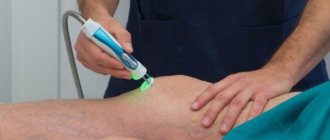
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is good for getting rid of wandering arthritis
Physiotherapeutic methods are widely used in the treatment of wandering arthritis. Most often prescribed:
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- ultrasound treatment;
- mud therapy;
- warm compresses;
- massage.
All these methods are aimed at improving metabolic processes and nourishing cartilage tissue. The purpose of such therapy in the treatment of wandering arthritis is due to the need to restore normal mobility in the joints.
It is advisable to prescribe electrophoresis in conjunction with vasodilating drugs, for example, nicotinic acid. This is an old, time-tested method of improving local blood circulation and normalizing the motor function of inflamed joints.
Manual therapy or massage can quickly improve joint movement and relieve swelling. This method of treatment is indicated for all types of arthritis, except infectious.
Diagnostics
Since joint pain is only a subjective symptom, clinical and anamnestic characteristics and physical examination come to the fore when determining the causes of their occurrence. Consultation with a rheumatologist or orthopedist is necessary. In order to differentiate the etiology of arthralgia, a number of objective studies are carried out:
- X-ray of joints.
It is a routine method that allows you to examine any joints for various diseases. Most often, radiography is performed in one or two projections; it is also possible to study in special settings and conduct contrast arthrography. A more detailed picture of the condition of the osteochondral and soft tissues of the joints is available with CT and MRI imaging. - Ultrasound of joints.
Allows you to detect effusion in the joint cavity, bone erosion, changes in the synovial membrane, and measure the width of the joint spaces. The availability of sonography makes it indispensable for diagnosing rheumatic joint pathologies. - Invasive methods.
According to indications, joint puncture and synovial biopsy are performed. In controversial cases, diagnostic arthroscopy is performed, which allows one to examine the joint cavity from the inside and carry out diagnostic and therapeutic measures. - Laboratory tests.
They help determine the presence of inflammation
and
rheumatic diseases. In peripheral blood, ESR, the level of C-reactive protein, uric acid, and specific markers of immunopathology (rheumatoid factor, antinuclear antibodies, ACCP) are determined. An important diagnostic method is microbiological and cytological examination of synovial fluid. - Additional diagnostic methods:
thermography, podography.
Plasmolifting of the joint
Surgery
Treating wandering arthritis with surgery is a last resort
Surgical methods for the treatment of wandering arthritis are practiced only in cases of severe wear and tear of the joint, which threatens disability. The method involves replacing the affected joint with an artificial prosthesis.
The operation allows you to quickly normalize the functioning of the joint and restore the former ease of movement, but is associated with a number of risks. After the operation, the patient requires a year-long course of rehabilitation.
Basic treatment methods
Symptoms and treatments for wandering arthritis are closely related. The adequacy of the therapy carried out to eliminate respiratory pathology - the cause of wandering arthritis - is also important.
Drug treatment
If pathological foci remain in the respiratory tract, then their sanitation (cleaning from pathogenic microorganisms) is necessary. Typically, lozenges, lozenges, and sprays with antimicrobial action are prescribed.
Although wandering arthritis is caused by pathogenic bacteria, antibiotic therapy may not be required. Taking antibiotics is advisable for untreated respiratory pathology, bacterial stomatitis, and caries complicated by infection. Inflammation in the joints during wandering arthritis is caused not by microbes, but by the reaction of the immune system to their introduction. Therefore, the disease can be acute even in the absence of streptococci in the body. If biochemical diagnostics reveal clear signs of streptococcal infection, then patients are prescribed drugs from the following groups:
- synthetic penicillins protected with clavulanic acid - Amoxiclav, Flemoklav, Panclave;
- macrolides - Clarithromycin, Azithromycin;
- cephalosporins - Cefazolin, Ceftriaxone, Cefotaxime.
To eliminate wandering pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used: Diclofenac, Nimesulide, Ketoprofen, Ibuprofen, Meloxicam. They are used in injection solutions, tablets, ointments and gels.
If NSAIDs are ineffective, glucocorticosteroids Diprospan, Triamcinolone, Prednisolone are prescribed. Hormonal drugs are rarely used in tablets; they are usually administered into the affected connective tissue structures (drug blockades).
An important part of therapy is a course of taking immunosuppressants Hydroxychloroquine, Chloroquine, Azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine, Chlorobutin. These drugs suppress the activity of the immune system, preventing the production of antibodies and their damage to the body's own cells.
Non-drug therapy
The patient is recommended to rest in bed; in case of severe pathology, he is hospitalized. To relieve pain, it is recommended to wear orthopedic products - elbow pads, knee pads, elastic bandages for the knee, hip, shoulder, and wrist joints. To enhance the effect of pharmacological drugs, physiotherapeutic procedures are performed:
- electrophoresis with NSAIDs, chondroprotectors, B vitamins;
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- UHF therapy.
Magnetic therapy session for damage to the knee joints.
At the rehabilitation stage, patients are prescribed massage, manual therapy, hirudotherapy, and balneotherapy. Daily exercise therapy and gymnastics can help restore the functional activity of joints.
Exercise therapy and diet
Diet and exercise will help strengthen joints
Physical therapy helps prevent joint destruction and stop the progression of the disease. Classes are held in the doctor's office. The set of exercises is selected individually for each patient and depends on the exact localization of the inflammatory process.
Exercises should be performed regularly. After a course of exercises in a physical therapy room, it is recommended to continue training at home.
Nutrition plays an important role in the treatment of wandering arthritis. You should avoid consuming large amounts of salt, fatty foods, fatty meats and sweets. It is recommended to eat fruits, vegetables, fish, nuts, and dairy products. To protect cartilage tissue, it is useful to eat jelly with gelatin and jellied chicken feet.
Folk remedies
Traditional methods of treatment can only be an addition to the main therapy
In case of exacerbation of pain, it is recommended to use alcohol rubbing. For this purpose, you can use alcohol tinctures of calendula, propolis, and garlic. These agents have a local irritant effect, reduce pain and relieve inflammation.
For non-infectious arthritis, you can make compresses with salt and snow, dry heating with hot salt, decongestant lotions with cabbage leaves.
It is important to understand that folk remedies only complement the complex treatment of arthritis, but cannot cope with the pathology on their own.