What is Treatment for Muscle Tears?
A tear in the calf muscle quite often occurs in athletes as a result of a jerk, when pushing off the ground or, conversely, landing from a great height. In addition, muscle tears can occur during fast, long or short distance running.
Also, people who are not involved in sports can get a tear in the calf muscle. It can occur as a result of a fall from a height, an amateur game of football, or a fall from a skateboard. For children - during regular games with friends in the yard (chasing, climbing trees, long jumping).
Causes and types of damage
On the back of the thigh there are quite powerful muscles: semimembranosus, semitendinosus and biceps, all of which perform the function of flexing the tibia at the knee joint. At the top they are attached to the ischial tuberosity of the pelvic bone, intertwined with the iliofemoral and ischiofemoral ligaments. The lower ends of the muscles are attached to the bones of the lower leg, intertwining with the fibers of the posterior popliteal ligament.
With a sharp and strong muscle contraction, both muscle fibers and collagen fibers of the ligaments of the upper or lower third of the thigh can be damaged.
Such injuries occur mainly in athletes when a sharp lunge of the leg occurs in sprinters, football players, and basketball players. The main group of such injuries are children and adolescents involved in sports. The reason is fragility, a lag in the development of muscle tissue during the period of increased bone growth.
Based on the degree of damage, there are 2 types of ruptures:
- Partial tear of muscles and ligaments;
- Complete rupture of muscles and ligaments.
Hamstring muscle tear
Tears of the thigh muscles are damage to part of the muscle fibers, a commonplace and, for the most part, not a serious injury that responds well to treatment. Symptoms of a thigh muscle tear are:
- Sharp pain in the posterior thighs, aggravated by flexion and extension of the knee joint;
- Difficulty walking;
- The appearance of edema and subcutaneous hematoma.
When palpating the thigh, its thickening is noted in the posterior lower parts due to swelling and muscle spasm. If the tear occurs in the area of the ischial tuberosity, the pain will be localized under the buttock.
First aid to the victim
When providing first aid for a thigh muscle tear, you must:
- Immobilize the limb. Fixation can be done by bandaging the entire leg loosely with a wide elastic bandage, bandaging a splint to the back surface - you can use a Cramer's scalene, or you can use a knee orthosis. The main thing is that there are no movements in the knee joint, which put stress on the thigh muscles.;
- Apply cold and a pressure bandage. Cooling is done by applying a bubble or plastic bag with ice to the area of injury for 15-20 minutes with a break of 1.5-2 hours;
- Give the victim an analgesic;
- Lay on your back with your leg slightly raised up and a cushion under it;
- The victim should be taken to a traumatologist as soon as possible.
Treatment of a thigh muscle tear
Tears of the thigh muscles are treated with conservative methods, which include:
- Immobilization;
- Compression - elastic bandaging of the leg;
- Cold on the damaged area;
- Analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Physiotherapeutic procedures;
- Exercise therapy and massage.
Treatment for a hamstring muscle tear:
- Immobilization. For immobilization there is no need for a plaster cast; orthopedic devices are indicated - orthoses that eliminate movement in the knee joint and can be removed at night. Also, in the first week after the injury, the patient should not step on his foot, but use crutches when walking.
- Compression and cold. Elastic bandaging of the thigh is necessary in order to narrow the blood vessels and reduce the increase in swelling and hematoma. Cold is applied in the first 2 days, this can be an ice pack, cooling compresses from a cloth moistened with cold water.
- Anesthesia. To relieve pain, the best effect is provided by modern drugs from the group of anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs - Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, Diclofenac, Nise and other analogues.
- Physiotherapy. Electrical procedures are prescribed for 3-4 days to improve blood flow, resolve swelling and hemorrhages, and stimulate muscle fusion. UHF, iontophoresis, infrared and magnetic therapy are used; for repeated and chronic tears, ultrasound and shock wave therapy are prescribed.
- Massage and exercise therapy. After about 1-1.5 weeks, as soon as the swelling subsides and the pain goes away, exercise therapy and massage are prescribed. These procedures should be performed by a specialist, starting with minimal loads and gradually increasing them. The massage should be shallow and not too intense, warming and improving lymphatic drainage. Physical therapy exercises are first aimed at generally increasing the tone of the leg muscles, improving its blood circulation, and only after 2 weeks they activate movements in the knee joint and do muscle stretching exercises. An example of recovery exercises is presented in the video:
Recovery time
Tears of muscle fibers, as a rule, heal well and quickly, and with adequate and timely treatment do not leave any consequences. Rehabilitation measures play an important role:
- Physiotherapy;
- Massage;
- Physiotherapy;
- Dosed walking.
The average recovery time after a hamstring tear usually does not exceed 4-6 weeks.
Diagnostic measures
The most reliable methods for diagnosing muscle tears are:
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound);
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Ultrasound in case of acute muscle tear reveals a decrease in echogenicity and the presence of a hematoma. With repeated tears, on the contrary, the echogenicity of the upper sections of the muscles is increased due to their compaction by scar tissue developing at the site of damage.
The most reliable and accurate study is MRI , which determines both the morphological and functional state of muscle fibers. It is prescribed in case of questionable ultrasound results.
Treatment of thigh muscle strain
Next begins the most important stage – treatment. Usually everything happens according to the same scheme, which the doctor must tell. This is a treatment for muscle strains of the 1st and 2nd degree:
1. Maintain complete rest. It is indicated because the sore muscle cannot be loaded for any time. If the doctor, after examining the patient, deems it necessary, he may prescribe the patient bed rest, or recommend the use of crutches or a cane when moving (walking);
2. Ice wrapped in a soft towel should be applied to the area of the tear several times a day. Keep ice on the injury site for no longer than 20 minutes;
3. You should either put a special stocking on the damaged thigh or bandage it with a special bandage. This is done so that bleeding does not start under the skin, and swelling does not appear;
4. Often the injured hip should be placed at a height at the level of the patient's heart. This helps reduce or completely eliminate swelling; If the patient experiences very severe pain, the doctor will definitely prescribe him a course of anti-inflammatory drugs. Sometimes the doctor prescribes painkillers to the patient. After the swelling goes away from the hip and the patient stops feeling pain, he will need to restore the damaged muscle. For this purpose, the patient will have to engage in physical exercise of a therapeutic nature, and will also have to attend physiotherapy procedures. These actions will help restore all physical activity of the muscle in the shortest possible time. {banner_st-d-2}
Damage to the biceps muscle
The biceps muscle can be damaged at the junction of the tendon, both in the lower third and at the top. Frequent stretching with tears in athletes leads to the development of the so-called hamstring syndrome (from the English hamstring - damage), when the upper section is damaged, an adhesive process develops after scarring of the damaged fibers, and the sciatic nerve is involved. In addition to the main symptoms, symptoms of sciatica appear - neuralgia of the sciatic nerve, which is not associated with spinal pathology.
Diagnosis, consequences and treatment of quadriceps tendon rupture
According to statistics, people who have passed the age of forty are susceptible to this disease.
Mechanisms of injury
Typical direct mechanisms of injury include:
- stumbling when climbing stairs, walking or running;
- excessive loads during physical education (less often).
In the elderly, indirect mechanisms of injury are also observed. The following patients are at risk:
- taking glucocorticoids;
- suffering from diabetes mellitus, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), chronic renal failure (CRF).
Typical signs of a tendon rupture
The most common signs are:
- pain in the affected area;
- difficulty walking;
- swelling;
- inability to straighten the leg at the knee;
- retraction of tissue in the area of the patella (kneecap).
Diagnosis of the disease
Unfortunately, in fifty percent of cases this injury is not diagnosed due to hemarthrosis (bleeding into the joint). Due to hemorrhage, tissue retraction is not determined, and the doctor assesses the tissue defect using palpation (palpation). At the same time, the activity of extension movements of the healthy leg is assessed.
A more accurate picture is obtained using x-rays, ultrasound and MRI.
X-ray examination is carried out directly and from the side. When a rupture occurs, 4 signs are observed:
- the kneecap moves downwards;
- the mass of tissue above the cup increases;
- the shadow of the injured tendon narrows, inflammation
is already obvious; - calcium deposits are observed.
Complete or partial ruptures are detected by ultrasound. The quality and information content of this method depends solely on the professionalism of the person conducting the procedure. The study is safe and does not involve radiation.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is usually prescribed in complex cases where swelling is obvious and there is suspicion of associated damage. The cost of MRI compared to the methods described above is high, so it is not used in simple and clear cases.
Treatment tactics
Tactics are chosen depending on the severity of the injury. In case of incomplete rupture, the specialist most often prescribes non-surgical therapy:
- the joint is extended, a plaster or splint is applied to it (application period is 6 weeks);
- after the application period has expired, the patient must undergo exercise therapy.
Physical therapy helps restore movement and strengthens muscles that have been weakened by periods of immobility. There are no statistics on this treatment tactic, so there is no exact data on the effectiveness of this method.
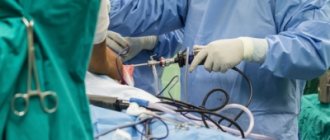
A complete tendon rupture can only be cured through surgery. Non-surgical treatment of injuries of this severity leads to functional disorders that do not allow full extension of the joint. The timing of seeking qualified help plays a big role. Early consultation with a doctor and surgical intervention within three days greatly increases the favorable outcome of the operation. In late treatment, when time is lost, the tendon shortens and its ends are more difficult to align. Recovery of the tendon is more difficult.
Some recovery techniques
The most common technique is used when the tear is located in the center, with sufficient tissue preserved on both sides. Surgical intervention comes down to matching and suturing the ends of the tendon with a thick thread that does not dissolve, then two sutures are applied.
Smaller sutures are used to sew together the ends of the tendons that support the kneecap. First of all, the central seams are tightened, then the smaller seams that have already been applied. For typical localization (closer to the base of the kneecap), a similar method is used. Before flattening, it is necessary to remove the remaining soft tissue and sand the base. Restoration of gaps on both sides is also carried out.
In the case of old ruptures, when the tendon has shrunk, it is mobilized with dissection of the adhesions. If this procedure does not work, tendon lengthening is performed. Therefore, it is so important to start treatment as early as possible.
After surgery, a splint or cast is applied, as in the case of a partial tear, for 6 weeks. The patient is allowed to walk and lean on the affected leg when the period of immobilization ends.
The next stage of recovery is gymnastics. This mandatory step should not be neglected under any circumstances. It is for injuries to ligaments and tendons that exercise therapy is necessary, as it helps to avoid complications. The rehabilitation program includes exercises with static loads on the quadriceps and posterior thigh muscles. The course includes active flexion and passive extension, and later active extension is added. General strengthening exercises are also useful.
The range of motion is restored after 3 months, rehabilitation lasts 4-6 months.
Most common complications
By following the recommendations of a specialist in therapeutic physical education, the patient avoids complications: the inability to bend the leg at the knee completely, delayed extension after passive flexion.
The following complications are less common:
- wound infection;
- tendon inflammation;
- filling the joint with blood;
- low position of the kneecap;
- violation of the compatibility of the hip and patella.
The recovery rate of patients who contact a medical facility as soon as possible ranges from 83 to 100 percent.
That’s why it’s so important not to delay your visit to a medical facility. According to researchers, only 51% of patients who have suffered the described injury return to their previous level of motor activity, but this is due to old age. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
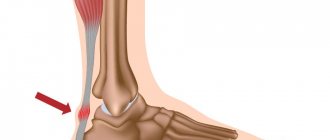
Tear of the ligaments of the posterior surface of the thigh
A ligament tear occurs near the knee or hip joint. The mechanism of injury is the same as for muscle damage. The peculiarity of this injury is that it is considered more severe. The blood circulation of the ligamentous apparatus is worse than that of muscle tissue, so the fusion of fibers takes longer.
Clinical symptoms are similar, but they are not as pronounced:
- Swelling and hematoma are less than with muscle tears;
- The pain is localized closer to the hip or knee joint and intensifies with flexion of the hip or extension of the leg.
The principles of treatment are the same as for muscle tears, but immobilization is imposed for a longer period - from 4 to 6 weeks.
Recovery time is also increased - up to 2-3 months. In case of old ruptures with loss of elasticity and lengthening of the ligaments, plastic surgery is performed.
Diagnosis of muscle damage
To confirm a muscle tear, the patient must undergo an ultrasound. An ultrasound examination will confirm or deny the presence of injury. If confirmed, ultrasound will detect a hematoma if it has formed. This is very important in order to evacuate blood from it in time and prevent inflammation.
It is also possible that the hematoma may not be detected. In such cases, the specialist prescribes a nerve block with novocaine to numb the injured muscle. The blockade is performed either every day or every 2-3 days, according to the doctor’s decision and in the presence of severe pain.
Differences between a tear and a rupture
Muscle and ligament ruptures differ significantly from tears clinically in terms of treatment and restoration of limb function. Distinctive features of gaps are:
- Complete damage to the integrity of muscle fibers or ligaments;
- Severe symptoms – severe pain, rapidly increasing, extensive swelling and hematoma;
- Complete impairment of limb function.
The impact of the force leading to rupture is much greater. There is a significant difference in the approach to treatment, a longer rehabilitation period.
Hamstring muscle tear
Complete muscle rupture can occur if the muscle is contracted too strongly and too quickly, as well as with a strong direct blow if the muscle is tense. A complete muscle rupture is characterized by contraction of fragments, this is an obstacle to their fusion.
A type of rupture is the separation of the muscle at the site of its attachment to the bone along with the periosteum, that is, a combination of rupture and fracture.
Most often, an avulsion occurs in the area of the ischial tuberosity along with its periosteum; such an injury is called an avulsion fracture.
Symptoms of the pathological process
A complete rupture (separation) of the posterior surface of the thigh is accompanied by pronounced symptoms:
- Intense pain;
- Inability to move and walk;
- Rapid increase in leg swelling;
- Severe muscle weakness.
Upon examination, the thigh is enlarged in volume; in people with low nutrition, one can notice deformation along the posterior surface - the presence of a characteristic area of tissue retraction due to the absence of contracted muscle.
The victim may also experience cramps in the thigh muscles due to their reflex contraction.
The swelling of the leg increases, and after a day a growing, extensive hematoma of a purplish-blue color appears, which can go down to the lower third of the leg. Symptoms of a thigh muscle rupture, especially in obese people, are very similar to the signs of a severe bruise with a hematoma.
Treatment of injury
The only effective method of treating a rupture of the hamstring muscle is surgery - the application of special sutures to the connected muscle fragments. This is only possible with a fresh injury, when no more than a week has passed.
In case of old ruptures, it is impossible to connect the ends; they are separated from the adhesions and an autograft cut from a section of other muscles of the patient is sewn to them.
If a section of bone comes off along with the muscle, it is fixed with special metal structures - anchors or anchors. They are screwed into the bone and threads are attached to them, fixing the muscle. Today, fixatives made of biomaterials are used, which dissolve over time and cease to be a foreign body in the bone.
After the operation, a plaster cast is applied for 3-4 weeks , then a course of rehabilitation treatment is prescribed: physiotherapeutic procedures, exercise therapy, massage.
Diagnostic measures
If a muscle rupture is suspected, radiography is required, because there is a high probability of an avulsion fracture of the pelvic or tibia bones, to which the muscle tendons are attached.
Ultrasound scanning is also prescribed; in case of severe hematoma, a duplex study (combination of ultrasound with Doppler sonography) is performed to visualize vascular damage.
If this study is not enough, for example, in patients with large body weight, an MRI is prescribed, which allows one to assess the condition of all structures of the hip - bones, muscles, ligaments.
Duration of the rehabilitation period
Recovery times may vary and depend on the quality of the rehabilitation treatment provided. The patient should spare the leg for 2-3 months and avoid:
- Heavy loads;
- Training;
- Running;
- Jumps.
Wear a knee brace that limits flexion and extension of the joint when walking. Along with this, it is necessary to attend exercise therapy classes, physiotherapeutic procedures, and massage sessions. With adequate treatment, complete restoration of function occurs no later than 3 months after surgery.
Rupture of the biceps femoris muscle (biceps)
The biceps femoris muscle (biceps) is one of the largest muscles in the human body. The name of the muscle is associated with an anatomical feature - it has two heads - long and short.
A rupture of the biceps femoris muscle occurs as a result of a sharp starting jerk in athletes or a sharp throw of the leg forward. The cause of the injury is insufficient warming up of the muscles, uneven distribution of the load, incorrect technique for performing exercises with sports equipment, a fall or blow.
Typical symptoms of a biceps femoris rupture:
- sharp intense local pain in the biceps area;
- noticeable weakness in the hip;
- pain when bending the knee joint;
- upon palpation, a depression is felt in the muscle in an uncharacteristic place;
- stiffness of the knee joint;
- Over time, extensive bruising appears.
If a hamstring injury occurs, a splint is applied until doctors arrive.
The treatment method depends on the degree of fiber rupture. If less than half of the fibers are damaged, conservative therapy is prescribed. The patient is bandaged and prescribed rest and rehabilitation measures. The doctor prescribes NSAIDs, electrophoresis, and, if necessary, makes a novocaine blockade. If the biceps femoris muscle is completely ruptured or the tendon is torn from the bone, surgery is prescribed, after which a plaster cast is applied to the leg. Then comes the rehabilitation period. As a rule, you can return to sports no earlier than 5 months after the injury.
Hamstring ligament rupture
Ligaments are made of dense collagen fibers, so a strong force is required to completely rupture them. This can happen during a quick lunge, jump, or high-speed run. Since the ligaments are localized in the joint area, pain will also appear in the back under the buttock or above the knee joint.
Ligament rupture is characterized by a gradual increase in pain, swelling and hematoma. With a complete rupture, a symptom of instability in the joints appears; a parallel posterior dislocation of the hip and instability in the knee joint may occur. The rupture can only be treated surgically, stitching and plastic surgery are performed to strengthen the ligaments.
For any hip injury with suspected muscle or ligament damage, you must urgently visit a traumatologist.
The sooner treatment is started, surgery is performed, and high-quality rehabilitation is carried out, the better the results and the greater the likelihood of complete restoration of function.